Factors affecting power US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Factors affecting power. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 1: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 2: You are conducting a study comparing the efficacy of two different statin medications. Two groups are placed on different statin medications, statin A and statin B. Baseline LDL levels are drawn for each group and are subsequently measured every 3 months for 1 year. Average baseline LDL levels for each group were identical. The group receiving statin A exhibited an 11 mg/dL greater reduction in LDL in comparison to the statin B group. Your statistical analysis reports a p-value of 0.052. Which of the following best describes the meaning of this p-value?
- A. There is a 95% chance that the difference in reduction of LDL observed reflects a real difference between the two groups
- B. Though A is more effective than B, there is a 5% chance the difference in reduction of LDL between the two groups is due to chance
- C. If 100 permutations of this experiment were conducted, 5 of them would show similar results to those described above
- D. This is a statistically significant result
- E. There is a 5.2% chance of observing a difference in reduction of LDL of 11 mg/dL or greater even if the two medications have identical effects (Correct Answer)
Factors affecting power Explanation: **There is a 5.2% chance of observing a difference in reduction of LDL of 11 mg/dL or greater even if the two medications have identical effects**
- The **p-value** represents the probability of observing results as extreme as, or more extreme than, the observed data, assuming the **null hypothesis** is true (i.e., there is no true difference between the groups).
- A p-value of 0.052 means there's approximately a **5.2% chance** that the observed 11 mg/dL difference (or a more substantial difference) occurred due to **random variation**, even if both statins were equally effective.
*There is a 95% chance that the difference in reduction of LDL observed reflects a real difference between the two groups*
- This statement is an incorrect interpretation of the p-value; it confuses the p-value with the **probability that the alternative hypothesis is true**.
- A p-value does not directly tell us the probability that the observed difference is "real" or due to the intervention being studied.
*Though A is more effective than B, there is a 5% chance the difference in reduction of LDL between the two groups is due to chance*
- This statement implies that Statin A is more effective, which cannot be concluded with a p-value of 0.052 if the significance level (alpha) was set at 0.05.
- While it's true there's a chance the difference is due to chance, claiming A is "more effective" based on this p-value before statistical significance is usually declared is misleading.
*If 100 permutations of this experiment were conducted, 5 of them would show similar results to those described above*
- This is an incorrect interpretation. The p-value does not predict the outcome of repeated experiments in this manner.
- It refers to the **probability under the null hypothesis in a single experiment**, not the frequency of results across multiple hypothetical repetitions.
*This is a statistically significant result*
- A p-value of 0.052 is generally considered **not statistically significant** if the conventional alpha level (significance level) is set at 0.05 (or 5%).
- For a result to be statistically significant at alpha = 0.05, the p-value must be **less than 0.05**.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old man with a genetic disorder presents for genetic counseling because he is concerned about the risk that any children he has will have the same disease as himself. Specifically, since childhood he has had difficulty breathing requiring bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and chest physiotherapy. He has also had diarrhea and malabsorption requiring enzyme replacement therapy. If his wife comes from a population where 1 in 10,000 people are affected by this same disorder, which of the following best represents the likelihood a child would be affected as well?
- A. 0.01%
- B. 2%
- C. 0.5%
- D. 1% (Correct Answer)
- E. 50%
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***Correct Option: 1%***
- The patient's symptoms (difficulty breathing requiring bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and chest physiotherapy; diarrhea and malabsorption requiring enzyme replacement therapy) are classic for **cystic fibrosis (CF)**, an **autosomal recessive disorder**.
- For an autosomal recessive disorder with a prevalence of 1 in 10,000 in the general population, **q² = 1/10,000**, so **q = 1/100 = 0.01**. The carrier frequency **(2pq)** is approximately **2q = 2 × (1/100) = 1/50 = 0.02**.
- The affected man is **homozygous recessive (aa)** and will always pass on the recessive allele. His wife has a **1/50 chance of being a carrier (Aa)**. If she is a carrier, she has a **1/2 chance of passing on the recessive allele**.
- Therefore, the probability of an affected child = **(Probability wife is a carrier) × (Probability wife passes recessive allele) = 1/50 × 1/2 = 1/100 = 1%**.
*Incorrect Option: 0.01%*
- This percentage is too low and does not correctly account for the carrier frequency in the population and the probability of transmission from a carrier mother.
*Incorrect Option: 2%*
- This represents approximately the carrier frequency (1/50 ≈ 2%), but does not account for the additional 1/2 probability that a carrier mother would pass on the recessive allele.
*Incorrect Option: 0.5%*
- This value would be correct if the carrier frequency were 1/100 instead of 1/50, which does not match the given population prevalence.
*Incorrect Option: 50%*
- **50%** would be the risk if both parents were carriers of an autosomal recessive disorder (1/4 chance = 25% for affected, but if we know one parent passes the allele, conditional probability changes). More accurately, 50% would apply if the disorder were **autosomal dominant** with one affected parent, which is not the case here.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 4: A researcher is conducting a study to compare fracture risk in male patients above the age of 65 who received annual DEXA screening to peers who did not receive screening. He conducts a randomized controlled trial in 900 patients, with half of participants assigned to each experimental group. The researcher ultimately finds similar rates of fractures in the two groups. He then notices that he had forgotten to include 400 patients in his analysis. Including the additional participants in his analysis would most likely affect the study's results in which of the following ways?
- A. Wider confidence intervals of results
- B. Increased probability of committing a type II error
- C. Decreased significance level of results
- D. Increased external validity of results
- E. Increased probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is truly false (Correct Answer)
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***Increased probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is truly false***
- Including more participants increases the **statistical power** of the study, making it more likely to detect a true effect if one exists.
- A higher sample size provides a more precise estimate of the population parameters, leading to a greater ability to **reject a false null hypothesis**.
*Wider confidence intervals of results*
- A larger sample size generally leads to **narrower confidence intervals**, as it reduces the standard error of the estimate.
- Narrower confidence intervals indicate **greater precision** in the estimation of the true population parameter.
*Increased probability of committing a type II error*
- A **Type II error** (false negative) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis.
- Increasing the sample size typically **reduces the probability of a Type II error** because it increases statistical power.
*Decreased significance level of results*
- The **significance level (alpha)** is a pre-determined threshold set by the researcher before the study begins, typically 0.05.
- It is independent of sample size and represents the **acceptable probability of committing a Type I error** (false positive).
*Increased external validity of results*
- **External validity** refers to the generalizability of findings to other populations, settings, or times.
- While a larger sample size can enhance the representativeness of the study population, external validity is primarily determined by the **sampling method** and the study's design context, not just sample size alone.
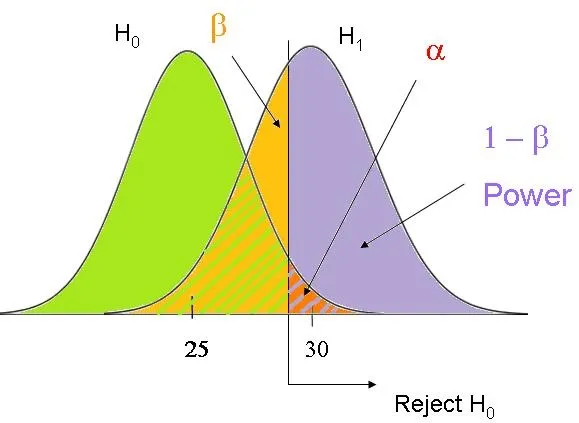
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 5: You are reading through a recent article that reports significant decreases in all-cause mortality for patients with malignant melanoma following treatment with a novel biological infusion. Which of the following choices refers to the probability that a study will find a statistically significant difference when one truly does exist?
- A. Type II error
- B. Type I error
- C. Confidence interval
- D. p-value
- E. Power (Correct Answer)
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***Power***
- **Power** is the probability that a study will correctly reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false (i.e., will find a statistically significant difference when one truly exists).
- A study with high power minimizes the risk of a **Type II error** (failing to detect a real effect).
*Type II error*
- A **Type II error** (or **beta error**) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference when one actually exists.
- This is the **opposite** of what the question describes, which asks for the probability of *finding* a difference.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (or **alpha error**) occurs when a study incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis, concluding there is a significant difference when one does not actually exist.
- This relates to the **p-value** and the level of statistical significance (e.g., p < 0.05).
*Confidence interval*
- A **confidence interval** provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain degree of confidence (e.g., 95%).
- It does not directly represent the probability of finding a statistically significant difference when one truly exists.
*p-value*
- The **p-value** is the probability of observing data as extreme as, or more extreme than, that obtained in the study, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- It is used to determine statistical significance, but it is not the probability of detecting a true effect.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 6: A study is being conducted on depression using the Patient Health questionnaire (PHQ-9) survey data embedded within a popular social media network with a response size of 500,000 participants. The sample population of this study is approximately normal. The mean PHQ-9 score is 14, and the standard deviation is 4. How many participants have scores greater than 22?
- A. 175,000
- B. 17,500
- C. 160,000
- D. 12,500 (Correct Answer)
- E. 25,000
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***12,500***
- To find the number of participants with scores greater than 22, first calculate the **z-score** for a score of 22: $Z = \frac{(X - \mu)}{\sigma} = \frac{(22 - 14)}{4} = 2$.
- A z-score of 2 means the score is **2 standard deviations above the mean**. Using the **empirical rule** for a normal distribution, approximately **2.5%** of the data falls beyond 2 standard deviations above the mean (5% total in both tails, so 2.5% in each tail).
- Therefore, $2.5\%$ of the total 500,000 participants is $0.025 \times 500,000 = 12,500$.
*175,000*
- This option would imply a much larger proportion of the population scoring above 22, inconsistent with the **normal distribution's properties** and the calculated z-score.
- It would correspond to a z-score closer to 0, indicating a score closer to the mean, not two standard deviations above it.
*17,500*
- This value represents **3.5%** of the total population ($17,500 / 500,000 = 0.035$).
- A proportion of 3.5% above the mean corresponds to a z-score that is not exactly 2, indicating an incorrect calculation or interpretation of the **normal distribution table**.
*160,000*
- This option represents a very large portion of the participants, roughly **32%** of the total population.
- This percentage would correspond to scores within one standard deviation of the mean, not scores 2 standard deviations above the mean as calculated.
*25,000*
- This value represents **5%** of the total population ($25,000 / 500,000 = 0.05$).
- A z-score greater than 2 corresponds to the far tail of the normal distribution, where only 2.5% of the data lies, not 5%. This would correspond to a z-score of approximately 1.65.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 7: An academic medical center in the United States is approached by a pharmaceutical company to run a small clinical trial to test the effectiveness of its new drug, compound X. The company wants to know if the measured hemoglobin a1c (Hba1c) of patients with type 2 diabetes receiving metformin and compound X would be lower than that of control subjects receiving only metformin. After a year of study and data analysis, researchers conclude that the control and treatment groups did not differ significantly in their Hba1c levels.
However, parallel clinical trials in several other countries found that compound X led to a significant decrease in Hba1c. Interested in the discrepancy between these findings, the company funded a larger study in the United States, which confirmed that compound X decreased Hba1c levels. After compound X was approved by the FDA, and after several years of use in the general population, outcomes data confirmed that it effectively lowered Hba1c levels and increased overall survival. What term best describes the discrepant findings in the initial clinical trial run by institution A?
- A. Type I error
- B. Hawthorne effect
- C. Type II error (Correct Answer)
- D. Publication bias
- E. Confirmation bias
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***Type II error***
- A **Type II error** occurs when a study fails to **reject a false null hypothesis**, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference or effect when one actually exists.
- In this case, the initial US trial incorrectly concluded that Compound X had no significant effect on HbA1c, while subsequent larger studies and real-world data proved it did.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (alpha error) occurs when a study incorrectly **rejects a true null hypothesis**, concluding there is a significant difference or effect when there isn't.
- This scenario describes the opposite: the initial study failed to find an effect that genuinely existed, indicating a Type II error, not a Type I error.
*Hawthorne effect*
- The **Hawthorne effect** is a type of reactivity in which individuals modify an aspect of their behavior in response to their awareness of being observed.
- This effect does not explain the initial trial's failure to detect a real drug effect; rather, it relates to participants changing behavior due to study participation itself.
*Publication bias*
- **Publication bias** occurs when studies with positive or statistically significant results are more likely to be published than those with negative or non-significant results.
- While relevant to the literature as a whole, it doesn't explain the discrepancy in findings within a single drug's development where a real effect was initially missed.
*Confirmation bias*
- **Confirmation bias** is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one's preexisting beliefs or hypotheses.
- This bias would likely lead researchers to *find* an effect if they expected one, or to disregard data that contradicts their beliefs, which is not what happened in the initial trial.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 8: You submit a paper to a prestigious journal about the effects of coffee consumption on mesothelioma risk. The first reviewer lauds your clinical and scientific acumen, but expresses concern that your study does not have adequate statistical power. Statistical power refers to which of the following?
- A. The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.
- B. The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.
- C. The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist. (Correct Answer)
- D. The first derivative of work.
- E. The square root of the variance.
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist.***
- **Statistical power** is defined as the probability that a study will correctly reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it will detect a true effect or association if one exists.
- A study with **adequate statistical power** is less likely to miss a real effect.
*The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.*
- This describes a **Type I error** or **false positive**, often represented by **alpha (α)**.
- It is the probability of incorrectly concluding an effect or association exists when, in reality, there is none.
*The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.*
- This refers to a **Type II error** or **false negative**, represented by **beta (β)**.
- **Statistical power** is calculated as **1 - β**, so this option describes the complement of power.
*The first derivative of work.*
- The first derivative of work with respect to time represents **power** in physics, which is the rate at which work is done.
- This option is a **distractor** from physics and is unrelated to statistical power in research.
*The square root of the variance.*
- The **square root of the variance** is the **standard deviation**, a measure of the dispersion or spread of data.
- This is a statistical concept but is not the definition of statistical power.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 9: A first-year medical student is conducting a summer project with his medical school's pediatrics department using adolescent IQ data from a database of 1,252 patients. He observes that the mean IQ of the dataset is 100. The standard deviation was calculated to be 10. Assuming that the values are normally distributed, approximately 87% of the measurements will fall in between which of the following limits?
- A. 85–115 (Correct Answer)
- B. 95–105
- C. 65–135
- D. 80–120
- E. 70–130
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***85–115***
- For a **normal distribution**, approximately 87% of data falls within **±1.5 standard deviations** from the mean.
- With a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 10, the range is 100 ± (1.5 * 10) = 100 ± 15, which gives **85–115**.
*95–105*
- This range represents **±0.5 standard deviations** from the mean (100 ± 5), which covers only about 38% of the data.
- This is a much narrower range and does not encompass 87% of the observations as required.
*65–135*
- This range represents **±3.5 standard deviations** from the mean (100 ± 35), which would cover over 99.9% of the data.
- Thus, this interval is too wide for 87% of the measurements.
*80–120*
- This range represents **±2 standard deviations** from the mean (100 ± 20), which covers approximately 95% of the data.
- While a common interval, it is wider than necessary for 87% of the data.
*70–130*
- This range represents **±3 standard deviations** from the mean (100 ± 30), which covers approximately 99.7% of the data.
- This interval is significantly wider than required to capture 87% of the data.
Factors affecting power US Medical PG Question 10: A health system implements a new sepsis protocol across 20 hospitals. A researcher plans to evaluate effectiveness using a stepped-wedge cluster randomized design where hospitals sequentially adopt the protocol every 3 months. She calculates sample size based on individual patient outcomes (mortality) needing 2,000 patients total. The biostatistician identifies a critical error. Evaluate what modification is needed.
- A. Adjust for multiple time periods using Bonferroni correction
- B. Use hospital-level outcomes instead of patient-level outcomes as unit of analysis
- C. Increase alpha to 0.10 to account for cluster randomization reducing power
- D. Include random effects for both hospital and time period in power calculation
- E. Account for intra-cluster correlation coefficient (ICC) requiring substantial sample size inflation (Correct Answer)
Factors affecting power Explanation: ***Account for intra-cluster correlation coefficient (ICC) requiring substantial sample size inflation***
- In cluster-randomized designs, observations within the same cluster (hospital) are not independent; the **Intra-cluster Correlation Coefficient (ICC)** quantifies this correlation and must be used to calculate a **design effect**.
- Neglecting the ICC leads to an **underpowered study** because the effective sample size is smaller than the total number of individual patients measured.
*Adjust for multiple time periods using Bonferroni correction*
- **Bonferroni correction** is used to control for **Type I error** when performing multiple independent hypothesis tests, not for determining sample size in nested longitudinal designs.
- While the stepped-wedge design involves multiple time points, the primary analysis typically uses a **single model** (e.g., GEE or GLMM) that accounts for time as a fixed effect.
*Use hospital-level outcomes instead of patient-level outcomes as unit of analysis*
- While the hospital is the **unit of randomization**, using hospital-level means as the unit of analysis simplifies the data and causes a significant loss of **statistical information** and precision.
- Modern biostatistical methods utilize **multilevel modeling** to maintain the richness of patient-level data while adjusting for the cluster-level randomization.
*Include random effects for both hospital and time period in power calculation*
- While random effects are important for the **analysis phase**, the "critical error" identified in the prompt refers to the initial failure to inflate the sample size based on **clustering (ICC)**.
- Power calculations for stepped-wedge designs are complex and certainly involve time parameters, but **ICC-based inflation** is the most fundamental adjustment required when moving from individual to cluster randomization.
*Increase alpha to 0.10 to account for cluster randomization reducing power*
- Increasing the **alpha level** (significance threshold) is not a standard or scientifically acceptable method to compensate for the loss of power due to **clustering**.
- Standard practice mandates maintaining an **alpha of 0.05** while appropriately increasing the **sample size** or number of clusters to reach the desired power (usually 80-90%).
More Factors affecting power US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.