Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cardiac biomarkers. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
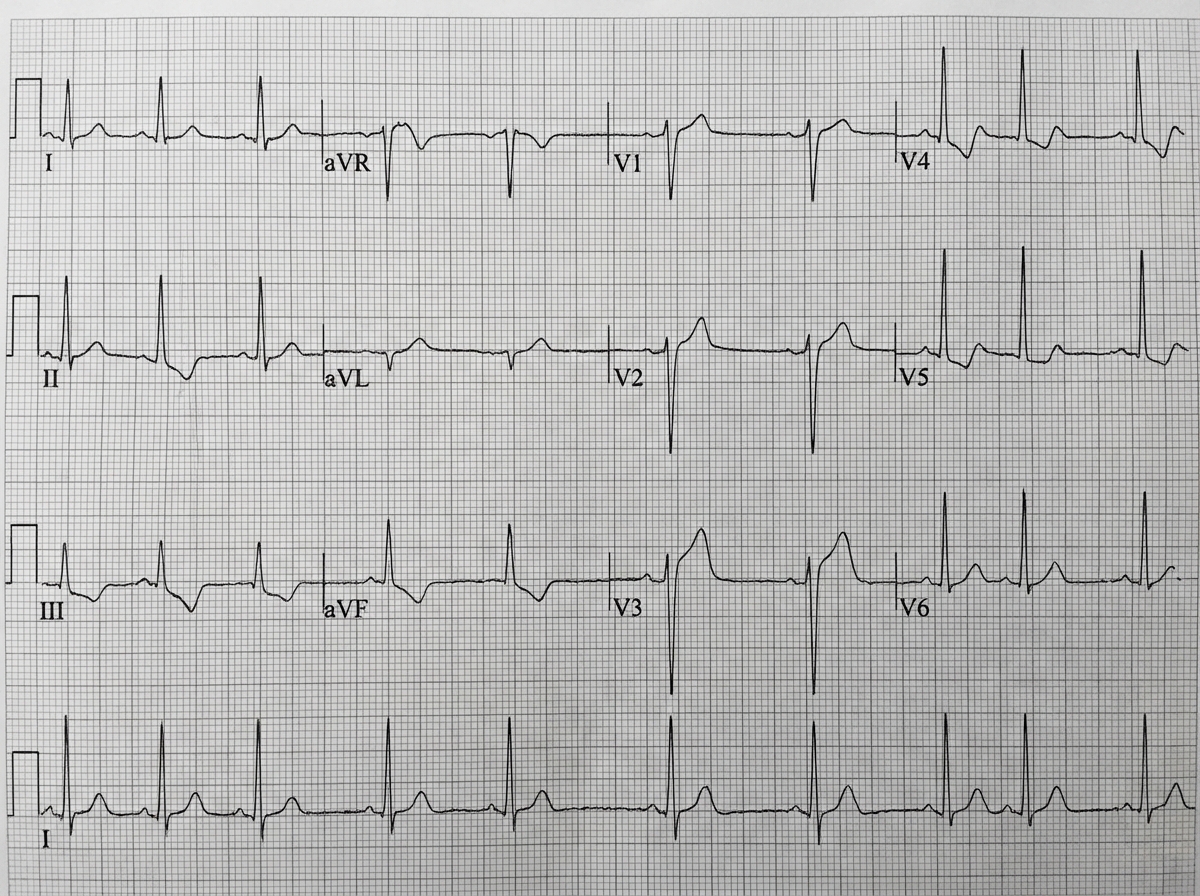
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 1: A 71-year-old man develops worsening chest pressure while shoveling snow in the morning. He tells his wife that he has a squeezing pain that is radiating to his jaw and left arm. His wife calls for an ambulance. On the way, he received chewable aspirin and 3 doses of sublingual nitroglycerin with little relief of pain. He has borderline diabetes and essential hypertension. He has smoked 15–20 cigarettes daily for the past 37 years. His blood pressure is 172/91 mm Hg, the heart rate is 111/min and the temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F). On physical examination in the emergency department, he looks pale, very anxious and diaphoretic. His ECG is shown in the image. Troponin levels are elevated. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient condition?
- A. CT scan of the chest with contrast
- B. Echocardiography
- C. Fibrinolysis
- D. Clopidogrel, atenolol, anticoagulation and monitoring (Correct Answer)
- E. Oral nifedipine
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Clopidogrel, atenolol, anticoagulation and monitoring***
- The ECG shows **ST depression in multiple leads (II, III, aVF, V3-V6)** and **ST elevation in aVR and V1**, which is highly suggestive of **non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)** or a **posterior MI/extensive anterior ischemia**. Given the elevated troponin, the patient has an NSTEMI.
- Initial management for NSTEMI includes **dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin and clopidogrel)**, **anticoagulation (e.g., heparin)**, and **beta-blockers (atenolol)**, along with continuous monitoring.
*CT scan of the chest with contrast*
- A CT scan with contrast would be indicated if **aortic dissection** was suspected, but the classic ECG findings and elevated troponins point away from that diagnosis as the primary concern.
- While other causes of chest pain should be considered, the **ECG and troponin elevation** make **acute coronary syndrome (ACS)** the most immediate and critical diagnosis.
*Echocardiography*
- Echocardiography is useful for assessing **cardiac function, wall motion abnormalities, and valvular disease**, but it is generally not the immediate next step in an NSTEMI after the initial stabilization and medication.
- It could be performed later to evaluate for complications such as **ventricular dysfunction** or **valvular issues**.
*Fibrinolysis*
- **Fibrinolysis** is indicated for **ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)** when PCI is not readily available, or for other thrombotic events, but not for NSTEMI.
- In NSTEMI, the primary treatment strategy includes **antiplatelets, anticoagulants**, and often **early invasive procedures (PCI)**, if indicated by risk stratification.
*Oral nifedipine*
- **Nifedipine**, a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, can be used for hypertension or angina, but it is **not first-line** therapy for **acute coronary syndrome**.
- **Beta-blockers like atenolol** are preferred in ACS to reduce myocardial oxygen demand and improve outcomes, whereas nifedipine can sometimes acutely worsen ischemia due to reflex tachycardia.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 2: A cardiologist is studying how a new virus that infects the heart affects the electrical conduction system of the cardiac myocytes. He decides to obtain electrocardiograms on patients with this disease in order to see how the wave patterns and durations change over time. While studying these records, he asks a medical student who is working with him to interpret the traces. Specifically, he asks her to identify the part that represents initial ventricular depolarization. Which of the following characteristics is most consistent with this feature of the electrocardiogram?
- A. Elevated in patients with full thickness ischemic injury of the heart
- B. Becomes peaked in states of hyperkalemia
- C. Becomes prominent in states of hypokalemia
- D. Normal duration defined as less than 120 milliseconds (Correct Answer)
- E. Normal duration defined as less than 200 milliseconds
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Normal duration defined as less than 120 milliseconds***
- The question asks for the representation of **initial ventricular depolarization**, which corresponds to the **QRS complex** on an ECG.
- The normal duration of the **QRS complex** is typically less than **0.12 seconds (120 milliseconds)**, reflecting efficient ventricular depolarization.
*Elevated in patients with full thickness ischemic injury of the heart*
- This description refers to the **ST segment elevation** seen in **ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)**, which represents myocardial injury, not initial ventricular depolarization.
- While related to cardiac electrical activity, **ST segment elevation** is a consequence of injury and refers to repolarization abnormalities, not the QRS complex itself.
*Becomes peaked in states of hyperkalemia*
- **Peaked T waves** are characteristic of **hyperkalemia**, indicating altered ventricular repolarization, not ventricular depolarization.
- The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, and its morphology changes significantly with potassium imbalances.
*Becomes prominent in states of hypokalemia*
- A **prominent U wave** is sometimes observed in **hypokalemia**, which follows the T wave and is thought to represent repolarization of Purkinje fibers.
- The U wave is distinct from the QRS complex and does not represent initial ventricular depolarization.
*Normal duration defined as less than 200 milliseconds*
- A duration of less than 200 milliseconds (0.20 seconds) typically refers to the normal duration of the **PR interval**, which represents atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node.
- The **QRS complex** (initial ventricular depolarization) has a shorter normal duration, typically less than 120 milliseconds.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 3: A 67-year-old man presents to the emergency department for squeezing and substernal chest pain. He states that he was at home eating dinner when his symptoms began. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. He is currently taking atorvastatin, lisinopril, insulin, metformin, metoprolol, and aspirin. Six days ago he underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 197/118 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam reveals an uncomfortable elderly man who is sweating. An ECG is ordered. Which of the following is the best next step in management for this patient?
- A. Stress testing
- B. Angiography (Correct Answer)
- C. Cardiac troponins
- D. Creatine kinase-MB
- E. Myoglobin
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Correct: Angiography***
- This patient presenting with **acute chest pain 6 days post-PCI** is at high risk for **stent thrombosis or acute in-stent restenosis**, which represents a life-threatening emergency.
- Given the **clinical instability** (severe hypertension 197/118, tachycardia 120/min, diaphoresis) and classic ACS symptoms in the immediate post-PCI period, **urgent coronary angiography** is the best next step in management.
- While ECG and troponins are important diagnostic tools, this patient requires **immediate intervention** to evaluate the recent PCI site and potentially perform emergent revascularization.
- In the setting of suspected **acute stent thrombosis**, time to reperfusion is critical, and angiography allows both diagnosis and treatment.
*Incorrect: Cardiac troponins*
- While troponins are essential biomarkers for myocardial injury and should be obtained, they are a **diagnostic test** rather than definitive management.
- Waiting for troponin results would delay definitive management in a patient with clear clinical evidence of ACS.
- In this high-risk post-PCI patient with active symptoms, management should not wait for biomarker confirmation.
*Incorrect: Stress testing*
- Stress testing is **absolutely contraindicated** in patients with active chest pain and suspected acute MI.
- It could precipitate further myocardial ischemia, arrhythmias, or cardiac arrest.
- Stress testing is reserved for risk stratification in stable patients or after ACS has been ruled out.
*Incorrect: Creatine kinase-MB*
- CK-MB is less sensitive and specific than troponins for myocardial injury, as it can be elevated in skeletal muscle conditions.
- It has a shorter elevation window and has largely been replaced by troponins in modern practice.
- Like troponins, it would not change the immediate management need in this clinically unstable patient.
*Incorrect: Myoglobin*
- Myoglobin lacks cardiac specificity (present in both cardiac and skeletal muscle) and has poor diagnostic accuracy for MI.
- Its rapid rise and fall make it unreliable, and it generates many false positives.
- It has no role in guiding management decisions in suspected ACS.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 4: A 56-year-old man presents to the emergency room with severe substernal chest pain associated with a 2-hour history of breathlessness and sweating. An electrocardiogram shows an ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Cardiac enzyme levels confirm a diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. The patient is rushed to the catheter lab for angioplasty with stenting. The patient complains of recurrent chest pain in the ICU 56 hours post-angioplasty. Which of the following enzymes facilitates the patient’s diagnosis based on his current symptoms?
- A. Creatine kinase (CK)-MB (Correct Answer)
- B. Creatine kinase – MM
- C. Troponin T
- D. Troponin I
- E. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Creatine kinase (CK)-MB***
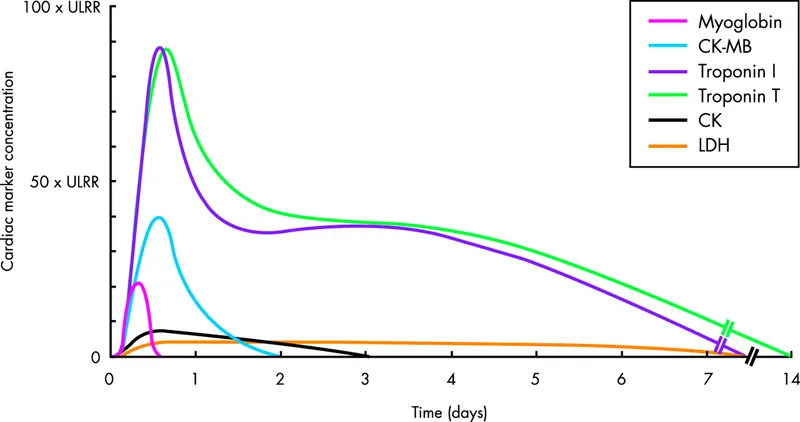
- **CK-MB** is elevated in myocardial infarction, rising within 4-6 hours, peaking at 24 hours, and **returning to baseline within 48-72 hours** after the initial event.
- At **56 hours post-angioplasty**, CK-MB levels should have normalized from the initial MI, making a **new elevation highly specific** for reinfarction or new myocardial injury.
- This makes CK-MB particularly useful for detecting **early reinfarction** when the timing allows it to have cleared from the initial event.
- **Clinical pearl**: This represents classical teaching about cardiac enzyme kinetics, though modern practice increasingly uses serial troponin measurements with delta criteria.
*Creatine kinase – MM*
- **CK-MM** is the predominant isoform of creatine kinase found in **skeletal muscle**, not cardiac muscle.
- While total CK (which includes CK-MM) increases in MI, CK-MM elevation is **not specific to cardiac injury** and can be elevated from skeletal muscle damage or other causes.
- Its lack of cardiac specificity makes it a **poor indicator for myocardial reinfarction**.
*Troponin T*
- **Troponin T** is highly sensitive and specific for myocardial injury, but levels remain **elevated for 7-10 days** following an acute MI.
- At 56 hours post-angioplasty, troponin T would **still be elevated from the initial MI**, making it difficult to distinguish baseline elevation from a new acute event.
- While a **significant rise (>20%) from the previous value** can indicate reinfarction, the persistently elevated baseline makes interpretation more complex compared to CK-MB which should have normalized.
*Troponin I*
- **Troponin I** remains elevated for **5-7 days** following an acute MI, similar to troponin T.
- At 56 hours post-initial MI, troponin I levels would **still be elevated**, making it challenging to clearly identify a new ischemic event without comparing to prior values.
- Though troponins are the **gold standard for MI diagnosis**, their prolonged elevation window makes CK-MB more straightforward for detecting reinfarction at this specific timepoint (when CK-MB should have returned to baseline).
*Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)*
- **LDH** elevation occurs later in MI (24-48 hours after onset) and remains elevated for **10-14 days**.
- Due to its **delayed rise and prolonged elevation**, LDH is not useful for diagnosing acute reinfarction in the early post-MI period.
- LDH lacks the rapid kinetics and cardiac specificity needed for timely diagnosis of new myocardial injury.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 5: A 69-year-old man is scheduled to undergo radical retropubic prostatectomy for prostate cancer in 2 weeks. He had a myocardial infarction at the age of 54 years. He has a history of GERD, unstable angina, hyperlipidemia, and severe osteoarthritis in the left hip. He is unable to climb up stairs or walk fast because of pain in his left hip. He had smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years but quit 25 years ago. He drinks one glass of wine daily. Current medications include aspirin, metoprolol, lisinopril, rosuvastatin, omeprazole, and ibuprofen as needed. His temperature is 36.4°C (97.5°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 136/88 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. A 12-lead ECG shows Q waves and inverted T waves in leads II, III, and aVF. His B-type natriuretic protein is 84 pg/mL (N < 125). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management to assess this patient's perioperative cardiac risk?
- A. No further testing
- B. 24-hour ambulatory ECG monitoring
- C. Radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging (Correct Answer)
- D. Treadmill stress test
- E. Resting echocardiography
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging***
- This patient requires **perioperative cardiac risk assessment** before intermediate-risk surgery (radical prostatectomy).
- Key factors include: history of **myocardial infarction**, current cardiac risk factors, and **inability to exercise** due to severe osteoarthritis.
- Since he cannot perform exercise stress testing, **pharmacologic stress testing** with radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging (using agents like adenosine, dipyridamole, or regadenoson) is the most appropriate test to assess for **inducible myocardial ischemia**.
- This provides functional assessment of coronary perfusion under pharmacologic stress, helping guide perioperative risk stratification and management.
- *Note: The presence of unstable angina would typically require cardiac stabilization first; this question focuses on selecting the appropriate stress test modality for a patient unable to exercise.*
*No further testing*
- This patient has significant cardiac risk factors including **prior MI**, ongoing cardiac medications, and ECG changes suggesting old infarction.
- Proceeding directly to surgery without functional cardiac assessment would be **inappropriate** given his risk profile and the intermediate-risk nature of the planned surgery.
*24-hour ambulatory ECG monitoring*
- Holter monitoring detects arrhythmias and silent ischemic episodes but does not provide **functional capacity assessment** or evaluation of inducible ischemia under stress conditions.
- It is not the primary tool for **perioperative cardiac risk stratification** before major surgery.
*Treadmill stress test*
- The patient's **severe osteoarthritis** prevents him from climbing stairs or walking fast, making him unable to achieve adequate exercise workload for a treadmill stress test.
- This functional limitation makes **exercise stress testing contraindicated**; pharmacologic stress testing is required instead.
*Resting echocardiography*
- Resting echocardiography assesses **baseline left ventricular function**, wall motion abnormalities from prior infarction, and valvular disease.
- While useful for structural assessment, it does **not evaluate for exercise-induced or stress-induced ischemia**, which is critical for perioperative risk assessment in patients with coronary artery disease.
- His normal BNP (84 pg/mL) suggests adequate baseline ventricular function, making functional ischemia assessment more relevant than structural evaluation alone.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 6: A 42-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 20 minutes after the sudden onset of severe chest pain, diaphoresis, shortness of breath, and palpitations. His symptoms occurred while he was at a party with friends. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 24 years. He uses cocaine occasionally. The last use was three hours ago. He appears pale. His pulse is 110/min, blood pressure is 178/106 mm Hg, and respirations are 24/min. His pupils are dilated and react sluggishly to light. The lungs are clear to auscultation. An ECG shows tachycardia and ST segment elevation in leads II, III, and aVF. While recording the ECG, the patient loses consciousness. A photo of the ECG at that point is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Administer lidocaine
- B. Unsynchronized cardioversion (Correct Answer)
- C. Administer epinephrine
- D. Coronary angiography
- E. Synchronized cardioversion
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Unsynchronized cardioversion***
- The ECG shows **ventricular fibrillation (VF)**, characterized by chaotic, irregular electrical activity without distinct QRS complexes, indicating a life-threatening arrhythmia.
- In a patient who has lost consciousness due to VF, immediate **defibrillation (unsynchronized cardioversion)** is crucial to restore normal sinus rhythm and prevent sudden cardiac death.
- Note: Unsynchronized cardioversion and defibrillation are **synonymous terms** for delivering an unsynchronized shock, with "defibrillation" being the preferred ACLS terminology for VF/pulseless VT.
*Administer lidocaine*
- While lidocaine is an **antiarrhythmic** used in some ventricular arrhythmias, it is typically administered after initial defibrillation attempts have failed or as an adjunct therapy.
- It is not the primary treatment for **unstable ventricular fibrillation**, which requires immediate electrical therapy.
*Administer epinephrine*
- Epinephrine is a **vasopressor** used during cardiac arrest to improve coronary and cerebral perfusion.
- It is administered during **cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)** intervals, usually after initial defibrillation attempts, but not as the first line treatment for VF.
*Coronary angiography*
- Coronary angiography is an **invasive diagnostic procedure** to visualize coronary arteries and identify blockages, suggested by the patient's symptoms and ST elevation in the initial ECG leads.
- However, in the context of **cardiac arrest due to VF**, immediate life-saving interventions take precedence over diagnostic procedures.
*Synchronized cardioversion*
- **Synchronized cardioversion** delivers an electrical shock timed to the R-wave of the QRS complex to treat **tachyarrhythmias with a pulse** (e.g., ventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response).
- It is **contraindicated in ventricular fibrillation** because there are no organized QRS complexes to synchronize with, and attempting synchronization can delay life-saving defibrillation.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 7: Seventy-two hours after admission for an acute myocardial infarction, a 48-year-old man develops dyspnea and a productive cough with frothy sputum. Physical examination shows coarse crackles in both lungs and a blowing, holosystolic murmur heard best at the apex. ECG shows Q waves in the anteroseptal leads. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is 23 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s current condition?
- A. Rupture of the ventricular free wall
- B. Postmyocardial infarction syndrome
- C. Aortic root dilation
- D. Rupture of the interventricular septum
- E. Rupture of the chordae tendineae (Correct Answer)
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Rupture of the chordae tendineae***
- The combination of acute dyspnea, frothy sputum (**pulmonary edema**), a new **holosystolic murmur** loudest at the apex, suggestive of **mitral regurgitation**, and high **pulmonary capillary wedge pressure** (PCWP > 18 mmHg indicating pulmonary edema) is classic for papillary muscle or chordae tendineae rupture following an **acute myocardial infarction (MI)**.
- Antero-septal Q waves suggest an infarction in an area supplied by the **left anterior descending artery**, which can also affect the **anterolateral papillary muscle** of the mitral valve.
*Rupture of the ventricular free wall*
- This typically presents as **cardiac tamponade** with hypotension, jugular venous distension, and muffled heart sounds, often leading to rapid hemodynamic collapse and death.
- While it can occur post-MI, a new holosystolic murmur and prominent pulmonary edema are not characteristic features.
*Postmyocardial infarction syndrome*
- Also known as **Dressler syndrome**, this is a **pericarditis** that develops weeks to months after an MI.
- It presents with fever, pleuritic chest pain, and pericardial friction rub and would not typically cause acute pulmonary edema or a new holosystolic murmur within 72 hours.
*Aortic root dilation*
- This condition is not directly linked to an acute MI and typically causes **aortic regurgitation**, which manifests as a **diastolic murmur** (decrescendo early diastolic murmur), not a holosystolic murmur.
- While it can cause heart failure, the acute onset post-MI with a new apical holosystolic murmur points away from this diagnosis.
*Rupture of the interventricular septum*
- This would also present with a new **holosystolic murmur**, but it would be loudest at the **left sternal border** due to a **ventricular septal defect**.
- While it can cause pulmonary edema and elevated PCWP, the murmur's location at the apex strongly points towards mitral valve pathology rather than a septal defect.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 8: A 60-year-old African American gentleman presents to the emergency department with sudden onset "vice-like" chest pain, diaphoresis, and pain radiating to his left shoulder. He has ST elevations on his EKG and elevated cardiac enzymes. Concerning his current pathophysiology, which of the following changes would you expect to see in this patient?
- A. No change in cardiac output; decreased venous return
- B. Increased cardiac output; increased systemic vascular resistance
- C. Decreased cardiac output; increased systemic vascular resistance (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased cardiac output; decreased systemic vascular resistance
- E. Decreased cardiac output; decreased venous return
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Decreased cardiac output; increased systemic vascular resistance***
- The patient's symptoms (chest pain, diaphoresis, ST elevations, elevated cardiac enzymes) are classic for an **acute myocardial infarction (MI)**, which directly impairs the heart's pumping function, leading to **decreased cardiac output**.
- In response to decreased cardiac output and reduced tissue perfusion, the body activates the **sympathetic nervous system** and **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system**, causing **vasoconstriction** and thus **increased systemic vascular resistance** to maintain blood pressure.
*No change in cardiac output; decreased venous return*
- An acute MI significantly compromises the heart's ability to pump blood, meaning **cardiac output will almost certainly change** (decrease).
- While venous return might be affected, it's not the primary compensatory mechanism often leading to **decreased CO** in acute MI, which is largely due to impaired systolic function.
*Increased cardiac output; increased systemic vascular resistance*
- **Increased cardiac output** is highly unlikely in the context of an acute myocardial infarction because the heart muscle is damaged and unable to pump effectively.
- While **increased systemic vascular resistance** occurs as a compensatory mechanism, it's in response to a failed heart, not one that is effectively increasing its output.
*Increased cardiac output; decreased systemic vascular resistance*
- Both **increased cardiac output** and **decreased systemic vascular resistance** are typically signs of a hyperdynamic state (e.g., sepsis in its early stages) or vasodilation, which is contrary to the pathophysiology of an MI.
- An MI causes **cardiac dysfunction** and **compensatory vasoconstriction**, not increased output and vasodilation.
*Decreased cardiac output; decreased venous return*
- While **decreased cardiac output** is expected, **decreased venous return** is not the primary or most impactful immediate systemic response; the body often tries to maintain venous return initially to optimize filling pressures, although severe MI can eventually lead to overall circulatory collapse.
- The more prominent and immediate compensatory mechanism for a failing heart is often **increased systemic vascular resistance** to maintain perfusion pressure.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 9: A 25-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 1-week-history of progressively worsening dyspnea and intermittent chest pain that increases on inspiration. He had an upper respiratory tract infection 2 weeks ago. His pulse is 115/min and blood pressure is 100/65 mm Hg. Examination shows inspiratory crackles bilaterally. His serum troponin I is 0.21 ng/mL (N < 0.1). An x-ray of the chest shows an enlarged cardiac silhouette and prominent vascular markings in both lung fields; costophrenic angles are blunted. A rhythm strip shows inverted T waves. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient's condition?
- A. Opening snap with low-pitched diastolic rumble
- B. Elevated brain natriuretic peptide (Correct Answer)
- C. Sarcomere duplication
- D. Right ventricular dilation
- E. Electrical alternans
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: ***Elevated brain natriuretic peptide***
- This patient presents with symptoms of **dyspnea**, **chest pain**, **tachycardia**, elevated **troponin I**, an enlarged **cardiac silhouette** with prominent vascular markings, and **blunted costophrenic angles**, all consistent with **cardiomyopathy** and heart failure, likely post-viral **myocarditis**.
- **Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)** is released by myocardial cells in response to ventricular stretch and volume overload, making it a strong indicator for **heart failure**.
*Opening snap with low-pitched diastolic rumble*
- An **opening snap** followed by a **low-pitched diastolic rumble** is characteristic of **mitral stenosis**, a valvular disorder not suggested by the patient's acute presentation and other findings.
- Mitral stenosis would typically be associated with a history of **rheumatic fever** and more specific echocardiographic findings of valve abnormalities.
*Sarcomere duplication*
- **Sarcomere duplication** and disarray are characteristic pathological findings in **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)**, an inherited genetic disorder.
- While HCM can cause dyspnea and chest pain, this patient's acute presentation following a viral infection and evidence of fluid overload are more indicative of an **acquired cardiomyopathy** such as myocarditis.
*Right ventricular dilation*
- While the patient has signs of **heart failure**, the chest X-ray shows an **enlarged cardiac silhouette** and **prominent vascular markings in both lung fields** and **blunted costophrenic angles**, suggesting **left ventricular failure** with fluid redistribution and pleural effusions.
- Significant **right ventricular dilation** would typically be associated with signs of right-sided heart failure like **peripheral edema** and **jugular venous distension**, which are not explicitly mentioned as primary findings.
*Electrical alternans*
- **Electrical alternans** is a specific ECG finding characterized by beat-to-beat variation in the QRS amplitude or axis, most commonly associated with **pericardial effusion** leading to cardiac tamponade.
- Although the patient has an enlarged cardiac silhouette, which could indicate effusion, the primary findings point more broadly to **myocardial dysfunction** and **heart failure** rather than tamponade.
Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG Question 10: Two days after undergoing an uncomplicated total thyroidectomy, a 63-year-old woman has acute, progressive chest pain. The pain is sharp and burning. She feels nauseated and short of breath. The patient has a history of hypertension, type 1 diabetes mellitus, medullary thyroid cancer, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A, anxiety, coronary artery disease, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. She smoked half a pack of cigarettes daily for 24 years but quit 18 years ago. Current medications include lisinopril, insulin glargine, insulin aspart, sertraline, aspirin, ranitidine, and levothyroxine. She appears anxious and diaphoretic. Her temperature is 37.4°C (99.3°F), pulse is 64/min, respirations are 17/min, and blood pressure is 148/77 mm Hg. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Examination shows a 3-cm linear incision over the anterior neck with 1 mm of surrounding erythema and mild serous discharge. The chest wall and abdomen are nontender. There is 5/5 strength in all extremities and decreased sensation to soft touch on the feet bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Obtain an ECG and troponin T levels (Correct Answer)
- B. Administer IV pantoprazole and schedule endoscopy
- C. Discontinue levothyroxine and obtain fT4 levels
- D. Administer IV levofloxacin and obtain chest radiograph
- E. Obtain urine and plasma metanephrine levels
Cardiac biomarkers Explanation: **Obtain an ECG and troponin T levels**
- The patient presents with acute, progressive **chest pain that is sharp and burning**, along with nausea and shortness of breath, which are classic symptoms of an acute coronary syndrome, especially given her history of **coronary artery disease**, hypertension, diabetes, and prior smoking.
- An **ECG** and **troponin T levels** are crucial first steps to evaluate for myocardial ischemia or infarction in this high-risk patient.
*Administer IV pantoprazole and schedule endoscopy*
- While the patient has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and her pain is described as "burning," the **acuteness, progression, and associated symptoms** (nausea, shortness of breath) in a patient with significant cardiac risk factors make a GI cause less likely as the primary concern.
- Empiric treatment for GERD without first ruling out a life-threatening cardiac event would be inappropriate and potentially dangerous.
*Discontinue levothyroxine and obtain fT4 levels*
- The patient is taking levothyroxine after a thyroidectomy for medullary thyroid cancer, but there is no immediate indication of thyroid hormone imbalance (e.g., hyperthyroidism causing chest pain) that would warrant discontinuing her medication or rushing fT4 levels as the first step in an acute chest pain presentation.
- Her pulse of 64/min is not suggestive of hyperthyroidism, which typically causes tachycardia.
*Administer IV levofloxacin and obtain chest radiograph*
- While shortness of breath can be a symptom of pneumonia, the **sharp, burning nature of the chest pain**, coupled with the absence of fever (temperature 37.4°C is mild), cough, or abnormal lung sounds (lungs clear to auscultation), makes an acute infection like pneumonia less probable as the primary diagnosis.
- Antibiotics and a chest radiograph would be considered after ruling out more immediate life-threatening conditions like acute coronary syndrome.
*Obtain urine and plasma metanephrine levels*
- The patient has a history of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A (MEN2A), which includes medullary thyroid cancer and can be associated with pheochromocytoma (adrenal tumor secreting catecholamines). However, her blood pressure (148/77 mm Hg) is not acutely elevated to crisis levels, and her symptoms are more consistent with cardiac ischemia than a pheochromocytoma crisis.
- While metanephrine levels would be important for long-term follow-up of MEN2A, they are not the immediate next step for acute chest pain in a patient with known coronary artery disease.
More Cardiac biomarkers US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.