Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Syndrome recognition. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 1: A 66-year old man with a 45-pack-year smoking history presents with abdominal pain and constipation. He reports that he has had a worsening cough for several months and has lost 20 pounds over this time period. You order a complete metabolic profile, which demonstrates hypercalcemia. A chest radiograph shows a centrally located mass suspicious for malignancy. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
- A. Metastatic abdominal cancer
- B. Carcinoid tumor causing carcinoid syndrome
- C. Squamous cell carcinoma producing a peptide with hormonal activity (Correct Answer)
- D. Small cell carcinoma producing a peptide with hormonal activity
- E. Squamous cell carcinoma producing parathyroid hormone
Syndrome recognition Explanation: ***Squamous cell carcinoma producing a peptide with hormonal activity***
- The combination of **hypercalcemia**, a **central lung mass** in a patient with a heavy **smoking history**, and symptoms like abdominal pain and constipation (due to hypercalcemia) strongly suggests **paraneoplastic syndrome** due to squamous cell carcinoma.
- **Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)** of the lung is well-known to produce **parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP)**, leading to **humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy (HHM)**, which mimics the effects of PTH.
*Metastatic abdominal cancer*
- While metastatic cancer can cause weight loss and abdominal symptoms, it doesn't typically present with a **central lung mass** as the primary suspicious finding for malignancy and **hypercalcemia** without bone metastases.
- This option does not explain the presence of a **central lung mass** and associated hypercalcemia.
*Carcinoid tumor causing carcinoid syndrome*
- **Carcinoid tumors** can cause weight loss and abdominal pain, but they are typically associated with **carcinoid syndrome** (flushing, diarrhea, bronchospasm), not hypercalcemia.
- **Carcinoid tumors** rarely cause hypercalcemia and are not typically associated with large central lung masses and a heavy smoking history in this manner.
*Small cell carcinoma producing a peptide with hormonal activity*
- **Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC)** is associated with **paraneoplastic syndromes**, most notably **SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion)** leading to hyponatremia, and **Cushing's syndrome** due to ectopic ACTH production.
- While SCLC is a central lung mass and associated with smoking, it is **less commonly linked to PTHrP-mediated hypercalcemia** than squamous cell carcinoma.
*Squamous cell carcinoma producing parathyroid hormone*
- **Squamous cell carcinoma** produces **parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP)**, not true **parathyroid hormone (PTH)**.
- **PTHrP** mimics PTH in its effects but is structurally different; ectopic production of actual PTH by a non-parathyroid tumor is extremely rare.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 2: A 24-year-old man presents with a complaint of breathlessness while jogging. He says that he recently started marathon training. He does not have any family history of asthma nor has any allergies. He currently takes no medication. The blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and the heart rate is 67/min. With each heartbeat, he experiences pounding in his chest, and his head bobs. On physical examination, he has long fingers, funnel chest, and disproportionate body proportions with a decreased upper-to-lower segment ratio. On auscultation over the 2nd right intercostal space, an early diastolic murmur is heard, and 3rd and 4th heart sounds are heard. Echocardiography shows aortic root dilatation. The patient is scheduled for surgery. Which of the following is associated with this patient's condition?
- A. Klinefelter syndrome
- B. Intravenous drug abuse
- C. Marfan's Syndrome (Correct Answer)
- D. Kawasaki syndrome
- E. Gonorrhea
Syndrome recognition Explanation: ***Marfan's Syndrome***
- The patient presents with **tall stature**, **long fingers (arachnodactyly)**, **funnel chest (pectus excavatum)**, and **aortic root dilation** with **aortic regurgitation** (early diastolic murmur, head bobbing, pounding in the chest), all classic features of Marfan syndrome.
- This is a **connective tissue disorder** caused by a mutation in the **FBN1 gene**, leading to defective **fibrillin-1**, which is crucial for structural integrity in the heart, blood vessels, eyes, and skeleton.
*Klinefelter syndrome*
- Characterized by a **47, XXY karyotype** and typically presents with infertility, small testes, gynecomastia, and tall stature, but not the specific cardiovascular or skeletal features described.
- While it can cause tall stature, it does not explain the **arachnodactyly**, **pectus excavatum**, or the severe **aortic root dilation** and regurgitation.
*Intravenous drug abuse*
- Primarily associated with **infective endocarditis**, particularly affecting the **tricuspid valve**, leading to heart murmurs related to infection, not the skeletal and aortic root abnormalities seen here.
- This history would lead to a different clinical presentation, potentially involving fever, chills, and vegetations on valve leaflets, none of which are mentioned.
*Kawasaki syndrome*
- An **acute inflammatory vasculitis** primarily affecting young children, characterized by fever, rash, conjunctivitis, lymphadenopathy, and oral mucosal changes.
- While it can cause **coronary artery aneurysms**, it does not explain the skeletal abnormalities or the specific presentation of aortic root dilation with regurgitation in an adult.
*Gonorrhea*
- A **sexually transmitted infection** that can lead to disseminated gonococcal infection, causing arthritis, tenosynovitis, and dermatitis.
- It does not cause the specific skeletal abnormalities or the primary cardiac pathology of aortic root dilation and regurgitation described in this patient.
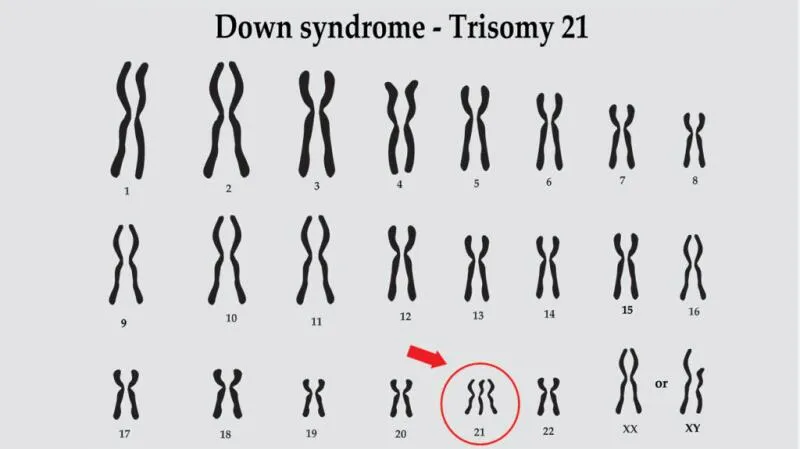
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 3: A 2720-g (6-lb) female newborn is delivered at term to a 39-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2. Examination in the delivery room shows micrognathia, prominent occiput with flattened nasal bridge, and pointy low-set ears. The eyes are upward slanting with small palpebral fissures. The fists are clenched with fingers tightly flexed. The index finger overlaps the third finger and the fifth finger overlaps the fourth. A 3/6 holosystolic murmur is heard at the lower left sternal border. The nipples are widely spaced and the feet have prominent heels and convex, rounded soles. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Deletion of Chromosome 5p
- B. Trisomy 13
- C. Fetal alcohol syndrome
- D. Trisomy 18 (Correct Answer)
- E. Trisomy 21
Syndrome recognition Explanation: **_Trisomy 18_**
- The constellation of findings, including **micrognathia**, prominent occiput, **low-set ears**, short palpebral fissures, **clenched fists with overlapping fingers**, widely spaced nipples, and **rocker-bottom feet**, are classic signs of **Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)**.
- The **holosystolic murmur** suggests a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)**, which is commonly associated with Trisomy 18.
*Deletion of Chromosome 5p*
- This is associated with **Cri-du-chat syndrome**, characterized by a **cat-like cry**, microcephaly, and intellectual disability.
- The classic features described in the case, such as rocker-bottom feet and overlapping fingers, are not typical of Cri-du-chat syndrome.
*Trisomy 13*
- This is **Patau syndrome**, characterized by **polydactyly**, cleft lip/palate, microphthalmia, and cutis aplasia.
- While it shares some features of severe developmental abnormalities, the specific hand posture and ear/facial anomalies point away from Trisomy 13.
*Fetal alcohol syndrome*
- This condition presents with **facial dysmorphology** (short palpebral fissures, thin upper lip, smooth philtrum), growth restriction, and intellectual disability.
- It does not typically include the prominent occiput, micrognathia, or characteristic finger positioning and foot deformities seen in this patient.
*Trisomy 21*
- Also known as **Down syndrome**, characterized by features such as **epicanthal folds**, upslanting palpebral fissures, a single palmar crease, and hypotonia.
- While some features like a VSD can overlap, the specific facial features and skeletal anomalies (e.g., clenched fists with overlapping fingers, rocker-bottom feet) are distinctly different from Down syndrome.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 4: A 68-year-old man presents to his primary care provider after noticing that his urine has been pink for the last week. He does not have any pain with urination, nor has he had any associated fevers or infections. On his review of systems, the patient notes that he thinks he has lost some weight since his belt is looser, and he has also had occasional dull pressure in his back for the past two months. His temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 132/90 mmHg, pulse is 64/min, and respirations are 12/min. The patient weighs 210 lbs (95.3 kg, BMI 31.9 kg/m²), compared to his weight of 228 lbs (103.4 kg, BMI 34.7 kg/m²) at his last visit 2 years prior. On exam, the patient does not have any back or costovertebral angle tenderness. On abdominal palpation, a firm mass can be appreciated deep in the left abdomen. Given the suspected diagnosis, the clinical workup should also assess for which of the following paraneoplastic syndromes?
- A. Hypercalcemia (Correct Answer)
- B. Polycythemia
- C. Anemia
- D. Stauffer syndrome
- E. Hypercortisolism
Syndrome recognition Explanation: ***Hypercalcemia***
- The patient's presentation with **painless hematuria**, unexplained weight loss, flank pain, and a palpable abdominal mass is highly suggestive of **renal cell carcinoma (RCC)**.
- **Hypercalcemia** is the **most common paraneoplastic syndrome** associated with RCC, occurring in 10-20% of cases, often due to the tumor secreting **parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP)**.
- This is the most important metabolic abnormality to screen for in the initial workup.
*Polycythemia*
- While **polycythemia** can be a paraneoplastic syndrome in RCC due to **erythropoietin (EPO) production**, it occurs in only 3-10% of cases, making it less common than hypercalcemia.
- The patient's symptoms do not specifically point to an excess red blood cell count.
*Anemia*
- **Anemia** is actually the most common hematologic finding in RCC (20-40% of cases), more common than polycythemia.
- It represents a paraneoplastic effect related to chronic disease and inflammatory cytokines.
- However, **hypercalcemia is the more critical paraneoplastic syndrome to assess** given its prognostic significance and need for intervention.
*Stauffer syndrome*
- **Stauffer syndrome** is a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with RCC characterized by **non-metastatic hepatic dysfunction** with elevated alkaline phosphatase and prolonged prothrombin time.
- While it occurs in 3-20% of cases, **hypercalcemia is more common** and typically assessed first in the metabolic workup.
*Hypercortisolism*
- **Hypercortisolism (Cushing's syndrome)** is rarely associated with RCC; it is more typically seen with **small cell lung carcinoma** or **adrenal tumors** producing ectopic ACTH.
- There are no symptoms mentioned in the patient's presentation to suggest excess cortisol production.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 5: A 66-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of shortness of breath and confusion. His pulse is 98/min, and blood pressure is 109/73 mm Hg. He is oriented to person but not time or place. A graph of his breathing pattern and oxygen saturation is shown. Which of the following additional findings is most likely present in this patient?
- A. Rib fracture
- B. Fruity breath odor
- C. Ventricular gallop (Correct Answer)
- D. Miotic pupils
- E. Barrel chest
Syndrome recognition Explanation: ***Ventricular gallop***
- The patient's presentation with **shortness of breath**, **confusion**, and **oxygen desaturation** coupled with the breathing pattern shown (likely Cheyne-Stokes respiration from the image) strongly suggests **heart failure**. A **ventricular gallop (S3 heart sound)** is a classic finding in heart failure, indicating rapid ventricular filling into a stiff or dilated ventricle.
- The **confusional state** and **tachypnea (implied by oxygen desaturation)** are consistent with **hypoxia** and **reduced cardiac output** often seen in decompensated heart failure, where an S3 gallop is frequently heard.
*Rib fracture*
- While a rib fracture can cause shortness of breath due to pain and reduced chest expansion, it would not typically lead to **confusion** or a specific cyclical breathing pattern like Cheyne-Stokes, nor would it directly cause a ventricular gallop.
- The patient's vital signs and mental status point towards a more systemic issue rather than isolated chest trauma.
*Fruity breath odor*
- A **fruity breath odor** is a hallmark of **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)**, caused by the exhalation of acetone. This condition would also present with confusion and tachypnea, but would typically involve hyperglycemia and metabolic acidosis.
- There is no information to suggest diabetes, and the presentation of a specific breathing pattern in correlation with cardiac findings makes heart failure more likely.
*Miotic pupils*
- **Miotic pupils (pinpoint pupils)** are strongly associated with **opioid overdose** or organophosphate poisoning. These conditions would cause respiratory depression, not necessarily the specific breathing pattern, and would not explain the other findings in this specific context.
- The patient's pulse and blood pressure are also not typical of severe opioid overdose, which often involves bradycardia and hypotension.
*Barrel chest*
- A **barrel chest** is a physical finding typically associated with **chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)** due to chronic air trapping. While COPD can cause shortness of breath and confusion (in acute exacerbations), it does not directly lead to a ventricular gallop.
- Although the patient's age makes COPD possible, the acute presentation with a specific breathing pattern and the likelihood of heart failure make a barrel chest a less specific or primary finding in this context.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 6: A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department for sudden weakness. The patient states that he was at home enjoying his morning coffee when his symptoms began. He says that his left arm suddenly felt very odd and weak thus prompting him to come to the ED. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes, COPD, hypertension, anxiety, alcohol abuse, and PTSD. He recently fell off a horse while horseback riding but claims to not have experienced any significant injuries. He typically drinks 5-7 drinks per day and his last drink was yesterday afternoon. His current medications include insulin, metformin, atorvastatin, lisinopril, albuterol, and fluoxetine. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 177/118 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 18/min, and oxygen saturation is 93% on room air. On physical exam, you note an elderly man who is mildly confused. Cardiopulmonary exam demonstrates bilateral expiratory wheezes and a systolic murmur along the right upper sternal border that radiates to the carotids. Neurological exam reveals cranial nerves II-XII as grossly intact with finger-nose exam mildly abnormal on the left and heel-shin exam within normal limits. The patient has 5/5 strength in his right arm and 3/5 strength in his left arm. The patient struggles to manipulate objects such as a pen with his left hand. The patient is given a dose of diazepam and started on IV fluids. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Bridging vein tear
- B. Cerebellar bleeding
- C. Berry aneurysm rupture
- D. Hypertensive encephalopathy
- E. Lipohyalinosis (Correct Answer)
Syndrome recognition Explanation: ***Lipohyalinosis***
- This patient's history of **hypertension** and **diabetes** are major risk factors for **lipohyalinosis**, which leads to **lacunar infarcts** and presents with sudden onset **pure motor hemiparesis**, as seen with the left arm weakness.
- The elevated blood pressure of 177/118 mmHg further supports a diagnosis involving **cerebral small vessel disease** secondary to chronic hypertension.
*Bridging vein tear*
- A bridging vein tear would typically lead to a **subdural hematoma**, characterized by a **gradual onset of symptoms** like headache, confusion, and neurological deficits, often following trauma, which is inconsistent with the sudden onset in this case.
- While the patient recently fell off a horse, his symptoms are acute and focal, not typical of the delayed presentation often seen with subdural hematomas.
*Cerebellar bleeding*
- **Cerebellar bleeding** usually presents with symptoms such as **ataxia**, **nystagmus**, vertigo, and vomiting, along with potential truncal instability, which are not the primary symptoms observed here.
- While the patient has some mild abnormality on the finger-nose test, the predominant symptom is **pure motor weakness** of the left arm, making a cerebellar bleed less likely.
*Berry aneurysm rupture*
- A **berry aneurysm rupture** typically causes a **sudden, severe headache** (thunderclap headache), neck stiffness, photophobia, and altered mental status due to subarachnoid hemorrhage, which are not reported by the patient.
- The patient's primary complaint is **focal motor weakness** and mild confusion, not the classic diffuse hemorrhagic symptoms of aneurysm rupture.
*Hypertensive encephalopathy*
- **Hypertensive encephalopathy** presents with a more generalized and rapidly progressive decline in neurological function, including severe headache, altered mental status, seizures, and visual disturbances, usually with **diastolic blood pressure >120 mmHg**.
- While the patient's blood pressure is high, the presentation of **focal motor deficit without severe headache** or global neurological decline makes this less likely than a lacunar stroke due to lipohyalinosis.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 7: A 75-year-old gentleman is brought to the ED with confusion that started earlier this morning. His family notes that he was complaining of feeling weak last night and also had a slight tremor at the time. He is afebrile and he has no known chronic medical conditions. Physical exam reveals a cooperative but confused gentleman. His mucous membranes are moist, he has no focal neurological deficits, and his skin turgor is within normal limits. His lab results are notable for:
Serum Na+: 123 mEq/L
Plasma osmolality: 268 mOsm/kg
Urine osmolality: 349 mOsm/kg
Urine Na+: 47 mEq/L
Which of the following malignancies is most likely to be responsible for this patient's presentation?
- A. Gastric adenocarcinoma
- B. Small cell lung cancer (Correct Answer)
- C. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- D. Non-seminomatous germ cell tumor
- E. Rib osteosarcoma
Syndrome recognition Explanation: ***Small cell lung cancer***
- This patient's laboratory values (hyponatremia, low plasma osmolality, and inappropriately high urine osmolality with elevated urine sodium) are classic for the **Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)**.
- **Small cell lung cancer** is the most common malignancy associated with paraneoplastic SIADH due to its ability to ectopically produce ADH.
*Gastric adenocarcinoma*
- While gastric adenocarcinomas can cause paraneoplastic syndromes, SIADH is an **uncommon** paraneoplastic manifestation of this type of cancer.
- Other paraneoplastic syndromes, such as **Trousseau's syndrome** (migratory thrombophlebitis), are more classically associated with gastric adenocarcinoma.
*Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma*
- Esophageal cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma, is **rarely associated** with SIADH.
- Its paraneoplastic manifestations are less defined and not prominent for ADH production.
*Non-seminomatous germ cell tumor*
- Germ cell tumors, particularly non-seminomatous types, are more commonly associated with paraneoplastic syndromes involving **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)** or **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)** production.
- While some germ cell tumors *can* release ADH, it is **not a primary cause** of SIADH compared to small cell lung cancer.
*Rib osteosarcoma*
- Osteosarcoma is a primary bone tumor and is **not typically associated** with paraneoplastic syndromes like SIADH.
- Its primary clinical manifestations are related to local bone destruction and metastasis.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 8: A 9-year-old boy is brought to the physician because his parents are concerned that he has been unable to keep up with his classmates at school. He is at the 4th percentile for height and at the 15th percentile for weight. Physical examination shows dysmorphic facial features. Psychologic testing shows impaired intellectual and adaptive functions. Genetic analysis shows a deletion of the long arm of chromosome 7. Which of the following is the most likely additional finding in this patient?
- A. Absent thymus gland
- B. Supravalvular aortic stenosis (Correct Answer)
- C. Brushfield spots on the iris
- D. Testicular enlargement
- E. Hand flapping movements
Syndrome recognition Explanation: ***Supravalvular aortic stenosis***
- The clinical presentation, including **dysmorphic facial features**, **growth restriction**, and **intellectual disability**, coupled with a **deletion on the long arm of chromosome 7**, is highly suggestive of **Williams syndrome**.
- **Supravalvular aortic stenosis** is a classic cardiovascular finding in **Williams syndrome**, present in about 75% of affected individuals.
*Absent thymus gland*
- An absent thymus gland is characteristic of **DiGeorge syndrome**, which is caused by a **deletion on chromosome 22q11**.
- This patient's genetic analysis indicates a deletion on **chromosome 7**, not chromosome 22.
*Brushfield spots on the iris*
- **Brushfield spots** are characteristic of **Down syndrome** (**trisomy 21**).
- The genetic finding of a **deletion on chromosome 7** rules out Down syndrome as the underlying cause.
*Testicular enlargement*
- **Testicular enlargement** is a hallmark feature of **Fragile X syndrome**, a genetic condition caused by an **FMR1 gene mutation** on the X chromosome.
- This patient's symptoms and genetic findings of a **chromosome 7 deletion** are not consistent with Fragile X syndrome.
*Hand flapping movements*
- **Hand flapping** is a common repetitive behavior observed in individuals with **autism spectrum disorder** and is also seen in some other genetic conditions like **Rett syndrome**.
- While individuals with Williams syndrome may have unique behavioral profiles, hand flapping is not a specific or typical feature of the syndrome, and the genetic finding points to Williams syndrome.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Syndrome recognition Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Syndrome recognition US Medical PG Question 10: A 67-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for fatigue. This has persisted for the past several months and has been steadily worsening. The patient has a past medical history of hypertension and diabetes; however, he is not currently taking any medications and does not frequently visit his physician. The patient has lost 20 pounds since his last visit. His laboratory values are shown below:
Hemoglobin: 9 g/dL
Hematocrit: 29%
Mean corpuscular volume: 90 µm^3
Serum:
Na+: 139 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 4.3 mEq/L
Ca2+: 11.8 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Intravascular hemolysis
- B. Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency
- C. Bone marrow aplasia
- D. Malignancy (Correct Answer)
- E. Iron deficiency
Syndrome recognition Explanation: **Malignancy**
- The patient's **unexplained weight loss**, worsening fatigue, and **anemia** are highly suspicious for an underlying malignancy.
- The elevated **calcium level (11.8 mg/dL)** suggests a paraneoplastic syndrome or bone involvement, which is common in many cancers (e.g., multiple myeloma, solid tumors with bony metastases).
*Intravascular hemolysis*
- This would typically present with signs of red blood cell destruction, such as **jaundice**, dark urine, and elevated **lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)**, none of which are mentioned.
- The **normocytic anemia (MCV 90 µm^3)** is less typical for acute hemolysis, which can sometimes cause macrocytosis due to reticulocytosis.
*Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency*
- These deficiencies primarily cause **macrocytic anemia**, characterized by an **elevated mean corpuscular volume (MCV)**, which is not present here (MCV is 90 µm^3).
- While fatigue can be a symptom, the unexplained weight loss and hypercalcemia point away from these as the primary diagnosis.
*Bone marrow aplasia*
- **Aplastic anemia** typically presents with **pancytopenia** (low red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets), which is not indicated here beyond the anemia.
- This condition does not directly explain the significant weight loss or hypercalcemia.
*Iron deficiency*
- **Iron deficiency anemia** is typically a **microcytic, hypochromic anemia**, meaning the **MCV would be low**, which is not the case here (MCV is 90 µm^3).
- While it can cause fatigue, it does not explain the unexplained weight loss or hypercalcemia reported in this patient.
More Syndrome recognition US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.