Making the most of available information US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Making the most of available information. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
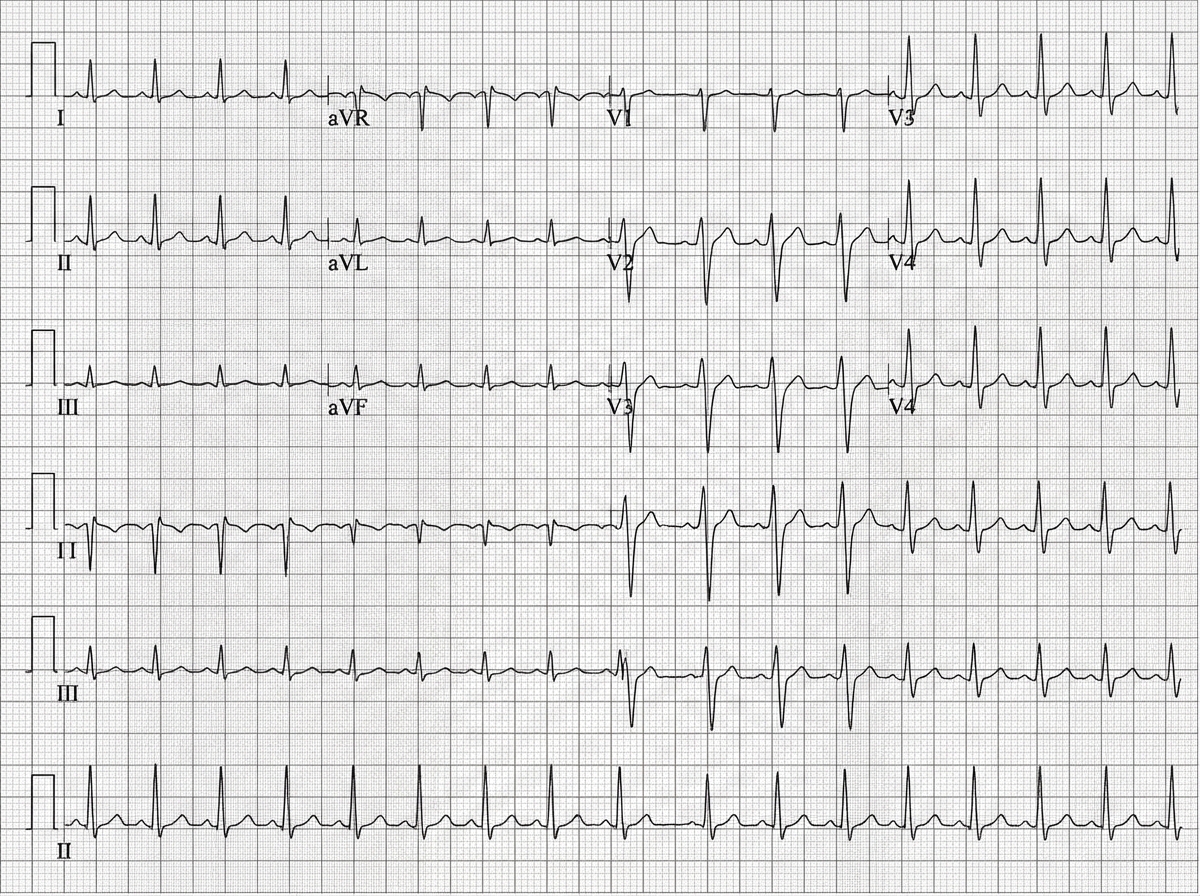
Making the most of available information US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after a car accident with pain in the middle of his chest and some shortness of breath. He has sustained injuries to his right arm and leg. He did not lose consciousness. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg. He is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. Examination shows several injuries to the upper extremities and chest. There are jugular venous pulsations 10 cm above the sternal angle. Heart sounds are faint on cardiac examination. The lungs are clear to auscultation. An ECG is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Contrast-enhanced CT angiography
- B. Transthoracic echocardiography (Correct Answer)
- C. X-ray of the chest
- D. CT scan of the brain
- E. Contrast esophagram with gastrografin
Making the most of available information Explanation: ***Transthoracic echocardiography***
- The patient's presentation with **chest pain**, shortness of breath, **hypotension**, **elevated jugular venous pressure (JVP)**, and **faint heart sounds** after trauma strongly suggests **Beck's triad**, which is classic for **cardiac tamponade**.
- **Transthoracic echocardiography** is the fastest and most accurate method to diagnose cardiac tamponade by visualizing pericardial fluid and its hemodynamic effects.
*Contrast-enhanced CT angiography*
- While CT angiography can detect vascular injuries or aortic dissection, it is not the initial diagnostic test for suspected cardiac tamponade.
- The patient's **hemodynamic instability** requires a rapid diagnostic tool to identify life-threatening conditions like tamponade.
*X-ray of the chest*
- A chest X-ray might show a **widened mediastinum** or **cardiomegaly** if there's a large effusion, but it is not sensitive enough to detect smaller effusions causing tamponade or to assess their hemodynamic impact.
- It does not provide real-time visualization of the heart and pericardium, which is crucial in this emergent setting.
*CT scan of the brain*
- A CT scan of the brain is indicated for suspected head injuries or neurological deficits, but the patient is alert and oriented, and his immediate life threat is clearly thoracic.
- Addressing the signs of cardiac tamponade takes precedence over evaluating the brain given his stable neurological status.
*Contrast esophagram with gastrografin*
- This study is used to diagnose **esophageal perforations**. While possible in significant trauma, the patient's symptoms of **Beck's triad** point specifically to cardiac tamponade, making esophageal perforation a less likely primary diagnosis and this investigation less urgent.
- It would not address the immediate, life-threatening cardiovascular compromise.
Making the most of available information US Medical PG Question 2: A 75-year-old man presents to the emergency department after an episode of syncope while walking outside with his wife. His wife states that he suddenly appeared pale and collapsed to the ground. She says he remained unconscious for 1 minute. He says he noticed a fluttering in his chest and excessive sweating before the episode. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus, essential hypertension, and chronic stable angina. He has not started any new medications in the past few months. Vital signs reveal: temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 135/72 mm Hg, and pulse 72/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. ECG shows an old bifascicular block. Echocardiogram and 24-hour Holter monitoring are normal. Which of the following is the best next step in the evaluation of this patient's condition?
- A. Cardiac enzymes
- B. Continuous loop recorder (Correct Answer)
- C. Valsalva maneuver
- D. Electroencephalography (EEG)
- E. Tilt-table test
Making the most of available information Explanation: ***Continuous loop recorder***
- This patient's syncope is preceded by **palpitations (fluttering in chest)** and **sweating**, suggesting a cardiac etiology, specifically a **transient arrhythmia** not captured on a standard ECG or 24-hour Holter.
- A continuous loop recorder provides prolonged monitoring (months to years), increasing the likelihood of detecting intermittent arrhythmias responsible for syncopal episodes.
*Cardiac enzymes*
- While cardiac enzymes (e.g., troponin) are crucial for evaluating **acute myocardial ischemia** or infarction, the patient presents with syncope and no new chest pain, and his stable angina suggests chronic disease rather than an acute event leading to syncope in this specific instance.
- An **ECG showing an old bifascicular block** and an **unremarkable physical exam** make an acute cardiac event less likely as the primary cause of syncope when an arrhythmia is suspected.
*Valsalva maneuver*
- The Valsalva maneuver is a diagnostic tool often used to differentiate between certain types of **tachyarrhythmias** or to evaluate for **autonomic dysfunction**, but it is not an evaluative step for a patient presenting with unexplained syncope where an arrhythmia has not yet been documented.
- It would not help in identifying the cause of intermittent syncope in a patient whose standard workup has been unremarkable, as it's a test for immediate physiological response, not prolonged cardiac rhythm monitoring.
*Electroencephalography (EEG)*
- EEG is indicated when **seizure disorder** is suspected as the cause of loss of consciousness, often characterized by tonic-clonic movements, post-ictal confusion, or focal neurologic signs, which are absent in this patient's presentation.
- The patient's pre-syncopal symptoms of **palpitations and sweating** point away from a seizure and towards a cardiac cause.
*Tilt-table test*
- A tilt-table test is used to evaluate for **vasovagal syncope** or **postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS)**, often considered when other cardiac causes are ruled out or when syncope is typically triggered by prolonged standing.
- Given the patient's pre-syncopal **palpitations**, a **cardiac arrhythmia** remains a higher suspicion than vasovagal syncope at this stage, especially after normal echocardiogram and Holter monitoring, necessitating further arrhythmia investigation.
Making the most of available information US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old man presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle collision. He was in the front seat and unrestrained driver in a head on collision. His temperature is 99.2°F (37.3°C), blood pressure is 90/65 mmHg, pulse is 152/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a young man who opens his eyes spontaneously and is looking around. He answers questions with inappropriate responses but discernible words. He withdraws from pain but does not have purposeful movement. Which of the following is this patient's Glasgow coma scale?
- A. 9
- B. 15
- C. 7
- D. 11 (Correct Answer)
- E. 13
Making the most of available information Explanation: ***11***
- **Eye-opening (E)**: The patient opens his eyes spontaneously, scoring **E4**.
- **Verbal response (V)**: He gives inappropriate responses but discernible words, scoring **V3**.
- **Motor response (M)**: He withdraws from pain but does not have purposeful movement, scoring **M4**.
- Therefore, the total Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is **E4 + V3 + M4 = 11**.
*9*
- This score would imply a lower verbal or motor response, such as **incomprehensible sounds (V2)** or **abnormal flexion (M3)**, which is not consistent with the patient's presentation.
- For example, E4 + V2 + M3 would equal 9.
*15*
- A GCS of 15 indicates **normal neurological function**, meaning the patient would be fully oriented, obey commands, and open eyes spontaneously, which is not the case here.
- This score is for a patient who is fully conscious and responsive.
*7*
- A GCS of 7 suggests a **severe brain injury**, which would typically present with a much poorer response, such as **no verbal response (V1)** or **abnormal extension (M2)**.
- For example, E4 + V1 + M2 would equal 7.
*13*
- This score would mean a higher level of consciousness, such as **confused conversation (V4)** or **localizing pain (M5)**, which is better than the patient's described responses.
- For example, E4 + V4 + M5 would equal 13.
Making the most of available information US Medical PG Question 4: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of a cough and hoarseness. He reports that the cough is worse when he lies down after lunch. His temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F); the remainder of his vital signs are within normal limits. Because the physician has recently been seeing several patients with the common cold, the diagnosis of a viral upper respiratory tract infection readily comes to mind. The physician fails to consider the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease, which the patient is later found to have. Which of the following most accurately describes the cognitive bias that the physician had?
- A. Framing
- B. Anchoring
- C. Visceral
- D. Confirmation
- E. Availability (Correct Answer)
Making the most of available information Explanation: ***Availability***
- The physician recently seeing several patients with the common cold led to this diagnosis readily coming to mind, demonstrating how easily recalled examples can disproportionately influence diagnosis.
- This bias occurs when easily recalled instances or information (like recent cases of common cold) are used to estimate the likelihood or frequency of an event, even if other more relevant data exist.
*Framing*
- This bias occurs when the way information is presented (e.g., as a gain or a loss) influences a decision, rather than the intrinsic characteristics of the options themselves.
- The scenario does not involve the presentation of information in different ways to sway the physician's judgment.
*Anchoring*
- This bias involves relying too heavily on an initial piece of information (the "anchor") when making subsequent judgments, often leading to insufficient adjustment away from that anchor.
- While the physician initially considered a viral URI, the setup is more about the ease of recall influencing the decision rather than being stuck on an initial data point.
*Visceral*
- This is not a commonly recognized cognitive bias in the context of medical decision-making; "visceral" largely refers to emotional or intuitive feelings rather than a structured cognitive bias.
- Cognitive biases describe systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment, not merely emotional responses.
*Confirmation*
- This bias involves seeking, interpreting, favoring, and recalling information in a way that confirms one's pre-existing beliefs or hypotheses.
- The physician did not actively seek information to confirm the common cold diagnosis; rather, the diagnosis came to mind due to recent encounters, which aligns with availability bias.
Making the most of available information US Medical PG Question 5: A 39-year-old woman presents with progressive weakness, exercise intolerance, and occasional dizziness for the past 3 months. Past medical history is unremarkable. She reports an 18-pack-year smoking history and drinks alcohol rarely. Her vital signs include: temperature 36.6°C (97.8°F), blood pressure 139/82 mm Hg, pulse 98/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Her laboratory results are significant for the following:
Hemoglobin 9.2 g/dL
Erythrocyte count 2.1 million/mm3
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 88 μm3
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) 32 pg/cell
Leukocyte count 7,500/mm3
Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient’s condition?
- A. Serum ferritin level
- B. Direct antiglobulin test
- C. C-reactive protein (CRP)
- D. Bone marrow biopsy
- E. Reticulocyte count (Correct Answer)
Making the most of available information Explanation: ***Reticulocyte count***
- A **normocytic anemia** (MCV 88) with signs of weakness and exercise intolerance requires evaluation of **red blood cell production**.
- A reticulocyte count helps differentiate between **hypoproliferative** (low count) and **hyperproliferative** (high count) anemias, guiding further diagnostic steps.
*Serum ferritin level*
- While often low in **iron-deficiency anemia**, this patient’s **normocytic MCV** makes iron deficiency less likely as the primary cause without other features.
- A normal ferritin doesn't rule out other causes of anemia, and a high ferritin could indicate **anemia of chronic disease**, but further understanding of RBC production is needed first.
*Direct antiglobulin test*
- This test is used to diagnose **autoimmune hemolytic anemia**, which typically presents with **jaundice**, **splenomegaly**, and elevated **lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)**, none of which are noted here.
- While anemia can result from hemolysis, the initial presentation doesn't strongly suggest an immune-mediated destruction process, and determining the bone marrow's response is more immediate.
*C-reactive protein (CRP)*
- CRP is a marker of **inflammation**, and elevated levels could suggest **anemia of chronic disease**.
- However, knowing the **reticulocyte count** will provide more direct information about bone marrow function, which is crucial for characterizing the anemia.
*Bone marrow biopsy*
- A bone marrow biopsy is an **invasive procedure** typically reserved for complex anemias where initial, less invasive tests have failed to provide a diagnosis or when conditions like **aplastic anemia** or **myelodysplastic syndromes** are strongly suspected.
- It is not the appropriate **first diagnostic step** in evaluating an undifferentiated normocytic anemia like this.
Making the most of available information US Medical PG Question 6: A 41-year-old woman comes to the primary care physician’s office with a 7-day history of headaches, sore throat, diarrhea, fatigue, and low-grade fevers. The patient denies any significant past medical history, recent travel, or recent sick contacts. On review of systems, the patient endorses performing sex acts in exchange for money and recreational drugs over the last several months. You suspect primary HIV infection, but the patient refuses further evaluation. At a follow-up appointment 1 week later, she reports that she had been previously tested for HIV, and it was negative. Physical examination does not reveal any external abnormalities of her genitalia. Her heart and lung sounds are normal on auscultation. Her vital signs show a blood pressure of 123/82 mm Hg, heart rate of 82/min, and a respiratory rate of 16/min. Of the following options, which is the next best step in patient management?
- A. Retest with HIV antigen/antibody test in 1 year
- B. Perform VDRL
- C. Repeat rapid HIV at this office check-up
- D. Perform monospot test
- E. Retest with 4th generation HIV antigen/antibody test in 2-4 weeks and again in 3 months (Correct Answer)
Making the most of available information Explanation: ***Retest with 4th generation HIV antigen/antibody test in 2-4 weeks and again in 3 months***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **acute retroviral syndrome** (primary HIV infection), including headaches, sore throat, diarrhea, fatigue, and low-grade fevers in the context of high-risk behavior (sex work and recreational drug use).
- A previous negative HIV test was likely obtained during the **window period**, when the infection was too recent to be detected. The **4th generation antigen/antibody immunoassay** detects both HIV antibodies and p24 antigen, reducing the window period to approximately **2-4 weeks** post-exposure.
- **Follow-up testing at 3 months** is recommended to definitively rule out HIV, as rare cases may have delayed seroconversion.
- Current **CDC guidelines** recommend 4th generation testing as the initial screening test for HIV.
*Retest with HIV antigen/antibody test in 1 year*
- Waiting a full year to retest would result in significant delay in diagnosis and treatment, potentially allowing disease progression to AIDS and increasing transmission risk.
- The patient's acute symptoms warrant more immediate re-evaluation within weeks, not months.
*Perform VDRL*
- **VDRL** (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) tests for syphilis, not HIV.
- While co-infection with syphilis is possible in high-risk patients, it does not explain the constellation of symptoms typical of **acute retroviral syndrome**.
- Syphilis testing may be appropriate as part of comprehensive STI screening but is not the priority given the clinical presentation.
*Repeat rapid HIV at this office check-up*
- While **4th generation rapid tests** have improved sensitivity, repeating the test only **1 week** after the previous negative result and during the likely window period may still yield a false negative.
- The patient needs time for antibodies and/or antigen to develop to detectable levels (typically 2-4 weeks from exposure).
*Perform monospot test*
- A **monospot test** diagnoses **infectious mononucleosis** caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
- While EBV can cause fatigue, sore throat, and low-grade fevers, the patient's high-risk sexual behavior, diarrhea, and acute presentation are more consistent with **acute HIV infection** than mononucleosis.
- EBV mononucleosis typically presents with prominent lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly, which are not mentioned here.
Making the most of available information US Medical PG Question 7: A 21-year-old U.S. born first year medical student with no prior hospital or healthcare work presents to the physician for a routine physical exam. The patient is HIV negative, denies drug use, and denies sick contacts. The physician places a purified protein tuberculin test in the patient's right forearm intradermally. What is the proper time to read the test and induration diameter that would indicate a positive test result?
- A. 36 hours and 7mm diameter
- B. 48 hours and 11mm diameter
- C. 72 hours and 16mm diameter (Correct Answer)
- D. 96 hours and 14mm diameter
- E. 24 hours and 18mm diameter
Making the most of available information Explanation: ***72 hours and 16mm diameter***
- The **purified protein derivative (PPD) test** should ideally be read between 48 and 72 hours after administration to allow for the **Type IV hypersensitivity reaction** to fully develop.
- For individuals with no known risk factors for tuberculosis and no prior exposure, an induration of **≥15 mm** is considered a positive result. A 16mm diameter falls within this range.
*36 hours and 7mm diameter*
- **36 hours** is too early to accurately read a PPD test, as the delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction may not have fully manifested.
- A **7mm induration** would generally be considered negative in a low-risk individual, as the threshold for positivity in this group is higher.
*48 hours and 11mm diameter*
- While **48 hours** is within the acceptable window for reading a PPD test, an **11mm induration** is not considered positive for a young, low-risk individual without any predisposing conditions like HIV or organ transplant.
- The threshold for a positive result in this demographic is typically **≥15 mm**.
*96 hours and 14mm diameter*
- **96 hours** (4 days) is generally too late to accurately read a PPD test, as the reaction may begin to fade, leading to a potentially false negative.
- A **14mm induration** is still below the positive threshold of ≥15mm for a low-risk individual.
*24 hours and 18mm diameter*
- **24 hours** is significantly too early to read a PPD test, as the immune response will not have fully developed, leading to unreliable results.
- While **18mm induration** would be a positive result, the timing makes the reading invalid.
Making the most of available information US Medical PG Question 8: A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency department for weight loss and abdominal pain. The patient states that he has felt steadily more fatigued over the past month and has lost 22 pounds without effort. Today, he fainted prompting his presentation. The patient has no significant past medical history. He does have a 33 pack-year smoking history and drinks 4 to 5 alcoholic drinks per day. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 100/58 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. On physical exam, you see a patient who is very thin and appears to be pale. Stool fecal occult blood testing is positive. A CT scan of the abdomen is performed demonstrating a mass in the colon with multiple metastatic lesions scattered throughout the abdomen. The patient is informed of his diagnosis of metastatic colon cancer. When the patient conveys the information to his family he focuses his efforts on discussing the current literature in the field and the novel therapies that have been invented. He demonstrates his likely mortality outcome which he calculated using the results of a large multi-center study. Which of the following is this patient most likely demonstrating?
- A. Intellectualization (Correct Answer)
- B. Dissociation
- C. Rationalization
- D. Optimism
- E. Pessimism
Making the most of available information Explanation: ***Intellectualization***
- This defense mechanism involves **focusing on the intellectual aspects** of a stressful situation, using logical reasoning and factual analysis to avoid experiencing distressing emotions.
- The patient demonstrates this by discussing **literature, novel therapies, and mortality statistics** regarding his metastatic colon cancer.
*Dissociation*
- **Dissociation** involves a mental process that causes a lack of connection in a person's thoughts, memory, and sense of identity.
- This patient is actively engaging with the information, not disconnecting from it.
*Rationalization*
- **Rationalization** is creating logical but false explanations for unacceptable thoughts, feelings, or behaviors to justify them.
- The patient is not trying to justify his actions or feelings, but rather to understand his disease intellectually.
*Optimism*
- **Optimism** is a disposition to look on the favorable side of events or conditions and to expect the most favorable outcome.
- While hope for novel therapies could be seen as optimistic, his detailed calculation of mortality outcomes is a realistic, rather than purely optimistic, approach.
*Pessimism*
- **Pessimism** is a tendency to see the worst aspect of things or believe that the worst will happen.
- The patient is engaging with the facts of his diagnosis, even calculating his mortality outcome, which is not necessarily a pessimistic but rather a realistic and intellectual approach.
More Making the most of available information US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.