Screening Fundamentals - The Why & How
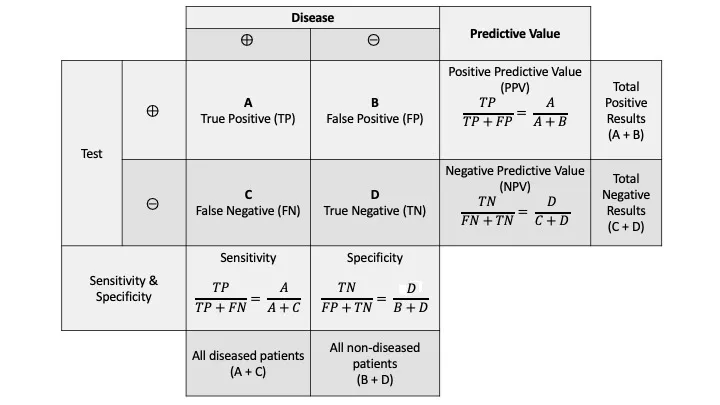
- Sensitivity: Detects disease in those who have it. $Sn = \frac{TP}{TP+FN}$
- Specificity: Rules out disease in those who don't. $Sp = \frac{TN}{TN+FP}$
- Positive Predictive Value (PPV): Probability of disease if test is positive. $PPV = \frac{TP}{TP+FP}$
- Negative Predictive Value (NPV): Probability of no disease if test is negative. $NPV = \frac{TN}{TN+FN}$
⭐ PPV and NPV are heavily influenced by disease prevalence. ↑ Prevalence → ↑ PPV & ↓ NPV.
- Wilson-Jungner Criteria: An effective screening program requires:
- Important problem, understood natural history.
- Accepted treatment, available facilities.
- Suitable & acceptable test.
- Cost-effective & continuous process.
📌 SPIN & SNOUT: SPecific test, when Positive, rules IN disease. SNensitive test, when Negative, rules OUT disease.
USPSTF Grades - Letters of the Law
| Grade | Recommendation | Clinical Action |
|---|---|---|
| A | Recommended. High certainty of substantial net benefit. | Offer or provide this service. |
| B | Recommended. High certainty of moderate net benefit or moderate certainty of moderate to substantial net benefit. | Offer or provide this service. |
| C | Selective Recommendation. Offer for individual patients based on professional judgment and patient preferences. At least moderate certainty of small net benefit. | Offer or provide for selected patients. Consider individual circumstances. |
| D | Not Recommended. Moderate or high certainty of no net benefit or that harms outweigh benefits. | Discourage the use of this service. |
| I | Insufficient Evidence. Evidence is lacking, of poor quality, or conflicting. Benefit cannot be determined. | Read the clinical considerations. If the service is offered, patients should understand the uncertainty. |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||
| flowchart TD |
Start["👤 Patient
• Clinical encounter• Preventive care"]
Assess["📋 Clinician Assessment
• USPSTF guidelines• Evaluate evidence"]
GradeAB["✅ Offer Service
• Grade A or B• High net benefit"]
GradeC["🤝 Shared Decision
• Grade C recommendation• Individual choice"]
GradeD["❌ Discourage Service
• Grade D recommendation• Harm outweights good"]
GradeI["❓ Discuss Uncertainty
• Grade I statement• Insufficient data"]
Start --> Assess Assess -->|Grade A/B| GradeAB Assess -->|Grade C| GradeC Assess -->|Grade D| GradeD Assess -->|Grade I| GradeI
style Start fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252 style Assess fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style GradeAB fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style GradeC fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1 style GradeD fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style GradeI fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8
> ⭐ Grade **C** recommendations are the most nuanced. The decision to screen rests on a collaborative conversation between the clinician and the patient, weighing the small potential benefit against individual patient factors like risk profile and personal values.
## Special Populations - High-Risk Nuances
Screening protocols adapt for individuals with higher baseline risk due to genetics, conditions, or exposures. The goal is earlier detection through more frequent or specialized testing.
| Special Population | Condition | Screening Guideline (vs. General Population) |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
| **Pregnancy** | Asymptomatic Bacteriuria | Urine culture at first prenatal visit (**12-16 wks**). Not routinely screened. |
| | Gestational Diabetes | **50g** 1-hr glucose challenge at **24-28 wks**. Not screened unless risk factors exist. |
| | Group B Strep | Rectovaginal culture at **36-37 wks**. Not screened. |
| **Strong Family Hx** | BRCA1/2 Mutation | Annual Breast MRI starting age **25**; annual mammogram at **30**. (vs. mammogram at **40-50**). |
| | Lynch (HNPCC) | Colonoscopy at **20-25**, repeat q**1-2 yrs**. (vs. age **45**, q**10 yrs**). |
| **Immunocompromised** | HIV & Cervical Cancer | Pap smear at diagnosis, then annually. (vs. q**3 yrs**). |
| | HIV (MSM) | Annual anal Pap test for Human Papillomavirus (HPV) related dysplasia. Not screened. |> ⭐ For patients with Lynch syndrome (HNPCC), screening extends beyond the colon. Regular upper endoscopy and screening for endometrial/ovarian cancer are also crucial due to increased extracolonic cancer risks.
## High-Yield Points - ⚡ Biggest Takeaways
> * **Smokers** with a ≥**20-pack-year** history require **annual low-dose CT** for lung cancer screening from age **50**-**80**.
> * Patients with **cirrhosis** need **biannual liver ultrasound** (+/- AFP) to screen for **hepatocellular carcinoma**.
> * A **first-degree relative** with CRC <**60** prompts colonoscopy at age **40** or **10 years** before the relative's diagnosis.
> * **BRCA carriers** undergo intensive screening with **annual mammograms and breast MRIs**.
> * **Lynch syndrome** (HNPCC) requires **colonoscopy every 1-2 years** beginning at age **20-25**.

