Diagnostic algorithms by presentation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Diagnostic algorithms by presentation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation US Medical PG Question 1: A 50-year-old male presents to the emergency with abdominal pain. He reports he has had abdominal pain associated with meals for several months and has been taking over the counter antacids as needed, but experienced significant worsening pain one hour ago in the epigastric region. The patient reports the pain radiating to his shoulders. Vital signs are T 38, HR 120, BP 100/60, RR 18, SpO2 98%. Physical exam reveals diffuse abdominal rigidity with rebound tenderness. Auscultation reveals hypoactive bowel sounds. Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. Admission and observation
- B. Chest radiograph
- C. 12 lead electrocardiogram
- D. Abdominal CT scan (Correct Answer)
- E. Abdominal ultrasound
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation Explanation: ***Abdominal CT scan***
- This patient presents with classic signs of a **perforated peptic ulcer**: sudden severe epigastric pain radiating to the shoulders (diaphragmatic irritation), fever, tachycardia, hypotension, and peritoneal signs (rigid abdomen with rebound tenderness).
- While the patient shows signs of **early shock** (BP 100/60, HR 120), he is **conscious and maintaining adequate oxygenation** (SpO2 98%), making him stable enough for rapid CT imaging.
- **Abdominal CT scan** is the **most sensitive and specific** test for detecting free air, identifying the location of perforation, and assessing for complications (abscess, contained perforation).
- CT provides **critical surgical planning information** about the extent and location of perforation, which can guide the surgical approach.
- This should be followed by **immediate surgical consultation** and preparation for emergency laparotomy.
*Chest radiograph*
- While an **upright chest X-ray** can detect free air under the diaphragm (pneumoperitoneum), it has **lower sensitivity** (70-80%) compared to CT scan (>95%).
- In a patient who is stable enough for imaging, **CT is preferred** as it provides more information for surgical planning.
- Chest X-ray would be the appropriate choice only if **CT is unavailable** or if the patient is **too unstable** to be transported to the CT scanner.
*Admission and observation*
- This patient has **acute peritonitis** from a likely perforated viscus, which is a **surgical emergency** requiring operative intervention.
- Observation would be inappropriate and dangerous, leading to **septic shock**, **multi-organ failure**, and death.
*12 lead electrocardiogram*
- While epigastric pain can sometimes be cardiac in origin, the **peritoneal signs** (rigid abdomen, rebound tenderness, hypoactive bowel sounds) clearly indicate an **intra-abdominal pathology**.
- The pain radiation to **both shoulders** (Kehr's sign) suggests diaphragmatic irritation from intraperitoneal air or fluid, not cardiac ischemia.
*Abdominal ultrasound*
- Ultrasound is useful for evaluating **solid organ injury**, **free fluid**, and conditions like **cholecystitis** or **appendicitis**.
- However, it is **poor at detecting free air** due to bowel gas artifact and has limited sensitivity for perforated viscus.
- It would not provide adequate information for this surgical emergency.
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation US Medical PG Question 2: A 15-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department one hour after sustaining an injury during football practice. He collided head-on into another player while wearing a mouthguard and helmet. Immediately after the collision he was confused but able to use appropriate words. He opened his eyes spontaneously and followed commands. There was no loss of consciousness. He also had a headache with dizziness and nausea. He is no longer confused upon arrival. He feels well. Vital signs are within normal limits. He is fully alert and oriented. His speech is organized and he is able to perform tasks demonstrating full attention, memory, and balance. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities. There is mild tenderness to palpation over the crown of his head but no signs of skin break or fracture. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- A. Discharge without activity restrictions
- B. Discharge and refrain from all physical activity for one week
- C. Observe for 6 hours in the ED and refrain from contact sports for one week (Correct Answer)
- D. Administer prophylactic levetiracetam and observe for 24 hours
- E. Administer prophylactic phenytoin and observe for 24 hours
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation Explanation: ***Observe for 6 hours in the ED and refrain from contact sports for one week***
- This patient experienced a brief period of **confusion, headache, dizziness**, and **nausea** immediately after a head injury, which are symptoms consistent with a **mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI)** or **concussion**.
- Although his symptoms have resolved at presentation, observation in the ED for a few hours is prudent to ensure no delayed onset of more severe symptoms, and he should **refrain from contact sports** for at least one week as part of concussion management.
*Discharge without activity restrictions*
- Discharging without activity restrictions is unsafe given the initial symptoms of **confusion** and the potential for delayed symptom presentation or complications from a concussion.
- Concussion management requires a period of **physical and cognitive rest** to allow the brain to heal and prevent **second impact syndrome**.
*Discharge and refrain from all physical activity for one week*
- While refraining from all physical activity for one week is part of concussion management, discharging immediately without any observation period after initial neurological symptoms could be risky.
- An observation period allows for monitoring of any **worsening neurological signs** or symptoms that might indicate a more serious injury.
*Administer prophylactic levetiracetam and observe for 24 hours*
- **Prophylactic anticonvulsants** like levetiracetam are typically not recommended for routine management of **mild traumatic brain injury** or concussion.
- Their use is generally reserved for patients with more severe injuries, evolving conditions, or those who have had **seizures post-trauma**.
*Administer prophylactic phenytoin and observe for 24 hours*
- Similar to levetiracetam, **phenytoin** is an anticonvulsant and its prophylactic use is not indicated for **mild head injuries** or concussions.
- Anticonvulsant prophylaxis is associated with potential side effects and is reserved for specific high-risk scenarios, such as **severe TBI** or **penetrating head trauma**.
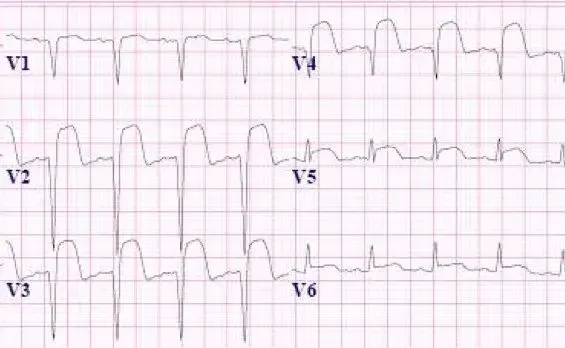
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation US Medical PG Question 3: A 71-year-old man develops worsening chest pressure while shoveling snow in the morning. He tells his wife that he has a squeezing pain that is radiating to his jaw and left arm. His wife calls for an ambulance. On the way, he received chewable aspirin and 3 doses of sublingual nitroglycerin with little relief of pain. He has borderline diabetes and essential hypertension. He has smoked 15–20 cigarettes daily for the past 37 years. His blood pressure is 172/91 mm Hg, the heart rate is 111/min and the temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F). On physical examination in the emergency department, he looks pale, very anxious and diaphoretic. His ECG is shown in the image. Troponin levels are elevated. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient condition?
- A. CT scan of the chest with contrast
- B. Echocardiography
- C. Fibrinolysis
- D. Clopidogrel, atenolol, anticoagulation and monitoring (Correct Answer)
- E. Oral nifedipine
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation Explanation: ***Clopidogrel, atenolol, anticoagulation and monitoring***
- The ECG shows **ST depression in multiple leads (II, III, aVF, V3-V6)** and **ST elevation in aVR and V1**, which is highly suggestive of **non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)** or a **posterior MI/extensive anterior ischemia**. Given the elevated troponin, the patient has an NSTEMI.
- Initial management for NSTEMI includes **dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin and clopidogrel)**, **anticoagulation (e.g., heparin)**, and **beta-blockers (atenolol)**, along with continuous monitoring.
*CT scan of the chest with contrast*
- A CT scan with contrast would be indicated if **aortic dissection** was suspected, but the classic ECG findings and elevated troponins point away from that diagnosis as the primary concern.
- While other causes of chest pain should be considered, the **ECG and troponin elevation** make **acute coronary syndrome (ACS)** the most immediate and critical diagnosis.
*Echocardiography*
- Echocardiography is useful for assessing **cardiac function, wall motion abnormalities, and valvular disease**, but it is generally not the immediate next step in an NSTEMI after the initial stabilization and medication.
- It could be performed later to evaluate for complications such as **ventricular dysfunction** or **valvular issues**.
*Fibrinolysis*
- **Fibrinolysis** is indicated for **ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)** when PCI is not readily available, or for other thrombotic events, but not for NSTEMI.
- In NSTEMI, the primary treatment strategy includes **antiplatelets, anticoagulants**, and often **early invasive procedures (PCI)**, if indicated by risk stratification.
*Oral nifedipine*
- **Nifedipine**, a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, can be used for hypertension or angina, but it is **not first-line** therapy for **acute coronary syndrome**.
- **Beta-blockers like atenolol** are preferred in ACS to reduce myocardial oxygen demand and improve outcomes, whereas nifedipine can sometimes acutely worsen ischemia due to reflex tachycardia.
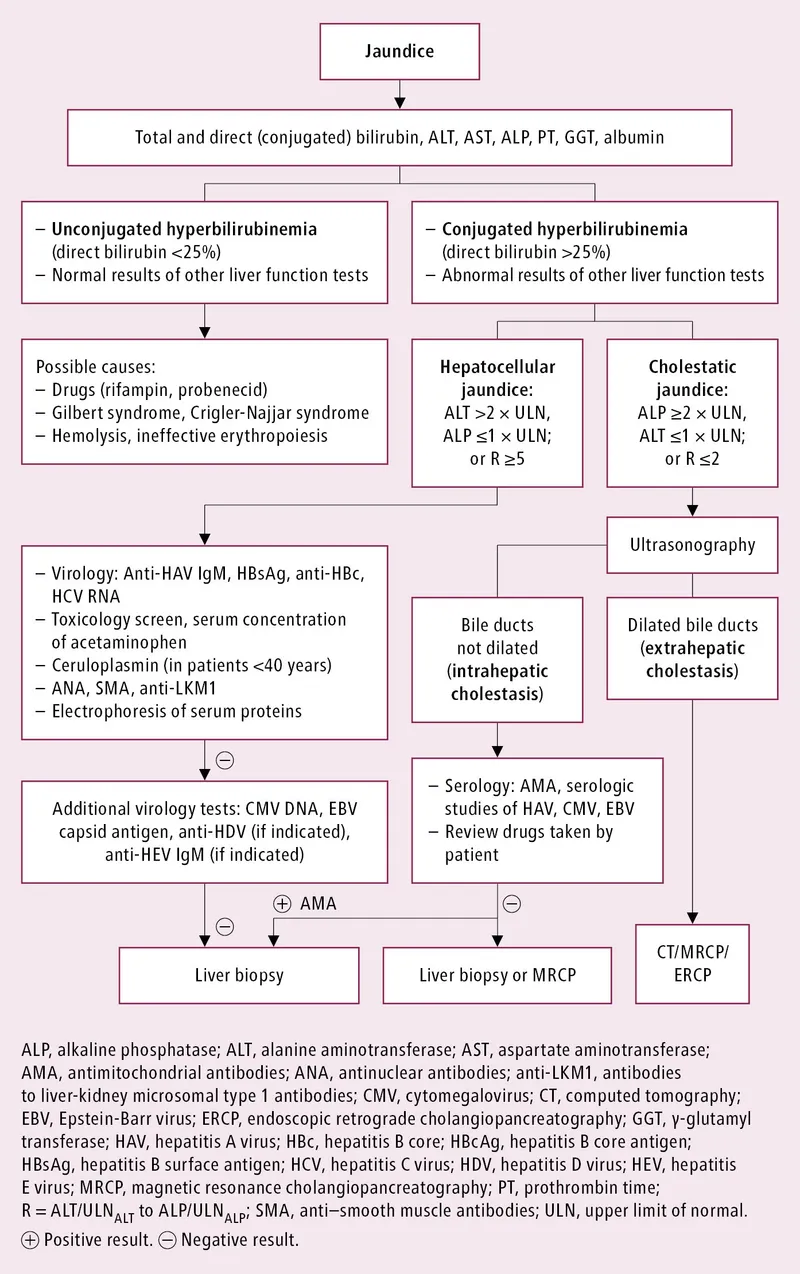
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation US Medical PG Question 4: A 25-year-old woman presents with slightly yellow discoloration of her skin and eyes. She says she has had multiple episodes with similar symptoms before. She denies any recent history of nausea, fatigue, fever, or change in bowel/bladder habits. No significant past medical history. The patient is afebrile and vital signs are within normal limits. On physical examination, she is jaundiced, and her sclera is icteric. Laboratory findings are significant only for a mild unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. The remainder of laboratory results is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II
- B. Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I
- C. Gilbert syndrome (Correct Answer)
- D. Hemolytic anemia
- E. Physiological jaundice
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation Explanation: ***Gilbert syndrome***
- This syndrome is characterized by **mild, intermittent unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia**, often triggered by stress, fasting, or illness, and typically **without other symptoms** or signs of liver disease.
- The patient's presentation with recurrent jaundice, absence of other symptoms, and normal liver function tests except for unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia are classic for **Gilbert syndrome**.
*Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II*
- While also involving unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, **Crigler-Najjar type II** typically presents with more severe and persistent jaundice with higher bilirubin levels than seen in Gilbert syndrome.
- This condition is rare and often requires intervention with **phenobarbital** to induce UGT1A1 activity, which is not indicated by the mild presentation here.
*Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I*
- This is a very severe and rare condition characterized by a **complete absence or near-complete absence of UGT1A1 activity**, leading to extremely high levels of unconjugated bilirubin from birth.
- Patients typically develop **kernicterus** and often die in infancy or early childhood without aggressive treatment, which is inconsistent with the patient's age and mild symptoms.
*Hemolytic anemia*
- **Hemolytic anemia** causes unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to the breakdown of red blood cells, but it would also present with other signs such as **anemia**, **reticulocytosis**, and potentially splenomegaly, which are not mentioned.
- The patient's laboratory results are otherwise unremarkable, ruling out red blood cell destruction as the primary cause.
*Physiological jaundice*
- **Physiological jaundice** is a common and transient condition in **newborns** due to immature liver function and increased red blood cell turnover.
- It resolves within the first few weeks of life and is not applicable to a 25-year-old woman with recurrent episodes.
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation US Medical PG Question 5: A 70-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with complaints of chest pain for the last 2 hours. He had been discharged from the hospital 10 days ago when he was admitted for acute myocardial infarction. It was successfully treated with percutaneous coronary intervention. During the physical exam, the patient prefers to hunch forwards as this decreases his chest pain. He says the pain is in the middle of the chest and radiates to his back. Despite feeling unwell, the patient denies any palpitations or shortness of breath. Vitals signs include: pulse 90/min, respiratory rate 20/min, blood pressure 134/82 mm Hg, and temperature 36.8°C (98.2°F). The patient is visibly distressed and is taking shallow breaths because deeper breaths worsen his chest pain. An ECG shows diffuse ST elevations. Which of the following should be administered to this patient?
- A. Ibuprofen (Correct Answer)
- B. Propranolol
- C. Levofloxacin
- D. Heparin
- E. Warfarin
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation Explanation: ***Ibuprofen***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **post-myocardial infarction (MI) pericarditis**, also known as **Dressler's syndrome**, indicated by recent MI, chest pain relieved by leaning forward, and diffuse ST elevations.
- **NSAIDs like ibuprofen** are the first-line treatment for pericarditis due to their potent anti-inflammatory properties, reducing pain and inflammation.
*Propranolol*
- **Propranolol** is a **beta-blocker** used to reduce heart rate and blood pressure, and manage angina or arrhythmias.
- It is not indicated for the management of **pericarditis**, as it does not address the underlying inflammation.
*Levofloxacin*
- **Levofloxacin** is an **antibiotic** used to treat bacterial infections.
- Pericarditis, especially Dressler's syndrome, is an inflammatory condition, not an infection, so antibiotics are **ineffective**.
*Heparin*
- **Heparin** is an anticoagulant used to prevent blood clot formation, particularly in acute coronary syndromes or pulmonary embolism.
- It is **contraindicated in pericarditis** as it can increase the risk of **hemorrhagic pericardial effusion** or **cardiac tamponade**.
*Warfarin*
- **Warfarin** is an **oral anticoagulant** used for long-term prevention of blood clots in conditions like atrial fibrillation or deep vein thrombosis.
- Similar to heparin, **anticoagulation with warfarin is contraindicated in pericarditis** due to the increased risk of potentially life-threatening bleeding into the pericardial space.
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation US Medical PG Question 6: A 31-year-old man presents with jaundice, scleral icterus, dark urine, and pruritus. He also says that he has been experiencing abdominal pain shortly after eating. He says that symptoms started a week ago and have not improved. The patient denies any associated fever or recent weight-loss. He is afebrile and vital signs are within normal limits. On physical examination, the patient’s skin appears yellowish. Scleral icterus is present. Remainder of physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory findings are significant for:
Conjugated bilirubin 5.1 mg/dL
Total bilirubin 6.0 mg/dL
AST 24 U/L
ALT 22 U/L
Alkaline phosphatase 662 U/L
A contrast CT of the abdomen is unremarkable. An ultrasound of the right upper quadrant reveals a normal gallbladder, but the common bile duct is not visible. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Serologies for antimitochondrial antibodies
- B. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) (Correct Answer)
- C. HIDA scan
- D. Hepatitis serologies
- E. Antibiotics and admit to observation
Diagnostic algorithms by presentation Explanation: ***Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)***
- The patient's presentation with **jaundice, scleral icterus, dark urine, pruritus, unremarked CT abdomen, and significantly elevated alkaline phosphatase** (suggesting **cholestasis**), coupled with an ultrasound showing **non-visualization of the common bile duct**, points to a **biliary obstruction**. ERCP is both diagnostic and therapeutic in this setting, allowing for direct visualization and potential relief of the obstruction.
- The combination of **conjugated hyperbilirubinemia** and isolated elevated alkaline phosphatase with normal AST/ALT indicates a **biliary outflow problem**, warranting further imaging of the biliary tree beyond initial ultrasound and CT.
*Serologies for antimitochondrial antibodies*
- **Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs)** are characteristic of **primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)**, which presents with similar symptoms like pruritus and elevated alkaline phosphatase.
- However, PBC primarily affects **intrahepatic bile ducts** and typically does not present with an acute, complete common bile duct obstruction that would lead to non-visualization on ultrasound.
*HIDA scan*
- A **HIDA scan** (hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan) is used to assess **gallbladder function** and patency of the cystic duct in cases of suspected **acute cholecystitis**.
- The ultrasound already showed a normal gallbladder, and the primary concern here is a common bile duct obstruction, not gallbladder inflammation or function.
*Hepatitis serologies*
- **Hepatitis serologies** (e.g., for Hepatitis A, B, C) would be appropriate if the clinical picture suggested **hepatitis** (e.g., markedly elevated AST/ALT, fever, malaise).
- In this patient, the **transaminases (AST, ALT) are normal**, which makes acute viral hepatitis an unlikely primary diagnosis for his acute presentation and cholestatic pattern.
*Antibiotics and admit to observation*
- While **cholangitis** (biliary infection) can cause fever and severe abdominal pain, the patient denies fever and his vital signs are stable, making acute cholangitis less likely as the primary problem needing immediate antibiotics.
- Admitting for observation without further diagnostic intervention would delay identifying and treating the underlying cause of the **biliary obstruction**, which could lead to serious complications.
More Diagnostic algorithms by presentation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.