Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Energy requirements of urea cycle. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
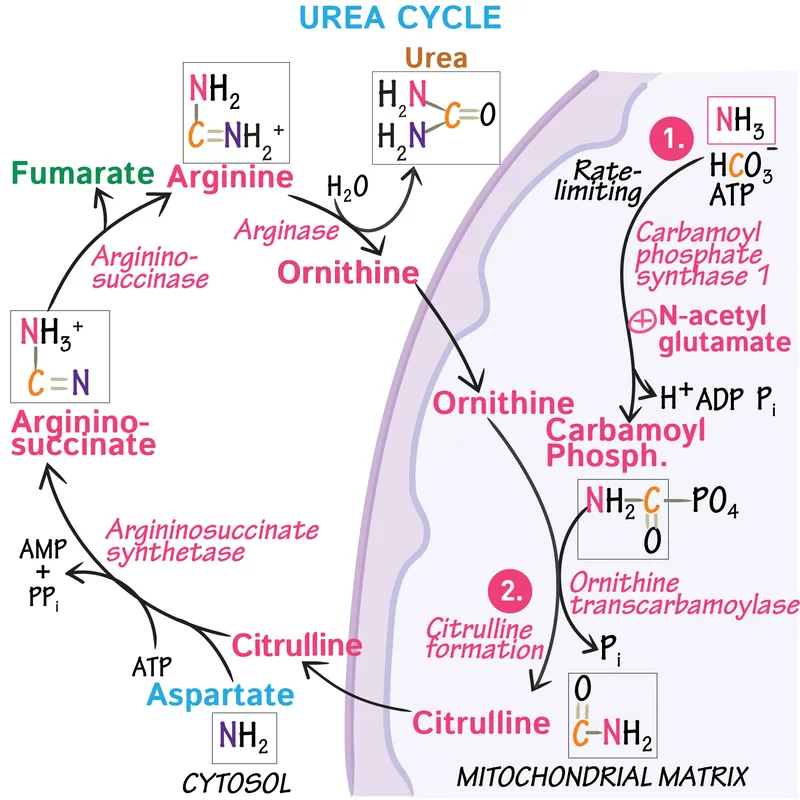
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 1: A 4-day-old male newborn delivered at 39 weeks' gestation is evaluated because of poor feeding, recurrent vomiting, and lethargy. Physical examination shows tachypnea with subcostal retractions. An enzyme assay performed on a liver biopsy specimen shows decreased activity of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I. This enzyme plays an important role in the breakdown and excretion of amino groups that result from protein digestion. Which of the following is an immediate substrate for the synthesis of the molecule needed for the excretion of amino groups?
- A. N-acetylglutamate
- B. Homocysteine
- C. Phenylalanine
- D. Valine
- E. Aspartate (Correct Answer)
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Aspartate***
- The question describes a case of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)** deficiency, which leads to **hyperammonemia** due to impaired urea cycle function.
- The urea cycle is responsible for excreting **amino groups** as urea; one of the key molecules directly incorporated into the urea molecule is **aspartate**, which donates an amino group to form **argininosuccinate**.
*N-acetylglutamate*
- **N-acetylglutamate** is an essential activator of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)**, the enzyme deficient in this patient.
- While crucial for the urea cycle's regulation, it is an **allosteric activator** rather than a direct substrate for the synthesis of molecules needed for amino group excretion.
*Homocysteine*
- **Homocysteine** is an intermediate in **methionine metabolism** and is primarily associated with cardiovascular disease and neurological issues when elevated.
- It plays no direct role as a substrate in the urea cycle for the excretion of amino groups.
*Phenylalanine*
- **Phenylalanine** is an **essential amino acid** that is a precursor to tyrosine and neurotransmitters.
- Its metabolism is separate from the urea cycle, and it is not a direct substrate for ammonia excretion in this pathway.
*Valine*
- **Valine** is a **branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)** primarily catabolized in muscles and used for energy.
- It is not a direct substrate in the urea cycle, which processes nitrogen from various amino acids into urea for excretion.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator is studying the activity level of several different enzymes in human subjects from various demographic groups. An elevated level of activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase is found in one of the study subjects. This patient is most likely to have which of the following conditions?
- A. Phenylketonuria
- B. Homocystinuria
- C. Gout (Correct Answer)
- D. Alkaptonuria
- E. Maple syrup urine disease
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Gout***
- **Elevated phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) synthetase activity** leads to increased production of PRPP, a precursor for **purine biosynthesis**.
- Increased purine synthesis results in overproduction of **uric acid**, which can precipitate as monosodium urate crystals in joints, causing **gout**.
*Phenylketonuria*
- Caused by a deficiency in **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, leading to an accumulation of **phenylalanine**.
- Not directly related to increased PRPP synthetase activity or purine metabolism.
*Homocystinuria*
- Primarily due to a deficiency in **cystathionine beta-synthase**, leading to elevated levels of **homocysteine**.
- This condition involves methionine metabolism, not purine metabolism or PRPP synthetase.
*Alkaptonuria*
- Results from a deficiency in **homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase**, causing the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- It is an inborn error of tyrosine metabolism and is unrelated to PRPP synthetase activity.
*Maple syrup urine disease*
- Caused by a deficiency in the **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex**, leading to accumulation of **leucine, isoleucine, and valine**.
- This condition affects branched-chain amino acid metabolism, not purine metabolism.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 3: A 26-year-old African American man comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fatigue, back pain, and dark urine. One week ago, he developed a headache and was treated with aspirin. He does not smoke or use illicit drugs. Physical examination shows conjunctival pallor. A peripheral blood smear shows erythrocytes with inclusions of denatured hemoglobin. Which of the following enzymes is involved in providing precursors for nucleotide synthesis in this patient?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
- C. Pyruvate carboxylase
- D. Transaldolase (Correct Answer)
- E. Enolase
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Transaldolase***
- This patient likely has **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**, indicated by fatigue, dark urine (hemolysis), and **Heinz bodies** (erythrocytes with inclusions of denatured hemoglobin) after aspirin exposure, which is an **oxidative stressor**.
- **Transaldolase** is an enzyme in the **non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)**, which produces **ribose-5-phosphate**, a precursor for nucleotide synthesis.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- **Glucose-6-phosphatase** is involved in **gluconeogenesis** and glycogenolysis, primarily in the liver and kidneys, to release free glucose into the bloodstream.
- Deficiency leads to **Von Gierke disease**, characterized by hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, lactic acidosis, and hyperlipidemia, which are not described here.
*Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I*
- **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)** is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in the **urea cycle**, converting ammonia and bicarbonate into carbamoyl phosphate.
- Its deficiency causes **hyperammonemia**, not hemolytic anemia or issues with nucleotide synthesis.
*Pyruvate carboxylase*
- **Pyruvate carboxylase** is a mitochondrial enzyme that converts **pyruvate to oxaloacetate**, a crucial step in **gluconeogenesis** and replenishing intermediates of the citric acid cycle.
- Deficiency can lead to lactic acidosis and hypoglycemia, which are not the primary symptoms here.
*Enolase*
- **Enolase** is an enzyme in **glycolysis** that catalyzes the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
- It is not directly involved in providing precursors for nucleotide synthesis.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 4: After being warned by the locals not to consume the freshwater, a group of American backpackers set off on a week-long hike into a region of the Ecuadorean Amazon forest known for large gold mines. The group of hikers stopped near a small stream and used the water they filtered from the stream to make dinner. Within the next half hour, the hikers began to experience headaches, vertigo, visual disturbances, confusion, tachycardia, and altered levels of consciousness. Which of the following enzymes was most likely inhibited in this group of hikers?
- A. NADH dehydrogenase
- B. ATP synthase
- C. Cytochrome c oxidase (Correct Answer)
- D. Cytochrome bc1 complex
- E. Succinate dehydrogenase
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Cytochrome c oxidase***
- The symptoms described (headaches, vertigo, visual disturbances, confusion, tachycardia, altered consciousness occurring within 30 minutes) are characteristic of **acute cyanide poisoning**.
- **Cyanide** is commonly found in water near **gold mining operations**, where it is used in the gold extraction process and can contaminate local water sources.
- **Cyanide** is a potent inhibitor of **cytochrome c oxidase** (Complex IV) in the electron transport chain, binding to the heme iron (Fe³⁺) and preventing oxygen utilization, leading to **histotoxic hypoxia**.
- This results in cellular energy failure, particularly affecting high-energy-demand organs like the brain and heart, explaining the acute neurological and cardiovascular symptoms.
*NADH dehydrogenase*
- While NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) is a component of the electron transport chain, it is not the primary target of **cyanide poisoning**.
- Inhibitors of Complex I include rotenone and barbiturates, which cause different clinical presentations and do not produce the rapid onset of symptoms seen with cyanide.
*ATP synthase*
- **ATP synthase** (Complex V) synthesizes ATP using the proton gradient, but it is not directly inhibited by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of ATP synthase, such as oligomycin, prevent ATP synthesis by blocking the enzyme directly, whereas cyanide acts upstream at Complex IV.
*Cytochrome bc1 complex*
- The **cytochrome bc1 complex** (Complex III) is involved in electron transfer and proton pumping, but it is not the primary enzyme inhibited by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of Complex III include antimycin A, which would disrupt the electron transport chain but do not cause the characteristic rapid-onset symptoms of cyanide poisoning.
*Succinate dehydrogenase*
- **Succinate dehydrogenase** (Complex II) participates in both the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain, but it is not targeted by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of Complex II, such as malonate, competitively block succinate oxidation but do not produce the acute systemic toxicity characteristic of cyanide poisoning.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 5: A 4-day-old boy is brought to the physician because of somnolence, poor feeding, and vomiting after his first few breast feedings. He appears lethargic. His respiratory rate is 73/min. Serum ammonia is markedly increased. Genetic analysis shows deficiency in N-acetylglutamate synthase. The activity of which of the following enzymes is most likely directly affected by this genetic defect?
- A. Ornithine translocase
- B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (Correct Answer)
- C. Argininosuccinase
- D. Argininosuccinate synthetase
- E. Arginase
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I***
- **N-acetylglutamate** (NAG) is an essential allosteric activator of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)**, the rate-limiting enzyme of the urea cycle.
- A deficiency in **N-acetylglutamate synthase** directly leads to a lack of NAG, significantly impairing CPS I activity and causing severe hyperammonemia.
*Ornithine translocase*
- This enzyme is responsible for transporting **ornithine** into the mitochondria for the urea cycle.
- While a defect in **ornithine translocase** also causes hyperammonemia, it is due to accumulation of ornithine and upstream substrates, not a defect in N-acetylglutamate synthase.
*Argininosuccinase*
- Also known as **argininosuccinate lyase**, this enzyme cleaves argininosuccinate into arginine and fumarate.
- A deficiency would lead to accumulation of **argininosuccinate**, and while it is a urea cycle disorder, it is not directly affected by N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency.
*Argininosuccinate synthetase*
- This enzyme catalyzes the condensation of **citrulline** and **aspartate** to form argininosuccinate.
- A defect in **argininosuccinate synthetase** causes citrullinemia but is not directly regulated by N-acetylglutamate.
*Arginase*
- **Arginase** is the final enzyme in the urea cycle, hydrolyzing arginine to form urea and ornithine.
- A deficiency would lead to hyperargininemia, which typically presents later in childhood and is not directly affected by N-acetylglutamate.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 6: An investigator is studying biomolecular mechanisms in human cells. A radioactive isotope that is unable to cross into organelles is introduced into a sample of cells. The cells are then fragmented via centrifugation and the isotope-containing components are isolated. Which of the following reactions is most likely to be present in this cell component?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose
- B. Isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate
- C. Carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline
- D. Fatty acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA
- E. Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone (Correct Answer)
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone***
- This reaction is the first step of the **pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)**, which occurs in the **cytosol**.
- Since the isotope cannot cross into organelles and is found in the cytosolic fraction, this pathway is a likely candidate.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose*
- This reaction describes the dephosphorylation of **glucose-6-phosphate** to **glucose**, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- While important for glucose release, this enzyme is primarily located in the **endoplasmic reticulum** of the liver and kidneys, an organelle.
*Isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate*
- This is a step in the **Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)**, which takes place in the **mitochondrial matrix**.
- The isotope would not be found in this compartmentalized reaction because it cannot enter organelles.
*Carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline*
- This reaction is part of the **urea cycle**, which has steps occurring in both the **mitochondrial matrix** and the cytosol. The initial step, forming carbamoyl phosphate, is mitochondrial.
- The isotope, being unable to cross into organelles, would not readily participate in the mitochondrial portion of this pathway.
*Fatty acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA*
- This reaction represents **beta-oxidation of fatty acids**, a process that primarily occurs in the **mitochondria** and peroxisomes.
- As the isotope is excluded from organelles, it would not be involved in these reactions.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 7: A 4-year-old boy presents with vomiting and one day of lethargy after a one week history of flu-like symptoms and low-grade fevers. The vomiting is nonbilious and nonbloody. The patient has had no other symptoms aside from mild rhinorrhea and cough. He has no past medical history, and is on no medications except for over-the-counter medications for his fever. His temperature is 98.5°F (36.9°C), pulse is 96/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 108/80 mmHg. The patient appears lethargic and is oriented only to person. Otherwise, the physical exam is benign and the patient has no other neurologic symptoms. What is the mechanism of the most likely cause of this patient’s presentation?
- A. Deficient erythrocyte enzyme
- B. Chemical ingestion
- C. Bacterial infection
- D. Irreversible enzyme inhibition (Correct Answer)
- E. Reversible enzyme inhibition
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Irreversible enzyme inhibition***
- This presentation is highly suggestive of **Reye syndrome**, which is associated with **aspirin use** in children with viral illnesses. Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) **irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes** by acetylating a serine residue at the active site.
- While aspirin's primary mechanism is COX inhibition, **Reye syndrome** involves **mitochondrial dysfunction** in hepatocytes, leading to impaired fatty acid beta-oxidation, hyperammonemia, hepatic steatosis, and **encephalopathy**. This explains the vomiting, lethargy, and altered mental status after flu-like symptoms.
- The key connection is that aspirin acts through **irreversible enzyme inhibition**, making this the correct mechanistic classification for the causative agent.
*Reversible enzyme inhibition*
- While some aspects of Reye syndrome involve mitochondrial enzyme dysfunction, aspirin itself does **not** act through reversible competitive inhibition—it **irreversibly acetylates** COX enzymes.
- Reversible inhibition would imply the drug effect could be easily overcome by increasing substrate concentration, which is not the case with aspirin's mechanism.
*Deficient erythrocyte enzyme*
- This mechanism is associated with conditions like **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**, which primarily causes **hemolytic anemia** with jaundice and pallor.
- While G6PD deficiency can be triggered by certain medications, it does not typically present with the **encephalopathy** and liver dysfunction seen in this patient.
*Chemical ingestion*
- While aspirin is technically a chemical, the question asks about the **mechanism** rather than the route of exposure. The specific mechanism is irreversible enzyme inhibition.
- The history of **flu-like symptoms** and use of over-the-counter fever medications strongly suggests aspirin-associated Reye syndrome rather than accidental toxic ingestion.
*Bacterial infection*
- A severe bacterial infection (e.g., **bacterial meningitis** or **sepsis**) could cause lethargy and vomiting, but the clinical picture (normal vital signs, benign physical exam, no fever) is not typical for acute bacterial infection.
- The association with a recent **viral illness** and potential over-the-counter medication use strongly favors Reye syndrome, a non-infectious etiology.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 8: A 3-year-old boy is seen in clinic. He was born at home without perinatal care. He was apparently normal at birth, but later developed failure to thrive and developmental delay. He also has a history of cataracts. His older brother had a myocardial infarction at the age of 18 and is rather lanky and tall in appearance. Laboratory testing of his urine showed an increase in the level of an amino acid. What is the most likely mechanism responsible for this boy's pathology?
- A. Hereditary defect of renal amino acid transporter
- B. Inability to degrade branched chain amino acids
- C. Cystathionine synthase deficiency (Correct Answer)
- D. Deficiency of homogentisic acid oxidase
- E. Deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Cystathionine synthase deficiency***
- The constellation of **developmental delay, failure to thrive, cataracts**, and a history of **myocardial infarction** in an older sibling with a **marfanoid habitus** points to **homocystinuria**.
- **Cystathionine synthase deficiency** is the most common cause of homocystinuria, leading to an **accumulation of homocysteine** and methionine, which can be detected in urine.
*Hereditary defect of renal amino acid transporter*
- Conditions like **cystinuria** involve defective renal transport of specific amino acids (cystine, ornithine, lysine, arginine) but typically present with **kidney stones**, not cataracts or thrombotic events.
- This defect would lead to elevated levels of the affected amino acids in the urine but does not explain the systemic features observed.
*Inability to degrade branched chain amino acids*
- This describes **Maple Syrup Urine Disease**, characterized by the inability to metabolize **leucine, isoleucine, and valine**.
- It presents with symptoms like **poor feeding, lethargy, seizures, and a distinctive sweet odor** in urine, which are not detailed here, and generally has a more acute and severe neonatal presentation without a typical marfanoid habitus or thrombotic events.
*Deficiency of homogentisic acid oxidase*
- This deficiency causes **alkaptonuria**, an inborn error of tyrosine metabolism.
- It is characterized by **dark urine** upon standing, **ochronosis** (darkening of connective tissues), and **arthropathy**, none of which are consistent with the patient's symptoms.
*Decreased in phenylalanine hydroxylase*
- This is the enzyme deficient in **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, which leads to the accumulation of **phenylalanine**.
- PKU typically presents with **intellectual disability, seizures, fair skin, and a musty odor** if untreated, but generally does not involve cataracts or thrombotic events.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 9: A newborn boy develops projectile vomiting 48 hours after delivery. He is found to be lethargic, with poor muscle tone, and is hyperventilating. Within hours, he suffers important neurological deterioration, leading to seizures, coma, and, ultimately, death. An autopsy is performed and the pathology team makes a diagnosis of a rare genetic disorder that leads to low levels of N-acetylglutamate. Which of the following enzymes would be secondarily affected by this process?
- A. Argininosuccinate lyase
- B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (Correct Answer)
- C. Argininosuccinate synthetase
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase
- E. Arginase
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I***
- **N-acetylglutamate** is an **obligate activator** for **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)**, the rate-limiting enzyme of the **urea cycle**. Low levels of N-acetylglutamate directly impair CPS I activity.
- Reduced CPS I activity leads to a severe **urea cycle disorder**, causing **hyperammonemia**, which manifests with lethargy, poor muscle tone, hyperventilation, neurological deterioration, seizures, coma, and death in newborns.
*Argininosuccinate lyase*
- This enzyme is involved downstream in the **urea cycle**, catalyzing the cleavage of **argininosuccinate** into **arginine** and **fumarate**.
- Its activity is not directly regulated by **N-acetylglutamate**, so it would not be secondarily affected in the same manner as CPS I.
*Argininosuccinate synthetase*
- This enzyme acts after CPS I and ornithine transcarbamylase in the **urea cycle**, synthesizing **argininosuccinate** from **citrulline** and **aspartate**.
- Its function is independent of **N-acetylglutamate** levels, making it unlikely to be secondarily affected.
*Ornithine transcarbamylase*
- This enzyme catalyzes the second step of the **urea cycle**, forming **citrulline** from **ornithine** and **carbamoyl phosphate**.
- While essential for the urea cycle, its activity is not directly modulated by **N-acetylglutamate**; rather, it depends on the availability of carbamoyl phosphate produced by CPS I.
*Arginase*
- This is the final enzyme in the **urea cycle**, converting **arginine** to **ornithine** and **urea**.
- Its activity is not directly or indirectly regulated by **N-acetylglutamate**, nor is it the enzyme primarily affected in this presentation.
Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG Question 10: A 3-week old boy is brought to the physician for the evaluation of lethargy, recurrent vomiting, and poor weight gain since birth. Physical examination shows decreased skin turgor and a bulging frontal fontanelle. Serum studies show an ammonia concentration of 170 μmol/L (N < 30) and low serum citrulline levels. The oral intake of which of the following nutrients should be restricted in this patient?
- A. Gluten
- B. Lactose
- C. Fructose
- D. Protein (Correct Answer)
- E. Vitamin A
Energy requirements of urea cycle Explanation: ***Protein***
- Elevated **ammonia** and low **citrulline** levels indicate a **urea cycle disorder**, which impairs the body's ability to excrete nitrogenous waste from protein metabolism.
- Restricting **protein intake** limits the production of ammonia, thereby reducing the toxic burden on the system and preventing further neurological damage.
*Gluten*
- **Gluten restriction** is primarily indicated for **celiac disease**, which presents with gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea, malabsorption, and poor weight gain, but not directly with hyperammonemia or urea cycle dysfunction.
- While malabsorption can cause poor weight gain, the specific metabolic derangements here point away from celiac disease.
*Lactose*
- **Lactose intolerance** or **galactosemia** would necessitate **lactose restriction**. Symptoms usually include vomiting, diarrhea, and failure to thrive, but they do not typically present with the extreme hyperammonemia seen here.
- Galactosemia specifically would show elevated galactose and galactose-1-phosphate, not ammonia.
*Fructose*
- **Hereditary fructose intolerance** requires **fructose restriction**. It generally presents with vomiting, hypoglycemia, and liver dysfunction (jaundice, hepatomegaly) upon exposure to fructose, not primarily with hyperammonemia.
- The metabolic pathway for fructose metabolism does not directly generate ammonia in the quantities seen with urea cycle disorders.
*Vitamin A*
- **Vitamin A restriction** is not a primary treatment for any known inborn error of metabolism or hyperammonemia.
- While deficiencies or toxicities of vitamins can occur, they do not present with the specific metabolic profile described (high ammonia, low citrulline).
More Energy requirements of urea cycle US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.