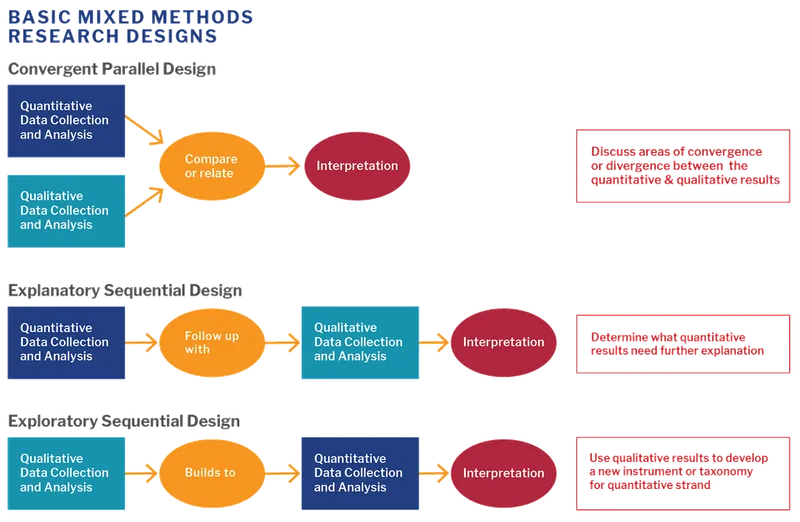
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Mixed methods research. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 1: A study is funded by the tobacco industry to examine the association between smoking and lung cancer. They design a study with a prospective cohort of 1,000 smokers between the ages of 20-30. The length of the study is five years. After the study period ends, they conclude that there is no relationship between smoking and lung cancer. Which of the following study features is the most likely reason for the failure of the study to note an association between tobacco use and cancer?
- A. Late-look bias
- B. Latency period (Correct Answer)
- C. Confounding
- D. Effect modification
- E. Pygmalion effect
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***Latency period***
- **Lung cancer** typically has a **long latency period**, often **20-30+ years**, between initial exposure to tobacco carcinogens and the development of clinically detectable disease.
- A **five-year study duration** in young smokers (ages 20-30) is **far too short** to observe the development of lung cancer, which explains the false negative finding.
- This represents a **fundamental flaw in study design** rather than a bias—the biological timeline of disease development was not adequately considered.
*Late-look bias*
- **Late-look bias** occurs when a study enrolls participants who have already survived the early high-risk period of a disease, leading to **underestimation of true mortality or incidence**.
- Also called **survival bias**, it involves studying a population that has already been "selected" by survival.
- This is not applicable here, as the study simply ended before sufficient time elapsed for disease to develop.
*Confounding*
- **Confounding** occurs when a third variable is associated with both the exposure and outcome, distorting the apparent relationship between them.
- While confounding can affect study results, it would not completely eliminate the detection of a strong, well-established association like smoking and lung cancer in a properly conducted prospective cohort study.
- The issue here is temporal (insufficient follow-up time), not the presence of an unmeasured confounder.
*Effect modification*
- **Effect modification** (also called interaction) occurs when the magnitude of an association between exposure and outcome differs across levels of a third variable.
- This represents a **true biological phenomenon**, not a study design flaw or bias.
- It would not explain the complete failure to detect any association.
*Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect** (observer-expectancy effect) refers to a psychological phenomenon where higher expectations lead to improved performance in the observed subjects.
- This concept is relevant to **behavioral and educational research**, not to objective epidemiological studies of disease incidence.
- It has no relevance to the biological relationship between carcinogen exposure and cancer development.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 2: Which of the following study designs would be most appropriate to investigate the association between electronic cigarette use and the subsequent development of lung cancer?
- A. Subjects with lung cancer who smoke and subjects with lung cancer who did not smoke
- B. Subjects who smoke electronic cigarettes and subjects who smoke normal cigarettes
- C. Subjects with lung cancer who smoke and subjects without lung cancer who smoke
- D. Subjects with lung cancer and subjects without lung cancer
- E. Subjects who smoke electronic cigarettes and subjects who do not smoke (Correct Answer)
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***Subjects who smoke electronic cigarettes and subjects who do not smoke***
- This design represents a **cohort study**, which is ideal for investigating the **incidence** of a disease (lung cancer) in groups exposed and unexposed to a risk factor (electronic cigarette use).
- By following these two groups over time, researchers can directly compare the **risk of developing lung cancer** in e-cigarette users versus non-smokers.
*Subjects with lung cancer who smoke and subjects with lung cancer who did not smoke*
- This option incorrectly compares two groups both with lung cancer, where the exposure to smoking can either be **electronic or traditional cigarettes,** but does not provide a control group without lung cancer to assess the association.
- This design would not allow for the calculation of an **incidence rate** or a **relative risk** of lung cancer development specific to electronic cigarette use.
*Subjects who smoke electronic cigarettes and subjects who smoke normal cigarettes*
- This design compares two different types of smoking, which might be useful for comparing their relative risks but doesn't include a **non-smoking control group** to establish the absolute association with electronic cigarettes.
- While it could show if e-cigarettes are "safer" than traditional cigarettes, it wouldn't directly answer whether e-cigarettes themselves **cause lung cancer**.
*Subjects with lung cancer who smoke and subjects without lung cancer who smoke*
- This describes a **case-control study** but focuses on smoking in general rather than specifically electronic cigarettes, which is the independent variable of interest.
- While valuable for identifying risk factors, it would need to specifically differentiate between **electronic cigarette smokers** and other smokers to answer the question adequately.
*Subjects with lung cancer and subjects without lung cancer*
- This general description of a **case-control study** is too broad; it does not specify the exposure of interest, which is electronic cigarette use.
- To be relevant, the study would need to gather data on **electronic cigarette use** in both the lung cancer group and the non-lung cancer control group.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 3: A research group wants to assess the safety and toxicity profile of a new drug. A clinical trial is conducted with 20 volunteers to estimate the maximum tolerated dose and monitor the apparent toxicity of the drug. The study design is best described as which of the following phases of a clinical trial?
- A. Phase 0
- B. Phase III
- C. Phase V
- D. Phase II
- E. Phase I (Correct Answer)
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***Phase I***
- **Phase I clinical trials** involve a small group of healthy volunteers (typically 20-100) to primarily assess **drug safety**, determine a safe dosage range, and identify side effects.
- The main goal is to establish the **maximum tolerated dose (MTD)** and evaluate the drug's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles.
*Phase 0*
- **Phase 0 trials** are exploratory studies conducted in a very small number of subjects (10-15) to gather preliminary data on a drug's **pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics** in humans.
- They involve microdoses, not intended to have therapeutic effects, and thus cannot determine toxicity or MTD.
*Phase III*
- **Phase III trials** are large-scale studies involving hundreds to thousands of patients to confirm the drug's **efficacy**, monitor side effects, compare it to standard treatments, and collect information that will allow the drug to be used safely.
- These trials are conducted after safety and initial efficacy have been established in earlier phases.
*Phase V*
- "Phase V" is not a standard, recognized phase in the traditional clinical trial classification (Phase 0, I, II, III, IV).
- This term might be used in some non-standard research contexts or for post-marketing studies that go beyond Phase IV surveillance, but it is not a formal phase for initial drug development.
*Phase II*
- **Phase II trials** involve several hundred patients with the condition the drug is intended to treat, focusing on **drug efficacy** and further evaluating safety.
- While safety is still monitored, the primary objective shifts to determining if the drug works for its intended purpose and at what dose.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 4: Study X examined the relationship between coffee consumption and lung cancer. The authors of Study X retrospectively reviewed patients' reported coffee consumption and found that drinking greater than 6 cups of coffee per day was associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer. However, Study X was criticized by the authors of Study Y. Study Y showed that increased coffee consumption was associated with smoking. What type of bias affected Study X, and what study design is geared to reduce the chance of that bias?
- A. Observer bias; double blind analysis
- B. Selection bias; randomization
- C. Lead time bias; placebo
- D. Measurement bias; blinding
- E. Confounding; randomization (Correct Answer)
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***Confounding; randomization***
- Study Y suggests that **smoking** is a **confounding variable** because it is associated with both increased coffee consumption (exposure) and increased risk of lung cancer (outcome), distorting the apparent relationship between coffee and lung cancer.
- **Randomization** in experimental studies (such as randomized controlled trials) helps reduce confounding by ensuring that known and unknown confounding factors are evenly distributed among study groups.
- In observational studies where randomization is not possible, confounding can be addressed through **stratification**, **matching**, or **multivariable adjustment** during analysis.
*Observer bias; double blind analysis*
- **Observer bias** occurs when researchers' beliefs or expectations influence the study outcome, which is not the primary issue described here regarding the relationship between coffee, smoking, and lung cancer.
- **Double-blind analysis** is a method to mitigate observer bias by ensuring neither participants nor researchers know who is in the control or experimental groups.
*Selection bias; randomization*
- **Selection bias** happens when the study population is not representative of the target population, leading to inaccurate results, which is not directly indicated by the interaction between coffee and smoking.
- While **randomization** is used to reduce selection bias by creating comparable groups, the core problem identified in Study X is confounding, not flawed participant selection.
*Lead time bias; placebo*
- **Lead time bias** occurs in screening programs when early detection without improved outcomes makes survival appear longer, an issue unrelated to the described association between coffee, smoking, and lung cancer.
- A **placebo** is an inactive treatment used in clinical trials to control for psychological effects, and its relevance here is limited to treatment intervention studies.
*Measurement bias; blinding*
- **Measurement bias** arises from systematic errors in data collection, such as inaccurate patient reporting of coffee consumption, but the main criticism from Study Y points to a third variable (smoking) affecting the association, not just flawed measurement.
- **Blinding** helps reduce measurement bias by preventing participants or researchers from knowing group assignments, thus minimizing conscious or unconscious influences on data collection.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 5: You submit a paper to a prestigious journal about the effects of coffee consumption on mesothelioma risk. The first reviewer lauds your clinical and scientific acumen, but expresses concern that your study does not have adequate statistical power. Statistical power refers to which of the following?
- A. The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.
- B. The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.
- C. The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist. (Correct Answer)
- D. The first derivative of work.
- E. The square root of the variance.
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist.***
- **Statistical power** is defined as the probability that a study will correctly reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it will detect a true effect or association if one exists.
- A study with **adequate statistical power** is less likely to miss a real effect.
*The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.*
- This describes a **Type I error** or **false positive**, often represented by **alpha (α)**.
- It is the probability of incorrectly concluding an effect or association exists when, in reality, there is none.
*The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.*
- This refers to a **Type II error** or **false negative**, represented by **beta (β)**.
- **Statistical power** is calculated as **1 - β**, so this option describes the complement of power.
*The first derivative of work.*
- The first derivative of work with respect to time represents **power** in physics, which is the rate at which work is done.
- This option is a **distractor** from physics and is unrelated to statistical power in research.
*The square root of the variance.*
- The **square root of the variance** is the **standard deviation**, a measure of the dispersion or spread of data.
- This is a statistical concept but is not the definition of statistical power.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 6: You are interested in studying the etiology of heart failure reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and attempt to construct an appropriate design study. Specifically, you wish to look for potential causality between dietary glucose consumption and HFrEF. Which of the following study designs would allow you to assess for and determine this causality?
- A. Cross-sectional study
- B. Case series
- C. Cohort study (Correct Answer)
- D. Case-control study
- E. Randomized controlled trial
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***Cohort study***
- A **cohort study** observes a group of individuals over time to identify risk factors and outcomes, allowing for the assessment of **temporal relationships** between exposure (dietary glucose) and outcome (HFrEF).
- This design is suitable for establishing a potential **causal link** as it tracks participants from exposure to outcome, enabling the calculation of incidence rates and relative risks.
*Cross-sectional study*
- A **cross-sectional study** measures exposure and outcome simultaneously at a single point in time, making it impossible to determine the **temporal sequence** of events.
- This design can only identify **associations** or correlations, not causation, as it cannot establish whether high glucose consumption preceded HFrEF.
*Case series*
- A **case series** describes characteristics of a group of patients with a particular disease or exposure, often to highlight unusual clinical features, but it lacks a **comparison group**.
- It cannot assess causality because it does not provide information on the frequency of exposure in healthy individuals or the incidence of the disease in unexposed individuals.
*Case-control study*
- A **case-control study** compares individuals with the outcome (cases) to those without the outcome (controls) to determine past exposures, which makes it prone to **recall bias**.
- While it can suggest associations, it cannot definitively establish a temporal relationship or causation as the outcome is already known when exposure is assessed.
*Randomized controlled trial*
- A **randomized controlled trial (RCT)** is the gold standard for establishing causation by randomly assigning participants to an intervention or control group, but it may not be ethical or feasible for studying long-term dietary exposures and chronic diseases like HFrEF due to the long follow-up period and complexity of diet.
- While ideal for causality, directly controlling and randomizing dietary glucose intake over decades to observe HFrEF development might be practically challenging or unethical.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 7: A statistician wants to study the effects of a medicine in three groups-humans, animals, and plants. He then selects randomly from these three groups. Which type of sampling is being performed?
- A. Simple random sampling
- B. Systematic sampling
- C. Stratified random sampling (Correct Answer)
- D. Cluster sampling
- E. Convenience sampling
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***Stratified random sampling***
- This method involves dividing the population into **distinct subgroups (strata)** based on shared characteristics (in this case, humans, animals, and plants), and then performing a simple random sample within each stratum.
- This ensures that all subgroups are proportionally represented in the sample, which is appropriate when studying effects across different biological categories.
*Simple random sampling*
- This method involves selecting individuals from the entire population **purely by chance**, without first dividing them into subgroups.
- It would not guarantee representation from all three distinct groups (humans, animals, and plants), which is essential for studying differential effects.
*Systematic sampling*
- This involves selecting samples at **regular intervals** from an ordered list or sequence.
- This method is not suitable here because the population is divided into distinct, non-ordered groups rather than a continuous sequence.
*Cluster sampling*
- This method involves dividing the population into **clusters**, then randomly selecting some clusters and sampling all individuals within those selected clusters.
- In this scenario, the initial groups (humans, animals, plants) are strata, not clusters, as the intent is to sample from within each group, not to treat the groups themselves as primary sampling units.
*Convenience sampling*
- This is a **non-probability sampling method** where subjects are selected based on ease of access rather than random selection.
- The question explicitly states that random selection is performed from each group, ruling out convenience sampling.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 8: A study was undertaken to establish the relationship between the consumption of a vegetarian or non-vegetarian diet and the presence of diseases. Which statistical test should be used?
- A. Chi-square test (Correct Answer)
- B. T-test
- C. ANOVA
- D. Fisher's exact test
- E. Mann-Whitney U test
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***Chi-square test***
- The **chi-square test** is appropriate when analyzing the relationship between two **categorical variables**. In this scenario, "diet type" (vegetarian/non-vegetarian) and "presence of disease" (yes/no) are both categorical variables.
- This test determines if there is a statistically significant association between the frequency counts of these two variables in a contingency table.
*T-test*
- A **t-test** is used to compare the **means** of two groups, typically when the dependent variable is continuous.
- This test is unsuitable here because the presence of disease and diet type are categorical, not continuous, variables.
*ANOVA*
- **ANOVA** (Analysis of Variance) is used to compare the **means** of three or more groups, often with a continuous dependent variable.
- Similar to the t-test, ANOVA is not applicable as the study involves categorical variables, not the comparison of means across multiple groups.
*Fisher's exact test*
- **Fisher's exact test** is similar to the chi-square test but specifically used for **small sample sizes** where the expected frequencies in any cell of the contingency table are less than 5.
- While it analyzes categorical data, the chi-square test is the more general and commonly preferred test for larger sample sizes, which is generally assumed unless otherwise specified.
*Mann-Whitney U test*
- The **Mann-Whitney U test** is a non-parametric test used to compare differences between two independent groups when the dependent variable is **ordinal or continuous** but not normally distributed.
- This test is not appropriate for analyzing the association between two categorical variables, as it requires at least one variable to have ranked or continuous data.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 9: A group of 80 people is being studied to determine the effect of diet modification on cholesterol levels. To compare the mean cholesterol levels before and after the diet modification in this group, which statistical test should be used?
- A. Paired t-test (Correct Answer)
- B. McNemar test
- C. Chi-square test
- D. Wilcoxon signed-rank test
- E. Independent t-test
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***Paired t-test***
- A **paired t-test** is appropriate for comparing means from two related samples, such as "before" and "after" measurements on the **same individuals**.
- It assesses whether there is a statistically significant difference between these **dependent observations**.
*Independent t-test*
- The independent t-test compares means between **two separate groups** (unrelated samples).
- It is inappropriate here because we have **paired data** from the same individuals measured twice, not two independent groups.
*McNemar test*
- The McNemar test is used for comparing **paired nominal data**, typically in a 2×2 table, for example, before-after changes in a proportion or categorical outcome.
- It is not suitable for **continuous data** like cholesterol levels.
*Chi-square test*
- The chi-square test is used to assess the association between **two categorical variables** or to compare observed frequencies with expected frequencies.
- It is not designed for comparing means of **continuous variables** in paired samples.
*Wilcoxon signed-rank test*
- The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a **non-parametric alternative to the paired t-test**, used when the data are not normally distributed or when the sample size is small.
- While it's used for paired data, the paired t-test is generally preferred when parametric assumptions (like **normality**) can be met, especially with a sample size of 80.
Mixed methods research US Medical PG Question 10: A study recorded the survival times (in months) of 8 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer who received a new chemotherapy regimen. The survival times were: 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 months. What is the median survival time for these patients?
- A. 4.0
- B. 4.5 (Correct Answer)
- C. 5.0
- D. 5.5
- E. 3.5
Mixed methods research Explanation: ***4.5***
- The given survival times are already ordered: 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8.
- Since there is an **even number of observations (n=8)**, the median is the average of the two middle values, which are the 4th and 5th values. (4 + 5) / 2 = **4.5**.
*3.5*
- This value would result from incorrectly averaging the 3rd and 4th observations (3 + 4) / 2 = 3.5.
- This error occurs when miscounting the middle positions in an even-numbered dataset.
*4.0*
- This value represents the **fourth observation** in the ordered list, not the true median for an even number of data points.
- While it is one of the middle values, the median for an even dataset requires averaging the two middle-most values.
*5.0*
- This value represents the **fifth observation** in the ordered list, not the true median for an even number of data points.
- It would be the median if the dataset contained an odd number of observations and 5 was the middle term.
*5.5*
- This value would be the mean of 5 and 6, which are the 5th and 6th values, not the correct middle values.
- This calculation does not represent the correct methodology for finding the median in this dataset.
More Mixed methods research US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.