Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Basic electrophysiology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
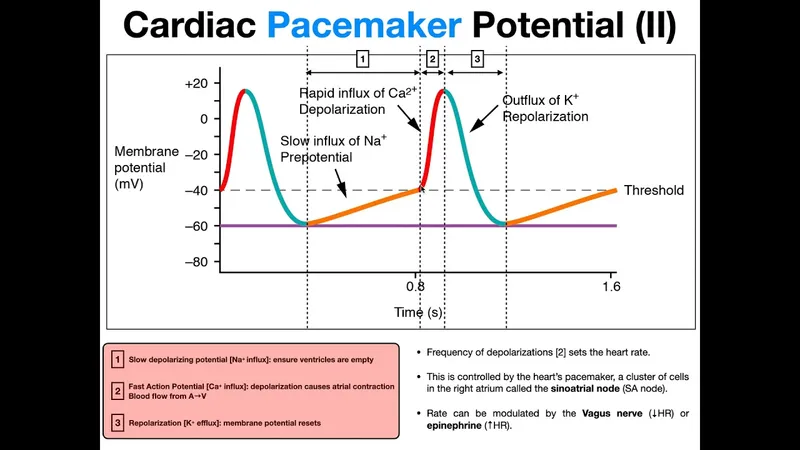
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 1: A molecular biologist is studying the roles of different types of ion channels regulating cardiac excitation. He identifies a voltage-gated calcium channel in the sinoatrial node, which is also present throughout the myocardium. The channel is activated at ~ -40 mV of membrane potential, undergoes voltage-dependent inactivation, and is highly sensitive to nifedipine. Which of the following phases of the action potential in the sinoatrial node is primarily mediated by ion currents through the channel that the molecular biologist is studying?
- A. Phase 2
- B. Phase 3
- C. Phase 1
- D. Phase 4
- E. Phase 0 (Correct Answer)
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***Phase 0***
- The description of the channel (**activated at -40 mV**, **voltage-dependent inactivation**, sensitive to **nifedipine**) points to an **L-type calcium channel**.
- In the **sinoatrial node**, **L-type calcium channels** are primarily responsible for the **Phase 0 depolarization** (upstroke) of the action potential.
*Phase 2*
- In **myocardial cells**, **Phase 2** (plateau phase) is primarily mediated by **L-type calcium channels**, but the question refers to the **sinoatrial node action potential**.
- **Sinoatrial node cells** typically lack a distinct **Phase 2** plateau, distinguishing them from ventricular myocytes.
*Phase 3*
- **Phase 3** (repolarization) in the **sinoatrial node** is primarily mediated by the **efflux of potassium ions** through various **potassium channels**.
- The described channel, being a **calcium channel**, would contribute to depolarization rather than repolarization.
*Phase 1*
- **Phase 1** (initial repolarization) is characteristic of **ventricular myocytes** and is mediated by a transient outward **potassium current (Ito)**.
- The **sinoatrial node** action potential typically lacks a distinct **Phase 1**, as it does not have this rapid initial repolarization.
*Phase 4*
- **Phase 4** (spontaneous depolarization) in the **sinoatrial node** is primarily driven by the "funny" current (**If**, carried by **HCN channels**) and a gradually increasing **calcium current** (mainly through **T-type calcium channels**), leading to the threshold for **Phase 0**.
- While L-type channels contribute to reaching the threshold, their primary role is the rapid depolarization of **Phase 0**.
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 2: An ECG from an 8-year-old male with neurosensory deafness and a family history of sudden cardiac arrest demonstrates QT-interval prolongation. Which of the following is this patient most at risk of developing?
- A. Hypertrophic cardiac myopathy
- B. Cardiac tamponade
- C. Essential hypertension
- D. Torsades de pointes (Correct Answer)
- E. First degree atrioventricular block
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***Torsades de pointes***
- The combination of **neurosensory deafness**, **QT-interval prolongation**, and a family history of **sudden cardiac arrest** is highly suggestive of **Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome**, a form of **long QT syndrome**.
- Patients with long QT syndrome are at significant risk for developing **polymorphic ventricular tachycardia** known as **Torsades de pointes**, which can degenerate into **ventricular fibrillation** and cause sudden cardiac death.
*Hypertrophic cardiac myopathy*
- This condition involves thickening of the **ventricular walls** and is associated with outflow tract obstruction, not primarily with QT prolongation.
- While it can cause sudden cardiac arrest, it typically presents with symptoms like **dyspnea, chest pain**, or syncope during exertion, and its ECG findings usually include **left ventricular hypertrophy** and **deep Q waves**.
*Cardiac tamponade*
- **Cardiac tamponade** results from the accumulation of fluid in the **pericardial sac**, compressing the heart and impairing its filling.
- This condition is not related to **QT prolongation** or **sensorineural deafness** and would present with signs of **hemodynamic instability**, such as **pulsus paradoxus** and muffled heart sounds.
*Essential hypertension*
- **Essential hypertension** is chronic high blood pressure with no identifiable secondary cause, commonly affecting adults.
- It is not associated with **congenital neurosensory deafness** or significant **QT-interval prolongation** in childhood.
*First degree atrioventricular block*
- **First-degree AV block** is characterized by a prolonged **PR interval** on ECG, indicating delayed conduction through the AV node.
- While it's an electrical abnormality, it is distinct from **QT prolongation** and is not typically associated with **neurosensory deafness** or the same risk of sudden cardiac arrest as long QT syndrome.
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 3: An 8-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents for the evaluation of an episode of unconsciousness while at the playground that morning. She was unconscious for about 15 seconds and did not shake, bite her tongue, or lose bowel or bladder control. Her grandfather died suddenly at the age of 29 of an unknown heart condition; her parents are both healthy. An ECG shows sinus rhythm and a QT interval corrected for heart rate (QTc) of 470 milliseconds. Laboratory studies are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely additional finding in this patient?
- A. Oblique palpebral fissures
- B. Subvalvular ventricular outflow obstruction murmur
- C. Sensorineural hearing loss (Correct Answer)
- D. Brachial-femoral pulse delay
- E. Skin folds between the mastoid process and acromion
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***Sensorineural hearing loss***
- This patient presents with an episode of syncope, a **prolonged QTc interval** (470 ms; normal <450 ms in prepubertal females, diagnostic threshold >460 ms), and a family history of **sudden cardiac death**, highly suggestive of **Long QT syndrome (LQTS)**.
- **Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome** is a specific form of LQTS (autosomal recessive) characterized by both **prolonged QT interval** and **congenital sensorineural hearing loss**, making this the most likely additional finding.
*Oblique palpebral fissures*
- **Oblique palpebral fissures**, along with epicanthal folds and a flat facial profile, are characteristic features of **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)**.
- These features are not typically associated with cardiac arrhythmias or Long QT syndrome, and there is no other information to suggest a chromosomal abnormality.
*Subvalvular ventricular outflow obstruction murmur*
- A **subvalvular ventricular outflow obstruction murmur** is indicative of conditions like **hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)**.
- While HOCM can cause syncope and sudden cardiac death, the primary finding in this patient is a **prolonged QTc interval**, which is characteristic of LQTS, not HOCM.
*Brachial-femoral pulse delay*
- A **brachial-femoral pulse delay** is the classic physical exam finding for **coarctation of the aorta**, a congenital narrowing of the aorta.
- There is no clinical information to suggest coarctation, and it does not explain the prolonged QTc interval and family history of sudden cardiac death.
*Skin folds between the mastoid process and acromion*
- **Skin folds between the mastoid process and acromion** (webbed neck or pterygium colli) are a classic sign of **Turner syndrome (XO)** or **Noonan syndrome**.
- These conditions are not primarily associated with a prolonged QTc interval and exert their cardiac effects through structural defects like coarctation or pulmonary stenosis, not typically primary arrhythmias.
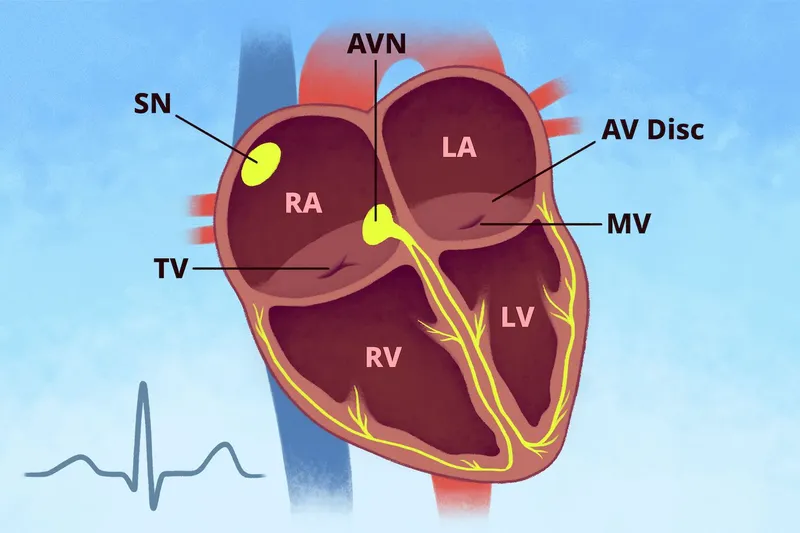
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 4: A researcher is studying how electrical activity propagates across the heart. In order to do this, he decides to measure the rate at which an action potential moves within various groups of cardiac muscle tissue. In particular, he isolates fibers from areas of the heart with the following characteristics:
A) Dysfunction leads to fixed PR intervals prior to a dropped beat
B) Dysfunction leads to increasing PR intervals prior to a dropped beat
C) Dysfunction leads to tachycardia with a dramatically widened QRS complex
D) Dysfunction leads to tachycardia with a sawtooth pattern on electrocardiogram
Which of the following is the proper order of these tissues from fastest action potential propagation to slowest action potential propagation.
- A. B > D > C > A
- B. D > C > A > B
- C. B > C > D > A
- D. A > D > C > B (Correct Answer)
- E. A > C > D > B
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***A > D > C > B***
* **Purkinje fibers (A)** have the fastest conduction velocity in the heart to ensure rapid and synchronous ventricular depolarization. The description of "fixed PR intervals prior to a dropped beat" in **Mobitz type II second-degree AV block** indicates an issue with conduction distal to the AV node, often in the His-Purkinje system, while still maintaining typical conduction through the atria and AV node for conducted beats.
* **Atrial muscle (D)** has a faster conduction velocity than the AV node but slower than Purkinje fibers. The "sawtooth pattern on electrocardiogram" unequivocally points to **atrial flutter**, which is characterized by rapid, regular depolarization of the atria.
* **Ventricular muscle (C)** has a conduction velocity slower than Purkinje fibers but faster than the AV node. "Tachycardia with a dramatically widened QRS complex" is characteristic of **ventricular tachycardia (VT)**, which arises from abnormal electrical activity within the ventricles.
* **AV node (B)** has the slowest conduction velocity in the heart, which allows for proper ventricular filling. "Increasing PR intervals prior to a dropped beat" describes **Mobitz type I second-degree AV block (Wenckebach phenomenon)**, which is due to progressive prolongation of conduction delay within the AV node itself.
*B > D > C > A*
* This order incorrectly places the **AV node (B)** as the fastest and **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the slowest, which is contrary to the known conduction velocities in the heart.
* The AV node is critical for delaying the impulse, making it the slowest, while Purkinje fibers are designed for rapid spread, making them the fastest.
*D > C > A > B*
* This option incorrectly places **atrial muscle (D)** as faster than **Purkinje fibers (A)**. Purkinje fibers have the fastest conduction velocity in the heart, considerably faster than atrial muscle.
*B > C > D > A*
* This arrangement incorrectly lists the **AV node (B)** as the fastest and **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the slowest. The AV node is the slowest for its physiological role of delaying ventricular contraction, while Purkinje fibers are optimized for rapid conduction.
*A > C > D > B*
* While placing **Purkinje fibers (A)** as the fastest and the **AV node (B)** as the slowest is correct, this order incorrectly places **ventricular muscle (C)** as faster than **atrial muscle (D)**. Atrial muscle generally conducts faster than ventricular muscle in normal physiology.
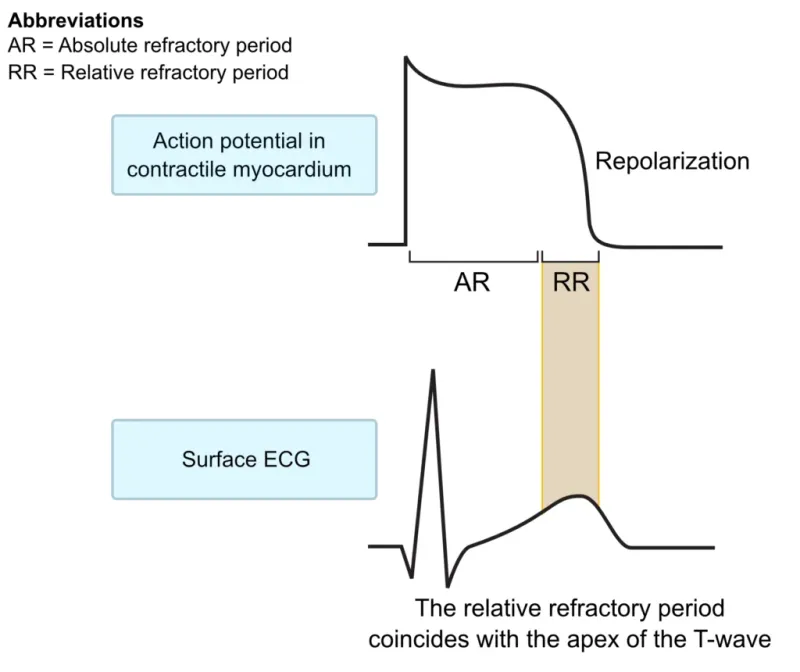
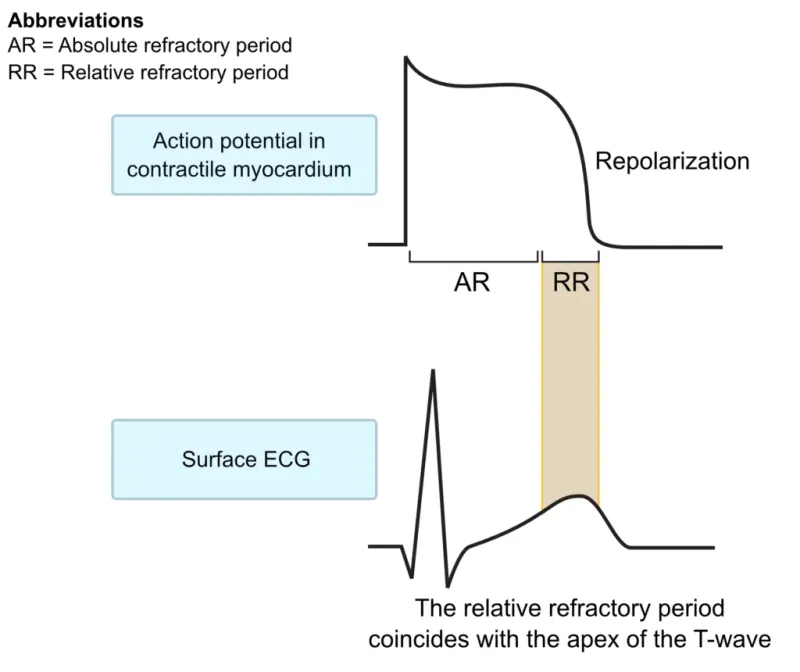
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old man presents to the clinic for his annual physical examination. He was diagnosed with a rare arrhythmia a couple of years ago following an episode of dizziness. A mutation in the gene encoding for the L-type calcium channel protein was identified by genetic testing. He feels fine today. His vitals include: blood pressure 122/89 mm Hg, pulse 90/min, respiratory rate 14/min, and temperature 36.7°C (98.0°F). The cardiac examination is unremarkable. The patient has been conducting some internet research on how the heart works and specifically asks you about his own “ventricular action potential”. Which of the following would you expect to see in this patient?
- A. Abnormal phase 2 (Correct Answer)
- B. Abnormal phase 4
- C. Abnormal phase 0
- D. Abnormal phase 3
- E. Abnormal phase 1
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***Abnormal phase 2***
- Phase 2 of the ventricular action potential, also known as the **plateau phase**, is primarily maintained by the influx of **L-type calcium channels** and the efflux of potassium.
- A mutation in the gene encoding for the L-type calcium channel protein would directly affect phase 2 and likely **result in an abnormal plateau phase** of the action potential.
*Abnormal phase 4*
- Phase 4 represents the **resting membrane potential** in ventricular myocytes and is maintained by **inward-rectifier potassium channels**.
- Mutations affecting L-type calcium channels would not directly or primarily cause an abnormality in the resting potential.
*Abnormal phase 0*
- Phase 0, the **depolarization phase**, is driven by the rapid influx of **sodium ions** through fast voltage-gated sodium channels.
- While calcium channels play a minor role, their primary impact is not on the initial rapid upstroke of phase 0.
*Abnormal phase 3*
- Phase 3, the **repolarization phase**, is primarily mediated by the **efflux of potassium ions** through various potassium channels (e.g., delayed rectifier potassium channels).
- Although calcium channel inactivation contributes to the end of the plateau, the **dominant ion flux** determining phase 3 is potassium efflux.
*Abnormal phase 1*
- Phase 1, the **initial repolarization phase**, is characterized by the **inactivation of sodium channels** and a brief efflux of potassium ions through transient outward potassium channels.
- L-type calcium channel activity is just beginning during this phase and is not the primary determinant of its shape.
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 6: A group of investigators is studying a drug to treat refractory angina pectoris. This drug works by selectively inhibiting the late influx of sodium ions into cardiac myocytes. At high doses, the drug also partially inhibits the degradation of fatty acids. Which of the following is the most likely effect of this drug?
- A. Increased prolactin release
- B. Decreased uric acid excretion
- C. Decreased serum pH
- D. Increased oxygen efficiency (Correct Answer)
- E. Decreased insulin release
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***Increased oxygen efficiency***
- Inhibiting the **late sodium current** reduces intracellular calcium overload, preventing diastolic dysfunction and improving myocardial relaxation.
- Partial inhibition of **fatty acid degradation** shifts myocardial metabolism towards glucose utilization, which is more oxygen-efficient.
*Increased prolactin release*
- This drug does not act on **dopamine receptors**, which are typically involved in regulating prolactin release.
- **Ranolazine**, the drug described, has no known effect on the endocrine system, specifically prolactin.
*Decreased uric acid excretion*
- **Uric acid excretion** is primarily affected by renal handling, often influenced by diuretics or drugs that compete for renal transporters, which is not a mechanism of this drug.
- This drug does not interfere with the **organic anion transporters (OATs)** responsible for uric acid secretion.
*Decreased serum pH*
- Changes in **serum pH** are usually associated with severe metabolic or respiratory disturbances, which are not direct effects of a drug targeting cardiac ion channels and metabolism.
- The drug's mechanism of action does not directly produce **acidic byproducts** or inhibit acid-base regulatory systems.
*Decreased insulin release*
- Insulin release is primarily stimulated by **glucose** and modulated by various endocrine pathways, none of which are directly targeted by a drug that inhibits cardiac sodium channels and fatty acid oxidation.
- There is no evidence that this class of drugs affects **pancreatic beta-cell function**.
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 7: While explaining the effects of hypokalemia and hyperkalemia on the cardiac rhythm, a cardiologist explains that the electrophysiology of cardiac tissue is unique. He mentions that potassium ions play an important role in the electrophysiology of the heart, and the resting membrane potential of the cardiac myocytes is close to the equilibrium potential of K+ ions. This is because of the high resting potassium conductance of the ventricular myocytes, which is regulated by specific potassium channels. These are open at rest and are closed when there is depolarization. Which of the following potassium channels is the cardiologist talking about?
- A. Inward rectifier IKACh potassium channels
- B. Fast delayed rectifier IKr potassium channels
- C. Slow delayed rectifier IKs potassium channels
- D. Inward rectifier IK1 potassium channels (Correct Answer)
- E. Transient outward current Ito potassium channels
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***Inward rectifier IK1 potassium channels***
- These channels are primarily responsible for maintaining the **resting membrane potential** of ventricular myocytes close to the **equilibrium potential of potassium (EK)**.
- They exhibit **inward rectification**, meaning they conduct potassium current more readily in the inward direction (at negative potentials) than outward. They are open at negative resting potentials and **close upon depolarization due to blockage by intracellular magnesium and polyamines**.
- They contribute to phase 4 of the action potential and prevent early repolarization during the plateau phase.
*Inward rectifier IKACh potassium channels*
- These channels are activated by **acetylcholine** via muscarinic receptors (M2), leading to hyperpolarization and reduced heart rate.
- They are primarily found in the **sinoatrial (SA) node and atrioventricular (AV) node**, not the main determinants of ventricular myocyte resting potential.
*Fast delayed rectifier IKr potassium channels*
- These channels contribute to the **repolarization phase (phase 3)** of the cardiac action potential, along with IKs.
- Their primary role is in **potassium efflux during repolarization**, not in establishing the resting membrane potential.
*Slow delayed rectifier IKs potassium channels*
- These channels also contribute to the **repolarization phase (phase 3)** of the cardiac action potential, acting more slowly than IKr.
- Their main function is to **terminate the action potential**, not to set the resting membrane potential.
*Transient outward current Ito potassium channels*
- These channels contribute to **early repolarization (phase 1)** in ventricular and atrial myocytes, and some Purkinje fibers.
- They cause a **brief outward potassium current** after the upstroke of the action potential, but do not maintain the resting membrane potential.
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 8: A 40-year-old woman comes to the physician for a 6-month history of recurrent episodes of chest pain, racing pulse, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. The episodes last up to several minutes. She also reports urinary urgency and two episodes of loss of consciousness followed by spontaneous recovery. There is no personal or family history of serious illness. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Vitals signs are within normal limits. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Holter monitoring is performed. ECG recordings during episodes of tachycardia show a QRS duration of 100 ms, regular RR-interval, and absent P waves. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's condition?
- A. AV node with slow and fast pathway (Correct Answer)
- B. Pre-excitation of the ventricles
- C. Mutations in genes that code for myocyte ion channels
- D. Macroreentrant rhythm in the right atria through cavotricuspid isthmus
- E. Fibrosis of the sinoatrial node and surrounding myocardium
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***AV node with slow and fast pathway***
- This describes **AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT)**, a common cause of **paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT)**. The ECG findings of **narrow QRS (100 ms)**, regular RR-interval, and **absent P waves** (often hidden within the QRS complex) are characteristic of AVNRT.
- The patient's symptoms of recurrent chest pain, racing pulse, dizziness, and spontaneous recovery from loss of consciousness fit the episodic nature of **AVNRT**. The presence of two pathways (slow and fast) within the AV node facilitates the reentrant circuit.
*Pre-excitation of the ventricles*
- **Pre-excitation syndromes** (e.g., Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome) involve an accessory pathway that bypasses the AV node, leading to a **delta wave** and **short PR interval** on the baseline ECG.
- While they can cause SVT, the ECG during tachycardia would typically show a **wide QRS complex** if the accessory pathway is part of the reentrant circuit (antidromic), or a narrow QRS with a visible P wave if orthodromic and the accessory pathway is used for retrograde conduction, which doesn't fully align with the absent P waves and typically *normal* QRS during tachycardia as described.
*Mutations in genes that code for myocyte ion channels*
- This refers to **channelopathies** (e.g., long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome), which predispose to **ventricular arrhythmias** like **polymorphic ventricular tachycardia** and **ventricular fibrillation**.
- These conditions typically cause **wide QRS tachycardias** and have distinct ECG patterns (e.g., prolonged QT interval, Brugada pattern) not described here. The narrow QRS and regular rhythm point away from primary ventricular channelopathies as the cause of this specific tachycardia.
*Macroreentrant rhythm in the right atria through cavotricuspid isthmus*
- This describes **atrial flutter**, which typically presents with characteristic **"sawtooth" F waves** on ECG, representing atrial activity.
- While atrial flutter can cause recurrent episodes of rapid heart rate, the ECG description of **absent P waves** and a **narrow QRS complex** without F waves makes atrial flutter less likely.
*Fibrosis of the sinoatrial node and surrounding myocardium*
- **Sinoatrial node dysfunction (sick sinus syndrome)** can lead to bradycardia, sinus pauses, or alternating bradycardia and tachycardia (tachy-brady syndrome).
- It does not primarily cause the described paroxysmal narrow-complex tachycardia with absent P waves. The patient's symptoms are more consistent with an abrupt-onset, regular supraventricular tachycardia.
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He has no history of serious illness. His mother has hypertension and his father died of testicular cancer at the age of 51 years. He does not smoke or drink. He is sexually active and uses condoms consistently. He takes no medications. His immunization records are unavailable. He works as a financial consultant and will go on a business trip to Mexico City in 2 weeks. His temperature is 36.7°C (98.7° F), pulse is 78/min, and blood pressure is 122/78 mm Hg. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.4 g/dL
Leukocyte count 9800/mm3
Platelet count 168,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 113 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
Which of the following recommendations is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Malaria chemoprophylaxis
- B. Rabies vaccine
- C. Cholera vaccine
- D. Hepatitis A vaccine (Correct Answer)
- E. Yellow fever vaccine
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: **Hepatitis A vaccine**
- Travel to Mexico City, even for business, carries a risk of exposure to **Hepatitis A**, especially with potential for consuming local food or water.
- The **Hepatitis A vaccine** is recommended for unvaccinated individuals traveling to areas with intermediate or high endemicity, which includes Mexico.
*Malaria chemoprophylaxis*
- **Mexico City** is at a high altitude and is not considered a **malaria-endemic area**, so chemoprophylaxis is not typically recommended for this destination.
- Prophylaxis is generally reserved for travel to regions with a higher risk of **mosquito-borne malaria infection**.
*Rabies vaccine*
- Routine **pre-exposure rabies vaccination** is not typically recommended for general travel to Mexico City unless there is a specific risk, such as prolonged outdoor activities, animal handling, or substantial interaction with wildlife.
- The presented scenario does not indicate such high-risk exposure for a financial consultant on a business trip.
*Cholera vaccine*
- **Cholera** is rare in travelers, and the vaccine is generally only recommended for individuals traveling to areas with active cholera transmission and who are at high risk due to poor hygiene or unstable living conditions.
- Mexico City is not considered a high-risk area for **cholera for a typical tourist or business traveler**.
*Yellow fever vaccine*
- **Yellow fever** is not endemic in Mexico, and a **yellow fever vaccine** is not required or recommended for travel to Mexico City.
- This vaccine is primarily for travel to parts of Africa and South America where the disease is prevalent.
Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG Question 10: Match the following
A. Atrial fibrillation
B. Atrial flutter
C. PSVT
D. Ventricular tachycardia
- A. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
- B. A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4 (Correct Answer)
- C. A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
- D. A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
- E. A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Basic electrophysiology Explanation: ***A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4***
- Image 2 shows irregularly irregular QRS complexes with no discernible P waves, which is characteristic of **atrial fibrillation**.
- Image 1 shows a "sawtooth" pattern of atrial activity, indicative of **atrial flutter**.
- Image 3 displays a narrow complex tachycardia with a very regular rhythm, consistent with **PSVT**.
- Image 4 demonstrates wide, regular QRS complexes without clear P waves, which is the hallmark of **ventricular tachycardia**.
*A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4*
- This option incorrectly matches atrial fibrillation with the "sawtooth" pattern (image 1) and atrial flutter with the irregularly irregular rhythm (image 2).
- Atrial fibrillation is characterized by the absence of discrete P waves and irregular ventricular response (image 2), while atrial flutter shows organized atrial activity with a "sawtooth" pattern (image 1).
*A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3*
- This option misidentifies image 1 as atrial fibrillation and image 2 as atrial flutter, which are reversed.
- It also incorrectly matches PSVT with image 4 (ventricular tachycardia) and ventricular tachycardia with image 3 (PSVT).
*A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3*
- This option correctly identifies atrial fibrillation (A-2) and atrial flutter (B-1), but incorrectly swaps the ventricular and supraventricular tachycardias.
- Image 3 shows narrow complex tachycardia (PSVT), not the wide complex pattern of ventricular tachycardia seen in image 4.
*A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1*
- This option incorrectly matches all the rhythms to the wrong images, demonstrating a fundamental misunderstanding of their characteristic ECG features.
- For example, it matches atrial fibrillation to image 4 (ventricular tachycardia) and ventricular tachycardia to image 1 (atrial flutter).
More Basic electrophysiology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.