Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old man undergoes an esophagogastroduodenoscopy for his recurrent episodes of epigastric pain. He also lost a significant amount of weight in the last 6 months. He says that he has been taking a number of dietary supplements "to cope". His past medical history is insignificant, and a physical examination is within normal limits. The endoscopy shows a bleeding ulcer in the proximal duodenum. Lab tests reveal a serum iron level of 130 μg/dL. However, his stool guaiac test is negative for occult blood. Over-ingestion of which of the following substances is the most likely cause for this patient’s lab findings?
- A. Red meat
- B. Folate
- C. Tocopherol
- D. Ascorbic acid (Correct Answer)
- E. Thiamine
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: **Ascorbic acid**
- **Excessive intake of ascorbic acid (vitamin C)** can lead to false-negative stool guaiac tests because it reduces the orthotolidine reagent, interfering with the peroxidase reaction that detects hemoglobin.
- While the patient has a bleeding ulcer, the negative guaiac test despite active bleeding is explained by this **reductive interference** from large doses of vitamin C, which he might be taking as part of his "dietary supplements."
*Red meat*
- **Red meat intake** can cause **false-positive** stool guaiac tests due to the presence of peroxidases in the meat.
- This is the opposite of the patient's presentation, which shows a **false-negative** result.
*Folate*
- **Folate (vitamin B9)** does not significantly interfere with the chemical reaction used in the guaiac test.
- High doses of folate are not known to cause either false-positive or false-negative results in stool occult blood testing.
*Tocopherol*
- **Tocopherol (vitamin E)** does not interfere with the chemical reaction of the guaiac test for occult blood.
- While vitamin E can have some anticoagulant properties at very high doses, it does not directly affect the chemical detection of blood in stool.
*Thiamine*
- **Thiamine (vitamin B1)** does not interfere with the chemical reaction of the guaiac test for occult blood.
- There is no known mechanism by which thiamine supplementation would lead to false-negative results in a stool guaiac test.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old woman presents to the clinic with a 2-week history of headaches. She was in her usual state of health until 2 weeks ago, when she started having headaches. The headaches are throughout her whole head and rated as a 7/10. They are worse in the mornings and when she bends over. She has some mild nausea, but no vomiting. The headaches are not throbbing and are not associated with photophobia or phonophobia. On further questioning, she has noticed more hair than usual on her pillow in the morning and coming out in her hands when she washes her hair. The past medical history is unremarkable; she takes no prescription medications, but for the past year she has been taking an oral 'health supplement' recommended by her sister, which she orders over the internet. She cannot recall the supplement's name and does not know its contents. The physical exam is notable for some mild hepatomegaly but is otherwise unremarkable. This patient's presentation is most likely related to which of the following micronutrients?
- A. Vitamin D
- B. Vitamin B12
- C. Vitamin C
- D. Vitamin K
- E. Vitamin A (Correct Answer)
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Vitamin A***
- The patient's symptoms, including **headaches worse in the mornings and with bending over**, **mild nausea**, and **diffuse hair loss**, along with **hepatomegaly**, are classic signs of **chronic vitamin A toxicity** (**hypervitaminosis A**).
- The likely source is a high-dose oral "health supplement" of unknown content, as vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin stored in the liver, leading to toxicity with excessive intake.
*Vitamin D*
- **Vitamin D toxicity** (hypervitaminosis D) typically presents with **hypercalcemia**, leading to symptoms like polyuria, polydipsia, renal stones, and muscle weakness, which are not described here.
- While headaches can occur, **hair loss** and **hepatomegaly** are not characteristic features of vitamin D toxicity.
*Vitamin B12*
- **Vitamin B12 toxicity** is extremely rare, as it is a water-soluble vitamin and excess is readily excreted.
- There are no well-established adverse effects or toxicity syndromes associated with high doses of vitamin B12 that would explain these symptoms.
*Vitamin C*
- **Vitamin C** is a water-soluble vitamin, and acute toxicity is uncommon because excess is excreted in urine.
- High doses can lead to **gastrointestinal upset** (diarrhea, nausea, abdominal cramps) and, rarely, kidney stones, but not the constellation of headache, hair loss, and hepatomegaly seen in this patient.
*Vitamin K*
- **Vitamin K toxicity** is generally rare and primarily associated with synthetic forms (menadione).
- In infants, high doses can cause **hemolytic anemia** and **jaundice**, but these symptoms are not typical for adults, nor do they explain the described presentation of headache, hair loss, and hepatomegaly.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 3: A 13-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents for the evaluation of progressive hair loss over the past 2 months. The parents report that they have noticed increased number of hairless patches on their daughter's head. The patient denies any itching. There is no personal or family history of serious illness. The patient states that she has been feeling tense since her boyfriend broke up with her. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She does not use illicit drugs. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows ill-defined patchy hair loss and hair of different lengths with no scaling or reddening of the scalp. Further examination shows poor hair growth of the eyebrows and eyelashes. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Telogen effluvium
- B. Alopecia areata
- C. Trichotillomania (Correct Answer)
- D. Scarring alopecia
- E. Tinea capitis
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Correct: Trichotillomania***
- This is a **hair-pulling disorder** classified as an obsessive-compulsive related disorder in which individuals repeatedly pull out their own hair.
- The diagnostic features in this case are highly characteristic: **ill-defined patchy hair loss with hairs of different lengths** (indicating repeated pulling over time), absence of scalp inflammation (no scaling or redness), and involvement of **eyebrows and eyelashes**.
- The patient's recent emotional stressor (breakup) is a common **precipitating factor** for this impulse control behavior, particularly in adolescents.
- The lack of itching and inflammatory changes helps distinguish this from dermatological causes of hair loss.
*Incorrect: Telogen effluvium*
- This condition presents with **diffuse hair shedding** following a significant physiological or emotional stressor (typically 2-3 months after the trigger).
- While stress can precipitate telogen effluvium, it causes **uniform hair thinning** across the scalp rather than distinct patches with hairs of different lengths.
- The patchy distribution and varying hair lengths are inconsistent with telogen effluvium.
*Incorrect: Alopecia areata*
- An autoimmune condition characterized by **well-demarcated, smooth, circular patches** of complete hair loss, often with "exclamation point hairs" at the margins.
- While it can affect eyebrows and eyelashes, the description of **"ill-defined" patches with hairs of different lengths** is atypical for alopecia areata, which typically shows complete hair loss in well-circumscribed areas.
- The patches in alopecia areata are usually round and sharply defined, not ill-defined.
*Incorrect: Scarring alopecia*
- Involves **permanent destruction of hair follicles** with fibrosis, leading to smooth, atrophic patches where hair cannot regrow.
- Usually presents with **visible scarring, scaling, erythema, or signs of inflammation** on the scalp.
- The absence of any inflammatory changes, scaling, or scarring on examination makes this diagnosis unlikely.
*Incorrect: Tinea capitis*
- A **fungal infection** of the scalp that typically presents with scaling, erythema, and broken hairs, often accompanied by pruritus.
- Characteristic findings include **"black dot" pattern** (broken hairs at scalp surface), cervical lymphadenopathy, and inflammatory changes.
- The patient's lack of itching and absence of scaling or redness effectively rule out this diagnosis.
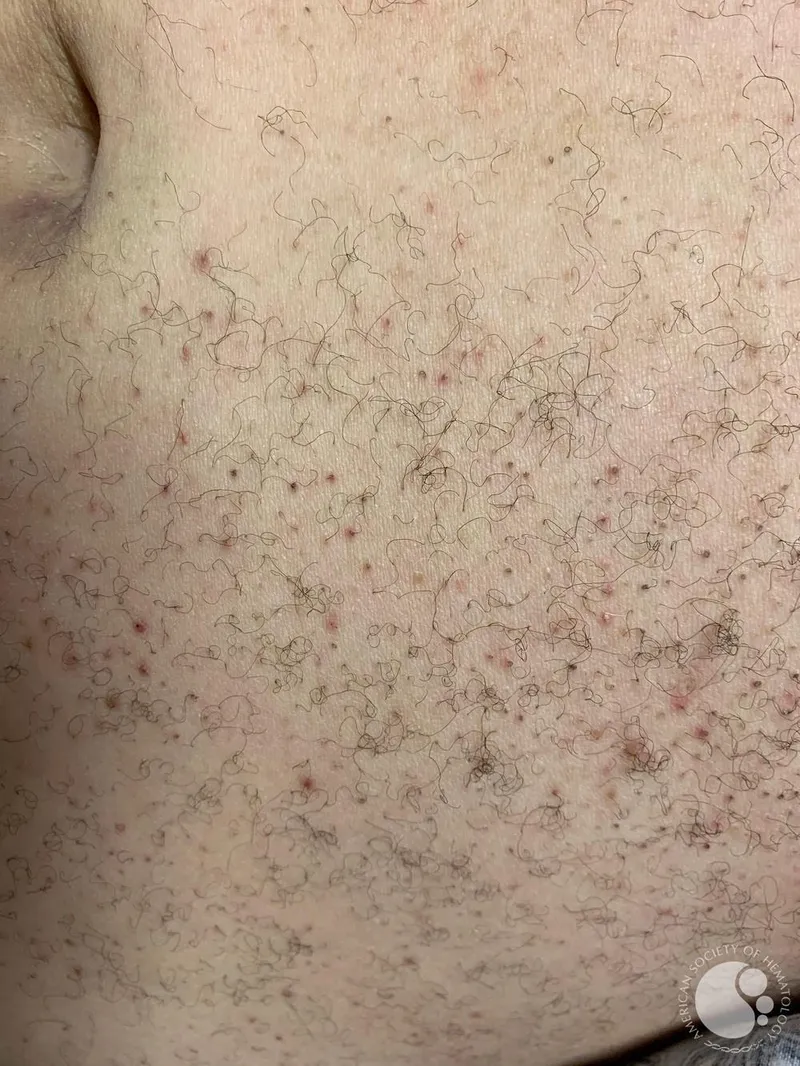
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 4: A 59-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with signs of spontaneous bruising of the lower legs. The patient has a history of alcohol use disorder and has been unemployed for the last 2 years. He reports a 1-year history of fatigue and joint pain. Physical examination of the patient’s legs reveals the findings illustrated in the image. Oral examination shows swollen gums, petechiae of the hard palate, and poor dentition. The most likely underlying cause of this patient's current findings involves which of the following metabolic deficiencies?
- A. Gamma-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues
- B. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
- C. Intestinal absorption of Ca2+ and PO43-
- D. Methylation of homocysteine
- E. Hydroxylation of proline and lysine residues (Correct Answer)
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Hydroxylation of proline and lysine residues***
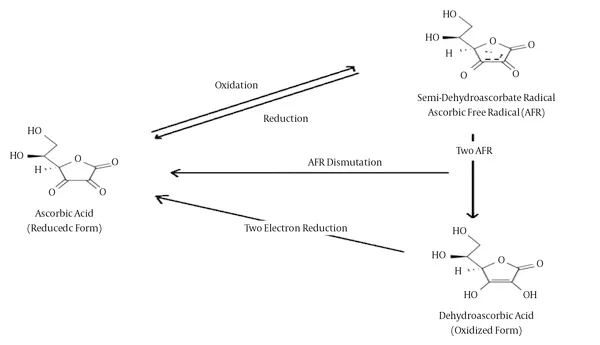
- This patient exhibits classic signs of **scurvy**, caused by **Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) deficiency**.
- Vitamin C is an essential cofactor for **prolyl hydroxylase** and **lysyl hydroxylase**, enzymes that hydroxylate proline and lysine residues during collagen synthesis.
- **Hydroxyproline** and **hydroxylysine** are critical for collagen triple helix stability and cross-linking.
- The clinical findings of **petechiae**, **spontaneous bruising**, **swollen/bleeding gums**, and **perifollicular hemorrhages** result from defective collagen in blood vessels and connective tissues.
- Risk factors include **alcohol use disorder**, **poor nutrition**, and **social isolation**, all present in this patient.
*Gamma-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues*
- This process requires **Vitamin K** as a cofactor for the post-translational modification of clotting factors (II, VII, IX, X, protein C, protein S).
- Vitamin K deficiency presents with **coagulopathy** (elevated PT/INR), **ecchymoses**, and **bleeding**, but NOT the gingival and mucosal findings seen in scurvy.
- The absence of coagulation abnormalities makes this less likely.
*Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA*
- This reaction requires **Thiamine (Vitamin B1)** as a cofactor for pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
- Thiamine deficiency causes **beriberi** (wet: heart failure; dry: peripheral neuropathy) or **Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome** (confusion, ataxia, ophthalmoplegia).
- While common in alcoholics, it does not cause the **hemorrhagic and gingival manifestations** seen here.
*Intestinal absorption of Ca2+ and PO43-*
- This process requires **Vitamin D**, which promotes calcium and phosphate absorption in the gut.
- Vitamin D deficiency causes **rickets** (children) or **osteomalacia** (adults) with bone pain, fractures, and hypocalcemia.
- The patient's findings reflect **vascular and connective tissue fragility**, not bone mineralization defects.
*Methylation of homocysteine*
- This reaction requires **Vitamin B12** (methionine synthase cofactor) and **folate** (methyl donor).
- Deficiency causes **hyperhomocysteinemia**, leading to **megaloblastic anemia**, **neurologic symptoms** (subacute combined degeneration with B12), and increased cardiovascular risk.
- Does not cause the **hemorrhagic and gingival manifestations** characteristic of scurvy.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 5: A 60-year-old male presents with fatigue, dyspnea on exertion, and lower extremity edema. Physical examination reveals an elevated jugular venous pressure and an S3 heart sound. Which of the following medications is most likely to improve this patient's symptoms?
- A. Metoprolol
- B. Furosemide (Correct Answer)
- C. Losartan
- D. Lisinopril
- E. Spironolactone
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Correct: Furosemide***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **heart failure with fluid overload**: dyspnea on exertion, lower extremity edema, elevated jugular venous pressure, and an S3 heart sound (indicating volume overload).
- **Furosemide**, a **loop diuretic**, is the most effective medication for **rapid symptomatic relief** in heart failure with congestion. It works by blocking sodium and water reabsorption in the loop of Henle, promoting diuresis and reducing **pulmonary congestion** and **peripheral edema**.
- While other medications like ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists are crucial for **long-term mortality reduction** and disease modification, loop diuretics provide the **fastest and most direct symptomatic improvement** for fluid overload.
*Incorrect: Metoprolol*
- **Metoprolol** is a **beta-blocker** that is essential for chronic HFrEF management, providing **mortality reduction** and **reverse cardiac remodeling**.
- However, beta-blockers take **weeks to months** to show symptomatic benefit and can initially **worsen symptoms** due to negative inotropic effects, especially in acute decompensation.
- While important for long-term management, metoprolol does not provide immediate symptomatic relief from fluid overload.
*Incorrect: Losartan*
- **Losartan** is an **angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)** used as an alternative to ACE inhibitors in HFrEF, particularly in patients who develop cough with ACE inhibitors.
- ARBs reduce **afterload** and prevent **cardiac remodeling**, contributing to improved long-term outcomes and mortality reduction.
- However, they do not directly address fluid overload and do not provide rapid symptomatic relief compared to diuretics.
*Incorrect: Spironolactone*
- **Spironolactone** is an **aldosterone antagonist** that improves mortality in HFrEF by preventing myocardial fibrosis, reducing cardiac remodeling, and preventing potassium loss.
- While beneficial for long-term management, spironolactone has **weak diuretic effects** and takes weeks to provide symptomatic benefit.
- It is not the first-line choice for **acute symptomatic relief** of volume overload, though it is an important component of chronic HFrEF therapy.
*Incorrect: Lisinopril*
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor** and a cornerstone of HFrEF therapy, reducing **mortality**, **hospitalizations**, and preventing **cardiac remodeling** by reducing afterload and preload.
- While ACE inhibitors improve symptoms over time, they do not provide the **rapid diuretic effect** needed for immediate relief of dyspnea and edema.
- Lisinopril is essential for long-term management but is not the most effective option for acute symptomatic improvement of fluid overload.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 6: A 35-year-old female presents to her primary care physician complaining of right upper quadrant pain over the last 6 months. Pain is worst after eating and feels like intermittent squeezing. She also admits to lighter colored stools and a feeling of itchiness on her skin. Physical exam demonstrates a positive Murphy's sign. The vitamin level least likely to be affected by this condition is associated with which of the following deficiency syndromes?
- A. Rickets and osteomalacia
- B. Hemolytic anemia
- C. Night blindness
- D. Increased prothrombin time and easy bleeding
- E. Scurvy (Correct Answer)
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Scurvy***
- This condition is likely **cholestasis** due to common bile duct obstruction, given the RUQ pain after eating, light-colored stools, itchiness, and **positive Murphy's sign**.
- Cholestasis impairs the absorption of **fat-soluble vitamins** (A, D, E, K), but not **water-soluble vitamins** like vitamin C, which prevents scurvy.
*Rickets and osteomalacia*
- These conditions are caused by **vitamin D deficiency**, which is a **fat-soluble vitamin**.
- Impaired fat absorption in cholestasis would significantly impact vitamin D levels, leading to increased risk of rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
*Hemolytic anemia*
- This can be caused by **vitamin E deficiency**, a **fat-soluble vitamin**.
- Cholestasis impairs vitamin E absorption, which can lead to increased red blood cell fragility and hemolytic anemia.
*Night blindness*
- This is a classic symptom of **vitamin A deficiency**, which is a **fat-soluble vitamin**.
- Impaired fat absorption in cholestasis would reduce vitamin A uptake, contributing to night blindness.
*Increased prothrombin time and easy bleeding*
- These symptoms are indicative of **vitamin K deficiency**, a **fat-soluble vitamin**.
- Vitamin K is essential for the synthesis of clotting factors, and its absorption is severely hindered in cholestasis, leading to coagulopathies.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 7: A homeless woman presents with shortness of breath on exertion and pedal edema. Cardiac workup performed shows evidence of dilated cardiomyopathy and increased cardiac output. She also has decreased sensation over both extremities bilaterally. Which vitamin deficiency most likely caused these symptoms?
- A. Vitamin B6
- B. Vitamin C
- C. Vitamin B1 (Correct Answer)
- D. Vitamin B3
- E. Vitamin A
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Vitamin B1***
- The combination of **dilated cardiomyopathy**, **high-output heart failure** (manifesting as shortness of breath and pedal edema), and **peripheral neuropathy** (decreased sensation) is classic for **wet beriberi**, caused by thiamine (Vitamin B1) deficiency.
- **Homelessness** is a significant risk factor for nutritional deficiencies, including thiamine deficiency, due to inadequate diet.
*Vitamin B6*
- Deficiency can cause **peripheral neuropathy**, but it does not typically lead to **dilated cardiomyopathy** or **high-output heart failure**.
- Other manifestations of B6 deficiency include **sideroblastic anemia** and **seizures**.
*Vitamin C*
- Deficiency causes **scurvy**, characterized by **gingivitis**, **poor wound healing**, **petechiae**, and joint pain.
- It does not present with **cardiomyopathy** or **neuropathy** as described.
*Vitamin B3*
- Deficiency causes **pellagra**, characterized by the "3 Ds": **dermatitis**, **diarrhea**, and **dementia**.
- While it can affect the nervous system (dementia), it does not typically cause **dilated cardiomyopathy** or **peripheral neuropathy**.
*Vitamin A*
- Deficiency primarily affects **vision** (e.g., **night blindness**, **xerophthalmia**) and immune function.
- It is not associated with **cardiac** or **neurological symptoms** like those described in the patient.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 8: A 38-year-old, working, first-time mother brings her 9-month-old male infant to the pediatrician for "wounds that simply won't heal" and bleeding gums. She exclaims, "I have been extra careful with him making sure to not let him get dirty, I boil his baby formula for 15 minutes each morning before I leave for work to give to the caregiver, and he has gotten all of his vaccinations." This infant is deficient in a molecule that is also an essential co-factor for which of the following reactions?
- A. Conversion of homocysteine to methionine
- B. Conversion of alpha ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA
- C. Conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine (Correct Answer)
- D. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
- E. Conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine***
- The infant's symptoms of "wounds that simply won't heal" and **bleeding gums** are classic signs of **scurvy**, caused by a deficiency in **vitamin C (ascorbic acid)**.
- **Vitamin C** is an essential cofactor for **dopamine beta-hydroxylase**, the enzyme responsible for converting **dopamine to norepinephrine**.
*Conversion of homocysteine to methionine*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **methionine synthase**, which requires **vitamin B12** (cobalamin) and **folate (vitamin B9)** as cofactors.
- Deficiency in these vitamins would lead to **megaloblastic anemia** and neurological symptoms, not delayed wound healing and bleeding gums.
*Conversion of alpha ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA*
- This step in the **Krebs cycle** is catalyzed by **alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**, which requires **thiamine (vitamin B1)**, **lipoic acid**, **Mg2+**, **NAD+**, and **FAD** as cofactors.
- Thiamine deficiency can cause **beriberi** or **Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome**, not scurvy symptoms.
*Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA*
- This reaction is catalyzed by the **pyruvate dehydrogenase complex**, which requires **thiamine (vitamin B1)**, **lipoic acid**, **coenzyme A**, **FAD**, and **NAD+** as cofactors.
- A deficiency in any of these, particularly thiamine, leads to impaired carbohydrate metabolism and lactic acidosis.
*Conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **pyruvate carboxylase**, which requires **biotin (vitamin B7)** as a cofactor and is essential for **gluconeogenesis**.
- Biotin deficiency is rare and can present with dermatitis, hair loss, and neurological symptoms, not the classic signs of scurvy.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 9: A 54-year-old man comes to the physician because of generalized fatigue and numbness of his legs and toes for 5 months. He has hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. He underwent a partial gastrectomy for peptic ulcer disease 15 years ago. Current medications include amlodipine and atorvastatin. He is a painter. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 101/min, respirations are 17/min, and blood pressure is 122/82 mm Hg. Examination shows conjunctival pallor and glossitis. Sensation to vibration and position is absent over the lower extremities. He has a broad-based gait. The patient sways when he stands with his feet together and closes his eyes. His hemoglobin concentration is 10.1 g/dL, leukocyte count is 4300/mm3, and platelet count is 110,000/mm3. Which of the following laboratory findings is most likely to be seen in this patient?
- A. Oligoclonal bands in cerebrospinal fluid
- B. Elevated methylmalonic acid levels (Correct Answer)
- C. Positive rapid plasma reagin test
- D. Decreased serum iron levels
- E. Basophilic stippling on peripheral smear
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Elevated methylmalonic acid levels***
- The patient's history of **partial gastrectomy**, followed by **fatigue**, **neurological symptoms** (numbness, gait instability, absent vibration/position sensation, positive Romberg sign), **conjunctival pallor**, **glossitis**, and **pancytopenia** (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) are all classic signs of **vitamin B12 deficiency**.
- **Methylmalonic acid (MMA)** and **homocysteine** are biochemical markers that accumulate when vitamin B12 is deficient, as vitamin B12 acts as a cofactor in their metabolism. Elevated MMA is a more specific indicator of vitamin B12 deficiency than homocysteine.
*Oligoclonal bands in cerebrospinal fluid*
- **Oligoclonal bands** in the CSF are characteristic of **multiple sclerosis** and other inflammatory disorders of the central nervous system, which do not align with this patient's clinical presentation, particularly the history of gastrectomy and pancytopenia.
- While the patient has neurological symptoms, they are more consistent with a metabolic neuropathy secondary to vitamin B12 deficiency rather than demyelinating disease.
*Positive rapid plasma reagin test*
- A **positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test** indicates **syphilis**, which can cause neurological symptoms (neurosyphilis).
- However, the patient's **pancytopenia**, **glossitis**, and history of **gastrectomy** are not typical features of syphilis.
*Decreased serum iron levels*
- **Decreased serum iron levels** would suggest **iron deficiency anemia**. While iron deficiency can cause fatigue and pallor, it typically does not lead to the specific neurological symptoms (demyelinating neuropathy) seen here or pancytopenia.
- The patient's **glossitis** can be seen in both iron and B12 deficiency, but the neurological signs point specifically to B12 deficiency.
*Basophilic stippling on peripheral smear*
- **Basophilic stippling** on a peripheral smear is a classic finding in **lead poisoning** or other conditions causing ribosomal precipitation, such as **thalassemia** or **sideroblastic anemia**.
- While lead poisoning can cause neuropathy and anemia, it would not typically present with the specific history of gastrectomy or the pronounced pancytopenia seen in this patient.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old woman presents her physician with a complaint of feeling tired and low on energy for the past 6 months. She also has noticed she has been having trouble performing daily tasks and at times experiencing near-fainting spells. She has no recollection of similar instances in the past. Her past medical history is insignificant, except for the fact that she has been a strict vegan for the last 5 years. Her vital signs are stable. On physical examination, she is visibly pale and has decreased position and vibratory sensation in her both lower extremities. There is decreased lower limb reflexes with sensation intact. A complete blood count - done last week, - shows hemoglobin of 9.7 g/dL with an MCV of 110 fL. The serum levels of which of the following will most likely aid in the physician’s treatment plan?
- A. Methylmalonic acid (Correct Answer)
- B. Folate
- C. Homocysteine
- D. Succinyl CoA
- E. Ferritin
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Explanation: ***Methylmalonic acid***
- Elevated **methylmalonic acid (MMA)** levels, along with **macrocytic anemia (MCV 110 fL)** and neurological symptoms (decreased position and vibratory sensation, lower limb reflexes), are highly suggestive of **vitamin B12 deficiency**.
- As a strict **vegan**, the patient is at high risk for vitamin B12 deficiency because B12 is primarily found in animal products.
*Folate*
- While folate deficiency can cause **macrocytic anemia**, it typically does **not cause neurological symptoms** like those described.
- Furthermore, the neurological symptoms point more strongly towards vitamin B12 deficiency, which is crucial to differentiate from folate deficiency as folate supplementation alone can mask B12 deficiency and worsen neurological symptoms.
*Homocysteine*
- Elevated **homocysteine** can be seen in both **vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies**, making it less specific for differentiating between the two.
- Therefore, while it might be elevated, measuring MMA is more specific for confirming vitamin B12 deficiency.
*Succinyl CoA*
- **Succinyl CoA** is an intermediate in metabolism and is not directly measured to diagnose vitamin deficiencies.
- While its metabolism is affected by vitamin B12, measuring its precursor, **methylmalonic acid**, is the clinical diagnostic test.
*Ferritin*
- **Ferritin** levels are used to assess **iron stores** and diagnose iron deficiency anemia, which typically presents as **microcytic anemia**, not the **macrocytic anemia** seen in this patient (MCV 110 fL).
- Iron deficiency would not explain the neurological symptoms.
More Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.