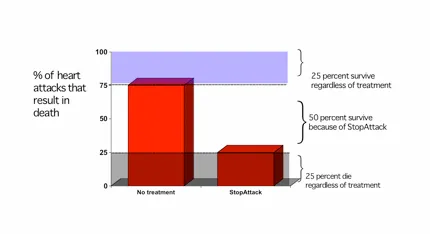
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Definition of NNT/NNH. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 1: You have been asked to quantify the relative risk of developing bacterial meningitis following exposure to a patient with active disease. You analyze 200 patients in total, half of which are controls. In the trial arm, 30% of exposed patients ultimately contracted bacterial meningitis. In the unexposed group, only 1% contracted the disease. Which of the following is the relative risk due to disease exposure?
- A. (30 * 99) / (70 * 1)
- B. [30 / (30 + 70)] / [1 / (1 + 99)] (Correct Answer)
- C. [70 / (30 + 70)] / [99 / (1 + 99)]
- D. [[1 / (1 + 99)] / [30 / (30 + 70)]]
- E. (70 * 1) / (30 * 99)
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***[30 / (30 + 70)] / [1 / (1 + 99)]***
- This formula correctly calculates the **relative risk (RR)**. The numerator represents the **incidence rate in the exposed group** (30% of 100 exposed patients = 30 cases out of 100), and the denominator represents the **incidence rate in the unexposed group** (1% of 100 unexposed patients = 1 case out of 100).
- Relative risk is the ratio of the **risk of an event** in an **exposed group** to the **risk of an event** in an **unexposed group**.
*[(30 * 99) / (70 * 1)]*
- This formula is for calculating the **odds ratio (OR)**, specifically using a 2x2 table setup where 30 represents exposed cases, 70 represents exposed non-cases, 1 represents unexposed cases, and 99 represents unexposed non-cases.
- The odds ratio is a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome, representing the **odds of an outcome** given exposure compared to the odds of the outcome without exposure.
*[70 / (30 + 70)] / [99 / (1 + 99)]*
- This formula calculates the **relative risk of *not* developing the disease**, which is the inverse of what the question asks for.
- It compares the proportion of exposed individuals who *do not* contract the disease to the proportion of unexposed individuals who *do not* contract the disease.
*[[1 / (1 + 99)] / [30 / (30 + 70)]]*
- This formula calculates the **inverse of the relative risk**, which is not what the question asks for.
- It would represent the ratio of the incidence in the unexposed group to the incidence in the exposed group.
*[(70 * 1) / (30 * 99)]*
- This is an **incorrect variation** of the odds ratio calculation, with the terms in the numerator and denominator swapped compared to the standard formula.
- Therefore, it does not represent the relative risk or a correctly calculated odds ratio.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 2: A research group wants to assess the safety and toxicity profile of a new drug. A clinical trial is conducted with 20 volunteers to estimate the maximum tolerated dose and monitor the apparent toxicity of the drug. The study design is best described as which of the following phases of a clinical trial?
- A. Phase 0
- B. Phase III
- C. Phase V
- D. Phase II
- E. Phase I (Correct Answer)
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***Phase I***
- **Phase I clinical trials** involve a small group of healthy volunteers (typically 20-100) to primarily assess **drug safety**, determine a safe dosage range, and identify side effects.
- The main goal is to establish the **maximum tolerated dose (MTD)** and evaluate the drug's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles.
*Phase 0*
- **Phase 0 trials** are exploratory studies conducted in a very small number of subjects (10-15) to gather preliminary data on a drug's **pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics** in humans.
- They involve microdoses, not intended to have therapeutic effects, and thus cannot determine toxicity or MTD.
*Phase III*
- **Phase III trials** are large-scale studies involving hundreds to thousands of patients to confirm the drug's **efficacy**, monitor side effects, compare it to standard treatments, and collect information that will allow the drug to be used safely.
- These trials are conducted after safety and initial efficacy have been established in earlier phases.
*Phase V*
- "Phase V" is not a standard, recognized phase in the traditional clinical trial classification (Phase 0, I, II, III, IV).
- This term might be used in some non-standard research contexts or for post-marketing studies that go beyond Phase IV surveillance, but it is not a formal phase for initial drug development.
*Phase II*
- **Phase II trials** involve several hundred patients with the condition the drug is intended to treat, focusing on **drug efficacy** and further evaluating safety.
- While safety is still monitored, the primary objective shifts to determining if the drug works for its intended purpose and at what dose.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 3: In 2006, three researchers from North Carolina wanted to examine the benefits of treating the risk of suicidality in children and adolescents by looking at randomized, multicenter, controlled trials of sertraline usage compared to placebo. Their analysis found clinically significant benefits of the drug and a positive benefit-to-risk ratio for sertraline in adolescents with major depressive disorder. They also found that 64 depressed children and adolescents need to receive the drug for 1 extra patient to experience suicidality as an adverse outcome. In other words, if 64 treated individuals received sertraline, some would experience suicidality due to their illness, some would not experience suicidality, and 1 individual would become suicidal due to the unique contribution of sertraline. Which of the following statements is true for this measure (defined as the inverse of the attributable risk), which aims to describe adverse outcomes this way?
- A. Higher measures indicate greater risk.
- B. Input values must be probabilities of the events of interest. (Correct Answer)
- C. Multiple risks can be contained and described within one result.
- D. The final metric represents proportions in percentage terms.
- E. The measure can include multiple events at one time.
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***Input values must be probabilities of the events of interest.***
- The measure described (- the inverse of the **attributable risk** - or more accurately, the **Number Needed to Harm** or **NNH**) is derived from **absolute risk reduction**, which requires the risk of an event in the exposed group and the risk of the event in the unexposed/control group to be expressed as **probabilities or proportions**.
- These probabilities are essential for calculating the difference in event rates, which is then inverted to get the NNH.
*Higher measures indicate greater risk.*
- A **higher NNH** (e.g., 64 in this case) indicates that a larger number of patients need to be treated for one additional adverse event to occur, implying a **lower risk** associated with the treatment.
- Conversely, a **lower NNH** (e.g., 10) would mean fewer patients need to be treated for one additional adverse event, indicating a **higher risk**.
*Multiple risks can be contained and described within one result.*
- The NNH (or Number Needed to Treat) is typically calculated for a **single specific outcome** (either beneficial or harmful).
- While an overall benefit-to-risk analysis might involve considering multiple outcomes, the NNH itself quantifies the impact for **one defined event**.
*The final metric represents proportions in percentage terms.*
- The final metric (NNH) is expressed as a **whole number** (e.g., 64), representing the number of patients.
- It does **not represent a proportion or a percentage**; rather, it indicates how many individuals need to be exposed to experience one additional event.
*The measure can include multiple events at one time.*
- The NNH is event-specific; it calculates the number of patients for **one particular adverse event**.
- To analyze multiple events, one would need to calculate **separate NNH values** for each individual event.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 4: You submit a paper to a prestigious journal about the effects of coffee consumption on mesothelioma risk. The first reviewer lauds your clinical and scientific acumen, but expresses concern that your study does not have adequate statistical power. Statistical power refers to which of the following?
- A. The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.
- B. The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.
- C. The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist. (Correct Answer)
- D. The first derivative of work.
- E. The square root of the variance.
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist.***
- **Statistical power** is defined as the probability that a study will correctly reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it will detect a true effect or association if one exists.
- A study with **adequate statistical power** is less likely to miss a real effect.
*The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.*
- This describes a **Type I error** or **false positive**, often represented by **alpha (α)**.
- It is the probability of incorrectly concluding an effect or association exists when, in reality, there is none.
*The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.*
- This refers to a **Type II error** or **false negative**, represented by **beta (β)**.
- **Statistical power** is calculated as **1 - β**, so this option describes the complement of power.
*The first derivative of work.*
- The first derivative of work with respect to time represents **power** in physics, which is the rate at which work is done.
- This option is a **distractor** from physics and is unrelated to statistical power in research.
*The square root of the variance.*
- The **square root of the variance** is the **standard deviation**, a measure of the dispersion or spread of data.
- This is a statistical concept but is not the definition of statistical power.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 5: A survey was conducted in a US midwestern town in an effort to assess maternal mortality over the past year. The data from the survey are given in the table below:
Women of childbearing age 250,000
Maternal deaths 2,500
Number of live births 100, 000
Number of deaths of women of childbearing age 7,500
Maternal death is defined as the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy from any cause related to or aggravated by, the pregnancy. Which of the following is the maternal mortality rate in this midwestern town?
- A. 1,000 per 100,000 live births
- B. 33 per 100,000 live births
- C. 3,000 per 100,000 live births
- D. 33,300 per 100,000 live births
- E. 2,500 per 100,000 live births (Correct Answer)
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***2,500 per 100,000 live births***
- The maternal mortality rate is calculated as the number of **maternal deaths** per 100,000 **live births**. The given data directly provide these values.
- Calculation: (2,500 maternal deaths / 100,000 live births) × 100,000 = **2,500 per 100,000 live births**.
*1,000 per 100,000 live births*
- This value is incorrect as it does not align with the provided numbers for maternal deaths and live births in the calculation.
- It might result from a miscalculation or using incorrect numerator/denominator values from the dataset.
*33 per 100,000 live births*
- This value is significantly lower than the correct rate and suggests a substantial error in calculation or an incorrect understanding of how the maternal mortality rate is derived.
- It could potentially result from dividing the number of live births by maternal deaths, which is the inverse of the correct formula.
*3,000 per 100,000 live births*
- This option is close to the correct answer but slightly higher, indicating a possible calculation error, for instance, including non-maternal deaths or other causes of deaths in the numerator.
- The definition of maternal death is specific to pregnancy-related or aggravated causes, so extraneous deaths would inflate the rate.
*33,300 per 100,000 live births*
- This figure results from incorrectly calculating the proportion of maternal deaths among all deaths of women of childbearing age: (2,500 / 7,500) × 100,000 = 33,333.
- This is a conceptual error as the maternal mortality rate should use live births as the denominator, not total deaths of women of childbearing age.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 6: In a randomized controlled trial studying a new treatment, the primary endpoint (mortality) occurred in 14.4% of the treatment group and 16.7% of the control group. Which of the following represents the number of patients needed to treat to save one life, based on the primary endpoint?
- A. 1/(0.144 - 0.167)
- B. 1/(0.167 - 0.144) (Correct Answer)
- C. 1/(0.300 - 0.267)
- D. 1/(0.267 - 0.300)
- E. 1/(0.136 - 0.118)
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***1/(0.167 - 0.144)***
- The **Number Needed to Treat (NNT)** is calculated as **1 / Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR)**.
- The **Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR)** is the difference between the event rate in the control group (16.7%) and the event rate in the treatment group (14.4%), which is **0.167 - 0.144**.
*1/(0.144 - 0.167)*
- This calculation represents 1 divided by the **Absolute Risk Increase**, which would be relevant if the treatment increased mortality.
- The **NNT should always be a positive value**, indicating the number of patients to treat to prevent one adverse event.
*1/(0.300 - 0.267)*
- This option uses arbitrary numbers (0.300 and 0.267) that do not correspond to the given **mortality rates** in the problem.
- It does not reflect the correct calculation for **absolute risk reduction** based on the provided data.
*1/(0.267 - 0.300)*
- This option also uses arbitrary numbers not derived from the problem's data, and it would result in a **negative value** for the denominator.
- The difference between event rates of 0.267 and 0.300 is not present in the given information for this study.
*1/(0.136 - 0.118)*
- This calculation uses arbitrary numbers (0.136 and 0.118) that are not consistent with the reported **mortality rates** of 14.4% and 16.7%.
- These values do not represent the **Absolute Risk Reduction** required for calculating NNT in this specific scenario.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 7: You are reviewing raw data from a research study performed at your medical center examining the effectiveness of a novel AIDS screening examination. The study enrolled 250 patients with confirmed AIDS, and 240 of these patients demonstrated a positive screening examination. The control arm of the study enrolled 250 patients who do not have AIDS, and only 5 of these patients tested positive on the novel screening examination. What is the NPV of this novel test?
- A. 240 / (240 + 15)
- B. 240 / (240 + 5)
- C. 240 / (240 + 10)
- D. 245 / (245 + 10) (Correct Answer)
- E. 245 / (245 + 5)
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***245 / (245 + 10)***
- The **negative predictive value (NPV)** is calculated as **true negatives (TN)** divided by the sum of **true negatives (TN)** and **false negatives (FN)**.
- In this study, there are 250 patients with AIDS; 240 tested positive (true positives, TP), meaning 10 tested negative (false negatives, FN = 250 - 240). There are 250 patients without AIDS; 5 tested positive (false positives, FP), meaning 245 tested negative (true negatives, TN = 250 - 5). Therefore, NPV = 245 / (245 + 10).
*240 / (240 + 15)*
- This calculation incorrectly uses the number of **true positives** (240) in the numerator and denominator, which is relevant for **positive predictive value (PPV)**, not NPV.
- The denominator `(240 + 15)` does not correspond to a valid sum for calculating NPV from the given data.
*240 / (240 + 5)*
- This calculation incorrectly uses **true positives** (240) in the numerator, which is not part of the NPV formula.
- The denominator `(240 + 5)` mixes true positives and false positives, which is incorrect for NPV.
*240 / (240 + 10)*
- This incorrectly places **true positives** (240) in the numerator instead of **true negatives**.
- The denominator `(240+10)` represents **true positives + false negatives**, which is related to sensitivity, not NPV.
*245 / (245 + 5)*
- This calculation correctly identifies **true negatives** (245) in the numerator but incorrectly uses **false positives** (5) in the denominator instead of **false negatives**.
- The denominator for NPV should be **true negatives + false negatives**, which is 245 + 10.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 8: A pharmaceutical company reports a new antihypertensive drug reduces cardiovascular events with an NNT of 50 over 5 years based on a trial of 10,000 patients. An independent analysis reveals the benefit was driven entirely by a subgroup with resistant hypertension (20% of participants, NNT=15), while the remaining 80% showed no benefit over standard therapy (NNT approaching infinity). Evaluate the ethical and regulatory implications of reporting the overall NNT.
- A. Conduct a new trial in the general hypertensive population to validate efficacy before broader approval
- B. The subgroup analysis represents data dredging; only the overall NNT should be used for clinical decisions
- C. The overall NNT of 50 is statistically valid and appropriate for regulatory approval and marketing
- D. Report both overall and subgroup NNTs; allow clinicians to determine appropriate use based on patient characteristics
- E. The overall NNT is misleading; approval should be restricted to resistant hypertension population where benefit is demonstrated (Correct Answer)
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***The overall NNT is misleading; approval should be restricted to resistant hypertension population where benefit is demonstrated***
- Reporting an **aggregate NNT** when the clinical benefit is confined to a specific **subgroup** obscures the fact that the drug is ineffective for 80% of the study population.
- Regulatory and ethical standards dictate that **indication for use** must be limited to populations where a **favorable benefit-risk ratio** has been proven, preventing unnecessary exposure to side effects in non-responders.
*The overall NNT of 50 is statistically valid and appropriate for regulatory approval and marketing*
- While the math is accurate for the trial population as a whole, it ignores **heterogeneity of treatment effect**, which is critical for making safe **clinical recommendations**.
- Marketing a drug based on an **averaged NNT** when the majority of patients derive zero benefit is considered **clinically misleading** and ethically questionable.
*Report both overall and subgroup NNTs; allow clinicians to determine appropriate use based on patient characteristics*
- This approach puts the burden of identifying the correct population on the clinician rather than setting **clear regulatory boundaries** through specific labelling.
- Merely reporting the **overall NNT** may lead to **off-label use** in populations where the NNT is effectively **infinity**, representing a failure in evidence-based guidance.
*Conduct a new trial in the general hypertensive population to validate efficacy before broader approval*
- The existing data already demonstrates that the **general population** (the 80% non-resistant group) showed no benefit over standard therapy.
- Conducting a new trial for the general population would be **unethical and redundant**, as the lack of efficacy in that specific group has already been established by the **independent analysis**.
*The subgroup analysis represents data dredging; only the overall NNT should be used for clinical decisions*
- **Data dredging** refers to finding random patterns; however, identifying a lack of benefit in 80% of a population is a critical **safety and efficacy finding** that cannot be ignored.
- Dismissing the **subgroup effect** would result in potentially treating millions of patients with an **ineffective medication**, violating the principle of **non-maleficence**.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 9: A public health agency must allocate a fixed budget between two interventions for diabetes prevention. Program A (intensive lifestyle modification): NNT=7, cost $3,500/person. Program B (metformin): NNT=14, cost $1,000/person. Both prevent one case of diabetes over 3 years. The budget allows treating 1,000 people with Program A or 3,500 people with Program B. Evaluate the optimal allocation strategy to maximize population health impact.
- A. Choose based on cost per case prevented: Program A ($24,500) vs Program B ($14,000), favoring Program B (Correct Answer)
- B. Choose Program B exclusively: higher population reach (3,500 vs 1,000) and lower cost per person treated maximizes prevention (250 cases) despite higher NNT
- C. Allocate budget equally between programs: provides both high-efficacy and broad-reach approaches
- D. Choose Program A for high-risk individuals and Program B for moderate-risk: risk-stratified approach optimizes NNT
- E. Choose Program A exclusively: lower NNT means superior efficacy, preventing 143 cases versus 250 with Program B
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***Choose based on cost per case prevented: Program A ($24,500) vs Program B ($14,000), favoring Program B***
- To maximize **population health impact** under a fixed budget, one must calculate the **cost per case prevented**, which is found by multiplying the **NNT** by the **cost per person** ($1,000 x 14 = $14,000 for Program B).
- Program B allows for a much higher total number of cases prevented (**250 cases**) compared to Program A (**142 cases**) because the **lower unit cost** outweighs the higher NNT.
*Choose Program A exclusively: lower NNT means superior efficacy, preventing 143 cases versus 250 with Program B*
- While Program A has a **lower NNT**, indicating it is more effective for an individual, it is significantly less **cost-effective** for a population due to its high cost.
- Exclusive use of Program A would result in fewer total cases prevented (142) compared to the 250 cases prevented by Program B, wasting **allocated resources**.
*Choose Program B exclusively: higher population reach (3,500 vs 1,000) and lower cost per person treated maximizes prevention (250 cases) despite higher NNT*
- This option correctly identifies the outcome but lacks the precise **economic justification** (cost per outcome) required for optimal health allocation decisions.
- Public health decisions are fundamentally based on **incremental cost-effectiveness ratios** or cost per case prevented rather than reach alone.
*Allocate budget equally between programs: provides both high-efficacy and broad-reach approaches*
- Managing a fixed budget by splitting it equally results in **196 total cases prevented**, which is mathematically inferior to the 250 cases prevented by prioritizing the more cost-efficient program.
- This approach fails to address the **opportunity cost** of not spending the entire budget on the more efficient intervention.
*Choose Program A for high-risk individuals and Program B for moderate-risk: risk-stratified approach optimizes NNT*
- While **risk stratification** is clinically sound, the prompt asks to maximize impact based on the provided fixed costs and NNTs for the general intervention group.
- Adding complexity to the delivery model can further increase **administrative costs**, which are not accounted for in this basic **cost-effectiveness analysis**.
Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG Question 10: A 45-year-old woman with a strong family history of breast cancer (lifetime risk 25%) is considering chemoprevention with tamoxifen. A trial shows tamoxifen reduces breast cancer incidence from 5% to 3% over 5 years in high-risk women, but increases endometrial cancer from 0.2% to 0.6% and thromboembolic events from 0.5% to 1.5%. Evaluate whether she should be recommended this therapy based on comprehensive risk-benefit analysis.
- A. Recommend alternative screening strategies as chemoprevention shows no net benefit when all outcomes are considered
- B. Recommend tamoxifen only if patient values breast cancer prevention significantly more than other risks, given similar absolute risk magnitudes (Correct Answer)
- C. Recommend tamoxifen: NNT=50 for breast cancer prevention outweighs combined NNH=250 for endometrial cancer and NNH=100 for thromboembolism
- D. Insufficient data to make recommendation without knowing patient's personal values and quality-of-life preferences
- E. Recommend against tamoxifen: The harms (2 complications per 100 treated) outweigh benefits (2 cancers prevented per 100 treated)
Definition of NNT/NNH Explanation: ***Recommend tamoxifen only if patient values breast cancer prevention significantly more than other risks, given similar absolute risk magnitudes***
- The **Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR)** for breast cancer is 2% (5% minus 3%), while the cumulative **Absolute Risk Increase (ARI)** for major harms is 1.4% (0.4% for endometrial cancer and 1.0% for thromboembolism).
- Because the magnitude of benefit (2 preventable cancers) is narrowly balanced against the magnitude of harm (1.4 serious complications), the decision relies on **patient preferences** and how they weigh the severity of different health outcomes.
*Recommend tamoxifen: NNT=50 for breast cancer prevention outweighs combined NNH=250 for endometrial cancer and NNH=100 for thromboembolism*
- While the **Number Needed to Treat (NNT)** is indeed 50 (1/0.02), the combined **Number Needed to Harm (NNH)** for any serious complication is approximately 71 (1/0.014), not 250 or 100 individually.
- This option oversimplifies the trade-off by suggesting a clear-cut advantage that does not exist when both serious adverse events are aggregated.
*Recommend against tamoxifen: The harms (2 complications per 100 treated) outweigh benefits (2 cancers prevented per 100 treated)*
- The calculation of harms is slightly inaccurate as the **ARI** is 1.4 per 100, which is numerically lower than the benefit of 2 cancers prevented per 100.
- A blanket recommendation against therapy ignores that a **2% ARR** in breast cancer may be clinically significant for a high-risk patient willing to accept the side-effect profile.
*Insufficient data to make recommendation without knowing patient's personal values and quality-of-life preferences*
- While patient values are crucial, the **clinical data** provided is sufficient to form a recommendation framework based on the **risk-benefit ratio**.
- The objective is to evaluate the therapy within the context of **evidence-based medicine**, which allows for a conditional recommendation rather than a claim of "insufficient data."
*Recommend alternative screening strategies as chemoprevention shows no net benefit when all outcomes are considered*
- This is incorrect because **chemoprevention** is a distinct primary prevention strategy that can be used in conjunction with, not just as a replacement for, high-risk screening.
- The data shows a **net numerical benefit** (2.0% reduction vs 1.4% increase), meaning it cannot be claimed there is "no net benefit" across all outcomes.
More Definition of NNT/NNH US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.