Urea cycle

On this page
🔄 The Nitrogen Detox Engine: Urea Cycle Mastery
Every day your body dismantles hundreds of grams of protein, liberating toxic ammonia that would devastate your brain within hours if left unchecked. The urea cycle is your metabolic guardian, transforming this cellular poison into harmless urea through an elegant five-enzyme pathway spanning mitochondria and cytosol. You'll master how this nitrogen detox engine operates, recognize the clinical fingerprints when it fails, distinguish inherited enzyme defects from acquired liver disease, and deploy emergency protocols that prevent irreversible neurological damage in hyperammonemic crises.
The urea cycle represents the liver's most critical detoxification pathway, transforming lethal ammonia into harmless urea through a sophisticated biochemical assembly line. This nitrogen disposal system processes 20-30 grams of protein-derived ammonia daily, maintaining plasma ammonia levels below the neurotoxic threshold of 50 μmol/L. Understanding this metabolic masterpiece unlocks the logic behind hyperammonemic crises, inborn errors of metabolism, and hepatic encephalopathy patterns.
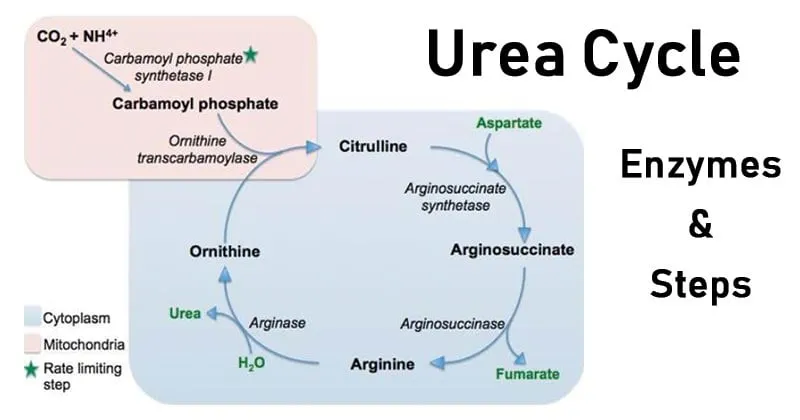
📌 Remember: CPS-OTC-ASS-ASL-ARG = "Careful Operators Always Avoid Ammonia" - The five enzymes that save your brain from nitrogen poisoning
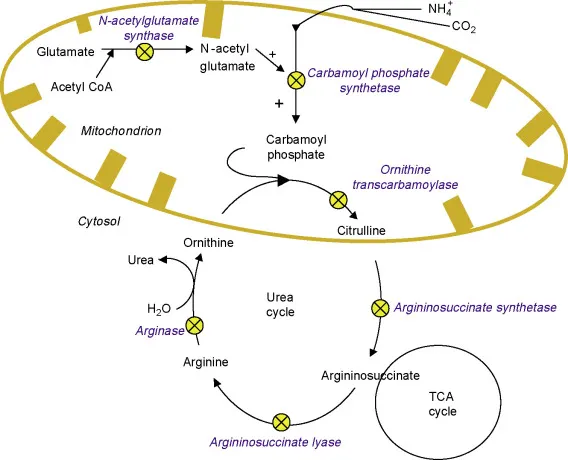
The cycle's architectural brilliance lies in its dual-compartment design: mitochondrial initiation (CPS1, OTC) followed by cytosolic completion (ASS, ASL, arginase). This compartmentalization enables precise regulation while maintaining the 4 ATP energy cost per urea molecule - a metabolic investment that prevents the 10-fold higher energy cost of neuronal damage from hyperammonemia.
- Mitochondrial Phase (Steps 1-2)
- CPS1: Ammonia + CO₂ → Carbamoyl phosphate (2 ATP consumed)
- OTC: Carbamoyl phosphate + Ornithine → Citrulline
- Rate-limiting step with Km = 0.3 mM for ammonia
- N-acetylglutamate allosteric activation (10-fold increase)
- Cytosolic Phase (Steps 3-5)
- ASS: Citrulline + Aspartate → Argininosuccinate (1 ATP consumed)
- ASL: Argininosuccinate → Arginine + Fumarate
- Fumarate links to TCA cycle for energy recovery
- Arginase: Arginine → Urea + Ornithine (regenerates cycle)
| Enzyme | Location | Km (mM) | Regulation | Deficiency Frequency | Clinical Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS1 | Mitochondria | 0.3 (NH₃) | NAG activation | 1:1,300,000 | Severe (neonatal) |
| OTC | Mitochondria | 0.04 (ornithine) | Product inhibition | 1:14,000 | X-linked, variable |
| ASS | Cytosol | 0.1 (citrulline) | Arginine feedback | 1:70,000 | Moderate-severe |
| ASL | Cytosol | 0.02 (argininosuccinate) | None identified | 1:70,000 | Variable |
| Arginase | Cytosol | 5.0 (arginine) | Manganese cofactor | 1:300,000 | Mild (hyperargininemia) |
💡 Master This: The carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I step consumes 66% of cycle energy (2 of 3 ATP) and represents the committed step - once ammonia enters as carbamoyl phosphate, it must complete the cycle or accumulate as toxic intermediates
The cycle's stoichiometry reveals elegant nitrogen balance: 2 nitrogen atoms (1 from ammonia, 1 from aspartate) combine with 1 carbon (from CO₂) to form 1 urea molecule, consuming 3 ATP directly plus 1 ATP equivalent from aspartate synthesis. This 4 ATP investment prevents the catastrophic energy drain of neuronal glutamine synthesis during hyperammonemia.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Normal plasma ammonia levels remain <50 μmol/L, but levels >150 μmol/L cause cerebral edema within 6-12 hours, while >500 μmol/L produces irreversible neurological damage in <24 hours
Understanding the urea cycle's precision engineering provides the foundation for recognizing hyperammonemic emergencies and predicting the metabolic consequences of hepatic dysfunction.
🔄 The Nitrogen Detox Engine: Urea Cycle Mastery
⚡ The Ammonia Crisis: Neurotoxicity Mechanisms
📌 Remember: GABA-ATP-BBB = "Glutamine Accumulation Breaks Astrocytes, Triggers Pressure, Breaks Barrier Badly" - The three mechanisms of ammonia neurotoxicity
The primary mechanism involves glutamine synthetase saturation in astrocytes. Normal brain ammonia disposal relies on the reaction: NH₃ + Glutamate + ATP → Glutamine + ADP + Pi. This pathway handles baseline ammonia loads of 10-15 μmol/L efficiently, but becomes rate-limiting when ammonia exceeds 50 μmol/L.
- Glutamine Accumulation Cascade
- Astrocyte glutamine synthesis increases 5-10 fold
- Intracellular glutamine rises from 5 mM to >20 mM
- Osmotic swelling begins at glutamine >15 mM
- Cell volume increases 15-25% within 2 hours
- Astrocyte foot processes detach from capillaries
- ATP Depletion Consequences
- Brain ATP levels drop 30-40% during hyperammonemia
- Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase function decreases >50%
- Neuronal depolarization threshold drops 10-15 mV
- Seizure susceptibility increases 8-fold
| Ammonia Level (μmol/L) | Clinical Stage | Onset Time | Glutamine (mM) | Mortality Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <50 | Asymptomatic | N/A | 3-5 | <1% |
| 50-100 | Lethargy, confusion | 2-6 hours | 8-12 | 5-10% |
| 100-200 | Stupor, asterixis | 1-3 hours | 15-20 | 20-30% |
| 200-400 | Coma, decerebrate | 30-60 minutes | >25 | 50-70% |
| >400 | Brain death risk | <30 minutes | >30 | >80% |
The secondary mechanism involves GABA receptor modulation. Ammonia enhances GABA-ergic inhibition by increasing chloride conductance and potentiating benzodiazepine binding. This creates the paradoxical sedation seen in hepatic encephalopathy, where patients become progressively obtunded despite normal oxygen delivery.
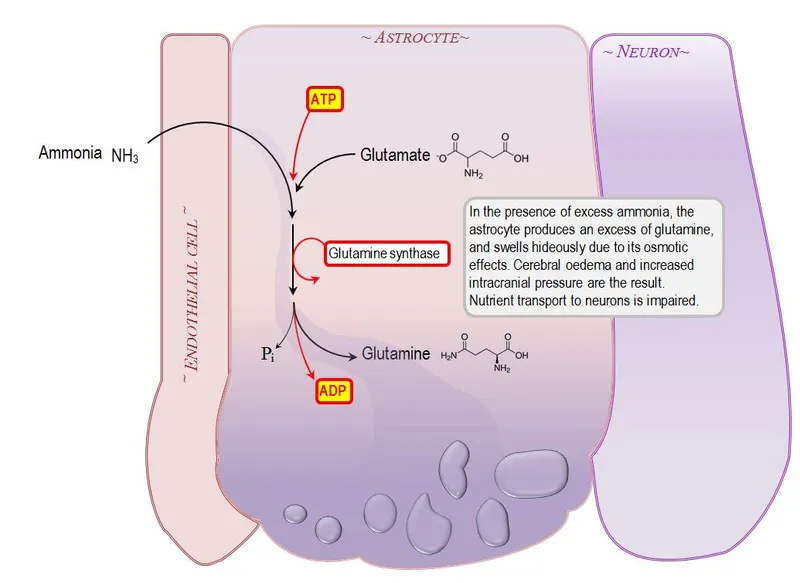
💡 Master This: The blood-brain barrier breakdown occurs when astrocyte foot processes swell and detach from capillaries, creating vasogenic edema that compounds the cytotoxic edema from glutamine accumulation - this dual-edema mechanism explains why mannitol alone fails in severe hyperammonemia
The tertiary mechanism involves mitochondrial dysfunction. Ammonia uncouples oxidative phosphorylation by dissipating proton gradients, reducing ATP synthesis efficiency by 40-60%. This energy crisis particularly affects neurons with high metabolic demands, explaining the selective vulnerability of cortical regions and basal ganglia.
- Mitochondrial Toxicity Pattern
- Complex I activity decreases 25-35%
- Respiratory control ratio drops from 4.5 to <2.0
- Cytochrome oxidase function reduced 30-45%
- Oxygen consumption efficiency falls >50%
- Lactate production increases 3-5 fold
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Plasma lactate >4 mM during hyperammonemia indicates mitochondrial dysfunction and predicts poor neurological recovery even after ammonia normalization - this metabolic signature helps guide prognosis discussions
Understanding ammonia's multi-system neurotoxicity reveals why rapid intervention becomes critical and explains the pathophysiology underlying hepatic encephalopathy grading systems.
⚡ The Ammonia Crisis: Neurotoxicity Mechanisms
🎯 Pattern Recognition: The Hyperammonemic Fingerprint
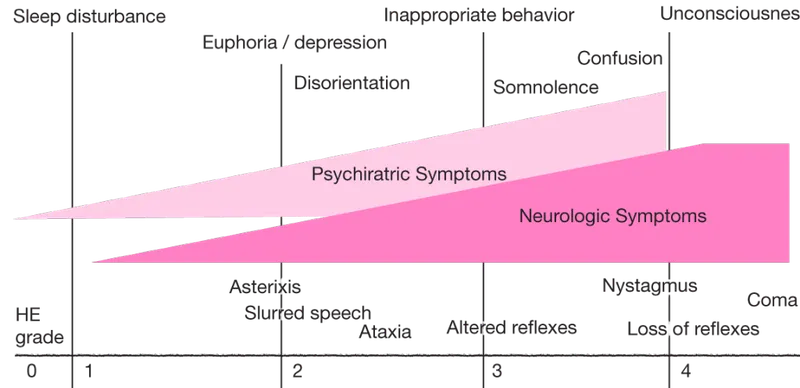
📌 Remember: FLAPS-COMA = "Flushing, Lethargy, Asterixis, Psychiatric, Seizures → Coma, Oposthotonus, Myoclonus, Apnea" - The progression pattern of hyperammonemic encephalopathy
Age-Stratified Recognition Patterns reveal distinct presentations that guide immediate diagnostic workup:
- Neonatal Pattern (0-28 days)
- Feeding intolerance within 24-72 hours of protein introduction
- Temperature instability with hypothermia <36°C
- Respiratory alkalosis (pH >7.45, PCO₂ <35 mmHg)
- Compensatory hyperventilation for metabolic acidosis
- Ammonia >250 μmol/L in >80% of cases
- Seizures in 60-70%, often refractory to standard anticonvulsants
- Infantile Pattern (1-12 months)
- Developmental regression with loss of milestones
- Protein aversion and failure to thrive
- Hepatomegaly in 40-50% of cases
- ALT/AST elevation 2-5x normal
- Coagulopathy with INR >1.5
- Adult Pattern (>18 years)
- Psychiatric symptoms preceding neurological decline
- Episodic confusion triggered by protein loads or illness
- Chronic liver disease in >90% of cases
| Clinical Stage | Ammonia Range (μmol/L) | Key Features | Intervention Window | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade I | 50-100 | Euphoria, sleep reversal | 12-24 hours | 100% |
| Grade II | 100-150 | Lethargy, asterixis | 6-12 hours | 95-100% |
| Grade III | 150-250 | Stupor, rigidity | 2-6 hours | 70-90% |
| Grade IV | >250 | Coma, decerebrate | <2 hours | 20-50% |
| Brain Death | >400 | Apnea, areflexia | Minutes | <5% |
Laboratory Constellation Patterns provide rapid diagnostic confirmation when interpreted systematically:
- Primary Markers
- Ammonia >100 μmol/L (normal <50 μmol/L)
- Glutamine >800 μmol/L (normal 400-600 μmol/L)
- Alanine >500 μmol/L (normal 200-400 μmol/L)
- Secondary Indicators
- Orotic acid elevation in OTC deficiency (>1000x normal)
- Citrulline >1000 μmol/L in ASS deficiency
- Arginine >300 μmol/L in arginase deficiency
- Normal citrulline with high arginine = arginase defect
- High citrulline with normal arginine = ASS/ASL defect
💡 Master This: The citrulline level acts as a metabolic GPS - low citrulline (<10 μmol/L) indicates proximal blocks (CPS1/OTC), moderate elevation (100-300 μmol/L) suggests distal blocks (ASL), while massive elevation (>1000 μmol/L) confirms ASS deficiency
Trigger Pattern Recognition identifies precipitating factors that unmask underlying urea cycle defects:
- Catabolic Stress Triggers (60-70% of presentations)
- Viral infections with fever >38.5°C
- Prolonged fasting >12 hours
- High-protein meals >2 g/kg/day
- Pharmacological Triggers (15-20% of presentations)
- Valproic acid (inhibits CPS1)
- Corticosteroids (increase protein catabolism)
- Chemotherapy (massive cell lysis)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Adult-onset hyperammonemia without cirrhosis suggests heterozygote urea cycle defects unmasked by stress - 50% of OTC heterozygotes remain asymptomatic until pregnancy, illness, or medication exposure
Understanding these recognition patterns enables rapid diagnosis and immediate intervention, preventing the irreversible neurological damage that occurs when hyperammonemia remains unrecognized beyond the critical intervention window.
🎯 Pattern Recognition: The Hyperammonemic Fingerprint
🔬 Differential Mastery: Hyperammonemia's Many Faces
📌 Remember: CHILD-MEDS-LIVER = "Congenital Hyperammonemia, Inborn Liver Defects vs Medication Effects, Drug Side effects vs Liver Injury, Viral Encephalitis, Renal failure" - The major hyperammonemia categories
Primary Urea Cycle Disorders represent inherited enzyme deficiencies with predictable biochemical fingerprints:
| Enzyme Defect | Inheritance | Ammonia (μmol/L) | Citrulline (μmol/L) | Orotic Acid | Key Discriminator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS1 | Autosomal recessive | 200-800 | <10 | Normal | Low citrulline + normal orotic acid |
| OTC | X-linked | 150-600 | <10 | ↑↑↑ (>100x) | Low citrulline + high orotic acid |
| ASS | Autosomal recessive | 100-400 | >1000 | Normal | Massive citrulline elevation |
| ASL | Autosomal recessive | 80-300 | 100-300 | Normal | Argininosuccinic aciduria |
| Arginase | Autosomal recessive | 50-150 | Normal | Normal | High arginine + spasticity |
Secondary Hyperammonemia encompasses acquired conditions that overwhelm normal urea cycle capacity:
- Hepatic Causes (40-50% of adult cases)
- Acute liver failure: Ammonia >300 μmol/L with INR >3.0
- Cirrhosis with portosystemic shunting: Chronic elevation 100-200 μmol/L
- HELLP syndrome: Pregnancy-related with hemolysis and thrombocytopenia
- Ammonia elevation correlates with platelet count <50,000
- Delivery required for ammonia normalization
- Pharmacological Causes (15-20% of cases)
- Valproic acid: Dose-independent inhibition of CPS1
- 5-Fluorouracil: Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency
- Carbamazepine: Rare but severe hyperammonemia
- Genetic polymorphisms increase susceptibility 10-fold
💡 Master This: Neonatal hyperammonemia >250 μmol/L within 72 hours of birth indicates severe urea cycle defect requiring immediate dialysis - every hour of delay increases neurological sequelae risk by 15-20%
Metabolic Mimics present with hyperammonemia but require distinct therapeutic approaches:
- Organic Acidemias
- Methylmalonic acidemia: Ketosis + hyperammonemia + neutropenia
- Propionic acidemia: Odd-chain fatty acid accumulation
- Isovaleric acidemia: Sweaty feet odor + thrombocytopenia
- Glycine supplementation reduces ammonia by 40-60%
- Protein restriction to 0.5-1.0 g/kg/day
- Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects
- MCAD deficiency: Hypoketotic hypoglycemia + hyperammonemia
- LCHAD deficiency: Cardiomyopathy + retinopathy
- Fasting intolerance with ammonia spikes >200 μmol/L
- MCT oil supplementation bypasses defective pathway
| Condition | Ammonia (μmol/L) | Key Lab Findings | Diagnostic Test | Treatment Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severe UCD | >250 | Low citrulline | Amino acids | Dialysis + nitrogen scavengers |
| Liver failure | >200 | ↑ALT, ↑INR | LFTs, hepatitis panel | Transplant evaluation |
| Organic acidemia | 100-300 | Ketosis, acidosis | Urine organic acids | Protein restriction |
| Reye syndrome | 150-400 | ↑AST, hypoglycemia | Clinical + exclusion | Supportive care |
| Drug-induced | 80-200 | Normal LFTs | Medication history | Drug discontinuation |
Rapid Discrimination Protocol enables systematic evaluation within 30-60 minutes:
- Step 1: Age stratification (neonatal vs adult onset)
- Step 2: Liver function assessment (ALT, AST, INR, bilirubin)
- Step 3: Metabolic screening (glucose, ketones, lactate, pH)
- Step 4: Amino acid analysis (citrulline, arginine, glutamine)
- Step 5: Medication review (valproate, chemotherapy, supplements)
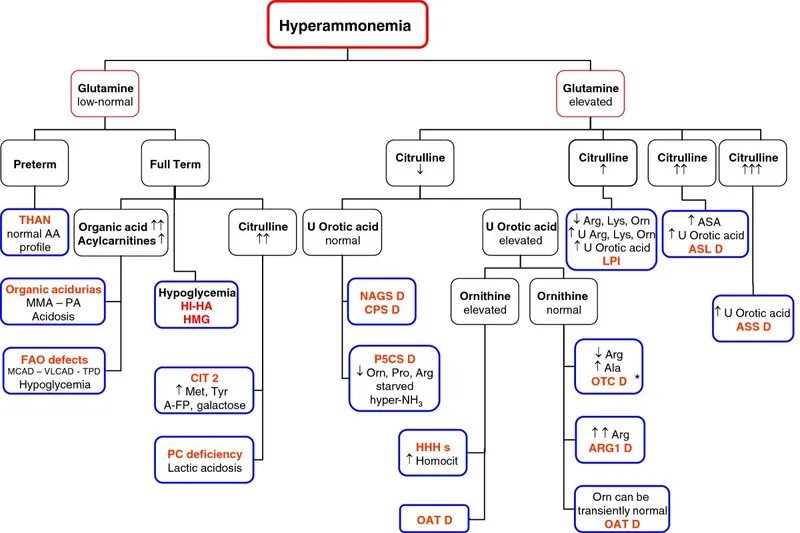
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Citrulline <10 μmol/L with orotic acid >100x normal confirms OTC deficiency with >99% specificity - this pathognomonic combination eliminates diagnostic uncertainty and guides immediate treatment
Understanding these differential patterns prevents misdiagnosis delays that transform treatable hyperammonemia into irreversible neurological catastrophe, while enabling targeted therapies that maximize survival and functional outcomes.
🔬 Differential Mastery: Hyperammonemia's Many Faces
⚕️ Treatment Algorithms: The Ammonia Emergency Protocol
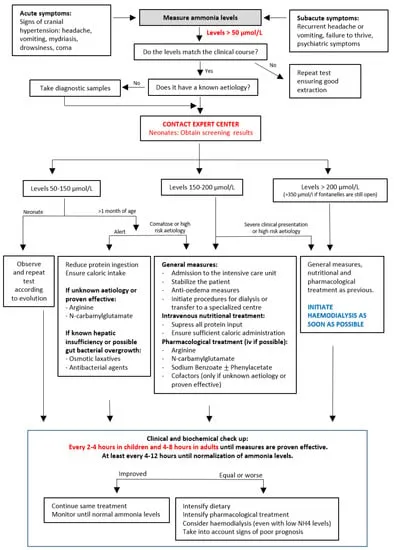
📌 Remember: DIAL-SCAV-STOP = "Dialysis Immediately At Levels >200, Scavengers Combined Always Vital, Stop Toxic Offenders Pronto" - The three-pillar emergency approach
Immediate Interventions (0-30 minutes) focus on stopping nitrogen input and initiating removal:
- Protein Cessation Protocol
- Complete protein restriction for 24-48 hours
- Glucose infusion 10-15 mg/kg/min to prevent catabolism
- Insulin therapy if glucose >200 mg/dL (prevents protein breakdown)
- Target glucose: 100-150 mg/dL
- Avoid hypoglycemia <70 mg/dL (triggers muscle catabolism)
- Medication Review and Cessation
- Discontinue valproate immediately (half-life 9-16 hours)
- Stop corticosteroids if possible (increase protein catabolism)
- Avoid sedatives that worsen encephalopathy
| Ammonia Level (μmol/L) | Intervention Urgency | Primary Treatment | Target Reduction | Time to Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100-150 | Urgent (4-6 hours) | Medical management | <100 μmol/L | 12-24 hours |
| 150-250 | Emergent (1-2 hours) | Dialysis + scavengers | <100 μmol/L | 6-12 hours |
| 250-400 | Critical (<1 hour) | Continuous dialysis | <50 μmol/L | 4-8 hours |
| >400 | Immediate (<30 min) | Emergency dialysis | <50 μmol/L | 2-4 hours |
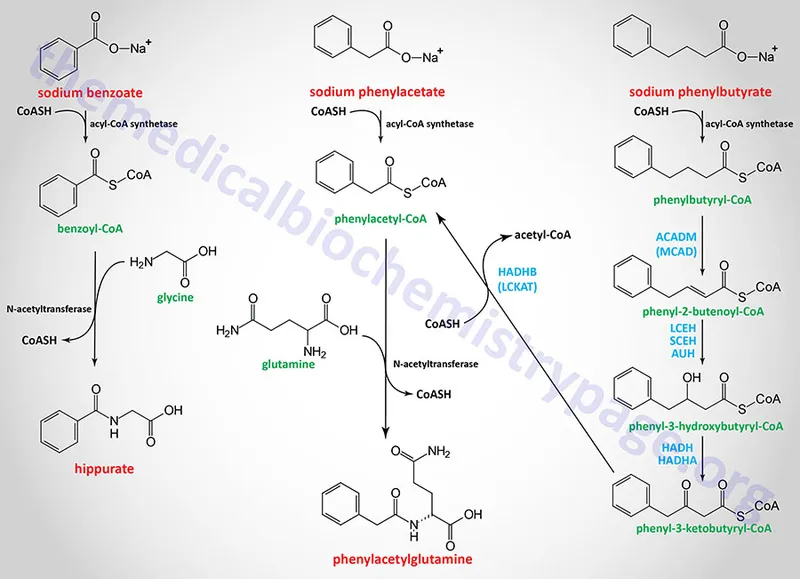
Nitrogen Scavenging Therapy provides alternative pathways for nitrogen disposal when urea cycle function is compromised:
- Sodium Benzoate (250-500 mg/kg/day)
- Mechanism: Benzoate + Glycine → Hippuric acid (renal excretion)
- Nitrogen removal: 1 mole benzoate = 1 mole nitrogen
- Onset: 2-4 hours for measurable effect
- Peak effect: 6-8 hours
- Duration: 12-16 hours
- Sodium Phenylacetate (250-500 mg/kg/day)
- Mechanism: Phenylacetate + Glutamine → Phenylacetylglutamine
- Nitrogen removal: 1 mole phenylacetate = 2 moles nitrogen
- Superior efficacy: 2x nitrogen removal versus benzoate
- Combined Therapy (Ammonul®)
- Sodium phenylacetate 2.5 g/m² + Sodium benzoate 2.5 g/m²
- Loading dose: Over 90-120 minutes
- Maintenance: Same dose over 24 hours
💡 Master This: Phenylacetate removes 2 nitrogen atoms per molecule through glutamine conjugation, making it twice as effective as benzoate - this stoichiometric advantage explains why combination therapy reduces ammonia 40-60% faster than single agents
Dialysis Selection Criteria determine optimal ammonia removal based on clinical severity and institutional capabilities:
- Hemodialysis Indications
- Ammonia >250 μmol/L in neonates
- Ammonia >400 μmol/L in adults
- Clinical deterioration despite medical management
- Worsening encephalopathy grade
- Seizures refractory to anticonvulsants
- Continuous Dialysis Advantages
- Prevents rebound hyperammonemia after intermittent dialysis
- Better hemodynamic stability in critically ill patients
- Sustained ammonia clearance 100-150 mL/min
- Target: Reduce ammonia by 50% every 4-6 hours
- Goal: <100 μmol/L within 12-24 hours
| Treatment Modality | Ammonia Clearance (mL/min) | Onset Time | Efficacy (% reduction/hour) | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical only | 5-10 | 4-6 hours | 5-10% | Minimal |
| Scavengers | 15-25 | 2-4 hours | 15-25% | Hypernatremia |
| Hemodialysis | 150-200 | 30-60 minutes | 40-60% | Hypotension, access |
| CVVHD | 100-150 | 1-2 hours | 30-50% | Anticoagulation |
| Combined | 200-300 | 30 minutes | 60-80% | Multiple |
Neuroprotective Strategies minimize secondary brain injury during ammonia reduction:
- Intracranial Pressure Management
- Mannitol 0.5-1.0 g/kg for acute cerebral edema
- Hypertonic saline 3% for refractory ICP elevation
- Avoid hyperventilation <30 mmHg PCO₂ (worsens cerebral perfusion)
- Seizure Control
- Levetiracetam preferred (no hepatic metabolism)
- Avoid valproate (worsens hyperammonemia)
- Phenytoin acceptable if levetiracetam ineffective
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Hypothermia to 32-34°C reduces cerebral metabolic rate by 30-40% and may improve outcomes in severe hyperammonemia >400 μmol/L, but requires specialized ICU management with continuous EEG monitoring
Understanding these treatment algorithms enables rapid, systematic intervention that maximizes neurological recovery while minimizing treatment-related complications in hyperammonemic emergencies.
⚕️ Treatment Algorithms: The Ammonia Emergency Protocol
🧠 Integration Nexus: Metabolic Crossroads Mastery
📌 Remember: FUEL-ACID-GLUCOSE-PRESSURE = "Fumarate Unites Energy Links, Aspartate Carries Integrated Demands, Glutamine Links Urea Cycle Output Systems, Energy Production Requires Efficient Synchronization Systems Under Regulated Environments" - The four major integration points
Energy Integration connects urea cycle flux to cellular ATP status through multiple feedback mechanisms:
- ATP-Dependent Regulation
- CPS1 requires 2 ATP per carbamoyl phosphate
- ASS consumes 1 ATP (converted to AMP + PPi)
- Total energy cost: 4 ATP equivalents per urea molecule
- Direct consumption: 3 ATP
- Aspartate synthesis: 1 ATP equivalent
- Energy Recovery Mechanisms
- Fumarate from ASL enters TCA cycle
- Malate formation generates NADH (2.5 ATP equivalents)
- Oxaloacetate supports gluconeogenesis
- Net energy recovery: 2.5 ATP per urea cycle
- Actual energy cost: 1.5 ATP per nitrogen disposal
| Integration Point | Metabolic Input | Energy Cost (ATP) | Recovery Pathway | Net Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS1 step | NH₃ + CO₂ | -2.0 | None | -2.0 |
| ASS step | Aspartate | -1.0 | Fumarate → TCA | +2.5 |
| Aspartate synthesis | Oxaloacetate | -1.0 | Transamination | 0 |
| Overall cycle | 2 N atoms | -4.0 | TCA integration | +2.5 |
| Net cost | Per urea | -1.5 | Sustainable | Efficient |
Acid-Base Integration reveals the urea cycle's role in pH homeostasis through bicarbonate consumption and proton buffering:
- Bicarbonate Consumption Pattern
- CPS1 reaction: NH₃ + HCO₃⁻ + 2ATP → Carbamoyl-PO₄
- Stoichiometry: 1 HCO₃⁻ consumed per nitrogen atom
- Daily bicarbonate demand: 300-400 mEq for protein metabolism
- Compensatory Mechanisms
- Renal bicarbonate regeneration increases 2-3 fold
- Respiratory compensation maintains PCO₂ 35-40 mmHg
- Bone buffering provides emergency alkaline reserve
💡 Master This: Metabolic acidosis increases renal ammonia production by 3-5 fold through enhanced glutaminase activity, creating competing demands between renal pH correction and hepatic nitrogen disposal - this metabolic competition explains hyperammonemia during severe acidosis
Gluconeogenic Integration demonstrates how amino acid catabolism supports glucose homeostasis while generating nitrogen waste:
- Alanine-Glucose Cycle
- Muscle protein breakdown → Alanine transport to liver
- Alanine deamination → Pyruvate + NH₃
- Pyruvate → Glucose (gluconeogenesis)
- NH₃ → Urea (nitrogen disposal)
- Cycle efficiency: 65-70% glucose recovery
- Daily flux: 150-200 g alanine during fasting
- Glutamine-Glucose Pathway
- Intestinal glutamine → Alanine + NH₃
- Portal circulation delivers both substrates to liver
- Coordinate processing: Glucose synthesis + Nitrogen disposal
| Amino Acid | Glucose Yield (mol/mol) | NH₃ Production | Urea Cycle Load | Metabolic Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | 0.5-0.7 | 1.0 | Moderate | Glucose > Nitrogen |
| Glutamine | 0.6-0.8 | 2.0 | High | Balanced |
| Glycine | 0.3-0.5 | 1.0 | Low | Nitrogen > Glucose |
| Serine | 0.5-0.7 | 1.0 | Moderate | Balanced |
| Branched-chain | 0.4-0.6 | 1.0 | Variable | Muscle-dependent |
Hormonal Integration coordinates urea cycle activity with nutritional status and stress responses:
- Insulin Effects
- Promotes protein synthesis (reduces amino acid catabolism)
- Inhibits gluconeogenesis (decreases nitrogen load)
- Enhances CPS1 activity through allosteric modulation
- Glucagon/Cortisol Effects
- Stimulates protein catabolism (increases nitrogen load)
- Enhances urea cycle enzyme expression (2-4 fold increase)
- Coordinates gluconeogenesis with nitrogen disposal
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Stress-induced hyperammonemia results from cortisol-mediated protein catabolism overwhelming urea cycle capacity - cortisol levels >50 μg/dL increase nitrogen load by 200-300% while urea cycle enzymes increase only 50-100%
Understanding these metabolic integrations reveals why urea cycle disorders affect multiple organ systems and why successful treatment requires comprehensive metabolic support rather than isolated interventions.
🧠 Integration Nexus: Metabolic Crossroads Mastery
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid-Fire Urea Cycle Command
📌 Essential Arsenal: 50-100-200-400 = The ammonia thresholds that dictate intervention intensity - <50 normal, >100 treatment, >200 dialysis, >400 emergency
Critical Threshold Mastery - Memorize These Numbers:
- Ammonia Levels (μmol/L)
- Normal: <50
- Treatment threshold: >100
- Dialysis threshold: >200
- Emergency threshold: >400
- Brain death risk: >500
- Intervention Timeframes
- Grade I-II: 6-12 hours to intervention
- Grade III: 2-4 hours to intervention
- Grade IV: <1 hour to intervention
- Rebound prevention: 48-72 hours scavenger therapy
| Clinical Scenario | Ammonia (μmol/L) | Immediate Action | Time Limit | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal UCD | >250 | Emergency dialysis + scavengers | <2 hours | 60-70% |
| Adult decompensation | 150-300 | Urgent dialysis + medical | <4 hours | 80-90% |
| Drug-induced | 100-200 | Stop drug + scavengers | <6 hours | >95% |
| Liver failure | >200 | Transplant evaluation + dialysis | <12 hours | 40-60% |
| Heterozygote crisis | 100-150 | Medical management | <12 hours | >90% |
Rapid Diagnostic Protocol - 30-Second Assessment:
- Step 1: Age + Onset (neonatal vs adult)
- Step 2: Liver enzymes (normal vs elevated)
- Step 3: Citrulline level (<10, 100-300, >1000 μmol/L)
- Step 4: Medication history (valproate, chemotherapy)
- Step 5: Family history (consanguinity, X-linked pattern)
💡 Clinical Pearl: Citrulline acts as the metabolic GPS - memorize the pattern: <10 = proximal block, 100-300 = distal block, >1000 = middle block
Treatment Protocol Arsenal:
- Immediate Interventions (0-30 minutes)
- Stop all protein intake
- Start glucose 10-15 mg/kg/min
- Obtain dialysis access if ammonia >200 μmol/L
- Load scavengers: Ammonul 5.5 g/m² over 90 minutes
- Ongoing Management (1-24 hours)
- Monitor ammonia every 2-4 hours
- Target reduction: 50% every 4-6 hours
- Continue scavengers for 48-72 hours after normalization
- Gradual protein reintroduction: 0.5 g/kg/day increments
| Drug | Dose | Mechanism | Onset | Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium benzoate | 250-500 mg/kg/day | Hippuric acid formation | 2-4 hours | Sodium levels |
| Sodium phenylacetate | 250-500 mg/kg/day | Glutamine conjugation | 2-4 hours | Sodium levels |
| Arginine | 200-700 mg/kg/day | Cycle substrate | 1-2 hours | Arginine levels |
| Citrulline | 100-200 mg/kg/day | Bypass CPS1/OTC | 2-6 hours | Citrulline levels |
| Carglumic acid | 100-250 mg/kg/day | CPS1 activation | 4-8 hours | Ammonia response |
Emergency Complications Management:
- Cerebral Edema Protocol
- Mannitol 0.5-1.0 g/kg IV push
- Hypertonic saline 3% for refractory ICP
- Avoid hyperventilation <30 mmHg PCO₂
- Consider hypothermia 32-34°C for ammonia >400 μmol/L
- Seizure Management
- Levetiracetam 20-40 mg/kg IV (preferred)
- Avoid valproate (worsens hyperammonemia)
- Phenytoin 15-20 mg/kg if levetiracetam fails
⭐ Critical Warning: Rebound hyperammonemia occurs in 60-80% after stopping dialysis - continue scavengers for 48-72 hours to prevent rebound
Long-Term Management Essentials:
- Protein Restriction Guidelines
- Neonates: 1.5-2.0 g/kg/day
- Infants: 1.0-1.5 g/kg/day
- Children: 0.8-1.2 g/kg/day
- Adults: 0.6-1.0 g/kg/day
- Essential Amino Acid Supplementation
- Branched-chain amino acids: Leucine, isoleucine, valine
- Essential amino acids: Histidine, lysine, methionine
- Avoid: High-nitrogen amino acids (arginine, glutamine)
💡 Master This: Successful long-term management requires balancing protein restriction with growth needs - too little protein causes growth failure, too much triggers hyperammonemic crises
Prognosis Predictors:
- Favorable Outcomes (>90% normal development)
- Peak ammonia <150 μmol/L
- Coma duration <24 hours
- Treatment initiation <6 hours from onset
- Poor Outcomes (>50% neurological sequelae)
- Peak ammonia >400 μmol/L
- Coma duration >72 hours
- Treatment delay >12 hours
This clinical arsenal provides the rapid-fire competency needed to recognize, diagnose, and treat urea cycle disorders with the precision and speed that saves lives and preserves neurological function.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid-Fire Urea Cycle Command
Practice Questions: Urea cycle
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 2-day-old male infant is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after his parents noticed that he was convulsing and unresponsive. He was born at home and appeared well initially; however, within 24 hours he became increasingly irritable and lethargic. Furthermore, he stopped feeding and began to experience worsening tachypnea. This continued for about 6 hours, at which point his parents noticed the convulsions and called for an ambulance. Laboratories are obtained with the following results: Orotic acid: 9.2 mmol/mol creatinine (normal: 1.4-5.3 mmol/mol creatinine) Ammonia: 135 µmol/L (normal: < 50 µmol/L) Citrulline: 2 µmol/L (normal: 10-45 µmol/L) Which of the following treatments would most likely be beneficial to this patient?











