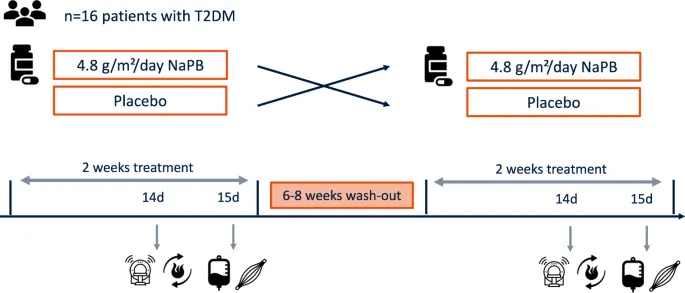
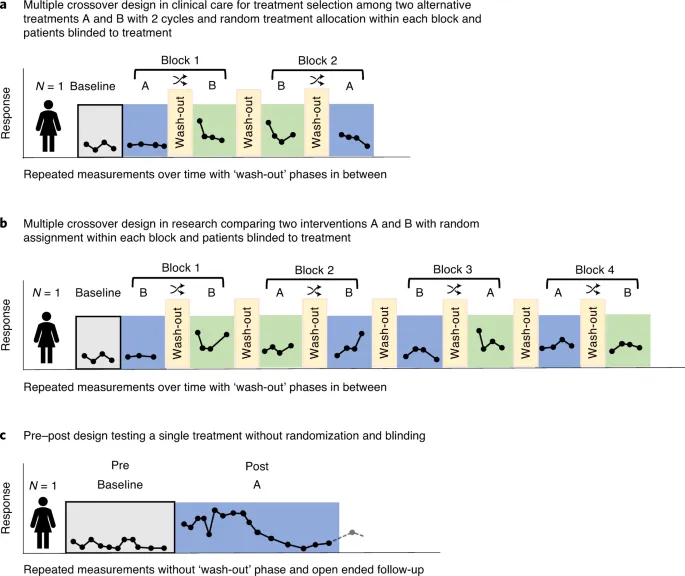
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for N-of-1 trials. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 1: A 21-year-old man presents to the office for a follow-up visit. He was recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus after being hospitalized for diabetic ketoacidosis following a respiratory infection. He is here today to discuss treatment options available for his condition. The doctor mentions a recent study in which researchers have developed a new version of the insulin pump that appears efficacious in type 1 diabetics. They are currently comparing it to insulin injection therapy. This new pump is not yet available, but it looks very promising. At what stage of clinical trials is this current treatment most likely at?
- A. Phase 0
- B. Phase 2
- C. Phase 3 (Correct Answer)
- D. Phase 1
- E. Phase 4
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***Phase 3***
- **Phase 3 trials** involve large-scale studies comparing the new treatment to standard therapy or placebo, often across multiple centers.
- The scenario describes a "new version of the insulin pump" being compared to "insulin injection therapy," indicating a definitive comparison for efficacy and safety against existing treatments.
*Phase 0*
- **Phase 0 trials** are exploratory, small-scale studies (10-15 subjects) using micro-doses to gather preliminary data on pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics, not efficacy comparisons.
- They are typically conducted very early in drug development, examining if the drug behaves as expected in humans.
*Phase 2*
- **Phase 2 trials** evaluate the efficacy and further assess safety of a new treatment in a larger group of patients (tens to hundreds).
- While they assess efficacy, they usually don't involve direct comparison with an established standard therapy on the scale implied by the question, which is typically reserved for Phase 3.
*Phase 1*
- **Phase 1 trials** primarily focus on safety, dosage, and side effects in a small group of healthy volunteers or patients with the condition (20-100 subjects).
- These trials are not designed to assess a treatment's efficacy against an existing therapy.
*Phase 4*
- **Phase 4 trials** occur after a drug or device has been approved and marketed, focusing on long-term safety, effectiveness in diverse populations, and new indications.
- The described pump "is not yet available," indicating it has not reached the market and thus is not in Phase 4.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 2: A researcher is trying to determine whether a newly discovered substance X can be useful in promoting wound healing after surgery. She conducts this study by enrolling the next 100 patients that will be undergoing this surgery and separating them into 2 groups. She decides which patient will be in which group by using a random number generator. Subsequently, she prepares 1 set of syringes with the novel substance X and 1 set of syringes with a saline control. Both of these sets of syringes are unlabeled and the substances inside cannot be distinguished. She gives the surgeon performing the surgery 1 of the syringes and does not inform him nor the patient which syringe was used. After the study is complete, she analyzes all the data that was collected and performs statistical analysis. This study most likely provides which level of evidence for use of substance X?
- A. Level 3
- B. Level 1 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 4
- D. Level 5
- E. Level 2
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***Level 1***
- The study design described is a **randomized controlled trial (RCT)**, which is considered the **highest level of evidence (Level 1)** in the hierarchy of medical evidence.
- Key features like **randomization**, **control group**, and **blinding (double-blind)** help minimize bias and strengthen the validity of the findings.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence typically comprises **well-designed controlled trials without randomization** (non-randomized controlled trials) or **high-quality cohort studies**.
- While strong, they do not possess the same level of internal validity as randomized controlled trials.
*Level 3*
- Level 3 evidence typically includes **case-control studies** or **cohort studies**, which are observational designs and carry a higher risk of bias compared to RCTs.
- These studies generally do not involve randomization or intervention assignment by the researchers.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence is usually derived from **case series** or **poor quality cohort and case-control studies**.
- These studies provide descriptive information or investigate associations without strong control for confounding factors.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, consisting of **expert opinion** or **animal research/bench research**.
- This level lacks human clinical data or systematic investigative rigor needed for higher evidence levels.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is measuring the blood calcium level in a sample of female cross country runners and a control group of sedentary females. If she would like to compare the means of the two groups, which statistical test should she use?
- A. Chi-square test
- B. Linear regression
- C. t-test (Correct Answer)
- D. ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
- E. F-test
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***t-test***
- A **t-test** is appropriate for comparing the means of two independent groups, such as the blood calcium levels between runners and sedentary females.
- It assesses whether the observed difference between the two sample means is statistically significant or occurred by chance.
*Chi-square test*
- The **chi-square test** is used to analyze categorical data to determine if there is a significant association between two variables.
- It is not suitable for comparing continuous variables like blood calcium levels.
*Linear regression*
- **Linear regression** is used to model the relationship between a dependent variable (outcome) and one or more independent variables (predictors).
- It aims to predict the value of a variable based on the value of another, rather than comparing means between groups.
*ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)*
- **ANOVA** is used to compare the means of **three or more independent groups**.
- Since there are only two groups being compared in this scenario, a t-test is more specific and appropriate.
*F-test*
- The **F-test** is primarily used to compare the variances of two populations or to assess the overall significance of a regression model.
- While it is the basis for ANOVA, it is not the direct test for comparing the means of two groups.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 4: In the study, all participants who were enrolled and randomly assigned to treatment with pulmharkimab were analyzed in the pulmharkimab group regardless of medication nonadherence or refusal of allocated treatment. A medical student reading the abstract is confused about why some participants assigned to pulmharkimab who did not adhere to the regimen were still analyzed as part of the pulmharkimab group. Which of the following best reflects the purpose of such an analysis strategy?
- A. To minimize type 2 errors
- B. To assess treatment efficacy more accurately
- C. To reduce selection bias (Correct Answer)
- D. To increase internal validity of study
- E. To increase sample size
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***To reduce selection bias***
- Analyzing participants in their originally assigned groups, regardless of adherence, is known as **intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis**.
- This method helps **preserve randomization** and minimizes **selection bias** that could arise if participants who did not adhere to treatment were excluded or re-assigned.
- **This is the most direct and specific purpose** of ITT analysis - preventing systematic differences between groups caused by post-randomization exclusions.
*To minimize type 2 errors*
- While ITT analysis affects statistical power, its primary purpose is not specifically to minimize **type 2 errors** (false negatives).
- ITT analysis may sometimes *increase* the likelihood of a type 2 error by diluting the treatment effect due to non-adherence.
*To assess treatment efficacy more accurately*
- ITT analysis assesses the **effectiveness** of *assigning* a treatment in a real-world setting, rather than the pure biological **efficacy** of the treatment itself.
- Efficacy is better assessed by a **per-protocol analysis**, which only includes compliant participants.
- ITT provides a more **conservative** and **pragmatic** estimate of treatment effect.
*To increase internal validity of study*
- While ITT analysis does contribute to **internal validity** by maintaining randomization, this is a **broader, secondary benefit** rather than the primary purpose.
- Internal validity encompasses many aspects of study design; ITT specifically addresses **post-randomization bias prevention**.
- The more precise answer is that ITT reduces **selection bias**, which is one specific threat to internal validity.
- Many other design features also contribute to internal validity (blinding, standardized protocols, etc.), making this option less specific.
*To increase sample size*
- ITT analysis includes all randomized participants, so it maintains the initial **sample size** that was randomized.
- However, the primary purpose is to preserve the integrity of randomization and prevent bias, not simply to increase the number of participants in the final analysis.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 5: In a randomized controlled trial studying a new treatment, the primary endpoint (mortality) occurred in 14.4% of the treatment group and 16.7% of the control group. Which of the following represents the number of patients needed to treat to save one life, based on the primary endpoint?
- A. 1/(0.144 - 0.167)
- B. 1/(0.167 - 0.144) (Correct Answer)
- C. 1/(0.300 - 0.267)
- D. 1/(0.267 - 0.300)
- E. 1/(0.136 - 0.118)
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***1/(0.167 - 0.144)***
- The **Number Needed to Treat (NNT)** is calculated as **1 / Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR)**.
- The **Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR)** is the difference between the event rate in the control group (16.7%) and the event rate in the treatment group (14.4%), which is **0.167 - 0.144**.
*1/(0.144 - 0.167)*
- This calculation represents 1 divided by the **Absolute Risk Increase**, which would be relevant if the treatment increased mortality.
- The **NNT should always be a positive value**, indicating the number of patients to treat to prevent one adverse event.
*1/(0.300 - 0.267)*
- This option uses arbitrary numbers (0.300 and 0.267) that do not correspond to the given **mortality rates** in the problem.
- It does not reflect the correct calculation for **absolute risk reduction** based on the provided data.
*1/(0.267 - 0.300)*
- This option also uses arbitrary numbers not derived from the problem's data, and it would result in a **negative value** for the denominator.
- The difference between event rates of 0.267 and 0.300 is not present in the given information for this study.
*1/(0.136 - 0.118)*
- This calculation uses arbitrary numbers (0.136 and 0.118) that are not consistent with the reported **mortality rates** of 14.4% and 16.7%.
- These values do not represent the **Absolute Risk Reduction** required for calculating NNT in this specific scenario.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 7: A scientist is designing a study to determine whether eating a new diet is able to lower blood pressure in a group of patients. In particular, he believes that starting the diet may help decrease peak blood pressures throughout the day. Therefore, he will equip study participants with blood pressure monitors and follow pressure trends over a 24-hour period. He decides that after recruiting subjects, he will start them on either the new diet or a control diet and follow them for 1 month. After this time, he will switch patients onto the other diet and follow them for an additional month. He will analyze the results from the first month against the results from the second month for each patient. This type of study design is best at controlling for which of the following problems with studies?
- A. Hawthorne effect
- B. Recall bias
- C. Confounding (Correct Answer)
- D. Selection bias
- E. Pygmalion effect
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***Confounding***
- This **crossover design** (switching patients to the other diet) effectively controls for **confounding variables** by making each patient their own control, ensuring that inherent patient characteristics do not bias the comparison between diets.
- By comparing the effects of both diets within the same individual, individual variability in factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and other co-morbidities are accounted for, reducing their potential as confounders.
*Hawthorne effect*
- The **Hawthorne effect** refers to subjects modifying their behavior in response to being observed, which this study design does not specifically address or eliminate.
- While patients are being monitored, the design aims to compare the diets' effects, not to prevent behavioral changes due to observation itself.
*Recall bias*
- **Recall bias** occurs when participants' memories of past events are inaccurate, often influenced by their current health status or beliefs.
- This study measures **real-time blood pressure** data, not relying on recollection of past exposures or outcomes, thereby mitigating recall bias.
*Selection bias*
- **Selection bias** arises from non-random selection of participants into study groups, leading to systematic differences between groups.
- While patient recruitment could introduce selection bias into the overall study population, the **crossover design** itself helps control for differences between treatment arms because all participants eventually receive both treatments.
*Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect** (or observer-expectancy effect) describes phenomena where higher expectations lead to increased performance, usually from a researcher influencing a subject.
- This effect is not directly addressed by the crossover design; the design focuses on controlling for patient-specific confounders rather than investigator bias in expectations.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 8: A doctor is interested in developing a new over-the-counter medication that can decrease the symptomatic interval of upper respiratory infections from viral etiologies. The doctor wants one group of affected patients to receive the new treatment, but he wants another group of affected patients to not be given the treatment. Of the following clinical trial subtypes, which would be most appropriate in comparing the differences in outcome between the two groups?
- A. Randomized controlled trial (Correct Answer)
- B. Case-control study
- C. Cohort study
- D. Historical cohort study
- E. Cross-sectional study
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***Randomized controlled trial***
- This design is ideal for evaluating the **efficacy of an intervention** (new medication) by randomly assigning participants to either a treatment group or a control group.
- **Randomization minimizes bias** and ensures that any observed differences in outcomes between the groups can be attributed to the intervention.
*Case-control study*
- This study design is retrospective and compares individuals with a **disease (cases)** to individuals without the disease (controls) to identify **risk factors** or exposures.
- It would not be suitable for testing the effectiveness of a new treatment as it starts with outcomes and looks backward at exposures, not forward at intervention effects.
*Cohort study*
- A cohort study observes a group of individuals (a cohort) over time to see who develops a disease or outcome, often starting with individuals exposed and unexposed to a **risk factor**.
- While it tracks outcomes, it usually doesn't involve an active intervention or random assignment, making it less suitable for directly comparing a new treatment's efficacy against a control.
*Historical cohort study*
- This is a type of cohort study that uses **past data or records** to identify the cohort and their exposures, then follows them forward in time using existing data to determine outcomes.
- It would not be appropriate for testing a *new* medication because it relies on historical exposures and outcomes, not a prospective, controlled intervention.
*Cross-sectional study*
- This study measures the **prevalence of a disease or condition** and related factors at a single point in time, essentially taking a "snapshot."
- It cannot establish causality or evaluate the effectiveness of an intervention over time due to its lack of follow-up and inability to determine the temporal sequence of events.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 9: A statistician wants to study the effects of a medicine in three groups-humans, animals, and plants. He then selects randomly from these three groups. Which type of sampling is being performed?
- A. Simple random sampling
- B. Systematic sampling
- C. Stratified random sampling (Correct Answer)
- D. Cluster sampling
- E. Convenience sampling
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***Stratified random sampling***
- This method involves dividing the population into **distinct subgroups (strata)** based on shared characteristics (in this case, humans, animals, and plants), and then performing a simple random sample within each stratum.
- This ensures that all subgroups are proportionally represented in the sample, which is appropriate when studying effects across different biological categories.
*Simple random sampling*
- This method involves selecting individuals from the entire population **purely by chance**, without first dividing them into subgroups.
- It would not guarantee representation from all three distinct groups (humans, animals, and plants), which is essential for studying differential effects.
*Systematic sampling*
- This involves selecting samples at **regular intervals** from an ordered list or sequence.
- This method is not suitable here because the population is divided into distinct, non-ordered groups rather than a continuous sequence.
*Cluster sampling*
- This method involves dividing the population into **clusters**, then randomly selecting some clusters and sampling all individuals within those selected clusters.
- In this scenario, the initial groups (humans, animals, plants) are strata, not clusters, as the intent is to sample from within each group, not to treat the groups themselves as primary sampling units.
*Convenience sampling*
- This is a **non-probability sampling method** where subjects are selected based on ease of access rather than random selection.
- The question explicitly states that random selection is performed from each group, ruling out convenience sampling.
N-of-1 trials US Medical PG Question 10: A study was undertaken to establish the relationship between the consumption of a vegetarian or non-vegetarian diet and the presence of diseases. Which statistical test should be used?
- A. Chi-square test (Correct Answer)
- B. T-test
- C. ANOVA
- D. Fisher's exact test
- E. Mann-Whitney U test
N-of-1 trials Explanation: ***Chi-square test***
- The **chi-square test** is appropriate when analyzing the relationship between two **categorical variables**. In this scenario, "diet type" (vegetarian/non-vegetarian) and "presence of disease" (yes/no) are both categorical variables.
- This test determines if there is a statistically significant association between the frequency counts of these two variables in a contingency table.
*T-test*
- A **t-test** is used to compare the **means** of two groups, typically when the dependent variable is continuous.
- This test is unsuitable here because the presence of disease and diet type are categorical, not continuous, variables.
*ANOVA*
- **ANOVA** (Analysis of Variance) is used to compare the **means** of three or more groups, often with a continuous dependent variable.
- Similar to the t-test, ANOVA is not applicable as the study involves categorical variables, not the comparison of means across multiple groups.
*Fisher's exact test*
- **Fisher's exact test** is similar to the chi-square test but specifically used for **small sample sizes** where the expected frequencies in any cell of the contingency table are less than 5.
- While it analyzes categorical data, the chi-square test is the more general and commonly preferred test for larger sample sizes, which is generally assumed unless otherwise specified.
*Mann-Whitney U test*
- The **Mann-Whitney U test** is a non-parametric test used to compare differences between two independent groups when the dependent variable is **ordinal or continuous** but not normally distributed.
- This test is not appropriate for analyzing the association between two categorical variables, as it requires at least one variable to have ranked or continuous data.
More N-of-1 trials US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.