Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Power for repeated measures designs. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 1: A study is funded by the tobacco industry to examine the association between smoking and lung cancer. They design a study with a prospective cohort of 1,000 smokers between the ages of 20-30. The length of the study is five years. After the study period ends, they conclude that there is no relationship between smoking and lung cancer. Which of the following study features is the most likely reason for the failure of the study to note an association between tobacco use and cancer?
- A. Late-look bias
- B. Latency period (Correct Answer)
- C. Confounding
- D. Effect modification
- E. Pygmalion effect
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Latency period***
- **Lung cancer** typically has a **long latency period**, often **20-30+ years**, between initial exposure to tobacco carcinogens and the development of clinically detectable disease.
- A **five-year study duration** in young smokers (ages 20-30) is **far too short** to observe the development of lung cancer, which explains the false negative finding.
- This represents a **fundamental flaw in study design** rather than a bias—the biological timeline of disease development was not adequately considered.
*Late-look bias*
- **Late-look bias** occurs when a study enrolls participants who have already survived the early high-risk period of a disease, leading to **underestimation of true mortality or incidence**.
- Also called **survival bias**, it involves studying a population that has already been "selected" by survival.
- This is not applicable here, as the study simply ended before sufficient time elapsed for disease to develop.
*Confounding*
- **Confounding** occurs when a third variable is associated with both the exposure and outcome, distorting the apparent relationship between them.
- While confounding can affect study results, it would not completely eliminate the detection of a strong, well-established association like smoking and lung cancer in a properly conducted prospective cohort study.
- The issue here is temporal (insufficient follow-up time), not the presence of an unmeasured confounder.
*Effect modification*
- **Effect modification** (also called interaction) occurs when the magnitude of an association between exposure and outcome differs across levels of a third variable.
- This represents a **true biological phenomenon**, not a study design flaw or bias.
- It would not explain the complete failure to detect any association.
*Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect** (observer-expectancy effect) refers to a psychological phenomenon where higher expectations lead to improved performance in the observed subjects.
- This concept is relevant to **behavioral and educational research**, not to objective epidemiological studies of disease incidence.
- It has no relevance to the biological relationship between carcinogen exposure and cancer development.
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 2: Researchers are studying the effects of a new medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. A randomized group of 100 subjects is given the new medication 1st for 2 months, followed by a washout period of 2 weeks, and then administration of the gold standard medication for 2 months. Another randomized group of 100 subjects is given the gold standard medication 1st for 2 months, followed by a washout period of 2 weeks, and then administration of the new medication for 2 months. What is the main disadvantage of this study design?
- A. Hawthorne effect
- B. Increasing selection bias
- C. Increasing confounding bias
- D. Decreasing power
- E. Carryover effect (Correct Answer)
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Carryover effect***
- The primary disadvantage here is the **carryover effect**, where the effects of the first treatment (new medication or gold standard) may persist into the period when the second treatment is administered, even after a washout period.
- This can **mask or alter the true effect** of the second treatment, making it difficult to accurately assess their individual efficacy.
*Hawthorne effect*
- The **Hawthorne effect** refers to subjects improving their behavior or performance in response to being observed or studied, not specifically an issue with sequential treatment administration.
- It would affect both groups equally and doesn't explain a disadvantage inherent to the crossover design itself.
*Increasing selection bias*
- **Selection bias** occurs when the randomization process fails to create comparable groups, but this study design involves **randomization** into two groups, and then a crossover, which typically aims to *reduce* selection bias by having each participant serve as their own control.
- The sequential administration within a randomized crossover design actually helps to mitigate selection bias between treatment arms.
*Increasing confounding bias*
- **Confounding bias** occurs when an unmeasured variable is associated with both the exposure and the outcome, distorting the observed relationship.
- This crossover design, where each participant receives both treatments, is intended to *reduce* confounding by inter-individual variability, as each subject acts as their own control, rather than increasing it.
*Decreasing power*
- **Power** is the ability of a study to detect a true effect if one exists. Crossover designs often *increase* statistical power compared to parallel designs because each participant receives both treatments, reducing inter-individual variability.
- This design typically requires a smaller sample size to achieve the same power as a parallel group study, so decreased power is not a disadvantage.
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 3: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
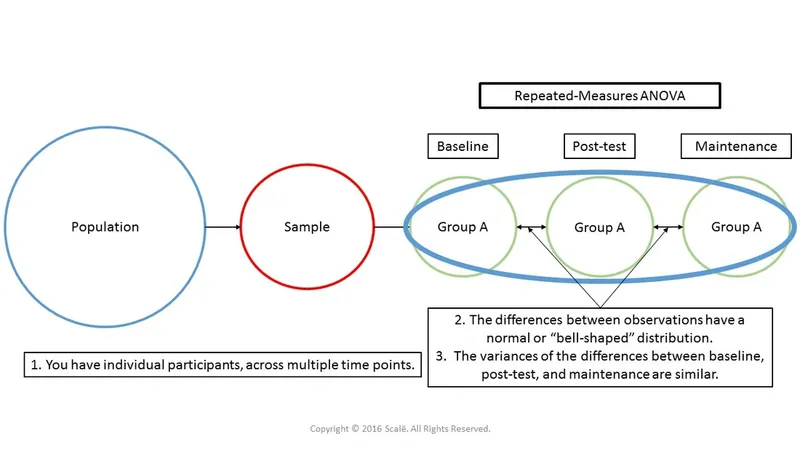
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 4: A surgeon is interested in studying how different surgical techniques impact the healing of tendon injuries. In particular, he will compare 3 different types of suture repairs biomechanically in order to determine the maximum load before failure of the tendon 2 weeks after repair. He collects data on maximum load for 90 different repaired tendons from an animal model. Thirty tendons were repaired using each of the different suture techniques. Which of the following statistical measures is most appropriate for analyzing the results of this study?
- A. Chi-squared
- B. Wilcoxon rank sum
- C. Pearson r coefficient
- D. Student t-test
- E. ANOVA (Correct Answer)
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***ANOVA***
- **ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)** is appropriate here because it compares the means of **three or more independent groups** (the three different suture techniques) on a continuous dependent variable (maximum load before failure).
- The study has three distinct repair techniques, each with 30 tendons, making ANOVA suitable for determining if there are statistically significant differences among their mean failure loads.
*Chi-squared*
- The **Chi-squared test** is used for analyzing **categorical data** (frequencies or proportions) to determine if there is an association between two nominal variables.
- This study involves quantitative measurement (maximum load), not categorical data, making Chi-squared inappropriate.
*Wilcoxon rank sum*
- The **Wilcoxon rank sum test** (also known as Mann-Whitney U test) is a **non-parametric test** used to compare two independent groups when the data is not normally distributed or is ordinal.
- While the study has independent groups, it involves three groups, and the dependent variable is continuous, making ANOVA a more powerful and appropriate choice assuming normal distribution.
*Pearson r coefficient*
- The **Pearson r coefficient** measures the **strength and direction of a linear relationship between two continuous variables**.
- This study aims to compare means across different groups, not to determine the correlation between two continuous variables.
*Student t-test*
- The **Student t-test** is used to compare the means of **exactly two groups** (either independent or paired) on a continuous dependent variable.
- This study involves comparing three different suture techniques, not just two, making the t-test unsuitable.
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 5: Which factor most strongly influences protein filtration at the glomerulus?
- A. Electrical charge
- B. Molecular size (Correct Answer)
- C. Shape
- D. Temperature
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Molecular size***
- The glomerular filtration barrier, particularly the **slit diaphragms** between podocytes, acts as a size-selective filter, restricting the passage of larger molecules.
- Proteins like **albumin** (molecular radius ~36 Å, molecular weight ~69 kDa) are significantly large, making them difficult to pass through the filtration barrier.
- Size selectivity is the **primary and most important** factor in protein filtration.
*Electrical charge*
- The glomerular basement membrane contains **negatively charged proteoglycans** (heparan sulfate), which repel negatively charged proteins like albumin, contributing to their retention.
- While important, the role of electrical charge is **secondary** to molecular size in preventing the bulk passage of most proteins.
*Shape*
- While abnormal protein shapes (e.g., **amyloid fibrils**) can impact filtration in specific disease states, the typical physiological filtration of most proteins is primarily governed by size and charge.
- The inherent shape of normal globular proteins plays a less direct role compared to their overall size.
*Temperature*
- **Physiological temperature** is relatively constant in the body and does not directly influence the molecular interactions and physical properties of the glomerular filtration barrier in a way that significantly alters protein filtration.
- Temperature changes would lead to denaturation or aggregation, which are not the primary determinants of normal protein filtration.
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 6: You are reading through a recent article that reports significant decreases in all-cause mortality for patients with malignant melanoma following treatment with a novel biological infusion. Which of the following choices refers to the probability that a study will find a statistically significant difference when one truly does exist?
- A. Type II error
- B. Type I error
- C. Confidence interval
- D. p-value
- E. Power (Correct Answer)
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Power***
- **Power** is the probability that a study will correctly reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false (i.e., will find a statistically significant difference when one truly exists).
- A study with high power minimizes the risk of a **Type II error** (failing to detect a real effect).
*Type II error*
- A **Type II error** (or **beta error**) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference when one actually exists.
- This is the **opposite** of what the question describes, which asks for the probability of *finding* a difference.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (or **alpha error**) occurs when a study incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis, concluding there is a significant difference when one does not actually exist.
- This relates to the **p-value** and the level of statistical significance (e.g., p < 0.05).
*Confidence interval*
- A **confidence interval** provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain degree of confidence (e.g., 95%).
- It does not directly represent the probability of finding a statistically significant difference when one truly exists.
*p-value*
- The **p-value** is the probability of observing data as extreme as, or more extreme than, that obtained in the study, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- It is used to determine statistical significance, but it is not the probability of detecting a true effect.
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 7: A physician attempts to study cirrhosis in his state. Using a registry of admitted patients over the last 10 years at the local hospital, he isolates all patients who have been diagnosed with cirrhosis. Subsequently, he contacts this group of patients, asking them to complete a survey assessing their prior exposure to alcohol use, intravenous drug abuse, blood transfusions, personal history of cancer, and other medical comorbidities. An identical survey is given to an equal number of patients in the registry who do not carry a prior diagnosis of cirrhosis. Which of the following is the study design utilized by this physician?
- A. Randomized controlled trial
- B. Case-control study (Correct Answer)
- C. Cross-sectional study
- D. Cohort study
- E. Meta-analysis
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Case-control study***
- This study design **identifies subjects based on their outcome (cases with cirrhosis, controls without cirrhosis)** and then retrospectively investigates their past exposures.
- The physician selected patients with cirrhosis (cases) and patients without cirrhosis (controls), then assessed their prior exposures to risk factors like alcohol use and intravenous drug abuse.
*Randomized controlled trial*
- This design involves randomly assigning participants to an **intervention group** or a **control group** to assess the effect of an intervention.
- There is no intervention being tested or randomization occurring in this study; it is observational.
*Cross-sectional study*
- A cross-sectional study measures the **prevalence of disease and exposure at a single point in time** in a defined population.
- This study collects retrospective exposure data and compares two distinct groups (cases and controls), rather than assessing prevalence at one time point.
*Cohort study*
- A cohort study **follows a group of individuals over time** to see if their exposure to a risk factor is associated with the development of a disease.
- This study starts with the outcome (cirrhosis) and looks backward at exposures, which is the opposite direction of a cohort study.
*Meta-analysis*
- A meta-analysis is a statistical method that **combines the results of multiple independent studies** to produce a single, more powerful estimate of treatment effect or association.
- This is an original research study collecting new data, not a systematic review or synthesis of existing studies.
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 8: A 30-year-old computer scientist receives negative feedback on a recent project from his senior associate. He is told sternly that he must improve his performance on the next project. Later that day, he yells at his intern, a college student, for not showing enough initiative, though he had voiced only satisfaction with his performance up until this point. Which of the following psychological defense mechanisms is he demonstrating?
- A. Acting out
- B. Countertransference
- C. Projection
- D. Displacement (Correct Answer)
- E. Transference
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Displacement***
- **Displacement** is a defense mechanism where a person redirects strong emotions, especially negative ones like anger, from the original source to a substitute target that is perceived as less threatening.
- The computer scientist's anger, initially generated by criticism from his senior associate, is redirected to his intern, who is a safer target.
*Acting out*
- **Acting out** involves expressing unconscious emotional conflicts or impulses through behavior, often inappropriate or destructive, rather than through words or feelings.
- While yelling at the intern is a behavior, the primary motive here is redirecting an emotion, not expressing a hidden conflict or impulse without awareness.
*Countertransference*
- **Countertransference** refers to the therapist's emotional reactions to a patient, rooted in their own unresolved conflicts, and is specific to the therapeutic relationship.
- This scenario involves an individual's reaction to workplace stress, not a dynamic within a therapeutic setting.
*Projection*
- **Projection** is attributing one's own unacceptable thoughts, feelings, or impulses to another person.
- In this case, the computer scientist isn't attributing his own poor performance or anger to the intern; rather, he is _redirecting_ his anger.
*Transference*
- **Transference** is the unconscious redirection of feelings and attitudes from a person in the past (e.g., a parent) to a person in the present (e.g., a therapist or boss).
- This scenario involves a direct reaction to a current stressor and redirection of emotion, not the reliving of past relationship dynamics with a new figure.
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 9: A health system implements a new sepsis protocol across 20 hospitals. A researcher plans to evaluate effectiveness using a stepped-wedge cluster randomized design where hospitals sequentially adopt the protocol every 3 months. She calculates sample size based on individual patient outcomes (mortality) needing 2,000 patients total. The biostatistician identifies a critical error. Evaluate what modification is needed.
- A. Adjust for multiple time periods using Bonferroni correction
- B. Use hospital-level outcomes instead of patient-level outcomes as unit of analysis
- C. Increase alpha to 0.10 to account for cluster randomization reducing power
- D. Include random effects for both hospital and time period in power calculation
- E. Account for intra-cluster correlation coefficient (ICC) requiring substantial sample size inflation (Correct Answer)
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Account for intra-cluster correlation coefficient (ICC) requiring substantial sample size inflation***
- In cluster-randomized designs, observations within the same cluster (hospital) are not independent; the **Intra-cluster Correlation Coefficient (ICC)** quantifies this correlation and must be used to calculate a **design effect**.
- Neglecting the ICC leads to an **underpowered study** because the effective sample size is smaller than the total number of individual patients measured.
*Adjust for multiple time periods using Bonferroni correction*
- **Bonferroni correction** is used to control for **Type I error** when performing multiple independent hypothesis tests, not for determining sample size in nested longitudinal designs.
- While the stepped-wedge design involves multiple time points, the primary analysis typically uses a **single model** (e.g., GEE or GLMM) that accounts for time as a fixed effect.
*Use hospital-level outcomes instead of patient-level outcomes as unit of analysis*
- While the hospital is the **unit of randomization**, using hospital-level means as the unit of analysis simplifies the data and causes a significant loss of **statistical information** and precision.
- Modern biostatistical methods utilize **multilevel modeling** to maintain the richness of patient-level data while adjusting for the cluster-level randomization.
*Include random effects for both hospital and time period in power calculation*
- While random effects are important for the **analysis phase**, the "critical error" identified in the prompt refers to the initial failure to inflate the sample size based on **clustering (ICC)**.
- Power calculations for stepped-wedge designs are complex and certainly involve time parameters, but **ICC-based inflation** is the most fundamental adjustment required when moving from individual to cluster randomization.
*Increase alpha to 0.10 to account for cluster randomization reducing power*
- Increasing the **alpha level** (significance threshold) is not a standard or scientifically acceptable method to compensate for the loss of power due to **clustering**.
- Standard practice mandates maintaining an **alpha of 0.05** while appropriately increasing the **sample size** or number of clusters to reach the desired power (usually 80-90%).
Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG Question 10: A 41-year-old research fellow designs a non-inferiority trial comparing oral to IV antibiotics for osteomyelitis. She sets the non-inferiority margin at 10% (cure rate difference), expects 85% cure in both groups, and calculates 300 patients per arm for 80% power with α=0.025 (one-sided). Her mentor suggests this underestimates required sample size. Evaluate the mentor's concern.
- A. Correct; non-inferiority trials require larger samples than superiority trials for equivalent power (Correct Answer)
- B. Incorrect; non-inferiority trials actually require smaller samples due to less stringent hypotheses
- C. Correct; dropout rates in antibiotic trials necessitate 20% inflation of calculated sample size
- D. Incorrect; the calculation appropriately uses one-sided alpha for non-inferiority testing
- E. Correct; the margin should be set at 5% requiring doubling of sample size
Power for repeated measures designs Explanation: ***Correct; non-inferiority trials require larger samples than superiority trials for equivalent power***
- **Non-inferiority trials** are designed to exclude a difference greater than a pre-specified margin, which typically requires a **larger sample size** than superiority trials investigating the same outcome.
- Because we are proving that the new treatment is "not much worse" (rather than "better"), the **statistical threshold** often necessitates higher enrollment to achieve adequate **power**.
*Incorrect; the calculation appropriately uses one-sided alpha for non-inferiority testing*
- While it is true that **non-inferiority testing** uses a **one-sided alpha (0.025)**, this does not negate the fact that such trials inherently require more participants.
- The mentor's concern is about the **total N**, which remains insufficient despite using the correct one-sided alpha convention.
*Correct; the margin should be set at 5% requiring doubling of sample size*
- There is no universal rule that the **non-inferiority margin** must be 5%; it is determined by **clinical significance** and regulatory standards for the specific condition.
- While a 5% margin would indeed increase the sample size, the 10% margin is often standard in **antibiotic trials** for osteomyelitis.
*Incorrect; non-inferiority trials actually require smaller samples due to less stringent hypotheses*
- This is a common misconception; non-inferiority trials are actually more demanding because the **null hypothesis** assumes the treatments are different (inferior).
- Disproving **inferiority** within a tight **margin (delta)** is statistically more intensive than proving a treatment is superior to a placebo.
*Correct; dropout rates in antibiotic trials necessitate 20% inflation of calculated sample size*
- While **attrition bias** is a concern, there is no fixed rule that every trial needs a **20% inflation** factor.
- The mentor's concern is specifically about the **base calculation** and the statistical nature of non-inferiority designs rather than just the **dropout rate**.
More Power for repeated measures designs US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.