Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 1: Group of 100 medical students took an end of the year exam. The mean score on the exam was 70%, with a standard deviation of 25%. The professor states that a student's score must be within the 95% confidence interval of the mean to pass the exam. Which of the following is the minimum score a student can have to pass the exam?
- A. 45%
- B. 63.75%
- C. 67.5%
- D. 20%
- E. 65% (Correct Answer)
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***65%***
- To find the **95% confidence interval (CI) of the mean**, we use the formula: Mean ± (Z-score × Standard Error). For a 95% CI, the Z-score is approximately **1.96**.
- The **Standard Error (SE)** is calculated as SD/√n, where n is the sample size (100 students). So, SE = 25%/√100 = 25%/10 = **2.5%**.
- The 95% CI is 70% ± (1.96 × 2.5%) = 70% ± 4.9%. The lower bound is 70% - 4.9% = **65.1%**, which rounds to **65%** as the minimum passing score.
*45%*
- This value is significantly lower than the calculated lower bound of the 95% confidence interval (approximately 65.1%).
- It would represent a score far outside the defined passing range.
*63.75%*
- This value falls below the calculated lower bound of the 95% confidence interval (approximately 65.1%).
- While close, this score would not meet the professor's criterion for passing.
*67.5%*
- This value is within the 95% confidence interval (65.1% to 74.9%) but is **not the minimum score**.
- Lower scores within the interval would still qualify as passing.
*20%*
- This score is extremely low and falls significantly outside the 95% confidence interval for a mean of 70%.
- It would indicate performance far below the defined passing threshold.
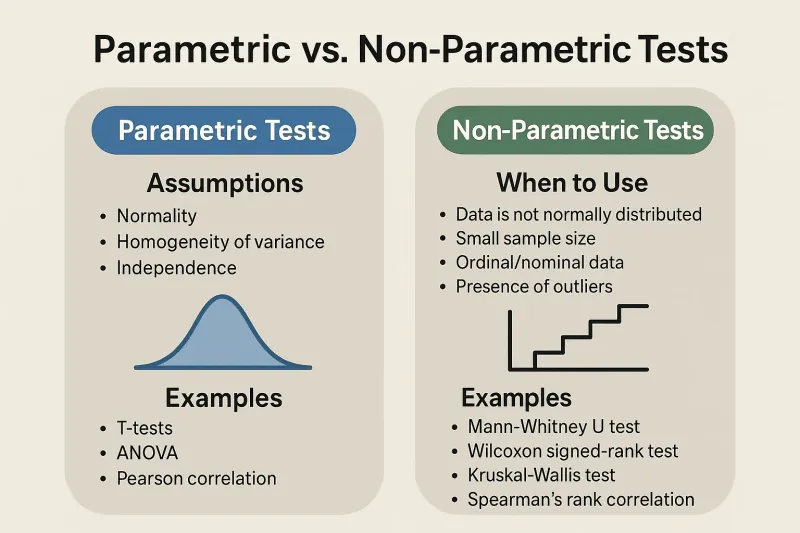
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 2: A surgeon is interested in studying how different surgical techniques impact the healing of tendon injuries. In particular, he will compare 3 different types of suture repairs biomechanically in order to determine the maximum load before failure of the tendon 2 weeks after repair. He collects data on maximum load for 90 different repaired tendons from an animal model. Thirty tendons were repaired using each of the different suture techniques. Which of the following statistical measures is most appropriate for analyzing the results of this study?
- A. Chi-squared
- B. Wilcoxon rank sum
- C. Pearson r coefficient
- D. Student t-test
- E. ANOVA (Correct Answer)
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***ANOVA***
- **ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)** is appropriate here because it compares the means of **three or more independent groups** (the three different suture techniques) on a continuous dependent variable (maximum load before failure).
- The study has three distinct repair techniques, each with 30 tendons, making ANOVA suitable for determining if there are statistically significant differences among their mean failure loads.
*Chi-squared*
- The **Chi-squared test** is used for analyzing **categorical data** (frequencies or proportions) to determine if there is an association between two nominal variables.
- This study involves quantitative measurement (maximum load), not categorical data, making Chi-squared inappropriate.
*Wilcoxon rank sum*
- The **Wilcoxon rank sum test** (also known as Mann-Whitney U test) is a **non-parametric test** used to compare two independent groups when the data is not normally distributed or is ordinal.
- While the study has independent groups, it involves three groups, and the dependent variable is continuous, making ANOVA a more powerful and appropriate choice assuming normal distribution.
*Pearson r coefficient*
- The **Pearson r coefficient** measures the **strength and direction of a linear relationship between two continuous variables**.
- This study aims to compare means across different groups, not to determine the correlation between two continuous variables.
*Student t-test*
- The **Student t-test** is used to compare the means of **exactly two groups** (either independent or paired) on a continuous dependent variable.
- This study involves comparing three different suture techniques, not just two, making the t-test unsuitable.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is measuring the blood calcium level in a sample of female cross country runners and a control group of sedentary females. If she would like to compare the means of the two groups, which statistical test should she use?
- A. Chi-square test
- B. Linear regression
- C. t-test (Correct Answer)
- D. ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
- E. F-test
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***t-test***
- A **t-test** is appropriate for comparing the means of two independent groups, such as the blood calcium levels between runners and sedentary females.
- It assesses whether the observed difference between the two sample means is statistically significant or occurred by chance.
*Chi-square test*
- The **chi-square test** is used to analyze categorical data to determine if there is a significant association between two variables.
- It is not suitable for comparing continuous variables like blood calcium levels.
*Linear regression*
- **Linear regression** is used to model the relationship between a dependent variable (outcome) and one or more independent variables (predictors).
- It aims to predict the value of a variable based on the value of another, rather than comparing means between groups.
*ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)*
- **ANOVA** is used to compare the means of **three or more independent groups**.
- Since there are only two groups being compared in this scenario, a t-test is more specific and appropriate.
*F-test*
- The **F-test** is primarily used to compare the variances of two populations or to assess the overall significance of a regression model.
- While it is the basis for ANOVA, it is not the direct test for comparing the means of two groups.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 4: You are reading through a recent article that reports significant decreases in all-cause mortality for patients with malignant melanoma following treatment with a novel biological infusion. Which of the following choices refers to the probability that a study will find a statistically significant difference when one truly does exist?
- A. Type II error
- B. Type I error
- C. Confidence interval
- D. p-value
- E. Power (Correct Answer)
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***Power***
- **Power** is the probability that a study will correctly reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false (i.e., will find a statistically significant difference when one truly exists).
- A study with high power minimizes the risk of a **Type II error** (failing to detect a real effect).
*Type II error*
- A **Type II error** (or **beta error**) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference when one actually exists.
- This is the **opposite** of what the question describes, which asks for the probability of *finding* a difference.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (or **alpha error**) occurs when a study incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis, concluding there is a significant difference when one does not actually exist.
- This relates to the **p-value** and the level of statistical significance (e.g., p < 0.05).
*Confidence interval*
- A **confidence interval** provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain degree of confidence (e.g., 95%).
- It does not directly represent the probability of finding a statistically significant difference when one truly exists.
*p-value*
- The **p-value** is the probability of observing data as extreme as, or more extreme than, that obtained in the study, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- It is used to determine statistical significance, but it is not the probability of detecting a true effect.
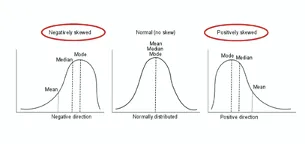
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 5: A biostatistician is processing data for a large clinical trial she is working on. The study is analyzing the use of a novel pharmaceutical compound for the treatment of anorexia after chemotherapy with the outcome of interest being the change in weight while taking the drug. While most participants remained about the same weight or continued to lose weight while on chemotherapy, there were smaller groups of individuals who responded very positively to the orexic agent. As a result, the data had a strong positive skew. The biostatistician wishes to report the measures of central tendency for this project. Just by understanding the skew in the data, which of the following can be expected for this data set?
- A. Mean = median = mode
- B. Mean < median < mode
- C. Mean > median > mode (Correct Answer)
- D. Mean > median = mode
- E. Mean < median = mode
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***Mean > median > mode***
- In a dataset with a **strong positive skew**, the tail of the distribution is on the right, pulled by a few **unusually large values**.
- These extreme high values disproportionately influence the **mean**, pulling it to the right (higher value), while the **median** (middle value) is less affected, and the **mode** (most frequent value) is often located at the peak of the distribution towards the left.
*Mean = median = mode*
- This relationship between the measures of central tendency is characteristic of a **perfectly symmetrical distribution**, such as a **normal distribution**, where there is no skew.
- In a symmetrical distribution, the mean, median, and mode are all located at the exact center of the data.
*Mean < median < mode*
- This order is typical for a dataset with a **negative skew**, where the tail is on the left due to a few **unusually small values**.
- In a negatively skewed distribution, the mean is pulled to the left (lower value) by the small values, making it less than the median and mode.
*Mean > median = mode*
- This configuration is generally not characteristic of standard skewed distributions and would imply a specific, less common bimodal or complex distribution shape where the mode coincides with the median, but the mean is pulled higher.
- While theoretically possible, it doesn't describe a typical positively skewed distribution where the mode is usually the lowest of the three.
*Mean < median = mode*
- This relationship would suggest a negatively skewed distribution where the median and mode are equal, but the mean is pulled to the left (lower value) by a leftward tail.
- Again, this is a less typical representation of a standard negatively skewed distribution, which often follows the Mean < Median < Mode pattern.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 6: A research group wants to assess the safety and toxicity profile of a new drug. A clinical trial is conducted with 20 volunteers to estimate the maximum tolerated dose and monitor the apparent toxicity of the drug. The study design is best described as which of the following phases of a clinical trial?
- A. Phase 0
- B. Phase III
- C. Phase V
- D. Phase II
- E. Phase I (Correct Answer)
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***Phase I***
- **Phase I clinical trials** involve a small group of healthy volunteers (typically 20-100) to primarily assess **drug safety**, determine a safe dosage range, and identify side effects.
- The main goal is to establish the **maximum tolerated dose (MTD)** and evaluate the drug's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles.
*Phase 0*
- **Phase 0 trials** are exploratory studies conducted in a very small number of subjects (10-15) to gather preliminary data on a drug's **pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics** in humans.
- They involve microdoses, not intended to have therapeutic effects, and thus cannot determine toxicity or MTD.
*Phase III*
- **Phase III trials** are large-scale studies involving hundreds to thousands of patients to confirm the drug's **efficacy**, monitor side effects, compare it to standard treatments, and collect information that will allow the drug to be used safely.
- These trials are conducted after safety and initial efficacy have been established in earlier phases.
*Phase V*
- "Phase V" is not a standard, recognized phase in the traditional clinical trial classification (Phase 0, I, II, III, IV).
- This term might be used in some non-standard research contexts or for post-marketing studies that go beyond Phase IV surveillance, but it is not a formal phase for initial drug development.
*Phase II*
- **Phase II trials** involve several hundred patients with the condition the drug is intended to treat, focusing on **drug efficacy** and further evaluating safety.
- While safety is still monitored, the primary objective shifts to determining if the drug works for its intended purpose and at what dose.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 7: You submit a paper to a prestigious journal about the effects of coffee consumption on mesothelioma risk. The first reviewer lauds your clinical and scientific acumen, but expresses concern that your study does not have adequate statistical power. Statistical power refers to which of the following?
- A. The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.
- B. The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.
- C. The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist. (Correct Answer)
- D. The first derivative of work.
- E. The square root of the variance.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist.***
- **Statistical power** is defined as the probability that a study will correctly reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it will detect a true effect or association if one exists.
- A study with **adequate statistical power** is less likely to miss a real effect.
*The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.*
- This describes a **Type I error** or **false positive**, often represented by **alpha (α)**.
- It is the probability of incorrectly concluding an effect or association exists when, in reality, there is none.
*The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.*
- This refers to a **Type II error** or **false negative**, represented by **beta (β)**.
- **Statistical power** is calculated as **1 - β**, so this option describes the complement of power.
*The first derivative of work.*
- The first derivative of work with respect to time represents **power** in physics, which is the rate at which work is done.
- This option is a **distractor** from physics and is unrelated to statistical power in research.
*The square root of the variance.*
- The **square root of the variance** is the **standard deviation**, a measure of the dispersion or spread of data.
- This is a statistical concept but is not the definition of statistical power.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 8: During identification of severely decomposed remains, which of the following methods provides the most reliable means of positive identification?
- A. Birthmarks
- B. Facial features
- C. DNA analysis (Correct Answer)
- D. Personal effects
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***DNA analysis***
- **DNA analysis** remains viable even in significantly degraded samples due to the stability and uniqueness of the genetic code, making it the most reliable method for positive identification of severely decomposed remains.
- It provides a definitive match that is **scientifically verifiable** and rarely subject to error when compared to ante-mortem samples or close relatives.
*Birthmarks*
- **Birthmarks** are soft tissue characteristics that often degrade or become indistinguishable in severely decomposed remains.
- Their presence and appearance can change over time or be obscured by **decomposition processes**, making them unreliable for identification in such cases.
*Facial features*
- **Facial features** rapidly deteriorate and distort after death, especially in severely decomposed remains, making visual recognition impossible.
- The soft tissues of the face are among the first to undergo **autolysis** and putrefaction.
*Personal effects*
- While **personal effects** (like jewelry or clothing) can provide circumstantial evidence, they do not offer positive identification of the individual's remains.
- These items can be easily lost, misplaced, or exchanged, and they do not directly identify the **biological individual**.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 9: The mean, median, and mode weight of 37 newborns in a hospital nursery is 7 lbs 2 oz. In fact, there are 7 infants in the nursery that weigh exactly 7 lbs 2 oz. The standard deviation of the weights is 2 oz. The weights follow a normal distribution. A newborn delivered at 10 lbs 2 oz is added to the data set. What is most likely to happen to the mean, median, and mode with the addition of this new data point?
- A. The mean will increase; the median will increase; the mode will stay the same
- B. The mean will increase; the median will stay the same; the mode will stay the same (Correct Answer)
- C. The mean will stay the same; the median will increase; the mode will stay the same
- D. The mean will increase; the median will increase; the mode will increase
- E. The mean will stay the same; the median will increase; the mode will increase
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***The mean will increase; the median will stay the same; the mode will stay the same***
- The **mean** is highly sensitive to outliers. Adding a newborn weighing 10 lbs 2 oz (significantly heavier than the original mean of 7 lbs 2 oz) will increase the total sum of weights, thus **increasing the mean**.
- The **median** is the middle value in an ordered dataset. With 37 newborns, the median is the 19th value. Adding one more (38 total) makes the median the average of the 19th and 20th values. Since the new value (10 lbs 2 oz) is added at the extreme high end of the distribution, the 19th and 20th positions contain the same values as before. Therefore, the median will **stay the same**.
- The **mode** is the most frequent value. Since there are 7 infants already at 7 lbs 2 oz, adding a single infant at 10 lbs 2 oz will not change the most frequent weight in the dataset. The mode will **stay the same** at 7 lbs 2 oz.
*The mean will increase; the median will increase; the mode will stay the same*
- While the **mean will increase** due to the added outlier, the **median will not change**. With 38 observations, the median becomes the average of the 19th and 20th values, which remain unchanged since the outlier is added at position 38.
- The **mode** correctly stays at 7 lbs 2 oz as the new data point does not become the most frequent value.
*The mean will stay the same; the median will increase; the mode will stay the same*
- The **mean will not stay the same** because an outlier significantly higher than the current mean will always pull the mean higher.
- The **median will also not increase** as the middle values (19th and 20th positions) remain unchanged when adding an extreme outlier.
*The mean will increase; the median will increase; the mode will increase*
- While the **mean will increase**, the **median will not change** because the middle positions are unaffected by adding one extreme outlier.
- The **mode will not change** as the new data point (10 lbs 2 oz) is unique and doesn't become the most frequent value; 7 lbs 2 oz remains most frequent with 7 occurrences.
*The mean will stay the same; the median will increase; the mode will increase*
- This option is incorrect because the **mean will definitely increase** with the addition of a much larger value.
- The **median will not increase** as it depends on the middle positions, not extreme values.
- The **mode will not increase** as adding one 10 lb 2 oz infant won't make that weight the most frequent.
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG Question 10: A first-year medical student is conducting a summer project with his medical school's pediatrics department using adolescent IQ data from a database of 1,252 patients. He observes that the mean IQ of the dataset is 100. The standard deviation was calculated to be 10. Assuming that the values are normally distributed, approximately 87% of the measurements will fall in between which of the following limits?
- A. 85–115 (Correct Answer)
- B. 95–105
- C. 65–135
- D. 80–120
- E. 70–130
Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests Explanation: ***85–115***
- For a **normal distribution**, approximately 87% of data falls within **±1.5 standard deviations** from the mean.
- With a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 10, the range is 100 ± (1.5 * 10) = 100 ± 15, which gives **85–115**.
*95–105*
- This range represents **±0.5 standard deviations** from the mean (100 ± 5), which covers only about 38% of the data.
- This is a much narrower range and does not encompass 87% of the observations as required.
*65–135*
- This range represents **±3.5 standard deviations** from the mean (100 ± 35), which would cover over 99.9% of the data.
- Thus, this interval is too wide for 87% of the measurements.
*80–120*
- This range represents **±2 standard deviations** from the mean (100 ± 20), which covers approximately 95% of the data.
- While a common interval, it is wider than necessary for 87% of the data.
*70–130*
- This range represents **±3 standard deviations** from the mean (100 ± 30), which covers approximately 99.7% of the data.
- This interval is significantly wider than required to capture 87% of the data.
More Confidence intervals for non-parametric tests US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.