Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
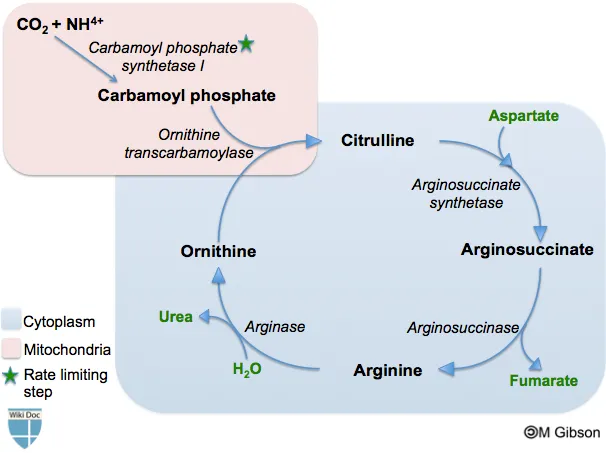
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 1: A 4-day-old male newborn delivered at 39 weeks' gestation is evaluated because of poor feeding, recurrent vomiting, and lethargy. Physical examination shows tachypnea with subcostal retractions. An enzyme assay performed on a liver biopsy specimen shows decreased activity of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I. This enzyme plays an important role in the breakdown and excretion of amino groups that result from protein digestion. Which of the following is an immediate substrate for the synthesis of the molecule needed for the excretion of amino groups?
- A. N-acetylglutamate
- B. Homocysteine
- C. Phenylalanine
- D. Valine
- E. Aspartate (Correct Answer)
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***Aspartate***
- The question describes a case of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)** deficiency, which leads to **hyperammonemia** due to impaired urea cycle function.
- The urea cycle is responsible for excreting **amino groups** as urea; one of the key molecules directly incorporated into the urea molecule is **aspartate**, which donates an amino group to form **argininosuccinate**.
*N-acetylglutamate*
- **N-acetylglutamate** is an essential activator of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)**, the enzyme deficient in this patient.
- While crucial for the urea cycle's regulation, it is an **allosteric activator** rather than a direct substrate for the synthesis of molecules needed for amino group excretion.
*Homocysteine*
- **Homocysteine** is an intermediate in **methionine metabolism** and is primarily associated with cardiovascular disease and neurological issues when elevated.
- It plays no direct role as a substrate in the urea cycle for the excretion of amino groups.
*Phenylalanine*
- **Phenylalanine** is an **essential amino acid** that is a precursor to tyrosine and neurotransmitters.
- Its metabolism is separate from the urea cycle, and it is not a direct substrate for ammonia excretion in this pathway.
*Valine*
- **Valine** is a **branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)** primarily catabolized in muscles and used for energy.
- It is not a direct substrate in the urea cycle, which processes nitrogen from various amino acids into urea for excretion.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 2: A 2-week-old boy presents to the emergency department because of unusual irritability and lethargy. The patient is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and minutes later develops metabolic encephalopathy. This progressed to a coma, followed by death before any laboratory tests are completed. The infant was born at home via vaginal delivery at 39 weeks' of gestation. His mother says that the symptoms started since the infant was 4-days-old, but since he only seemed ‘tired’, she decided not to seek medical attention. Further testing during autopsy shows hyperammonemia, low citrulline, and increased orotic acid. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase
- B. Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
- C. Homogentisic acid dioxygenase
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase (Correct Answer)
- E. Cystathionine beta-synthase
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: **Ornithine transcarbamylase**
- **Hyperammonemia**, **low citrulline**, and **increased orotic acid** are classic findings in **Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency**. OTC is an X-linked urea cycle disorder.
- The rapid progression to **metabolic encephalopathy** and death in a neonate with these laboratory findings is highly characteristic of severe OTC deficiency, often presenting in the first few days of life.
*Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Maple Syrup Urine Disease**, characterized by elevated **branched-chain amino acids** and their corresponding ketoacids in blood and urine.
- While it can cause neurological symptoms, it does not typically present with the specific constellation of **hyperammonemia**, low citrulline, and high orotic acid.
*Propionyl-CoA carboxylase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme leads to **Propionic acidemia**, a type of organic acidemia, characterized by **propionic acid accumulation** and often **metabolic acidosis**, ketosis, and hyperammonemia.
- However, it would not typically cause **low citrulline** or isolated **elevated orotic acid** as seen in urea cycle disorders.
*Homogentisic acid dioxygenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Alkaptonuria**, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- This condition is usually benign in infancy, with symptoms appearing later in life such as **dark urine** on standing and **ochronosis** (darkening of cartilage). It does not present with acute hyperammonemia or metabolic encephalopathy.
*Cystathionine beta-synthase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **homocystinuria**, an inborn error of methionine metabolism, leading to elevated **homocysteine** and methionine.
- Clinical features include **ectopia lentis**, skeletal abnormalities, and intellectual disability, but not usually acute neonatal hyperammonemia or the specific findings of low citrulline and high orotic acid.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is studying biomolecular mechanisms in human cells. A radioactive isotope that is unable to cross into organelles is introduced into a sample of cells. The cells are then fragmented via centrifugation and the isotope-containing components are isolated. Which of the following reactions is most likely to be present in this cell component?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose
- B. Isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate
- C. Carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline
- D. Fatty acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA
- E. Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone (Correct Answer)
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone***
- This reaction is the first step of the **pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)**, which occurs in the **cytosol**.
- Since the isotope cannot cross into organelles and is found in the cytosolic fraction, this pathway is a likely candidate.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose*
- This reaction describes the dephosphorylation of **glucose-6-phosphate** to **glucose**, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- While important for glucose release, this enzyme is primarily located in the **endoplasmic reticulum** of the liver and kidneys, an organelle.
*Isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate*
- This is a step in the **Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)**, which takes place in the **mitochondrial matrix**.
- The isotope would not be found in this compartmentalized reaction because it cannot enter organelles.
*Carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline*
- This reaction is part of the **urea cycle**, which has steps occurring in both the **mitochondrial matrix** and the cytosol. The initial step, forming carbamoyl phosphate, is mitochondrial.
- The isotope, being unable to cross into organelles, would not readily participate in the mitochondrial portion of this pathway.
*Fatty acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA*
- This reaction represents **beta-oxidation of fatty acids**, a process that primarily occurs in the **mitochondria** and peroxisomes.
- As the isotope is excluded from organelles, it would not be involved in these reactions.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 4: A newborn boy develops projectile vomiting 48 hours after delivery. He is found to be lethargic, with poor muscle tone, and is hyperventilating. Within hours, he suffers important neurological deterioration, leading to seizures, coma, and, ultimately, death. An autopsy is performed and the pathology team makes a diagnosis of a rare genetic disorder that leads to low levels of N-acetylglutamate. Which of the following enzymes would be secondarily affected by this process?
- A. Argininosuccinate lyase
- B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (Correct Answer)
- C. Argininosuccinate synthetase
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase
- E. Arginase
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I***
- **N-acetylglutamate** is an **obligate activator** for **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)**, the rate-limiting enzyme of the **urea cycle**. Low levels of N-acetylglutamate directly impair CPS I activity.
- Reduced CPS I activity leads to a severe **urea cycle disorder**, causing **hyperammonemia**, which manifests with lethargy, poor muscle tone, hyperventilation, neurological deterioration, seizures, coma, and death in newborns.
*Argininosuccinate lyase*
- This enzyme is involved downstream in the **urea cycle**, catalyzing the cleavage of **argininosuccinate** into **arginine** and **fumarate**.
- Its activity is not directly regulated by **N-acetylglutamate**, so it would not be secondarily affected in the same manner as CPS I.
*Argininosuccinate synthetase*
- This enzyme acts after CPS I and ornithine transcarbamylase in the **urea cycle**, synthesizing **argininosuccinate** from **citrulline** and **aspartate**.
- Its function is independent of **N-acetylglutamate** levels, making it unlikely to be secondarily affected.
*Ornithine transcarbamylase*
- This enzyme catalyzes the second step of the **urea cycle**, forming **citrulline** from **ornithine** and **carbamoyl phosphate**.
- While essential for the urea cycle, its activity is not directly modulated by **N-acetylglutamate**; rather, it depends on the availability of carbamoyl phosphate produced by CPS I.
*Arginase*
- This is the final enzyme in the **urea cycle**, converting **arginine** to **ornithine** and **urea**.
- Its activity is not directly or indirectly regulated by **N-acetylglutamate**, nor is it the enzyme primarily affected in this presentation.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 5: A 20-year-old male presents with confusion, asterixis, and odd behavior. Very early in the morning, his mother found him urinating on the floor of his bedroom. A detailed history taken from the mother revealed that he has been a vegetarian his entire life but decided to "bulk up" by working out and consuming whey protein several times a day. A blood test revealed increased levels of ammonia and orotic acid but a decreased BUN. The patient began hemodialysis and was given oral sodium benzoate and phenylbutyrate, which improved his condition. Gene therapy of the enzyme producing which product would correct his condition?
- A. Citrulline (Correct Answer)
- B. Fructose-1-phosphate
- C. Homocysteine
- D. Phenylalanine
- E. Uridine monophosphate
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***Citrulline***
- The clinical presentation (confusion, asterixis, bizarre behavior, high ammonia, low BUN, high orotic acid, improvement with sodium benzoate and phenylbutyrate) is classic for a **urea cycle disorder**, specifically **ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency**.
- OTC catalyzes the conversion of ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline. A deficiency in OTC leads to a buildup of carbamoyl phosphate, which is then shunted to the pyrimidine synthesis pathway, leading to increased orotic acid. Therefore, gene therapy for the enzyme producing citrulline (OTC) would address the underlying defect.
*Fructose-1-phosphate*
- This is an intermediate in **fructose metabolism**. Disorders related to this, such as **hereditary fructose intolerance**, are not associated with hyperammonemia or orotic aciduria in this manner.
- Symptoms typically involve hypoglycemia, vomiting, and liver dysfunction upon fructose ingestion.
*Homocysteine*
- Elevated homocysteine levels are characteristic of **homocystinuria**, which is due to defects in methionine metabolism, often involving **cystathionine beta-synthase** or enzymes in the folate/B12 pathways.
- Homocystinuria presents with developmental delay, skeletal abnormalities, and thromboembolic events, distinct from the patient's symptoms.
*Phenylalanine*
- Elevated phenylalanine is the hallmark of **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, an inherited disorder of amino acid metabolism where the body cannot process **phenylalanine**.
- PKU primarily causes neurological issues if untreated, but not typically hyperammonemia or orotic aciduria.
*Uridine monophosphate*
- While orotic acid is a precursor to uridine monophosphate in pyrimidine synthesis, a direct gene therapy for the enzyme producing uridine monophosphate is not the primary intervention for the underlying urea cycle disorder.
- The high orotic acid is a consequence of the urea cycle blockade, not the primary defect itself.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 6: During normal respiration in the lungs, oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is released. The oxygen is used in cells as the final electron acceptor during oxidative phosphorylation, and carbon dioxide is generated during each turn of the tricarboxylic citric acid cycle (TCA). Which of the following steps in the TCA cycle represents the first decarboxylation reaction that generates carbon dioxide?
- A. Isocitrate to alpha ketoglutarate (Correct Answer)
- B. Fumarate to Malate
- C. Citrate to isocitrate
- D. Malate to oxaloacetate
- E. Alpha-ketoglutarate to Succinyl-CoA
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***Isocitrate to alpha ketoglutarate***
- This is the **first decarboxylation reaction** in the TCA cycle, catalyzed by **isocitrate dehydrogenase**.
- During this reaction, **isocitrate** is oxidized and a molecule of **carbon dioxide** is released, along with the reduction of NAD+ to NADH.
- This is one of the three irreversible steps in the TCA cycle and a key regulatory point.
*Fumarate to Malate*
- This step involves the **hydration** of **fumarate** to **malate** by the enzyme **fumarase**.
- There is no release of carbon dioxide in this reaction; it's a simple addition of water.
*Citrate to isocitrate*
- This is an **isomerization** reaction, catalyzed by **aconitase**, where **citrate** is rearranged into its isomer, **isocitrate**.
- This step does not involve the removal of carbon atoms or the production of carbon dioxide.
*Malate to oxaloacetate*
- In this step, **malate** is oxidized to **oxaloacetate** by **malate dehydrogenase**, which produces NADH.
- This is an **oxidation** reaction, not a decarboxylation reaction, and no carbon dioxide is released.
*Alpha-ketoglutarate to Succinyl-CoA*
- This is the **second decarboxylation** step in the TCA cycle, catalyzed by the **alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex**.
- While this step also produces carbon dioxide and reduces NAD+ to NADH, it occurs after the isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate step, making it the second rather than the first decarboxylation reaction.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 7: In a lab experiment, a researcher treats early cells of the erythrocyte lineage with a novel compound called Pb82. Pb82 blocks the first step of heme synthesis. However, the experiment is controlled such that the cells otherwise continue to develop into erythrocytes. At the end of the experiment, the cells have developed into normal erythrocytes except that they are devoid of heme. A second compound, anti-Pb82 is administered which removes the effect of Pb82.
Which of the following is likely to be true of the mature red blood cells in this study?
- A. The cells will not produce heme since they lack mitochondria (Correct Answer)
- B. The cells will not produce heme because they lack iron
- C. The cells will not produce heme because they lack nucleoli
- D. The cells will now produce heme
- E. The cells will not produce heme because they lack cytosol
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***The cells will not produce heme since they lack mitochondria***
- Mature **red blood cells** are **anucleated** and also **lack mitochondria**, which are essential organelles for the initial and final steps of **heme synthesis**.
- Since **anti-Pb82** is administered, it only reverses the block of the first step of **heme synthesis** by Pb82, but does not provide mitochondria where the remaining steps of **heme synthesis** can happen.
*The cells will not produce heme because they lack iron*
- The problem states that the cells continue to develop into **erythrocytes**, implying that their iron content would typically be normal for mature red blood cells.
- **Iron** is incorporated into the final heme molecule but its absence isn't specifically stated or implied as the primary reason for heme synthesis failure in this context.
*The cells will not produce heme because they lack nucleoli*
- **Nucleoli** are involved in ribosome biogenesis and are found within the nucleus.
- While mature red blood cells are **anucleated** and thus lack nucleoli, nucleoli are not directly involved in **heme synthesis**.
*The cells will now produce heme*
- Although the compound **anti-Pb82** is administered to remove the effect of Pb82 (which blocked the first step of heme synthesis), mature **erythrocytes** are incapable of synthesizing heme.
- This is because they lack the necessary **mitochondria** and enzymes required for the complete pathway of heme synthesis, as they extrude their organelles during maturation.
*The cells will not produce heme because they lack cytosol*
- **Mature red blood cells** have a **cytosol** (cytoplasm without organelles).
- Several steps of **heme synthesis** occur in the cytosol, but the process also requires mitochondrial enzymes, which are absent in mature red blood cells.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 8: A 4-day-old boy is brought to the physician because of somnolence, poor feeding, and vomiting after his first few breast feedings. He appears lethargic. His respiratory rate is 73/min. Serum ammonia is markedly increased. Genetic analysis shows deficiency in N-acetylglutamate synthase. The activity of which of the following enzymes is most likely directly affected by this genetic defect?
- A. Ornithine translocase
- B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (Correct Answer)
- C. Argininosuccinase
- D. Argininosuccinate synthetase
- E. Arginase
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I***
- **N-acetylglutamate** (NAG) is an essential allosteric activator of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)**, the rate-limiting enzyme of the urea cycle.
- A deficiency in **N-acetylglutamate synthase** directly leads to a lack of NAG, significantly impairing CPS I activity and causing severe hyperammonemia.
*Ornithine translocase*
- This enzyme is responsible for transporting **ornithine** into the mitochondria for the urea cycle.
- While a defect in **ornithine translocase** also causes hyperammonemia, it is due to accumulation of ornithine and upstream substrates, not a defect in N-acetylglutamate synthase.
*Argininosuccinase*
- Also known as **argininosuccinate lyase**, this enzyme cleaves argininosuccinate into arginine and fumarate.
- A deficiency would lead to accumulation of **argininosuccinate**, and while it is a urea cycle disorder, it is not directly affected by N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency.
*Argininosuccinate synthetase*
- This enzyme catalyzes the condensation of **citrulline** and **aspartate** to form argininosuccinate.
- A defect in **argininosuccinate synthetase** causes citrullinemia but is not directly regulated by N-acetylglutamate.
*Arginase*
- **Arginase** is the final enzyme in the urea cycle, hydrolyzing arginine to form urea and ornithine.
- A deficiency would lead to hyperargininemia, which typically presents later in childhood and is not directly affected by N-acetylglutamate.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is studying severely ill patients who experience hypoglycemia and ketonuria during times of fasting. The investigator determines that during these episodes, amino acids liberated from muscle proteins are metabolized to serve as substrates for gluconeogenesis. Nitrogen from this process is transported to the liver primarily in the form of which of the following molecules?
- A. Glutamate
- B. α-ketoglutarate
- C. Alanine (Correct Answer)
- D. Arginine
- E. Pyruvate
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***Alanine***
- During prolonged fasting, **muscle proteins are catabolized** to provide amino acids for gluconeogenesis in the liver.
- **Alanine** is the primary amino acid released from muscle into the bloodstream to transport nitrogen to the liver through the **glucose-alanine cycle (Cahill cycle)**.
- In this cycle, pyruvate in muscle accepts an amino group from glutamate to form alanine, which is then transported to the liver, where it is deaminated back to pyruvate (for gluconeogenesis) and ammonia (for the urea cycle).
- **Glutamine** also serves as an important nitrogen transporter, particularly to the kidneys and intestines.
*Glutamate*
- **Glutamate** is an important amino acid in nitrogen metabolism within tissues, but it is not the primary form in which nitrogen is transported from muscle to the liver in significant quantities.
- While glutamate participates in transamination reactions within muscle, its efflux from muscle into the blood is less prominent than alanine for inter-organ nitrogen transport.
*α-ketoglutarate*
- **α-ketoglutarate** is a key intermediate in the **Krebs cycle** and accepts an amino group to form glutamate.
- It is an alpha-keto acid, not an amino acid, and therefore does not directly transport nitrogen in the form of an amino group to the liver via the bloodstream.
*Arginine*
- **Arginine** is primarily involved in the **urea cycle** within the liver, where it helps in the detoxification of ammonia, but it is not a major transporter of nitrogen from peripheral tissues to the liver for gluconeogenesis.
- Its role is mainly within the liver for urea synthesis, not for inter-organ nitrogen transport in this context.
*Pyruvate*
- **Pyruvate** is a keto acid that can be converted to alanine via transamination.
- While pyruvate is a precursor to alanine and a substrate for gluconeogenesis, it transports carbon skeletons and not nitrogen itself; **alanine is the actual nitrogen carrier** in this cycle.
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG Question 10: A 4-year-old boy presents with vomiting and one day of lethargy after a one week history of flu-like symptoms and low-grade fevers. The vomiting is nonbilious and nonbloody. The patient has had no other symptoms aside from mild rhinorrhea and cough. He has no past medical history, and is on no medications except for over-the-counter medications for his fever. His temperature is 98.5°F (36.9°C), pulse is 96/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 108/80 mmHg. The patient appears lethargic and is oriented only to person. Otherwise, the physical exam is benign and the patient has no other neurologic symptoms. What is the mechanism of the most likely cause of this patient’s presentation?
- A. Deficient erythrocyte enzyme
- B. Chemical ingestion
- C. Bacterial infection
- D. Irreversible enzyme inhibition (Correct Answer)
- E. Reversible enzyme inhibition
Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol Explanation: ***Irreversible enzyme inhibition***
- This presentation is highly suggestive of **Reye syndrome**, which is associated with **aspirin use** in children with viral illnesses. Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) **irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes** by acetylating a serine residue at the active site.
- While aspirin's primary mechanism is COX inhibition, **Reye syndrome** involves **mitochondrial dysfunction** in hepatocytes, leading to impaired fatty acid beta-oxidation, hyperammonemia, hepatic steatosis, and **encephalopathy**. This explains the vomiting, lethargy, and altered mental status after flu-like symptoms.
- The key connection is that aspirin acts through **irreversible enzyme inhibition**, making this the correct mechanistic classification for the causative agent.
*Reversible enzyme inhibition*
- While some aspects of Reye syndrome involve mitochondrial enzyme dysfunction, aspirin itself does **not** act through reversible competitive inhibition—it **irreversibly acetylates** COX enzymes.
- Reversible inhibition would imply the drug effect could be easily overcome by increasing substrate concentration, which is not the case with aspirin's mechanism.
*Deficient erythrocyte enzyme*
- This mechanism is associated with conditions like **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**, which primarily causes **hemolytic anemia** with jaundice and pallor.
- While G6PD deficiency can be triggered by certain medications, it does not typically present with the **encephalopathy** and liver dysfunction seen in this patient.
*Chemical ingestion*
- While aspirin is technically a chemical, the question asks about the **mechanism** rather than the route of exposure. The specific mechanism is irreversible enzyme inhibition.
- The history of **flu-like symptoms** and use of over-the-counter fever medications strongly suggests aspirin-associated Reye syndrome rather than accidental toxic ingestion.
*Bacterial infection*
- A severe bacterial infection (e.g., **bacterial meningitis** or **sepsis**) could cause lethargy and vomiting, but the clinical picture (normal vital signs, benign physical exam, no fever) is not typical for acute bacterial infection.
- The association with a recent **viral illness** and potential over-the-counter medication use strongly favors Reye syndrome, a non-infectious etiology.
More Compartmentalization between mitochondria and cytosol US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.