NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for NSTEMI diagnosis and management. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 1: A 64-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of chest pain and an episode of vomiting. He also complains of ongoing nausea and heavy sweating (diaphoresis). He denies having experienced such symptoms before and is quite upset. Medical history is significant for hypertension and types 2 diabetes mellitus. He currently smokes and has smoked at least half a pack daily for the last 40 years. Vitals show a blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg, pulse of 50/min, respirations of 20/min, temperature of 37.2°C (98.9°F), and oximetry is 99% before oxygen by facemask. Except for the patient being visibly distressed and diaphoretic, the examination is unremarkable. ECG findings are shown in the picture. Where is the most likely obstruction in this patient’s cardiac blood supply?
- A. Left anterior descending artery
- B. There is no obstruction
- C. Left circumflex artery
- D. Left main coronary artery
- E. Right coronary artery (Correct Answer)
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***Right coronary artery***
- The ECG shows significant **ST elevation in leads II, III, and aVF**, indicating an **inferior wall myocardial infarction**. This region of the heart is typically supplied by the **right coronary artery (RCA)**.
- The patient's presentation with **bradycardia (pulse 50/min)**, **hypotension (BP 80/50 mmHg)**, and **nausea/vomiting** is classic for an inferior MI, often due to RCA occlusion compromising blood supply to the **SA and AV nodes** (which are frequently supplied by the RCA).
*Left anterior descending artery*
- Obstruction of the **LAD** typically causes **ST elevation in anterior leads (V1-V4)**, which is not seen here.
- An LAD occlusion would present as an **anterior MI**, usually without the severe bradycardia and hypotension often seen with inferior MIs caused by RCA occlusion.
*There is no obstruction*
- The patient's symptoms of **sudden onset chest pain, nausea, diaphoresis**, and particularly the **ECG findings of ST elevation** are highly indicative of an **acute myocardial infarction**, which is caused by coronary artery obstruction.
- The severe hemodynamic instability (hypotension, bradycardia) further points towards a significant cardiac event due to occlusion.
*Left circumflex artery*
- **LCx occlusion** usually leads to **lateral wall MI**, characterized by ST elevation in leads **I, aVL, V5, and V6**, which is not the primary pattern observed in this ECG.
- While LCx can sometimes supply the inferior wall, the classic inferior pattern seen here is more commonly associated with RCA occlusion.
*Left main coronary artery*
- **Left main coronary artery** occlusion is a catastrophic event leading to extensive myocardial ischemia and typically presents with widespread ST depressions or elevation in aVR, reflecting global ischemia and often causing **cardiogenic shock** or **sudden cardiac death**.
- The ECG pattern here is localized to the inferior leads, making a left main occlusion an unlikely primary cause.
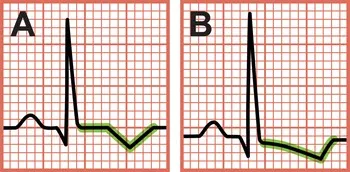
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 2: A 67-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of retrosternal chest pressure and shortness of breath for 4 hours. The symptoms started while he was walking to work and have only minimally improved with rest. He has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 35 years. He appears uncomfortable. His pulse is 95/min. Serum studies show a normal troponin concentration. An ECG shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Atherosclerotic plaque thrombus with complete coronary artery occlusion
- B. Stable atherosclerotic plaque with 85% coronary artery occlusion
- C. Aortic valve thickening and calcification
- D. Disruption of an atherosclerotic plaque with a non-occlusive coronary artery thrombus (Correct Answer)
- E. Coronary artery occlusion due to transient increase in vascular tone
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: **Disruption of an atherosclerotic plaque with a non-occlusive coronary artery thrombus**
- This scenario describes **unstable angina (UA)**, characterized by chest pain at rest or with minimal exertion, increased frequency/intensity of angina, or new-onset severe angina.
- While troponin is normal and ECG shows no abnormalities, the persistent symptoms and minimal improvement with rest, along with risk factors like **diabetes** and **smoking**, strongly suggest an **unstable coronary lesion** that is not yet fully occlusive.
*Atherosclerotic plaque thrombus with complete coronary artery occlusion*
- **Complete coronary artery occlusion** typically leads to myocardial infarction (MI), which would manifest with **elevated troponin levels** and often **ECG changes** (e.g., ST elevation or depression).
- The patient's normal troponin and ECG rule out an acute MI at this stage.
*Stable atherosclerotic plaque with 85% coronary artery occlusion*
- **Stable angina** symptoms usually improve promptly with rest and are predictable, occurring only during significant exertion.
- The described symptoms, including minimal improvement with rest and 4 hours duration, are not typical of stable angina.
*Aortic valve thickening and calcification*
- While **aortic stenosis** can cause chest pain and shortness of breath, these symptoms are typically exertional and not usually described as "retrosternal pressure" that minimally improves with rest in this acute context without other signs of flow obstruction.
- This condition is unlikely to be the sole cause of these acute, persistent symptoms without findings on initial workup.
*Coronary artery occlusion due to transient increase in vascular tone*
- **Coronary vasospasm** (Prinzmetal angina) can cause chest pain at rest and transient ECG changes, but it's typically **recurrent** and responds well to **vasodilators**.
- This patient's symptoms, combined with risk factors for atherosclerosis and the prolonged nature of the pain, are less indicative of vasospasm as the primary underlying cause.
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 3: A 49-year-old man was brought to the emergency department by ambulance with complaints of sudden-onset chest pain that radiates into his neck and down his left arm. This substernal pain started 2 hours ago while he was having dinner. His past medical history is remarkable for hypercholesterolemia that is responsive to therapy with statins and coronary artery disease. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 155/90 mm Hg, pulse is 112/min, and respiratory rate is 25/min. Troponin I levels are elevated. A 12-lead ECG was performed (see image). What is the most likely etiology of this patient’s presentation?
- A. Coronary vasospasm
- B. Right coronary artery occlusion (Correct Answer)
- C. Left circumflex artery occlusion
- D. Left anterior descending artery occlusion
- E. Left main coronary artery occlusion
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***Right coronary artery occlusion***
- The ECG shows significant **ST elevation in inferior leads (II, III, aVF)** and **ST depression in anterior leads (V1-V4)**, which is characteristic of an **inferior wall myocardial infarction**.
- **Inferior wall MIs** are typically caused by occlusion of the **right coronary artery (RCA)**. The reciprocal changes (ST depression in anterior leads) support this, indicating involvement of the posterolateral wall often supplied by the RCA.
*Coronary vasospasm*
- While coronary vasospasm (e.g., in **Prinzmetal angina**) can cause ST elevation, it usually presents with more transient symptoms that resolve with vasodilators, and the ST segment elevations are typically regional but often more widespread or dynamic.
- The patient's history of **coronary artery disease (CAD)** and persistent symptoms with elevated troponin point towards a fixed obstruction rather than vasospasm.
*Left circumflex artery occlusion*
- **Left circumflex artery occlusion** typically causes changes in leads I, aVL, V5, and V6 (high lateral or lateral wall MI), and sometimes posterior leads.
- The predominant ST elevation in leads II, III, and aVF is not characteristic of a primary **left circumflex artery occlusion**.
*Left anterior descending artery occlusion*
- **Left anterior descending (LAD) artery occlusion** usually results in **anterior or anteroseptal MI**, characterized by ST elevation in leads V1-V4 and potentially I and aVL.
- The ECG shows ST depression in V1-V4, which are reciprocal changes rather than direct signs of an **LAD occlusion**.
*Left main coronary artery occlusion*
- **Left main coronary artery occlusion** is a catastrophic event, often presenting with widespread ST depression in multiple leads with ST elevation in aVR (and sometimes V1).
- While life-threatening, the ECG pattern here with prominent inferior ST elevation and reciprocal anterior depression is more indicative of an **RCA occlusion** than a left main occlusion.
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 4: A medical research study is evaluating an investigational novel drug (medication 1) as compared with standard therapy (medication 2) in patients presenting to the emergency department with myocardial infarction (MI). The study enrolled a total of 3,000 subjects, 1,500 in each study arm. Follow-up was conducted at 45 days post-MI. The following are the results of the trial:
Endpoints Medication 1 Medication 2 P-Value
Primary: death from cardiac causes 134 210 0.03
Secondary: hyperkalemia 57 70 0.4
What is the relative risk of death from a cardiac cause, expressed as a percentage? (Round to the nearest whole number.)
- A. 64% (Correct Answer)
- B. 42%
- C. 72%
- D. 36%
- E. 57%
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***64%***
- The **relative risk (RR)** is calculated as the event rate in the exposed group divided by the event rate in the unexposed (control) group.
- For cardiac death, the event rate for Medication 1 is 134/1500 = 0.0893, and for Medication 2 is 210/1500 = 0.14. Therefore, RR = 0.0893 / 0.14 = 0.6378.
- Expressing as a percentage: 0.6378 × 100 = 63.78%, which rounds to **64%**.
- This indicates that Medication 1 has 64% of the risk of cardiac death compared to Medication 2, representing a **36% relative risk reduction**.
*42%*
- This option is incorrect as it does not reflect the accurate calculation of **relative risk** using the provided event rates.
- A calculation error or conceptual misunderstanding of the relative risk formula would lead to this value.
*72%*
- This percentage is higher than the calculated relative risk, suggesting an incorrect application of the formula or a misinterpretation of the event rates.
- It does not represent the ratio of risk between the two medication groups for cardiac death.
*36%*
- This value represents the **relative risk reduction** (100% - 64% = 36%), not the relative risk itself.
- This is a common error where students confuse relative risk with relative risk reduction.
*57%*
- While closer to the correct answer, this value is not the precise result when rounding to the nearest whole number.
- Small calculation discrepancies or rounding at intermediate steps could lead to this slightly different percentage.
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 5: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-month history of episodic, pressure-like chest pain. The chest pain occurs when he is walking up stairs and improves with rest. He has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. His father died from a myocardial infarction at the age of 50 years. Current medications include hydrochlorothiazide and metformin. His pulse is 85/min, respirations are 12/min, and blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. Cardiac examination shows normal heart sounds without any murmurs, rubs, or gallops. An ECG shows high amplitude of the S wave in lead V3. An exercise stress test is performed but stopped after 4 minutes because the patient experiences chest pain. An ECG obtained during the stress test shows sinus tachycardia and ST-segment depressions in leads V1–V4. Which of the following is the most appropriate long-term pharmacotherapy to reduce the frequency of symptoms in this patient?
- A. Metoprolol (Correct Answer)
- B. Clopidogrel
- C. Aspirin
- D. Nitroglycerin
- E. Isosorbide mononitrate
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***Metoprolol***
- **Beta-blockers** like metoprolol are first-line agents for **symptom relief** in stable angina by reducing myocardial oxygen demand.
- They decrease **heart rate**, **blood pressure**, and **myocardial contractility**, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of anginal episodes.
*Clopidogrel*
- **Clopidogrel** is an antiplatelet agent used primarily to prevent **thrombotic events** in patients with established cardiovascular disease or acute coronary syndromes.
- It does not directly reduce the frequency of anginal symptoms, but rather prevents progression to **myocardial infarction** or **stroke**.
*Aspirin*
- **Aspirin** is an antiplatelet medication used for **secondary prevention** of cardiovascular events by inhibiting platelet aggregation.
- While crucial for reducing cardiovascular risk, it does not directly alleviate the **frequency of anginal symptoms** themselves.
*Nitroglycerin*
- **Nitroglycerin** is a short-acting nitrate used to provide **immediate relief** of anginal pain during an acute episode.
- It is not a long-term pharmacotherapy for reducing the *frequency* of symptoms.
*Isosorbide mononitrate*
- **Isosorbide mononitrate** is a long-acting nitrate used to *prevent* angina, but it is typically a **second-line agent** after beta-blockers due to potential for **tolerance** and side effects.
- While it can reduce symptom frequency, beta-blockers are generally preferred as initial long-term therapy for symptom control.
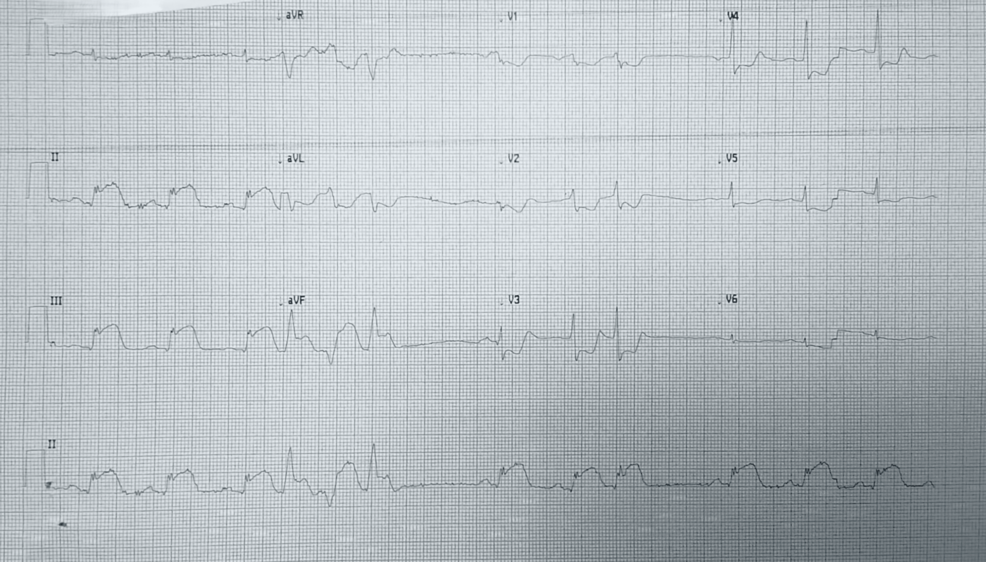
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 6: A 71-year-old man develops worsening chest pressure while shoveling snow in the morning. He tells his wife that he has a squeezing pain that is radiating to his jaw and left arm. His wife calls for an ambulance. On the way, he received chewable aspirin and 3 doses of sublingual nitroglycerin with little relief of pain. He has borderline diabetes and essential hypertension. He has smoked 15–20 cigarettes daily for the past 37 years. His blood pressure is 172/91 mm Hg, the heart rate is 111/min and the temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F). On physical examination in the emergency department, he looks pale, very anxious and diaphoretic. His ECG is shown in the image. Troponin levels are elevated. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient condition?
- A. CT scan of the chest with contrast
- B. Echocardiography
- C. Fibrinolysis
- D. Clopidogrel, atenolol, anticoagulation and monitoring (Correct Answer)
- E. Oral nifedipine
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***Clopidogrel, atenolol, anticoagulation and monitoring***
- The ECG shows **ST depression in multiple leads (II, III, aVF, V3-V6)** and **ST elevation in aVR and V1**, which is highly suggestive of **non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)** or a **posterior MI/extensive anterior ischemia**. Given the elevated troponin, the patient has an NSTEMI.
- Initial management for NSTEMI includes **dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin and clopidogrel)**, **anticoagulation (e.g., heparin)**, and **beta-blockers (atenolol)**, along with continuous monitoring.
*CT scan of the chest with contrast*
- A CT scan with contrast would be indicated if **aortic dissection** was suspected, but the classic ECG findings and elevated troponins point away from that diagnosis as the primary concern.
- While other causes of chest pain should be considered, the **ECG and troponin elevation** make **acute coronary syndrome (ACS)** the most immediate and critical diagnosis.
*Echocardiography*
- Echocardiography is useful for assessing **cardiac function, wall motion abnormalities, and valvular disease**, but it is generally not the immediate next step in an NSTEMI after the initial stabilization and medication.
- It could be performed later to evaluate for complications such as **ventricular dysfunction** or **valvular issues**.
*Fibrinolysis*
- **Fibrinolysis** is indicated for **ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)** when PCI is not readily available, or for other thrombotic events, but not for NSTEMI.
- In NSTEMI, the primary treatment strategy includes **antiplatelets, anticoagulants**, and often **early invasive procedures (PCI)**, if indicated by risk stratification.
*Oral nifedipine*
- **Nifedipine**, a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, can be used for hypertension or angina, but it is **not first-line** therapy for **acute coronary syndrome**.
- **Beta-blockers like atenolol** are preferred in ACS to reduce myocardial oxygen demand and improve outcomes, whereas nifedipine can sometimes acutely worsen ischemia due to reflex tachycardia.
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 7: A study is conducted to find an association between serum cholesterol and ischemic heart disease. Data is collected, and patients are classified into either the "high cholesterol" or "normal cholesterol" group and also into groups whether or not the patient experiences stable angina. Which type of data analysis is most appropriate for this study?
- A. Attributable risk
- B. Analysis of variance
- C. Chi-squared (Correct Answer)
- D. T-test
- E. Pearson correlation
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***Chi-squared***
- The **chi-squared test** is ideal for analyzing two **categorical variables**, such as cholesterol levels (high/normal) and the presence of stable angina (yes/no), to see if there's an association between them.
- It assesses whether the observed frequencies in each category differ significantly from the expected frequencies, under the assumption of no association.
*Attributable risk*
- **Attributable risk** quantifies the proportion of disease in an exposed group that is directly due to the exposure.
- While it might be calculated *after* establishing an association (e.g., using a chi-squared test), it's a measure of actual impact rather than a method for *finding the association* between two categorical variables.
*Analysis of variance*
- **Analysis of variance (ANOVA)** is used to compare the means of **three or more groups** for a continuous outcome variable.
- It works when you have a categorical independent variable with multiple levels and a continuous dependent variable, which is not the case here as both variables are categorical.
*T-test*
- A **t-test** is used to compare the means of **two groups** for a continuous outcome variable.
- It is not appropriate for analyzing the association between two categorical variables like cholesterol categories and angina presence.
*Pearson correlation*
- **Pearson correlation** measures the linear relationship between **two continuous variables**.
- It is unsuitable for this study as both cholesterol status and angina presence are categorical variables, not continuous.
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 8: Serum studies show a troponin T concentration of 6.73 ng/mL (N < 0.01), and fingerstick blood glucose concentration of 145 mg/dL. The cardiac catheterization team is activated. Treatment with unfractionated heparin, aspirin, ticagrelor, and sublingual nitroglycerin is begun, and the patient's pain subsides. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 65/min, respirations are 23/min, and blood pressure is 91/60 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 96%. Which of the following is the most appropriate additional pharmacotherapy?
- A. Intravenous morphine
- B. Intravenous furosemide
- C. Intravenous insulin
- D. Oral atorvastatin (Correct Answer)
- E. Intravenous nitroglycerin
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***Oral atorvastatin***
- All patients with **acute coronary syndrome (ACS)** should receive high-intensity statin therapy, such as **atorvastatin 80 mg daily**, as early as possible.
- Statins stabilize plaques, reduce inflammation, and improve endothelial function, which are crucial in the acute setting of a myocardial infarction.
*Intravenous morphine*
- Morphine can be used for persistent chest pain refractory to nitroglycerin, but its routine use is now questioned due to potential adverse effects like hypotension and delayed antiplatelet absorption.
- The patient's pain has already subsided with initial treatment, and his blood pressure is already low (91/60 mm Hg), making morphine less appropriate.
*Intravenous furosemide*
- Furosemide is a loop diuretic primarily used for treating **fluid overload** and **pulmonary edema**, which are not indicated by the patient's current presentation (oxygen saturation 96%, no mention of crackles or dyspnea).
- Its use in a patient with **borderline hypotension** could worsen hemodynamic stability.
*Intravenous insulin*
- While the patient has elevated fingerstick glucose (145 mg/dL), this level does not immediately require intravenous insulin unless there is evidence of **diabetic ketoacidosis** or **hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state**, or persistent severe hyperglycemia.
- More moderate hyperglycemia can often be managed with subcutaneous insulin or diet in the acute phase, and focuses remain on cardiac stabilization.
*Intravenous nitroglycerin*
- Intravenous nitroglycerin is indicated for ongoing ischemic chest pain or uncontrolled hypertension in ACS, but the patient's pain has subsided and he is **hypotensive** (91/60 mm Hg).
- Administering more nitroglycerin would likely worsen his hypotension and could compromise coronary perfusion.
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 9: A 50-year-old man presents the emergency department for intense chest pain, profuse sweating, and shortness of breath. The onset of these symptoms was 3 hours ago. The chest pain began after a heated discussion with a colleague at the community college where he is employed. Upon arrival, he is found conscious and responsive; the vital signs include a blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg, a heart rate at 90/min, a respiratory rate at 20/min, and a body temperature of 36.4°C (97.5°F). His medical history is significant for hypertension diagnosed 7 years ago, which is well-controlled with a calcium channel blocker. The initial electrocardiogram (ECG) shows ST-segment depression in multiple consecutive leads, an elevated cardiac troponin T level, and normal kidney function. Which of the following would you expect to find in this patient?
- A. Subendocardial necrosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Transmural necrosis
- C. Incomplete occlusion of a coronary artery
- D. Coronary artery spasm
- E. Ventricular pseudoaneurysm
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***Subendocardial necrosis***
- This patient's presentation with **ST-segment depression** and **elevated troponin T** indicates a **Non-ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI)**, which typically results from subendocardial ischemia and necrosis.
- Subendocardial tissue is most vulnerable to ischemia due to its high oxygen demand and distal location from the coronary arteries, making it the first region to suffer damage when oxygen supply is compromised.
*Transmural necrosis*
- **Transmural necrosis** is characteristic of a **ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)**, which presents with persistent **ST-segment elevation** on ECG.
- This patient's ECG shows **ST-segment depression**, ruling out transmural involvement at the time of presentation.
*Incomplete occlusion of a coronary artery*
- While an NSTEMI usually involves an **incomplete occlusion** or **critical stenosis** of a coronary artery, the question asks what would be *found* in the patient's heart tissue, not the mechanism.
- The direct tissue consequence of incomplete occlusion leading to NSTEMI is **subendocardial necrosis**, which is a more specific answer about the pathological finding.
*Coronary artery spasm*
- Although **coronary artery spasm (Prinzmetal angina)** can cause chest pain and ECG changes, it typically presents with **transient ST-segment elevation** (not depression) and often resolves spontaneously.
- The elevated troponin T indicates myocardial necrosis, which is not typically a feature of uncomplicated coronary artery spasm, and the duration of symptoms (3 hours) suggests a more sustained event than a transient spasm.
*Ventricular pseudoaneurysm*
- A **ventricular pseudoaneurysm** is a **late complication of myocardial infarction**, typically occurring weeks to months after the acute event, due to rupture of the ventricular free wall contained by pericardium.
- Given the 3-hour symptom onset, it is highly unlikely to be present in the acute phase of myocardial infarction.
NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG Question 10: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
NSTEMI diagnosis and management Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
More NSTEMI diagnosis and management US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.