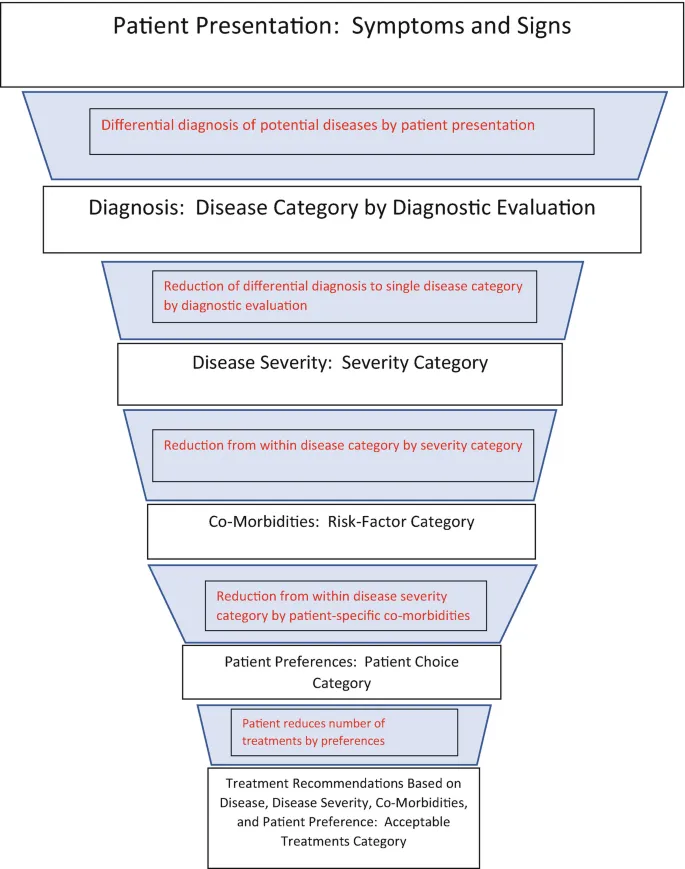
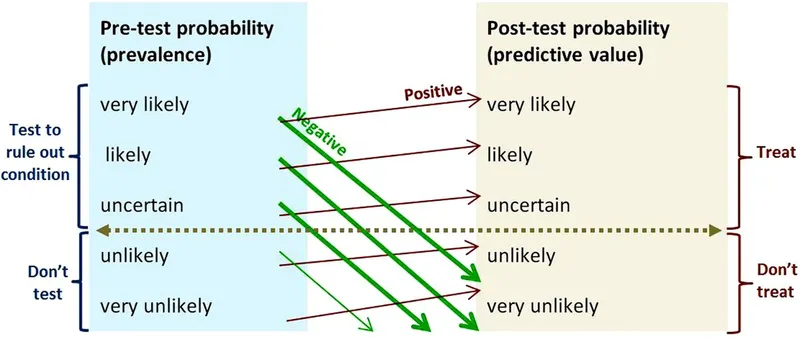
History-directed testing US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for History-directed testing. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 1: You are developing a new diagnostic test to identify patients with disease X. Of 100 patients tested with the gold standard test, 10% tested positive. Of those that tested positive, the experimental test was positive for 90% of those patients. The specificity of the experimental test is 20%. What is the positive predictive value of this new test?
- A. 10%
- B. 90%
- C. 95%
- D. 11% (Correct Answer)
- E. 20%
History-directed testing Explanation: ***11%***
- The positive predictive value (PPV) is calculated as **true positives / (true positives + false positives)**.
- From 100 patients, 10 have disease (prevalence 10%). With 90% sensitivity, the test correctly identifies **9 true positives** (90% of 10).
- Of 90 patients without disease, specificity of 20% means 20% are correctly identified as negative (18 true negatives), so **72 false positives** = 90 × (1 - 0.20).
- Therefore, PPV = 9 / (9 + 72) = 9/81 = **11.1% ≈ 11%**.
*10%*
- This value represents the **prevalence** of the disease in the population, not the positive predictive value of the test.
- Prevalence is the proportion of individuals who have the disease (10 out of 100 patients).
*90%*
- This figure represents the **sensitivity** of the test, which is the percentage of true positives correctly identified by the experimental test.
- Sensitivity = true positives / (true positives + false negatives) = 9/10 = 90%.
*95%*
- This value is not directly derivable from the given data and does not represent any standard test characteristic in this context.
- It would imply a much higher PPV than what can be calculated given the low specificity of 20%.
*20%*
- This is the stated **specificity** of the test, which measures the proportion of true negatives correctly identified.
- Specificity = true negatives / (true negatives + false positives) = 18/90 = 20%.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 2: A geriatric investigator is evaluating the consistency of Alzheimer dementia diagnoses based on clinical symptoms. Patients with known chart diagnoses of Alzheimer dementia were evaluated by multiple physicians during a fixed time interval. Each evaluator was blinded to the others' assessments. The extent to which the diagnosis by one physician was replicated by another clinician examining the same patient is best described by which of the following terms?
- A. Validity
- B. Specificity
- C. Predictive value
- D. Sensitivity
- E. Precision (Correct Answer)
History-directed testing Explanation: ***Precision***
- **Precision** refers to the consistency or reproducibility of a measurement or diagnosis. When multiple physicians reach the same diagnosis for the same patient, it indicates high precision.
- In this context, it specifically assesses **inter-rater reliability**, which is the extent to which different observers agree on the same assessment.
*Validity*
- **Validity** refers to the extent to which a test or measure accurately assesses what it is intended to measure. It is about the "truthfulness" of the diagnosis.
- While important for diagnosis, validity is about accuracy against a gold standard, not consistency among different observers.
*Specificity*
- **Specificity** is the ability of a test to correctly identify individuals who do *not* have the disease (true negatives).
- It measures the proportion of healthy individuals who are correctly identified as healthy by the test, which is not what is being evaluated here.
*Predictive value*
- **Predictive value** assesses the probability that a person *actually has* (positive predictive value) or *does not have* (negative predictive value) a disease given their test result.
- This concept relates to the diagnostic utility of a test in a population, not the consistency of different clinician diagnoses.
*Sensitivity*
- **Sensitivity** is the ability of a test to correctly identify individuals who *do* have the disease (true positives).
- It measures the proportion of diseased individuals who are correctly identified as diseased by the test, which is distinct from inter-rater agreement.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 3: You conduct a medical research study to determine the screening efficacy of a novel serum marker for colon cancer. The study is divided into 2 subsets. In the first, there are 500 patients with colon cancer, of which 450 are found positive for the novel serum marker. In the second arm, there are 500 patients who do not have colon cancer, and only 10 are found positive for the novel serum marker. What is the overall sensitivity of this novel test?
- A. 450 / (450 + 10)
- B. 490 / (10 + 490)
- C. 490 / (50 + 490)
- D. 450 / (450 + 50) (Correct Answer)
- E. 490 / (450 + 490)
History-directed testing Explanation: ***450 / (450 + 50)***
- **Sensitivity** is defined as the proportion of actual positive cases that are correctly identified by the test.
- In this study, there are **500 patients with colon cancer** (actual positives), and **450 of them tested positive** for the marker, while **50 tested negative** (500 - 450 = 50). Therefore, sensitivity = 450 / (450 + 50) = 450/500 = 0.9 or 90%.
*450 / (450 + 10)*
- This formula represents **Positive Predictive Value (PPV)**, which is the probability that a person with a positive test result actually has the disease.
- It incorrectly uses the total number of **test positives** in the denominator (450 true positives + 10 false positives) instead of the total number of diseased individuals, which is needed for sensitivity.
*490 / (10 + 490)*
- This is actually the correct formula for **specificity**, not sensitivity.
- Specificity = TN / (FP + TN) = 490 / (10 + 490) = 490/500 = 0.98 or 98%, which measures the proportion of actual negative cases correctly identified.
- The question asks for sensitivity, not specificity.
*490 / (50 + 490)*
- This formula incorrectly mixes **true negatives (490)** with **false negatives (50)** in an attempt to calculate specificity.
- The correct specificity formula should use false positives (10), not false negatives (50), in the denominator: 490 / (10 + 490).
*490 / (450 + 490)*
- This calculation incorrectly combines **true negatives (490)** and **true positives (450)** in the denominator, which does not correspond to any standard epidemiological measure.
- Neither sensitivity nor specificity uses both true positives and true negatives in the denominator.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 4: A 43-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with complaints of mild shortness of breath and right-sided chest pain for three days. She reports that lately she has had a nagging nonproductive cough and low-grade fevers. On examination, her vital signs are: temperature 99.1 deg F (37.3 deg C), blood pressure is 115/70 mmHg, pulse is 91/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation 97% on room air. She is well-appearing, with normal work of breathing, and no leg swelling. She is otherwise healthy, with no prior medical or surgical history, currently taking no medications. The attending has a low suspicion for the most concerning diagnosis and would like to exclude it with a very sensitive though non-specific test. Which of the following should this physician order?
- A. Obtain chest radiograph
- B. Obtain spiral CT chest with IV contrast
- C. Order a lower extremity ultrasound
- D. Order a D-dimer (Correct Answer)
- E. Obtain ventilation-perfusion scan
History-directed testing Explanation: ***Order a D-dimer***
- The physician has a **low suspicion based on clinical assessment** and wants to **exclude** a concerning diagnosis (likely **pulmonary embolism** or PE) using a **sensitive test**. A negative D-dimer test can effectively rule out PE in patients with a low pre-test probability.
- The D-dimer is a product of **fibrin degradation** and its elevation indicates recent or ongoing **thrombus formation** and lysis. It is highly sensitive for PE but has low specificity.
*Obtain chest radiograph*
- A chest radiograph is often **normal in pulmonary embolism** or may show non-specific findings, making it unsuitable for ruling out PE.
- While useful for diagnosing other conditions like pneumonia or pleural effusions, it is **not sensitive enough to exclude PE**.
*Obtain spiral CT chest with IV contrast*
- A **spiral CT chest with IV contrast (CT pulmonary angiography)** is the gold standard for diagnosing PE, but it is **not a sensitive rule-out test** for low-probability cases.
- It involves **radiation exposure** and **contrast administration**, which are generally avoided if a less invasive, equally effective rule-out test is available for low-risk patients.
*Order a lower extremity ultrasound*
- Lower extremity ultrasound is used to diagnose **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**, which is a common source of PE.
- While DVT can lead to PE, a negative lower extremity ultrasound **does not rule out PE** itself, as the clot may have already embolized or originated from elsewhere.
*Obtain ventilation-perfusion scan*
- A **ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan** is an alternative to CT angiography for diagnosing PE, particularly in patients with contraindications to contrast.
- However, it is **less definitive than CTPA** and is typically used when suspicion for PE is moderate or higher, rather than as a primary rule-out test for low-probability patients.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 5: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of a cough and hoarseness. He reports that the cough is worse when he lies down after lunch. His temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F); the remainder of his vital signs are within normal limits. Because the physician has recently been seeing several patients with the common cold, the diagnosis of a viral upper respiratory tract infection readily comes to mind. The physician fails to consider the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease, which the patient is later found to have. Which of the following most accurately describes the cognitive bias that the physician had?
- A. Framing
- B. Anchoring
- C. Visceral
- D. Confirmation
- E. Availability (Correct Answer)
History-directed testing Explanation: ***Availability***
- The physician recently seeing several patients with the common cold led to this diagnosis readily coming to mind, demonstrating how easily recalled examples can disproportionately influence diagnosis.
- This bias occurs when easily recalled instances or information (like recent cases of common cold) are used to estimate the likelihood or frequency of an event, even if other more relevant data exist.
*Framing*
- This bias occurs when the way information is presented (e.g., as a gain or a loss) influences a decision, rather than the intrinsic characteristics of the options themselves.
- The scenario does not involve the presentation of information in different ways to sway the physician's judgment.
*Anchoring*
- This bias involves relying too heavily on an initial piece of information (the "anchor") when making subsequent judgments, often leading to insufficient adjustment away from that anchor.
- While the physician initially considered a viral URI, the setup is more about the ease of recall influencing the decision rather than being stuck on an initial data point.
*Visceral*
- This is not a commonly recognized cognitive bias in the context of medical decision-making; "visceral" largely refers to emotional or intuitive feelings rather than a structured cognitive bias.
- Cognitive biases describe systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment, not merely emotional responses.
*Confirmation*
- This bias involves seeking, interpreting, favoring, and recalling information in a way that confirms one's pre-existing beliefs or hypotheses.
- The physician did not actively seek information to confirm the common cold diagnosis; rather, the diagnosis came to mind due to recent encounters, which aligns with availability bias.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 6: A medical research study is beginning to evaluate the positive predictive value of a novel blood test for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The diagnostic arm contains 700 patients with NHL, of which 400 tested positive for the novel blood test. In the control arm, 700 age-matched control patients are enrolled and 0 are found positive for the novel test. What is the PPV of this test?
- A. 400 / (400 + 0) (Correct Answer)
- B. 700 / (700 + 300)
- C. 400 / (400 + 300)
- D. 700 / (700 + 0)
- E. 700 / (400 + 400)
History-directed testing Explanation: ***400 / (400 + 0) = 1.0 or 100%***
- The **positive predictive value (PPV)** is calculated as **True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives)**.
- In this scenario, **True Positives (TP)** are the 400 patients with NHL who tested positive, and **False Positives (FP)** are 0, as no control patients tested positive.
- This gives a PPV of 400/400 = **1.0 or 100%**, indicating that all patients who tested positive actually had the disease.
*700 / (700 + 300)*
- This calculation does not align with the formula for PPV based on the given data.
- The denominator `(700+300)` suggests an incorrect combination of various patient groups.
*400 / (400 + 300)*
- The denominator `(400+300)` incorrectly includes 300, which is the number of **False Negatives** (patients with NHL who tested negative), not False Positives.
- PPV focuses on the proportion of true positives among all positive tests, not all diseased individuals.
*700 / (700 + 0)*
- This calculation incorrectly uses the total number of patients with NHL (700) as the numerator, rather than the number of positive test results in that group.
- The numerator should be the **True Positives** (400), not the total number of diseased individuals.
*700 / (400 + 400)*
- This calculation uses incorrect values for both the numerator and denominator, not corresponding to the PPV formula.
- The numerator 700 represents the total number of patients with the disease, not those who tested positive, and the denominator incorrectly sums up values that don't represent the proper PPV calculation.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 7: A 65-year-old man is admitted to the hospital because of a 1-month history of fatigue, intermittent fever, and weakness. Results from a peripheral blood smear taken during his evaluation are indicative of possible acute myeloid leukemia. Bone marrow aspiration and subsequent cytogenetic studies confirm the diagnosis. The physician sets aside an appointed time-slot and arranges a meeting in a quiet office to inform him about the diagnosis and discuss his options. He has been encouraged to bring someone along to the appointment if he wanted. He comes to your office at the appointed time with his daughter. He appears relaxed, with a full range of affect. Which of the following is the most appropriate opening statement in this situation?
- A. Your lab reports show that you have an acute myeloid leukemia
- B. What is your understanding of the reasons we did bone marrow aspiration and cytogenetic studies? (Correct Answer)
- C. You must be curious and maybe even anxious about the results of your tests.
- D. I may need to refer you to a blood cancer specialist because of your diagnosis. You may need chemotherapy or radiotherapy, which we are not equipped for.
- E. Would you like to know all the details of your diagnosis, or would you prefer I just explain to you what our options are?
History-directed testing Explanation: ***"What is your understanding of the reasons we did bone marrow aspiration and cytogenetic studies?"***
- This **open-ended question** allows the patient to express their current knowledge and perceptions, which helps the physician tailor the discussion.
- It establishes a **patient-centered approach**, respecting the patient's existing understanding and preparing them for further information.
*"You must be curious and maybe even anxious about the results of your tests."*
- While empathic, this statement makes an **assumption about the patient's feelings** rather than inviting them to share their own.
- It is often better to ask directly or use more open-ended questions that allow the patient to express their true emotions, especially given their **relaxed demeanor**.
*"I may need to refer you to a blood cancer specialist because of your diagnosis. You may need chemotherapy or radiotherapy, which we are not equipped for.”"*
- This statement immediately introduces **overwhelming and potentially alarming information** (referral, chemotherapy, radiotherapy) without first establishing the diagnosis or assessing the patient's readiness to receive it.
- It prematurely jumps to treatment and logistics, potentially causing **unnecessary distress** before the patient has processed the core diagnosis.
*"Would you like to know all the details of your diagnosis, or would you prefer I just explain to you what our options are?""*
- While it attempts to assess the patient's preference for information, this question is a **closed-ended "either/or" choice** that might limit the patient's ability to express nuanced needs.
- It also prematurely introduces the idea of "options" without first explaining the diagnosis in an understandable context.
*"Your lab reports show that you have an acute myeloid leukemia"*
- This is a **direct and blunt delivery of a serious diagnosis** without any preparatory context or assessment of the patient's existing knowledge or emotional state.
- Delivering such news abruptly can be shocking and overwhelming, potentially **hindering effective communication** and rapport building.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 8: A 65-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a pre-operative evaluation. He is scheduled for cataract surgery in 3 weeks. His past medical history is notable for diabetes, hypertension, and severe osteoarthritis of the right knee. His medications include metformin, hydrochlorothiazide, lisinopril, and aspirin. His surgeon ordered blood work 1 month ago, which showed a hemoglobin of 14.2 g/dL, INR of 1.2, and a hemoglobin A1c of 6.9%. His vital signs at the time of the visit show BP: 130/70 mmHg, Pulse: 80, RR: 12, and T: 37.2 C. He has no current complaints and is eager for his surgery. Which of the following is the most appropriate course of action for this patient at this time?
- A. Tell the patient he will have to delay his surgery for at least 1 year
- B. Medically clear the patient for surgery (Correct Answer)
- C. Repeat the patient's CBC and coagulation studies
- D. Schedule the patient for a stress test and ask him to delay surgery for at least 6 months
- E. Perform an EKG
History-directed testing Explanation: **Medically clear the patient for surgery**
- The patient's **blood pressure is well-controlled** (130/70 mmHg), and his **hemoglobin A1c of 6.9%** indicates good glycemic control, both of which are favorable for elective surgery.
- He is currently on **aspirin**, which, for cataract surgery (a low-risk bleeding procedure), can generally be continued, and his **INR of 1.2 is within a safe range** for surgery.
*Tell the patient he will have to delay his surgery for at least 1 year*
- There are **no indications for such a prolonged delay** based on the provided clinical information.
- His chronic conditions (diabetes, hypertension) are **adequately managed**, and his lab values are acceptable.
*Repeat the patient's CBC and coagulation studies*
- The **existing blood work from 1 month ago is recent enough** for a pre-operative evaluation for cataract surgery, especially with no new symptoms.
- Repeating these tests without a clinical indication would be **unnecessary and inefficient**.
*Schedule the patient for a stress test and ask him to delay surgery for at least 6 months*
- The patient has **no active cardiac symptoms** (e.g., chest pain, shortness of breath), and his well-controlled hypertension does not automatically warrant a stress test for low-risk surgery.
- A stress test and a **6-month delay are not indicated** for a low-risk procedure like cataract surgery in an asymptomatic patient.
*Perform an EKG*
- While an EKG might be considered in some pre-operative evaluations for patients with cardiac risk factors, there are **no specific symptoms or significant new risk factors** presented that necessitate an EKG for this low-risk cataract surgery.
- Given his stable condition and controlled hypertension, an EKG is **not a mandatory part of medical clearance** for this procedure.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 9: A 60-year-old-man presents to his physician with worsening myalgias and new symptoms of early fatigue, muscle weakness, and drooping eyelids. His wife presents with him and states that he never used to have such symptoms. His medical history is significant for gout, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus type II, and pilocytic astrocytoma as a teenager. He denies smoking, drinks a 6-pack of beer per day, and endorses a past history of cocaine use but currently denies any illicit drug use. His vital signs include temperature 36.7°C (98.0°F), blood pressure 126/74 mm Hg, heart rate 87/min, and respiratory rate 15/min. Physical examination shows minimal bibasilar rales, but otherwise clear lungs on auscultation, grade 2/6 holosystolic murmur, 3/5 strength in all extremities, and benign abdominal findings. The Tensilon test result is positive. Which of the following options explains why a chest CT should be ordered for this patient?
- A. Evaluation for mediastinal botulinum abscess
- B. Evaluation of congenital vascular anomaly
- C. Exclusion of underlying lung cancer
- D. Assessment for motor neuron disease
- E. Exclusion of a thymoma (Correct Answer)
History-directed testing Explanation: ***Exclusion of a thymoma***
- The positive **Tensilon test** strongly indicates **myasthenia gravis**, a condition frequently associated with **thymoma**, a tumor of the thymus gland.
- A **chest CT** is crucial for identifying or excluding a **thymoma** in patients with myasthenia gravis, as its resection can improve symptoms.
*Evaluation for mediastinal botulinum abscess*
- **Botulism** would present with descending paralysis and autonomic dysfunction, and an abscess is not a typical manifestation or diagnostic consideration in this context.
- While mediastinal abscesses can occur, they are usually associated with infection, trauma, or surgery and not directly linked to the patient's symptoms or positive Tensilon test.
*Evaluation of congenital vascular anomaly*
- Congenital vascular anomalies are typically diagnosed earlier in life and are not directly associated with the new onset of myalgias, fatigue, muscle weakness, and ptosis in a 60-year-old.
- There are no clinical signs or symptoms presented that would suggest a vascular anomaly as a cause for his current presentation.
*Exclusion of underlying lung cancer*
- Although lung cancer can cause **paraneoplastic syndromes** such as Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome, the symptoms of myalgias, muscle weakness, and ptosis improving with Tensilon strongly point to **myasthenia gravis**, not a paraneoplastic process.
- The specific combination of symptoms and a positive Tensilon test makes myasthenia gravis and its association with thymoma a more direct concern requiring evaluation.
*Assessment for motor neuron disease*
- **Motor neuron diseases** (e.g., ALS) typically present with progressive muscle weakness, spasticity, and fasciculations, but they do not show improvement with a **Tensilon test**.
- The positive Tensilon test specifically rules against motor neuron disease as the primary cause for the reported symptoms.
History-directed testing US Medical PG Question 10: A 28-year-old woman comes to the emergency department for a rash that began 3 days ago. She has low-grade fever and muscle aches. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. She has had 5 male sexual partners over the past year and uses condoms inconsistently. Her temperature is 38.1°C (100.6° F), pulse is 85/min, and blood pressure is 126/89 mm Hg. Examination shows a diffuse maculopapular rash that includes the palms and soles. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. A venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test is positive. Which of the following is the next appropriate step in management?
- A. Intravenous penicillin G
- B. Dark field microscopy
- C. Treponemal culture
- D. Oral doxycycline
- E. Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test (Correct Answer)
History-directed testing Explanation: ***Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test***
- A positive **VDRL** (a non-treponemal test) should be confirmed with a **treponemal-specific test** like the **fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS)** test or **Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TPPA)** assay to definitively diagnose syphilis.
- This confirmatory step helps differentiate true syphilis from false-positive VDRL results, which can occur in autoimmune diseases (SLE, antiphospholipid syndrome), other infections (malaria, mononucleosis), pregnancy, or recent vaccination.
- While this patient's presentation is highly suggestive of **secondary syphilis** (diffuse maculopapular rash involving palms and soles, fever, myalgias, positive VDRL), confirmatory testing is the standard next step before initiating treatment.
- Note: In some clinical settings with classic secondary syphilis, immediate treatment may be initiated, but confirmatory testing remains the most appropriate next diagnostic step.
*Intravenous penicillin G*
- IV aqueous penicillin G is the treatment for **neurosyphilis**, not uncomplicated secondary syphilis.
- **Secondary syphilis** is treated with **intramuscular benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units** as a single dose.
- Treatment should follow confirmed diagnosis with treponemal-specific testing.
*Dark field microscopy*
- This technique visualizes spirochetes directly from **primary lesions** (chancres) or moist secondary lesions (condyloma lata, mucous patches).
- It is not practical for this patient who has a diffuse maculopapular rash without obvious mucosal or genital lesions.
- Dark-field microscopy requires specialized equipment and expertise not readily available in most emergency departments.
*Treponemal culture*
- **Treponema pallidum** cannot be cultured on artificial media because it is an **obligate pathogen** that requires living host cells.
- Culture is not a diagnostic option for syphilis.
*Oral doxycycline*
- **Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 14 days** is an alternative treatment for early syphilis in **penicillin-allergic patients**.
- Treatment should only be initiated after diagnosis is confirmed with treponemal-specific testing.
- This is not the next appropriate step; confirmatory testing comes first.
More History-directed testing US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.