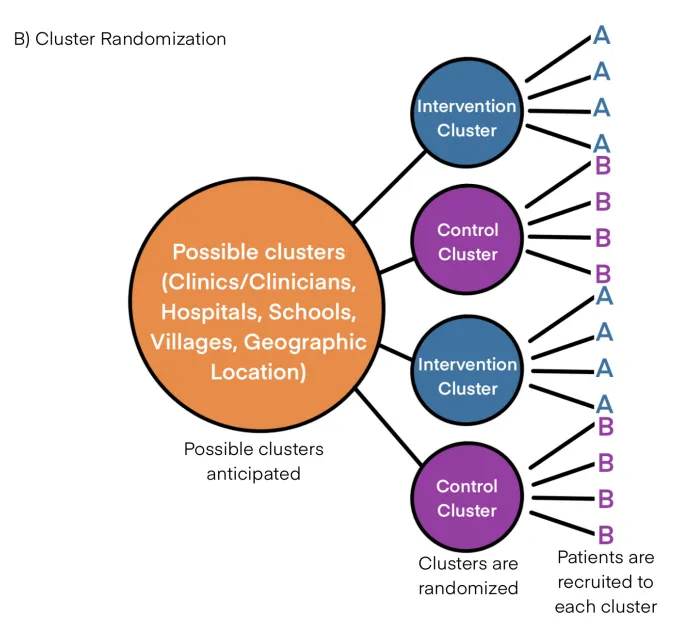
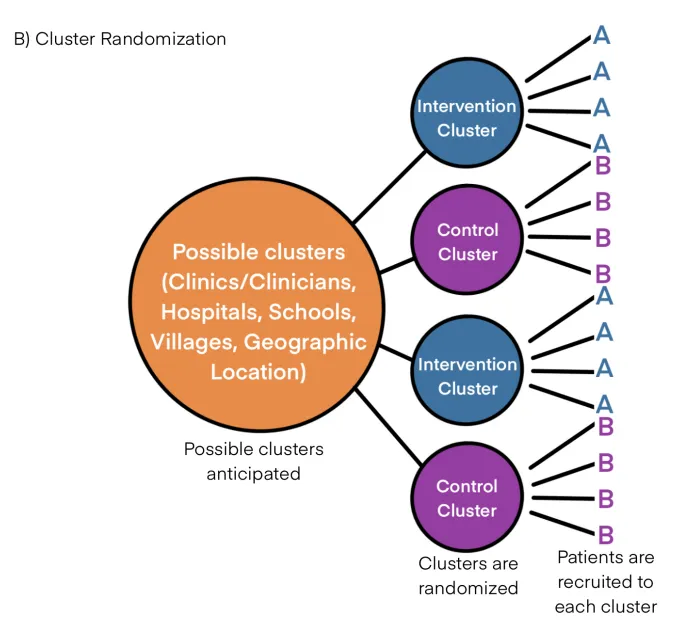
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cluster randomization. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 1: A study is funded by the tobacco industry to examine the association between smoking and lung cancer. They design a study with a prospective cohort of 1,000 smokers between the ages of 20-30. The length of the study is five years. After the study period ends, they conclude that there is no relationship between smoking and lung cancer. Which of the following study features is the most likely reason for the failure of the study to note an association between tobacco use and cancer?
- A. Late-look bias
- B. Latency period (Correct Answer)
- C. Confounding
- D. Effect modification
- E. Pygmalion effect
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***Latency period***
- **Lung cancer** typically has a **long latency period**, often **20-30+ years**, between initial exposure to tobacco carcinogens and the development of clinically detectable disease.
- A **five-year study duration** in young smokers (ages 20-30) is **far too short** to observe the development of lung cancer, which explains the false negative finding.
- This represents a **fundamental flaw in study design** rather than a bias—the biological timeline of disease development was not adequately considered.
*Late-look bias*
- **Late-look bias** occurs when a study enrolls participants who have already survived the early high-risk period of a disease, leading to **underestimation of true mortality or incidence**.
- Also called **survival bias**, it involves studying a population that has already been "selected" by survival.
- This is not applicable here, as the study simply ended before sufficient time elapsed for disease to develop.
*Confounding*
- **Confounding** occurs when a third variable is associated with both the exposure and outcome, distorting the apparent relationship between them.
- While confounding can affect study results, it would not completely eliminate the detection of a strong, well-established association like smoking and lung cancer in a properly conducted prospective cohort study.
- The issue here is temporal (insufficient follow-up time), not the presence of an unmeasured confounder.
*Effect modification*
- **Effect modification** (also called interaction) occurs when the magnitude of an association between exposure and outcome differs across levels of a third variable.
- This represents a **true biological phenomenon**, not a study design flaw or bias.
- It would not explain the complete failure to detect any association.
*Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect** (observer-expectancy effect) refers to a psychological phenomenon where higher expectations lead to improved performance in the observed subjects.
- This concept is relevant to **behavioral and educational research**, not to objective epidemiological studies of disease incidence.
- It has no relevance to the biological relationship between carcinogen exposure and cancer development.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 2: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 3: A surgeon is interested in studying how different surgical techniques impact the healing of tendon injuries. In particular, he will compare 3 different types of suture repairs biomechanically in order to determine the maximum load before failure of the tendon 2 weeks after repair. He collects data on maximum load for 90 different repaired tendons from an animal model. Thirty tendons were repaired using each of the different suture techniques. Which of the following statistical measures is most appropriate for analyzing the results of this study?
- A. Chi-squared
- B. Wilcoxon rank sum
- C. Pearson r coefficient
- D. Student t-test
- E. ANOVA (Correct Answer)
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***ANOVA***
- **ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)** is appropriate here because it compares the means of **three or more independent groups** (the three different suture techniques) on a continuous dependent variable (maximum load before failure).
- The study has three distinct repair techniques, each with 30 tendons, making ANOVA suitable for determining if there are statistically significant differences among their mean failure loads.
*Chi-squared*
- The **Chi-squared test** is used for analyzing **categorical data** (frequencies or proportions) to determine if there is an association between two nominal variables.
- This study involves quantitative measurement (maximum load), not categorical data, making Chi-squared inappropriate.
*Wilcoxon rank sum*
- The **Wilcoxon rank sum test** (also known as Mann-Whitney U test) is a **non-parametric test** used to compare two independent groups when the data is not normally distributed or is ordinal.
- While the study has independent groups, it involves three groups, and the dependent variable is continuous, making ANOVA a more powerful and appropriate choice assuming normal distribution.
*Pearson r coefficient*
- The **Pearson r coefficient** measures the **strength and direction of a linear relationship between two continuous variables**.
- This study aims to compare means across different groups, not to determine the correlation between two continuous variables.
*Student t-test*
- The **Student t-test** is used to compare the means of **exactly two groups** (either independent or paired) on a continuous dependent variable.
- This study involves comparing three different suture techniques, not just two, making the t-test unsuitable.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 4: Which of the following physiologic changes decreases pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR)?
- A. Inhaling the inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
- B. Exhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)
- C. Exhaling the expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
- D. Breath holding maneuver at functional residual capacity (FRC)
- E. Inhaling the entire vital capacity (VC) (Correct Answer)
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***Inhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)***
- As lung volume increases from FRC to TLC (which includes inhaling the entire VC), alveolar vessels are **stretched open**, and extra-alveolar vessels are **pulled open** by the increased radial traction, leading to a decrease in PVR.
- This **maximizes the cross-sectional area** of the pulmonary vascular bed, lowering resistance.
*Inhaling the inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)*
- While inhaling IRV increases lung volume, it's not the maximal inspiration of the entire VC where **PVR is typically at its lowest**.
- PVR continues to decrease as lung volume approaches total lung capacity (TLC).
*Exhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)*
- Exhaling the entire vital capacity leads to very low lung volumes, where PVR significantly **increases**.
- At low lung volumes, **alveolar vessels become compressed** and extra-alveolar vessels **narrow**, increasing resistance.
*Exhaling the expiratory reserve volume (ERV)*
- Exhaling the ERV results in a lung volume below FRC, which causes a **marked increase in PVR**.
- This is due to the **compression of alveolar vessels** and decreased radial traction on extra-alveolar vessels.
*Breath holding maneuver at functional residual capacity (FRC)*
- At FRC, the PVR is at an **intermediate level**, not its lowest.
- This is the point where the opposing forces affecting alveolar and extra-alveolar vessels are somewhat balanced, but not optimized for minimal resistance.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 5: A pharmaceutical corporation has asked you to assist in the development of a randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate the response of renal cell carcinoma to a novel chemotherapeutic agent. Despite all of the benefits that an RCT has to offer, which of the following would make an RCT unacceptable with regard to study design?
- A. Proper treatment response is very common
- B. The treatment is not widespread in use
- C. The treatment does not represent the best known option
- D. The treatment is expensive
- E. The treatment has a known, adverse outcome (Correct Answer)
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***The treatment has a known, adverse outcome***
- If a treatment is already known to cause **significant harm** or an adverse outcome, it would be unethical to randomize patients to receive it, as this would expose them to unnecessary risk.
- **Ethical considerations** are paramount in clinical trial design; exposing patients to a known harmful treatment violates the principle of non-maleficence.
*Proper treatment response is very common*
- A high treatment response rate would make it **easier to detect a difference** between the novel agent and a control group, potentially requiring a smaller sample size.
- This scenario actually **facilitates** an RCT, as it increases the likelihood of demonstrating efficacy for the novel agent.
*The treatment is not widespread in use*
- The purpose of an RCT for a novel agent is precisely to evaluate its efficacy and safety to determine if it **deserves widespread use**.
- Lack of widespread use is the **starting point** for clinical trials, not a contraindication.
*The treatment does not represent the best known option*
- An RCT is often conducted to determine if a novel treatment is **superior or non-inferior** to existing standard-of-care treatments, even if the existing options are not considered "the best."
- Comparing a new treatment against a suboptimal current standard is a common and **valid objective** in clinical research to seek improvement.
*The treatment is expensive*
- The cost of a treatment is a **practical consideration** for healthcare systems and patients but does not inherently make an RCT unacceptable in terms of study design or ethics.
- **Cost-effectiveness** is often evaluated after efficacy and safety are established, usually in addition to the RCT or in subsequent studies.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 6: A neuro-oncology investigator has recently conducted a randomized controlled trial in which the addition of a novel alkylating agent to radiotherapy was found to prolong survival in comparison to radiotherapy alone (HR = 0.7, p < 0.01). A number of surviving participants who took the alkylating agent reported that they had experienced significant nausea from the medication. The investigator surveyed all participants in both the treatment and the control group on their nausea symptoms by self-report rated mild, moderate, or severe. The investigator subsequently compared the two treatment groups with regards to nausea level.
| | Mild nausea | Moderate nausea | Severe nausea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment group (%) | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| Control group (%) | 35 | 35 | 30 |
Which of the following statistical methods would be most appropriate to assess the statistical significance of these results?
- A. Chi-square test (Correct Answer)
- B. Pearson correlation coefficient
- C. Multiple logistic regression
- D. Unpaired t-test
- E. Paired t-test
Cluster randomization Explanation: **Chi-square test**
- The **Chi-square test** is appropriate for comparing **categorical data** (mild, moderate, severe) between two or more independent groups (treatment vs. control).
- It assesses whether there is a statistically significant association between the two categorical variables (treatment group and nausea severity).
*Pearson correlation coefficient*
- The **Pearson correlation coefficient** is used to measure the **linear relationship** between two **continuous variables**.
- Nausea severity (mild, moderate, severe) is an **ordinal categorical variable**, not a continuous one.
*Multiple logistic regression*
- **Multiple logistic regression** is used to predict a **binary outcome** (e.g., presence or absence of nausea) based on one or more independent variables, which can be continuous or categorical.
- The outcome here is **ordinal categorical** (mild, moderate, severe nausea), not binary. While logistic regression can be adapted for ordinal outcomes, a simpler Chi-square test is more direct for comparing distributions without prediction.
*Unpaired t-test*
- An **unpaired t-test** is used to compare the **means of two independent continuous variables**.
- Nausea levels are categorical, and we are interested in comparing proportions within categories, not means.
*Paired t-test*
- A **paired t-test** is used to compare the **means of two related (paired) continuous variables**.
- The study involves independent treatment and control groups, and the nausea data is categorical, making the paired t-test unsuitable.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 7: A researcher is examining the relationship between socioeconomic status and IQ scores. The IQ scores of young American adults have historically been reported to be distributed normally with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. Initially, the researcher obtains a random sampling of 300 high school students from public schools nationwide and conducts IQ tests on all participants. Recently, the researcher received additional funding to enable an increase in sample size to 2,000 participants. Assuming that all other study conditions are held constant, which of the following is most likely to occur as a result of this additional funding?
- A. Increase in risk of systematic error
- B. Increase in range of the confidence interval
- C. Decrease in standard deviation
- D. Increase in probability of type II error
- E. Decrease in standard error of the mean (Correct Answer)
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***Decrease in standard error of the mean***
- **Increasing the sample size** (n) leads to a **decrease in the standard error of the mean** (SEM), which is calculated as σ/√n.
- A smaller SEM indicates that our sample mean is a more **precise estimate** of the true population mean.
*Increase in risk of systematic error*
- **Systematic error** is related to flaws in study design or implementation and is not directly affected by an increase in sample size.
- A larger sample size generally helps in detecting a true effect if one exists, but does not inherently introduce or correct systematic bias.
*Increase in range of the confidence interval*
- An **increase in sample size** typically leads to a **narrower confidence interval**, not a wider one, because the standard error of the mean decreases.
- A narrower confidence interval implies greater precision in estimating the population parameter.
*Decrease in standard deviation*
- The **standard deviation** is a measure of the data's spread within a sample or population and is an intrinsic characteristic of the data itself.
- Increasing the sample size typically does not change the true standard deviation of the population; it only provides a **more accurate estimate** of it.
*Increase in probability of type II error*
- An **increase in sample size** generally leads to an **increase in statistical power**, which in turn **decreases the probability of a Type II error** (failing to reject a false null hypothesis).
- A larger sample makes it easier to detect a true difference or effect if one exists.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 9: You are reading through a recent article that reports significant decreases in all-cause mortality for patients with malignant melanoma following treatment with a novel biological infusion. Which of the following choices refers to the probability that a study will find a statistically significant difference when one truly does exist?
- A. Type II error
- B. Type I error
- C. Confidence interval
- D. p-value
- E. Power (Correct Answer)
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***Power***
- **Power** is the probability that a study will correctly reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false (i.e., will find a statistically significant difference when one truly exists).
- A study with high power minimizes the risk of a **Type II error** (failing to detect a real effect).
*Type II error*
- A **Type II error** (or **beta error**) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference when one actually exists.
- This is the **opposite** of what the question describes, which asks for the probability of *finding* a difference.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (or **alpha error**) occurs when a study incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis, concluding there is a significant difference when one does not actually exist.
- This relates to the **p-value** and the level of statistical significance (e.g., p < 0.05).
*Confidence interval*
- A **confidence interval** provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain degree of confidence (e.g., 95%).
- It does not directly represent the probability of finding a statistically significant difference when one truly exists.
*p-value*
- The **p-value** is the probability of observing data as extreme as, or more extreme than, that obtained in the study, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- It is used to determine statistical significance, but it is not the probability of detecting a true effect.
Cluster randomization US Medical PG Question 10: A study seeks to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of treating asymptomatic subclinical hypothyroidism in preventing symptoms of hypothyroidism. The investigators found 300 asymptomatic patients with subclinical hypothyroidism, defined as serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) of 5 to 10 μU/mL with normal serum thyroxine (T4) levels. The patients were randomized to either thyroxine 75 μg daily or placebo. Both investigators and study subjects were blinded. Baseline patient characteristics were distributed similarly in the treatment and control group (p > 0.05). Participants' serum T4 and TSH levels and subjective quality of life were evaluated at a 3-week follow-up. No difference was found between the treatment and placebo groups. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the results of this study?
- A. Observer effect
- B. Berkson bias
- C. Latency period (Correct Answer)
- D. Confounding bias
- E. Lead-time bias
Cluster randomization Explanation: ***Latency period***
- A **latency period** refers to the time between exposure to a cause (e.g., treatment) and the manifestation of its effects (e.g., symptom improvement). The study's **3-week follow-up is too short** to observe the therapeutic benefits of thyroxine in subclinical hypothyroidism.
- Levothyroxine (T4) has a **half-life of approximately 7 days**, and it typically takes **6-8 weeks or longer** for steady-state levels to be achieved and for clinical symptoms to improve. The slow onset of action for thyroid hormone replacement and the gradual nature of symptom resolution mean a longer observation period (typically 3-6 months) is needed to assess efficacy in hypothyroidism.
- The null results likely reflect insufficient follow-up time rather than lack of treatment effect.
*Observer effect*
- The **observer effect**, or Hawthorne effect, occurs when subjects change their behavior because they know they are being observed. This study used **double-blinding** (both investigators and subjects), which effectively minimizes the observer effect.
- The primary issue here is the lack of observed therapeutic effect due to timing, not a change in behavior due to observation.
*Berkson bias*
- **Berkson bias** is a form of selection bias that arises in case-control studies conducted in hospitals, where the probability of being admitted to the hospital can be affected by both exposure and disease.
- This study is a **randomized controlled trial**, not a case-control study, and the selection of participants does not illustrate this specific bias.
*Confounding bias*
- **Confounding bias** occurs when an extraneous variable is associated with both the exposure and the outcome, distorting the observed relationship. The study states that **baseline patient characteristics were similarly distributed (p > 0.05)**, indicating successful randomization and minimization of confounding.
- While confounding is a common concern in observational studies, the RCT design and reported baseline similarities make it unlikely to be the primary explanation for the null results compared to an insufficient follow-up period.
*Lead-time bias*
- **Lead-time bias** is a form of detection bias where early detection of a disease through screening appears to prolong survival, even if the treatment does not change the course of the disease.
- This study is evaluating the **efficacy of treatment** in asymptomatic individuals with subclinical hypothyroidism, not the effect of screening on survival, making lead-time bias irrelevant to these results.
More Cluster randomization US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.