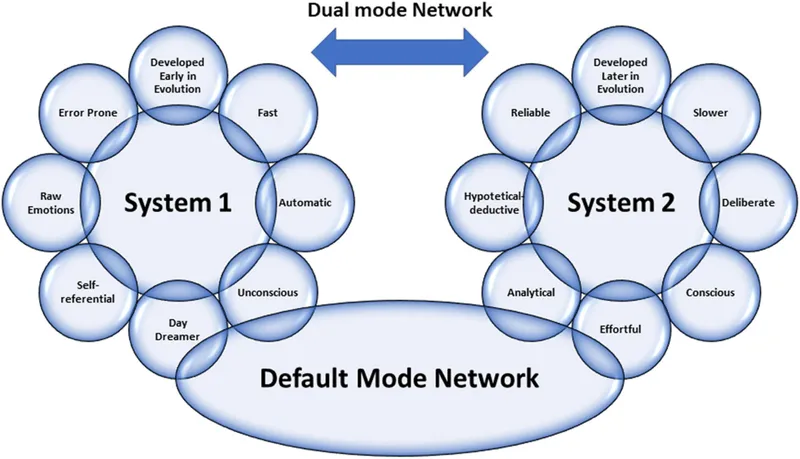
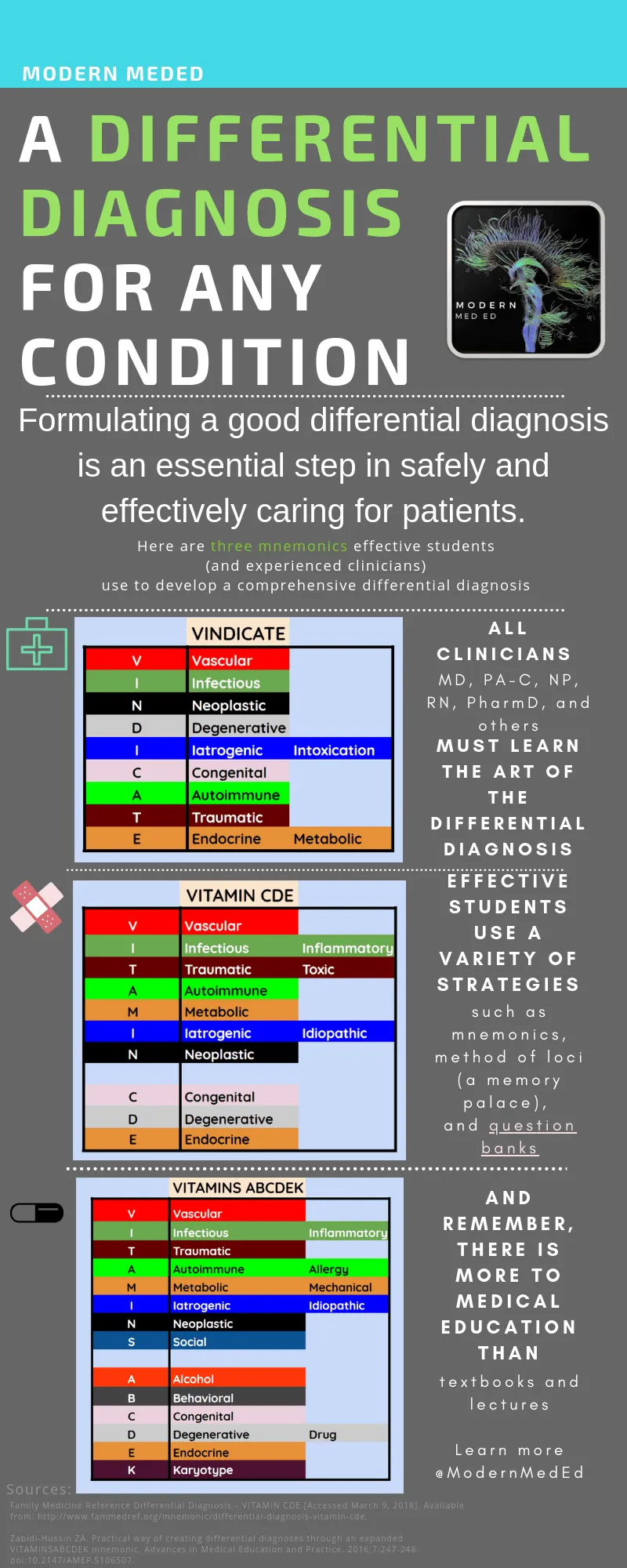
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 1: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 2: A 28-year-old woman dies shortly after receiving a blood transfusion. Autopsy reveals widespread intravascular hemolysis and acute renal failure. Investigation reveals that she received type A blood, but her medical record indicates she was type O. In a malpractice lawsuit, which of the following elements must be proven?
- A. Duty, breach, causation, and damages (Correct Answer)
- B. Only duty and breach
- C. Only breach and causation
- D. Duty, breach, and damages
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***Duty, breach, causation, and damages***
- In a medical malpractice lawsuit, all four elements—**duty, breach, causation, and damages**—must be proven for a successful claim.
- The healthcare provider had a **duty** to provide competent care, they **breached** that duty by administering the wrong blood type, this breach **caused** the patient's death and renal failure, and these injuries constitute **damages**.
*Only duty and breach*
- While **duty** and **breach** are necessary components, proving only these two is insufficient for a malpractice claim.
- It must also be demonstrated that the breach directly led to the patient's harm and resulted in legally recognized damages.
*Only breach and causation*
- This option omits the crucial elements of professional **duty** owed to the patient and the resulting **damages**.
- A claim cannot succeed without establishing that a duty existed and that quantifiable harm occurred.
*Duty, breach, and damages*
- This option misses the critical element of **causation**, which links the provider's breach of duty to the patient's injuries.
- Without proving that the breach *caused* the damages, even if a duty was owed and breached, and damages occurred, the claim would fail.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 3: A 60-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by police officers because he was acting strangely in public. The patient was found talking nonsensically to characters on cereal boxes in the store. Past medical history is significant for multiple hospitalizations for alcohol-related injuries and seizures. The patient’s vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows a disheveled male who is oriented to person, but not time or place. Neurologic examination shows nystagmus and severe gait ataxia. A T1/T2 MRI is performed and demonstrates evidence of damage to the mammillary bodies. The patient is given the appropriate treatment for recovering most of his cognitive functions. However, significant short-term memory deficits persist. The patient remembers events from his past such as the school and college he attended, his current job, and the names of family members quite well. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Schizophrenia
- B. Korsakoff's syndrome (Correct Answer)
- C. Wernicke encephalopathy
- D. Delirium
- E. Delirium tremens
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***Korsakoff's syndrome***
- The patient's history of **chronic alcohol abuse**, along with **gait ataxia**, **nystagmus**, and most notably, significant **anterograde amnesia** (inability to form new long-term memories) despite preserved remote memory, points to Korsakoff's syndrome.
- **Damage to the mammillary bodies** on MRI is a classic finding in Korsakoff's syndrome, a direct result of **thiamine deficiency**.
- The patient demonstrates the characteristic pattern: **impaired new memory formation** while retaining memories from his past (school, college, job, family names).
*Schizophrenia*
- Schizophrenia typically presents with **hallucinations and delusions** (e.g., talking to cereal box characters), but it is not commonly associated with physical signs like **nystagmus** or **gait ataxia**, nor with MRI findings of mammillary body damage.
- While the initial presentation of talking to cereal box characters might suggest psychosis, the complete clinical picture, especially the neurological deficits and persistent memory impairment, points away from schizophrenia as the primary diagnosis.
*Wernicke encephalopathy*
- Wernicke encephalopathy shares symptoms like **nystagmus** and **ataxia** with this patient and is also due to **thiamine deficiency** in alcoholics.
- However, Wernicke encephalopathy typically presents with more acute and severe symptoms, including **global confusion** and **ophthalmoplegia**, and represents the acute phase. The dominant chronic **anterograde amnesia** described here is characteristic of Korsakoff's syndrome, which represents the chronic sequela.
*Delirium*
- Delirium is characterized by an **acute disturbance in attention and cognition**, often with a fluctuating course, and can be seen in alcohol withdrawal.
- While the patient shows some disorientation, the chronic nature of the symptoms, the specific neurological deficits (nystagmus, ataxia), and particularly the persistent, isolated **anterograde amnesia** are not typical features of delirium.
*Delirium tremens*
- Delirium tremens is a severe form of **alcohol withdrawal** characterized by **autonomic hyperactivity**, severe delirium, hallucinations, and seizures.
- While the patient has a history of alcohol-related seizures, his current vital signs are normal, and the persistent, chronic memory deficits and specific MRI findings are not hallmarks of acute delirium tremens but rather a chronic neurological complication.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 4: A research study is comparing 2 novel tests for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The first is a serum blood test, and the second is a novel PET radiotracer that binds to beta-amyloid plaques. The researchers intend to have one group of patients with AD assessed via the novel blood test, and the other group assessed via the novel PET examination. In comparing these 2 trial subsets, the authors of the study may encounter which type of bias?
- A. Selection bias (Correct Answer)
- B. Confounding bias
- C. Recall bias
- D. Measurement bias
- E. Lead-time bias
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***Selection bias***
- This occurs when different patient groups are assigned to different interventions or measurements in a way that creates **systematic differences** between comparison groups.
- In this study, having **separate patient groups** assessed with different diagnostic methods (blood test vs. PET scan) means any differences observed could be due to **differences in the patient populations** rather than differences in test performance.
- To validly compare two diagnostic tests, both tests should ideally be performed on the **same patients** (paired design) or patients should be **randomly assigned** to receive one test or the other, ensuring comparable groups.
- This is a fundamental **study design flaw** that prevents valid comparison of the two diagnostic methods.
*Measurement bias*
- Also called information bias, this occurs when there are systematic errors in how outcomes or exposures are measured.
- While using different measurement tools could introduce measurement variability, the primary issue here is that **different patient populations** are being compared, not just different measurement methods on the same population.
- Measurement bias would be more relevant if the same patients were assessed with both methods but one method was systematically misapplied or measured incorrectly.
*Confounding bias*
- This occurs when an extraneous variable is associated with both the exposure and outcome, distorting the observed relationship.
- While patient characteristics could confound results, the fundamental problem is the **study design itself** (separate groups for separate tests), which is selection bias.
*Recall bias*
- This involves systematic differences in how participants remember or report past events, common in **retrospective case-control studies**.
- Not relevant here, as this involves prospective diagnostic testing, not recollection of past exposures.
*Lead-time bias*
- Occurs in screening studies when earlier detection makes survival appear longer without changing disease outcomes.
- Not applicable to this scenario, which focuses on comparing two diagnostic methods in separate patient groups, not on survival or disease progression timing.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 5: A 57-year-old man presents to his oncologist to discuss management of small cell lung cancer. The patient is a lifelong smoker and was diagnosed with cancer 1 week ago. The patient states that the cancer was his fault for smoking and that there is "no hope now." He seems disinterested in discussing the treatment options and making a plan for treatment and followup. The patient says "he does not want any treatment" for his condition. Which of the following is the most appropriate response from the physician?
- A. "You seem upset at the news of this diagnosis. I want you to go home and discuss this with your loved ones and come back when you feel ready to make a plan together for your care."
- B. "It must be tough having received this diagnosis; however, new cancer therapies show increased efficacy and excellent outcomes."
- C. "It must be very challenging having received this diagnosis. I want to work with you to create a plan." (Correct Answer)
- D. "We are going to need to treat your lung cancer. I am here to help you throughout the process."
- E. "I respect your decision and we will not administer any treatment. Let me know if I can help in any way."
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***"It must be very challenging having received this diagnosis. I want to work with you to create a plan."***
- This response **acknowledges the patient's emotional distress** and feelings of guilt and hopelessness, which is crucial for building rapport and trust.
- It also gently **re-engages the patient** by offering a collaborative approach to treatment, demonstrating the physician's commitment to supporting him through the process.
*"You seem upset at the news of this diagnosis. I want you to go home and discuss this with your loved ones and come back when you feel ready to make a plan together for your care."*
- While acknowledging distress, sending the patient home without further engagement **delays urgent care** for small cell lung cancer, which is aggressive.
- This response might be perceived as dismissive of his immediate feelings and can **exacerbate his sense of hopelessness** and isolation.
*"It must be tough having received this diagnosis; however, new cancer therapies show increased efficacy and excellent outcomes."*
- This statement moves too quickly to treatment efficacy without adequately addressing the patient's current **emotional state and fatalism**.
- While factual, it **lacks empathy** for his personal feelings of blame and hopelessness, potentially making him feel unheard.
*"We are going to need to treat your lung cancer. I am here to help you throughout the process."*
- This response is **too directive and authoritarian**, which can alienate a patient who is already feeling guilty and resistant to treatment.
- It fails to acknowledge his stated feelings of "no hope now" or his disinterest in treatment, which are critical to address before discussing the necessity of treatment.
*"I respect your decision and we will not administer any treatment. Let me know if I can help in any way."*
- While respecting patient autonomy is vital, immediately accepting a patient's decision to refuse treatment without exploring the underlying reasons (e.g., guilt, hopelessness, lack of information) is **premature and potentially harmful**.
- The physician has a responsibility to ensure the patient is making an informed decision, especially for a rapidly progressing condition like small cell lung cancer.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 6: An epidemiologist is evaluating the efficacy of Noxbinle in preventing HCC deaths at the population level. A clinical trial shows that over 5 years, the mortality rate from HCC was 25% in the control group and 15% in patients treated with Noxbinle 100 mg daily. Based on this data, how many patients need to be treated with Noxbinle 100 mg to prevent, on average, one death from HCC?
- A. 20
- B. 73
- C. 10 (Correct Answer)
- D. 50
- E. 100
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***10***
- The **number needed to treat (NNT)** is calculated by first finding the **absolute risk reduction (ARR)**.
- **ARR** = Risk in control group - Risk in treatment group = 25% - 15% = **10%** (or 0.10).
- **NNT = 1 / ARR** = 1 / 0.10 = **10 patients**.
- This means that **10 patients must be treated with Noxbinle to prevent one death from HCC** over 5 years.
*20*
- This would result from an ARR of 5% (1/0.05 = 20), which is not supported by the data.
- May arise from miscalculating the risk difference or incorrectly halving the actual ARR.
*73*
- This value does not correspond to any standard calculation of NNT from the given mortality rates.
- May result from confusion with other epidemiological measures or calculation error.
*50*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 2% (1/0.02 = 50), which significantly underestimates the actual risk reduction.
- Could result from incorrectly calculating the difference as a proportion rather than absolute percentage points.
*100*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 1% (1/0.01 = 100), grossly underestimating the treatment benefit.
- May result from confusing ARR with relative risk reduction or other calculation errors.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 7: An academic medical center in the United States is approached by a pharmaceutical company to run a small clinical trial to test the effectiveness of its new drug, compound X. The company wants to know if the measured hemoglobin a1c (Hba1c) of patients with type 2 diabetes receiving metformin and compound X would be lower than that of control subjects receiving only metformin. After a year of study and data analysis, researchers conclude that the control and treatment groups did not differ significantly in their Hba1c levels.
However, parallel clinical trials in several other countries found that compound X led to a significant decrease in Hba1c. Interested in the discrepancy between these findings, the company funded a larger study in the United States, which confirmed that compound X decreased Hba1c levels. After compound X was approved by the FDA, and after several years of use in the general population, outcomes data confirmed that it effectively lowered Hba1c levels and increased overall survival. What term best describes the discrepant findings in the initial clinical trial run by institution A?
- A. Type I error
- B. Hawthorne effect
- C. Type II error (Correct Answer)
- D. Publication bias
- E. Confirmation bias
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***Type II error***
- A **Type II error** occurs when a study fails to **reject a false null hypothesis**, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference or effect when one actually exists.
- In this case, the initial US trial incorrectly concluded that Compound X had no significant effect on HbA1c, while subsequent larger studies and real-world data proved it did.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (alpha error) occurs when a study incorrectly **rejects a true null hypothesis**, concluding there is a significant difference or effect when there isn't.
- This scenario describes the opposite: the initial study failed to find an effect that genuinely existed, indicating a Type II error, not a Type I error.
*Hawthorne effect*
- The **Hawthorne effect** is a type of reactivity in which individuals modify an aspect of their behavior in response to their awareness of being observed.
- This effect does not explain the initial trial's failure to detect a real drug effect; rather, it relates to participants changing behavior due to study participation itself.
*Publication bias*
- **Publication bias** occurs when studies with positive or statistically significant results are more likely to be published than those with negative or non-significant results.
- While relevant to the literature as a whole, it doesn't explain the discrepancy in findings within a single drug's development where a real effect was initially missed.
*Confirmation bias*
- **Confirmation bias** is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one's preexisting beliefs or hypotheses.
- This bias would likely lead researchers to *find* an effect if they expected one, or to disregard data that contradicts their beliefs, which is not what happened in the initial trial.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 8: During an evaluation of a new diagnostic imaging modality for detecting salivary gland tumors, 90 patients tested positive out of the 100 patients who tested positive with the gold standard test. A total of 80 individuals tested negative with the new test out of the 100 individuals who tested negative with the gold standard test. What is the positive likelihood ratio for this test?
- A. 80/90
- B. 90/100
- C. 90/20 (Correct Answer)
- D. 90/110
- E. 10/80
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***90/20***
- The **positive likelihood ratio (LR+)** is calculated as **sensitivity / (1 - specificity)**. To calculate this, we first need to determine the values for true positives (TP), false positives (FP), true negatives (TN), and false negatives (FN).
- Given that 90 out of 100 actual positive patients tested positive, **TP = 90** and **FN = 100 - 90 = 10**. Also, 80 out of 100 actual negative patients tested negative, so **TN = 80** and **FP = 100 - 80 = 20**.
- **Sensitivity** is the true positive rate (TP / (TP + FN)) = 90 / (90 + 10) = 90 / 100.
- **Specificity** is the true negative rate (TN / (TN + FP)) = 80 / (80 + 20) = 80 / 100.
- Therefore, LR+ = (90/100) / (1 - 80/100) = (90/100) / (20/100) = **90/20**.
*80/90*
- This option incorrectly represents the components for the likelihood ratio. It seems to misinterpret the **true negative** count and the **true positive** count.
- It does not follow the formula for LR+ which is **sensitivity / (1 - specificity)**.
*90/100*
- This value represents the **sensitivity** of the test, which is the proportion of true positives among all actual positives.
- It does not incorporate the **false positive rate** (1 - specificity) in the denominator required for the positive likelihood ratio.
*90/110*
- This option incorrectly combines different values, possibly by confusing the denominator for sensitivity or specificity calculations.
- It does not correspond to the formula for the **positive likelihood ratio**.
*10/80*
- This value seems to relate to the inverse of the **false negative rate** (10/100) or misrepresents the relationship between false negatives and true negatives.
- It is not correctly structured to represent the **positive likelihood ratio (LR+)**.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG Question 10: A 77-year-old female comes to a medical school's free clinic for follow-up examination after a urinary tract infection (UTI) and is seen by a fourth year medical student. The clinic serves largely uninsured low-income patients in a New York City neighborhood with a large African American and Latino population. Two weeks ago, the patient was treated in the local emergency department where she presented with altered mental state and dysuria. The medical student had recently read about a study that described a strong relationship between cognitive impairment and UTI hospitalization risk (RR = 1.34, p < 0.001). The attending physician at the medical student's free clinic is also familiar with this study and tells the medical student that the study was conducted in a sample of upper middle class Caucasian patients in the Netherlands. The attending states that the results of the study should be interpreted with caution. Which of the following concerns is most likely underlying the attending physician's remarks?
- A. Confounding bias
- B. Selection bias
- C. Poor reliability
- D. Low internal validity
- E. Low external validity (Correct Answer)
Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning Explanation: ***Low external validity***
- **External validity** refers to the generalizability of study findings to other populations, settings, or times.
- The findings from a study of **upper-middle-class Caucasian patients in the Netherlands** may not apply to low-income African American and Latino patients in New York City due to socioeconomic, genetic, and environmental differences, leading to low external validity.
*Confounding bias*
- **Confounding bias** occurs when an unobserved variable is associated with both the exposure and the outcome, distorting their true relationship.
- While confounding can affect internal validity, the attending's concern is specifically about the applicability of the findings to a different population, not the initial study's internal integrity.
*Selection bias*
- **Selection bias** arises when the study participants are not representative of the target population, often leading to systematic differences between groups.
- While the *initial study* might have had its own selection bias if its sample wasn't representative of the Netherlands population, the attending's concern relates to applying its findings to a *different* population.
*Poor reliability*
- **Reliability** refers to the consistency or reproducibility of a measurement or study result over time or across different observers.
- This concern is about the generalizability of the findings to a different population, not whether the initial study's measurements or results were inconsistent.
*Low internal validity*
- **Internal validity** refers to the extent to which a study establishes a cause-and-effect relationship between the intervention/exposure and the outcome within its own sample.
- The attending's concern is not that the study itself was poorly conducted or failed to demonstrate a true association within its *own* population, but rather that its findings may not hold true for *other* populations.
More Integrating evidence-based medicine into reasoning US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.