Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old man from India visits the clinic with complaints of feeling tired all the time and experiencing lack of energy for the past couple of weeks. He also complains of weakness and numbness of his lower limbs. He has been strictly vegan since the age of 18, including not consuming eggs and milk. He does not take any vitamin or dietary supplements. Physical examination reveals a smooth, red beefy tongue along with lower extremity sensory and motor deficits. What other finding is most likely to accompany this patient’s condition?
- A. Upper limb weakness
- B. Psychiatric symptoms
- C. Decreased visual acuity
- D. Microcytic anemia
- E. Ataxia (Correct Answer)
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: **Ataxia**
- The patient's history of being a strict vegan, fatigue, weakness, numbness, and neurological deficits (sensory and motor) along with a **smooth, red beefy tongue** are classic signs of **vitamin B12 deficiency**.
- **Vitamin B12 deficiency** often leads to **subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord**, which can manifest as **ataxia**, spasticity, and paresthesias due to demyelination.
*Upper limb weakness*
- While B12 deficiency can cause generalized weakness, the question specifically highlights **lower extremity sensory and motor deficits**, with **ataxia** being a more characteristic and often earlier neurological sign of spinal cord involvement than upper limb weakness.
- Upper limb weakness might develop in advanced stages, but it is not the **most likely** accompanying finding in the early or moderate stages often described with lower limb involvement and ataxia.
*Psychiatric symptoms*
- **Psychiatric symptoms** such as depression, irritability, and cognitive impairment can occur in **vitamin B12 deficiency**, but **ataxia** is a more direct and common neurological consequence stemming from the demyelination in the spinal cord.
- While possible, the question asks for the **most likely** additional finding given the specific neurological presentation.
*Decreased visual acuity*
- **Optic neuropathy** and **decreased visual acuity** can occur in some cases of **vitamin B12 deficiency**, but it is less common than the spinal cord and peripheral nerve manifestations like ataxia and paresthesias.
- The presented symptoms directly point to spinal cord involvement, making **ataxia** a more prominent associated neurological finding.
*Microcytic anemia*
- **Vitamin B12 deficiency** typically causes **megaloblastic (macrocytic) anemia**, not microcytic anemia.
- **Microcytic anemia** is primarily associated with **iron deficiency**, lead poisoning, or thalassemia.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 2: A 23-year-old man comes to the physician because of a tremor in his right hand for the past 3 months. The tremor has increased in intensity and he is unable to perform his daily activities. When he wakes up in the morning, his pillow is soaked in saliva. During this period, he has been unable to concentrate in his college classes. He has had several falls over the past month. He has no past history of serious illness. He appears healthy. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a broad-based gait. There is a low frequency tremor that affects the patient's right hand to a greater extent than his left. When the patient holds his arms fully abducted with his elbows flexed, he has a bilateral low frequency arm tremor that increases in amplitude the longer he holds his arms up. Muscle strength is normal in all extremities. Sensation is intact. Deep tendon reflexes are 4+ bilaterally. Dysmetria is present. A photograph of the patient's eye is shown. Mental status examination shows a restricted affect. The rate and rhythm of his speech is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Propranolol
- B. Penicillamine (Correct Answer)
- C. Prednisone
- D. Levodopa
- E. Deferoxamine
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***Penicillamine***
- This patient presents with symptoms suggestive of **Wilson's disease**, including a **tremor**, drooling (sialorrhea), falls, **broad-based gait**, **dysmetria**, and psychiatric changes (restricted affect, inability to concentrate). The mention of an eye photograph likely points to **Kayser-Fleischer rings**.
- **Penicillamine** is a **copper chelator** and is considered a first-line treatment for Wilson's disease, as it promotes the excretion of excess copper from the body.
*Propranolol*
- **Propranolol** is a **beta-blocker** commonly used to treat essential tremor.
- While the patient has a tremor, his constellation of symptoms (neurological, psychiatric, and liver involvement implied by copper accumulation) is more consistent with Wilson's disease, making beta-blockers insufficient as a primary treatment.
*Prednisone*
- **Prednisone** is a corticosteroid used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of Wilson's disease, which is a genetic disorder of copper metabolism, not an inflammatory or autoimmune condition.
*Levodopa*
- **Levodopa** is a precursor to dopamine and is the primary medication used to treat Parkinson's disease, particularly for its bradykinesia and rigidity.
- While there is a tremor, the overall clinical picture, including the age of onset, psychiatric symptoms, and gait abnormalities like dysmetria, is not typical for Parkinson's disease.
*Deferoxamine*
- **Deferoxamine** is an **iron-chelating agent** used to treat iron overload conditions like hemochromatosis.
- Wilson's disease involves copper overload, not iron overload, so deferoxamine would not be an appropriate treatment.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 3: A 43-year-old woman presents to the physician with the complaint of worsening fatigue over the past several months. She has found that she requires nearly double the amount of coffee consumption each day to stay awake at work and that despite maintaining a balanced, healthy diet, she has experienced significant weight gain. A blood test confirms the presence of anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies. Which of the following additional findings would be most consistent with the underlying pathophysiology of her condition?
- A. Galactorrhea (Correct Answer)
- B. Constipation
- C. Brisk deep tendon reflexes
- D. Diarrhea
- E. Heat intolerance
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***Galactorrhea***
- This patient has **Hashimoto's thyroiditis**, an autoimmune hypothyroidism, given the fatigue, weight gain, and positive **anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies**.
- **Hypothyroidism** can lead to **hyperprolactinemia** due to increased **TRH** (thyrotropin-releasing hormone), which stimulates both TSH and prolactin release from the anterior pituitary.
- Elevated prolactin can manifest as **galactorrhea**, representing a less commonly recognized endocrine consequence of primary hypothyroidism.
*Constipation*
- **Constipation** is a common symptom of **hypothyroidism** due to decreased gastrointestinal motility.
- While consistent with hypothyroidism, it is a direct consequence of reduced metabolic activity rather than a secondary endocrine effect.
- This is a well-known, expected finding rather than an additional pathophysiologic manifestation.
*Brisk deep tendon reflexes*
- **Hypothyroidism** typically causes **delayed relaxation of deep tendon reflexes** (hung-up reflexes), not brisk reflexes.
- **Brisk reflexes** are characteristic of **hyperthyroidism** due to increased neuromuscular excitability.
*Diarrhea*
- **Diarrhea** is typically associated with **hyperthyroidism** due to increased gastrointestinal motility from elevated metabolic rate.
- **Hypothyroidism** more commonly causes **constipation** due to decreased GI motility.
*Heat intolerance*
- **Heat intolerance** is a classic symptom of **hyperthyroidism** due to an elevated metabolic rate and increased thermogenesis.
- Patients with **hypothyroidism** usually experience **cold intolerance** due to decreased metabolic heat production.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 4: A 17-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with bilateral tremor of the hands. He is a senior in high school and during the year, his grades have plummeted to the point that he is failing. He says his memory is now poor, and he has trouble focusing on tasks. His behavior has changed in the past 6 months in that he has frequent episodes of depression, separated by episodes of bizarre behavior, including excessive alcohol drinking and shoplifting. His parents have started to suspect that he is using street drugs, which he denies. His handwriting has become very sloppy. His parents have noted slight slurring of his speech. Family history is irrelevant. Physical examination reveals upper extremity tremors, mild dystonia of the upper extremities, and mild incoordination involving his hands. The patient’s eye is shown. Which of the following is the best initial management of this patient’s condition?
- A. Watchful waiting
- B. Oral zinc
- C. Penicillamine (Correct Answer)
- D. Oral deferasirox
- E. Liver transplantation
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***Penicillamine***
- This patient presents with classic **Wilson's disease**: tremor, dystonia, cognitive decline, psychiatric symptoms, and **Kayser-Fleischer rings** visible on examination.
- For **symptomatic patients with neurological manifestations**, **chelation therapy** is the first-line initial treatment.
- **Penicillamine** is a copper-chelating agent that promotes urinary excretion of copper and is the **standard initial therapy** for symptomatic Wilson's disease.
- Alternative chelators like **trientine** may be used if penicillamine is not tolerated, but penicillamine remains a primary option for initial management.
- While penicillamine can have side effects, it is necessary for this patient who requires urgent copper removal due to significant neurological symptoms.
*Oral zinc*
- Zinc works by blocking intestinal copper absorption and is effective in Wilson's disease management.
- However, zinc is **too slow-acting** for symptomatic patients and is primarily used for:
- **Maintenance therapy** after initial chelation
- **Asymptomatic or presymptomatic patients**
- Patients who cannot tolerate chelators
- This patient has significant neurological symptoms requiring more aggressive initial therapy with chelation.
*Watchful waiting*
- Wilson's disease is **progressive and fatal if untreated**.
- This patient has significant neurological, cognitive, and psychiatric symptoms indicating active disease.
- Delaying treatment would lead to irreversible neurological damage and further deterioration.
*Oral deferasirox*
- Deferasirox is an **iron-chelating agent** used for iron overload conditions (hemochromatosis, transfusional hemosiderosis).
- It has **no role in copper overload** and is not used in Wilson's disease management.
*Liver transplantation*
- Liver transplantation is reserved for:
- **Fulminant hepatic failure** with Wilson's disease
- **Decompensated cirrhosis** unresponsive to medical therapy
- It is a major surgical procedure, not appropriate for **initial management** of a patient with predominantly neurological symptoms who can be treated medically.
- This patient shows no evidence of acute liver failure or end-stage liver disease.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 5: What is the primary mechanism for iron absorption in the duodenum?
- A. Simple diffusion
- B. Passive paracellular transport
- C. Endocytosis
- D. DMT1 transporter (Correct Answer)
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***DMT1 transporter***
- The **divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1)** is the primary mechanism for absorbing **non-heme iron (ferrous iron, Fe2+)** into duodenal enterocytes.
- This active transport process is pH-dependent and drives iron uptake against a concentration gradient.
*Simple diffusion*
- Applies to the movement of substances down their concentration gradient without the aid of membrane proteins, which is not the main mechanism for iron due to its ionic nature.
- While some highly lipid-soluble substances can cross membranes this way, metal ions like iron require specific transporters.
*Passive paracellular transport*
- Involves substances moving *between* cells, rather than *through* them, often occurring in leaky epithelia.
- While some fluid and electrolytes may use this route, it is not the primary or regulated pathway for iron absorption.
*Endocytosis*
- A process where cells engulf substances by forming vesicles from the plasma membrane.
- While some macromolecules are absorbed via endocytosis, it is not the major mechanism for absorbing dietary iron in the duodenum.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 6: A patient with Graves' disease is treated with thiocyanate (a historical antithyroid agent). Thiocyanate helps reduce thyroid hormone production by:
- A. Inhibiting thyroid peroxidase
- B. Inhibiting 5'-deiodinase
- C. Inhibiting iodide follicular uptake (Correct Answer)
- D. Inhibiting beta-adrenergic receptors
- E. Inhibiting thyroid deiodinase
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***Inhibiting iodide follicular uptake***
- Thiocyanate is a competitive inhibitor of the **sodium-iodide symporter (NIS)** on thyroid follicular cells, blocking the uptake of iodide into the thyroid gland.
- By preventing iodide entry, thiocyanate reduces the raw material needed for thyroid hormone synthesis, thereby mitigating the **hyperthyroidism** seen in Graves' disease.
*Inhibiting thyroid peroxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **thionamide drugs** (e.g., methimazole, propylthiouracil), which block the oxidation of iodide and its organification.
- While effective in Graves' disease, thiocyanate does not directly inhibit thyroid peroxidase activity.
*Inhibiting 5'-deiodinase*
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)**, but not thiocyanate, inhibits the peripheral conversion of T4 to the more active T3 by blocking 5'-deiodinase enzymes.
- This action helps to reduce the overall effect of thyroid hormones in the body.
*Inhibiting beta-adrenergic receptors*
- **Beta-blockers** (e.g., propranolol) are used to manage the symptomatic effects of hyperthyroidism, such as palpitations, tremor, and anxiety.
- They do not affect thyroid hormone synthesis or release, but rather block the peripheral actions of thyroid hormones on adrenergic receptors.
*Inhibiting thyroid deiodinase*
- This option refers to the enzymes responsible for removing iodine from thyroid hormones, which is part of the normal catabolism of these hormones or for converting T4 to T3.
- Thiocyanate does not primarily act by inhibiting these deiodinase enzymes within the thyroid gland or peripherally; its main action is on iodide uptake.
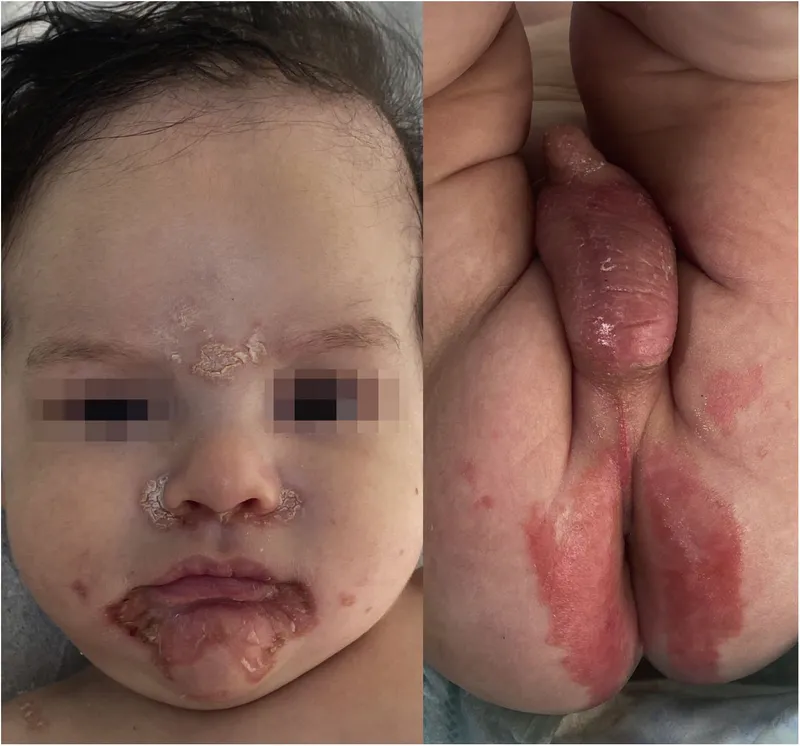
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 7: A 37-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because he was found down on a city sidewalk. Upon presentation he is found to be disheveled with multiple poorly healed wounds on his hands and feet. He has had dozens of previous presentations for alcohol intoxication and is currently known to be homeless. Physical examination reveals multiple minor wounds, alopecia, and decreased axillary hair. Upon being aroused, the patient reveals that he has had difficulty with taste and smell and has also had severe diarrhea over the last week. The deficient substance most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms is associated with which of the following proteins?
- A. Tyrosinase
- B. Hemoglobin
- C. Glutathione peroxidase
- D. RNA polymerase (Correct Answer)
- E. Thyroid hormone
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***Correct: RNA polymerase***
* The clinical presentation of **poorly healed wounds, alopecia, decreased axillary hair, dysgeusia/anosmia, and diarrhea** in a homeless patient with chronic alcoholism is classic for **zinc deficiency**.
* **Zinc is an essential cofactor for RNA polymerase**, the enzyme responsible for DNA transcription and ultimately protein synthesis. Zinc deficiency impairs cellular proliferation and protein synthesis, which explains the poor wound healing, hair loss, and other manifestations.
* Zinc is also a cofactor for over 300 enzymes including alkaline phosphatase, carbonic anhydrase, superoxide dismutase, and various matrix metalloproteinases critical for wound healing and tissue maintenance.
*Incorrect: Glutathione peroxidase*
* **Glutathione peroxidase requires SELENIUM, not zinc**, as its essential cofactor. This enzyme protects against oxidative damage by reducing hydrogen peroxide.
* Selenium deficiency presents with **cardiomyopathy (Keshan disease), myopathy, and thyroid dysfunction**, not the constellation of symptoms seen in this patient.
*Incorrect: Tyrosinase*
* **Tyrosinase is a copper-dependent enzyme** involved in melanin synthesis. Copper deficiency causes **anemia, neutropenia, and neurological symptoms** (myelopathy), not the dermatologic and sensory changes seen here.
* While copper deficiency can occur in alcoholism, the specific symptoms of taste/smell disturbances and characteristic skin findings point to zinc deficiency.
*Incorrect: Thyroid hormone*
* Thyroid hormone synthesis requires **iodine**, not zinc. Hypothyroidism presents with **fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and bradycardia**.
* The patient's acute presentation with diarrhea, taste/smell disturbances, and poor wound healing does not fit thyroid dysfunction.
*Incorrect: Hemoglobin*
* Hemoglobin requires **iron** for oxygen transport. Iron deficiency causes **microcytic anemia with fatigue, pallor, and koilonychia**.
* While chronic alcoholics may develop anemia (often macrocytic from folate/B12 deficiency), the specific symptoms of dysgeusia, anosmia, and characteristic dermatologic findings indicate zinc deficiency as the primary issue.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 8: A previously healthy 44-year-old man comes to his physician because of frequent urination and increased thirst for several weeks. Physical examination shows darkened skin and a firm mass in the right upper quadrant. His blood glucose is 220 mg/dL. A photomicrograph of a specimen obtained on liver biopsy is shown. Which of the following best describes the pathogenesis of the disease process in this patient?
- A. Defective serum copper transportation
- B. Defective transferrin receptor binding (Correct Answer)
- C. Absence of a serine protease inhibitor
- D. Upregulation of erythropoietin production
- E. Absence of β-globin synthesis
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***Defective transferrin receptor binding***
- This patient presents with symptoms of **diabetes mellitus** (frequent urination, increased thirst, elevated blood glucose), **bronze diabetes** (darkened skin), and signs of **liver disease** (firm mass in RUQ, biopsy showing iron deposition). This constellation of symptoms is characteristic of **hereditary hemochromatosis**.
- Hereditary hemochromatosis is an **autosomal recessive disorder** most commonly caused by mutations in the **HFE gene** (especially **C282Y mutation**). The HFE protein normally binds to **transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1)** on cell surfaces to sense iron levels. When HFE is mutated, this **interaction is defective**, impairing the cell's ability to sense iron status.
- This defective HFE-TfR1 binding leads to **inappropriately low hepcidin production** by the liver. With insufficient hepcidin, **ferroportin** (iron exporter) remains active on intestinal enterocytes, resulting in **excessive intestinal iron absorption** and **iron deposition** in multiple organs (liver, pancreas, heart, skin).
- The liver biopsy shows **iron accumulation within hepatocytes**, confirming the diagnosis.
*Defective serum copper transportation*
- This describes **Wilson's disease**, caused by mutations in the **ATP7B gene**, leading to **copper accumulation** in the liver, brain, cornea, and other tissues.
- Clinical features include **neurological symptoms** (tremor, dystonia), **Kayser-Fleischer rings** in the cornea, and **liver cirrhosis**. The presentation differs from iron overload with bronze diabetes.
*Absence of a serine protease inhibitor*
- This refers to **alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency**, where absence of this serine protease inhibitor leads to **uninhibited neutrophil elastase activity**, primarily causing **early-onset emphysema** and **liver cirrhosis**.
- Liver biopsy would show **PAS-positive, diastase-resistant globules** in hepatocytes, not iron deposition. The clinical presentation would not include bronze skin or secondary diabetes from pancreatic iron overload.
*Upregulation of erythropoietin production*
- **Upregulation of erythropoietin** occurs in response to **hypoxia** and stimulates **increased red blood cell production**, as seen in **polycythemia vera** or high-altitude adaptation.
- This mechanism does not cause the iron overload and multi-organ damage seen in hemochromatosis. While erythropoiesis requires iron, hemochromatosis results from primary defects in iron absorption regulation, not erythropoietin dysregulation.
*Absence of β-globin synthesis*
- This is characteristic of **beta-thalassemia**, where **reduced or absent beta-globin chain synthesis** leads to **ineffective erythropoiesis** and **hemolytic anemia**.
- While beta-thalassemia major can cause **secondary iron overload** (from chronic transfusions and increased GI absorption due to ineffective erythropoiesis), the **primary defect is in hemoglobin synthesis**, not in the iron regulatory pathway as seen in hereditary hemochromatosis.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 9: A homeless woman presents with shortness of breath on exertion and pedal edema. Cardiac workup performed shows evidence of dilated cardiomyopathy and increased cardiac output. She also has decreased sensation over both extremities bilaterally. Which vitamin deficiency most likely caused these symptoms?
- A. Vitamin B6
- B. Vitamin C
- C. Vitamin B1 (Correct Answer)
- D. Vitamin B3
- E. Vitamin A
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***Vitamin B1***
- The combination of **dilated cardiomyopathy**, **high-output heart failure** (manifesting as shortness of breath and pedal edema), and **peripheral neuropathy** (decreased sensation) is classic for **wet beriberi**, caused by thiamine (Vitamin B1) deficiency.
- **Homelessness** is a significant risk factor for nutritional deficiencies, including thiamine deficiency, due to inadequate diet.
*Vitamin B6*
- Deficiency can cause **peripheral neuropathy**, but it does not typically lead to **dilated cardiomyopathy** or **high-output heart failure**.
- Other manifestations of B6 deficiency include **sideroblastic anemia** and **seizures**.
*Vitamin C*
- Deficiency causes **scurvy**, characterized by **gingivitis**, **poor wound healing**, **petechiae**, and joint pain.
- It does not present with **cardiomyopathy** or **neuropathy** as described.
*Vitamin B3*
- Deficiency causes **pellagra**, characterized by the "3 Ds": **dermatitis**, **diarrhea**, and **dementia**.
- While it can affect the nervous system (dementia), it does not typically cause **dilated cardiomyopathy** or **peripheral neuropathy**.
*Vitamin A*
- Deficiency primarily affects **vision** (e.g., **night blindness**, **xerophthalmia**) and immune function.
- It is not associated with **cardiac** or **neurological symptoms** like those described in the patient.
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG Question 10: A 6-month-old boy presents with decreased growth, pigmented retinopathy, hemolytic anemia, and peripheral neuropathy. You suspect that these signs are the result of a vitamin deficiency leading to increased oxidative damage to lipids. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Excessive boiling of formula
- B. Goat milk ingestion
- C. Abetalipoproteinemia (Correct Answer)
- D. Pernicious anemia
- E. Hartnup disease
Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) Explanation: ***Abetalipoproteinemia***
- This condition is characterized by a defect in **microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP)**, leading to an inability to synthesize ApoB-containing lipoproteins.
- The resulting **malabsorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins (especially vitamin E)** leads to the neurological symptoms (retinopathy, neuropathy) and hemolytic anemia due to increased oxidative stress on red blood cell membranes.
*Excessive boiling of formula*
- Excessive boiling of formula could potentially degrade some **heat-sensitive vitamins**, such as vitamin C or thiamine (B1).
- However, this is unlikely to cause a severe, combined deficiency leading to the specific constellation of symptoms seen, particularly the ophthalmologic and neurological signs related to **fat-soluble vitamin malabsorption**.
*Goat milk ingestion*
- Goat milk is naturally low in **folate** and **vitamin D** and can cause **folate deficiency anemia** and rickets if it's the sole source of nutrition for an infant.
- However, it does not typically cause the entire spectrum of symptoms described, particularly **pigmented retinopathy** and **peripheral neuropathy**, which are more indicative of **vitamin E deficiency**.
*Pernicious anemia*
- Pernicious anemia is caused by a deficiency in **intrinsic factor**, leading to **vitamin B12 malabsorption**.
- Symptoms primarily include **megaloblastic anemia**, **glossitis**, and **neurological deficits** (subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord), but not pigmented retinopathy or hemolytic anemia due to increased fatty acid oxidation via vitamin E malabsorption.
*Hartnup disease*
- Hartnup disease is an inherited disorder of **amino acid transport**, specifically affecting the absorption of **neutral amino acids** like tryptophan.
- It leads to **niacin deficiency** (pellagra-like symptoms) and can cause skin rashes, ataxia, and psychiatric symptoms, but not hemolytic anemia or pigmented retinopathy.
More Trace minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Se, I) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.