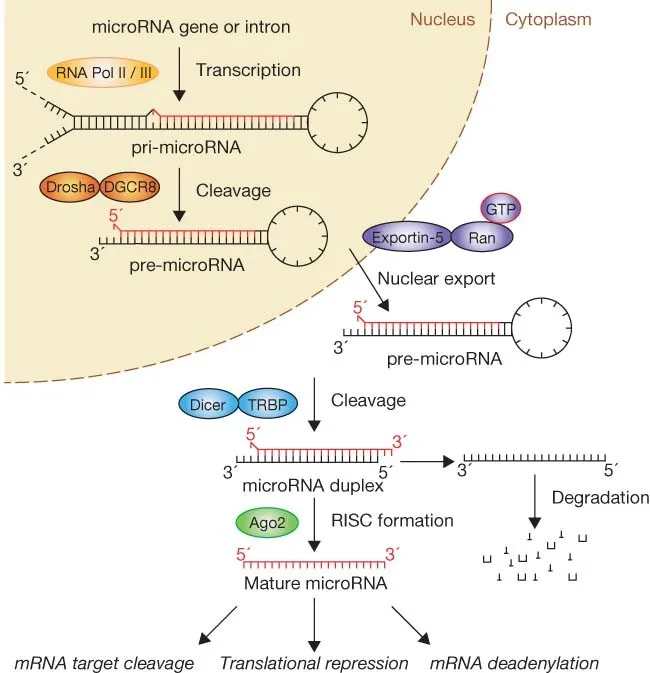
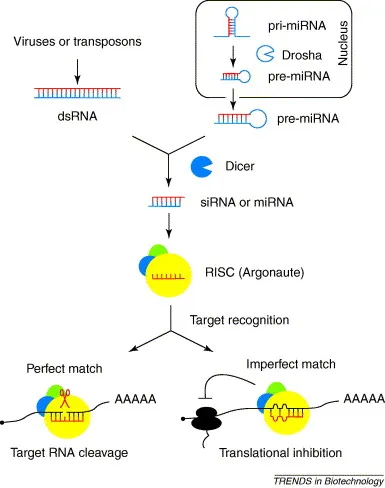
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for RNA interference and microRNAs. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 1: A 25-year-old female comes to the clinic complaining of fatigue and palpitations. She has been undergoing immense stress from her thesis defense and has been extremely tired. The patient denies any weight loss, diarrhea, cold/heat intolerance. TSH was within normal limits. She reports a family history of "blood disease" and was later confirmed positive for β-thalassemia minor. It is believed that abnormal splicing of the beta globin gene results in β-thalassemia. What is removed during this process that allows RNA to be significantly shorter than DNA?
- A. 3'-poly(A) tail
- B. Exons
- C. Introns (Correct Answer)
- D. microRNAs
- E. snRNPs
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: **Introns**
- **Introns** are non-coding regions within a gene that are removed from the pre-mRNA transcript during **splicing**.
- This removal and the subsequent ligation of exons lead to a mature mRNA molecule that is significantly shorter than the initial DNA template.
*3'-poly(A) tail*
- The **3'-poly(A) tail** is an addition to the 3' end of the mRNA molecule, not a removed segment during splicing, and it provides stability and aids in translation.
- While it contributes to mRNA processing, its addition does not involve removing existing sequences to shorten the transcript.
*Exons*
- **Exons** are the coding regions of a gene that are retained and ligated together to form the mature mRNA, which is then translated into protein.
- If exons were removed, the resulting protein would be truncated or non-functional, and the mRNA would not contain the necessary genetic information.
*microRNAs*
- **MicroRNAs (miRNAs)** are small non-coding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression by inhibiting translation or promoting mRNA degradation.
- They are not part of the pre-mRNA transcript that is processed into mRNA; rather, they are distinct regulatory molecules.
*snRNPs*
- **Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs)** are components of the spliceosome, the molecular machine responsible for carrying out splicing.
- They are involved in the process of intron removal but are not themselves removed from the RNA; they are catalytic machinery.
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 2: In translation, the wobble phenomenon is best illustrated by the fact that:
- A. Charged tRNA contains energy needed for peptide bonds to form
- B. The last nucleotide provides specificity for the given amino acid
- C. A tRNA with the UUU anticodon can bind to either AAA or AAG codons (Correct Answer)
- D. There are more amino acids than possible codons
- E. The genetic code is preserved without mutations
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: ***A tRNA with the UUU anticodon can bind to either AAA or AAG codons***
- The **wobble phenomenon** allows for non-standard base pairing between the **first nucleotide (5' position) of the tRNA anticodon** and the **third nucleotide (3' position) of the mRNA codon**.
- In this example, a tRNA with anticodon **3'-UUU-5'** can bind to either **5'-AAA-3'** or **5'-AAG-3'** codons (both encoding lysine) due to the relaxed base-pairing rules at the wobble position.
- This flexibility means fewer tRNAs are needed to recognize all 61 sense codons, illustrating the **degeneracy of the genetic code**.
- According to Crick's wobble hypothesis, **U at the 5' position of the anticodon** can pair with either **A or G at the 3' position of the codon**.
*Charged tRNA contains energy needed for peptide bonds to form*
- While **charged tRNA** (aminoacyl-tRNA) does carry an amino acid activated for peptide bond formation, this statement describes the energy source for translation, not the wobble phenomenon.
- The energy for peptide bond formation comes from the **high-energy ester bond** linking the amino acid to the tRNA, not from the base pairing itself.
*The last nucleotide provides specificity for the given amino acid*
- The **last nucleotide** (3' position) of the mRNA codon is where **wobble pairing** occurs, meaning it does *not* always provide strict specificity for the amino acid due to the relaxed base-pairing rules.
- It is often the *first two nucleotides* of the codon that are most critical in determining the specific amino acid incorporated.
*There are more amino acids than possible codons*
- This statement is incorrect; there are **20 standard amino acids** and **61 sense codons** (three are stop codons), meaning there are more codons than amino acids, leading to **code degeneracy**.
- The concept of wobble base pairing helps explain how this degeneracy is managed efficiently, but the premise of this option is false.
*The genetic code is preserved without mutations*
- This statement refers to the **fidelity of DNA replication and repair** or the evolutionary conservation of the genetic code, not the mechanism of translation or wobble base pairing.
- The genetic code being largely universal and degenerate does not mean that mutations never occur, but rather that it is robust.
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 3: A pharmaceutical company has modified one of its existing antibiotics to have an improved toxicity profile. The new antibiotic blocks protein synthesis by first entering the cell and then binding to active ribosomes. The antibiotic mimics the structure of aminoacyl-tRNA. The drug is covalently bonded to the existing growing peptide chain via peptidyl transferase, thereby impairing the rest of protein synthesis and leading to early polypeptide truncation. Where is the most likely site that this process occurs?
- A. E site
- B. 30S small subunit
- C. A site (Correct Answer)
- D. 40S small subunit
- E. P site
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: ***A site***
- The **A (aminoacyl) site** is where incoming aminoacyl-tRNAs bind during translation, bringing new amino acids to the ribosome. Since the antibiotic mimics **aminoacyl-tRNA** and is covalently bonded to the peptide chain by **peptidyl transferase**, its action must occur at the A site.
- Binding at the A site and subsequent peptide bond formation with the antibiotic would lead to premature polypeptide truncation, as no further amino acids can be added.
*E site*
- The **E (exit) site** is where deacylated tRNAs are released from the ribosome after having delivered their amino acid to the growing peptide chain in the P site.
- The antibiotic's mechanism of action, involving binding and covalent incorporation into the peptide, does not align with the function of the E site.
*30S small subunit*
- The **30S small ribosomal subunit** in prokaryotes is primarily involved in mRNA binding and decoding, ensuring the correct aminoacyl-tRNA binds to the mRNA codon.
- While the antibiotic binds to active ribosomes, its key action described as mimicking aminoacyl-tRNA and being incorporated by peptidyl transferase points to a specific binding site within the ribosome rather than the entire subunit's general function.
*40S small subunit*
- The **40S small ribosomal subunit** is found in **eukaryotic ribosomes**, not prokaryotic ones, and is involved in mRNA binding during initiation.
- The question implies an antibiotic targeting bacterial protein synthesis (given its discussion of modifying an existing antibiotic), making eukaryotic ribosomal subunits an unlikely target.
*P site*
- The **P (peptidyl) site** holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain. Peptidyl transferase activity forms a peptide bond between the amino acid in the A site and the peptide in the P site.
- While peptidyl transferase is involved, the antibiotic *mimics* aminoacyl-tRNA, which is delivered to the A site for peptide bond formation, rather than the P site which already holds the growing chain.
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator is studying the genetic profile of an isolated pathogen that proliferates within macrophages. The pathogen contains sulfatide on the surface of its cell wall to prevent fusion of the phagosome and lysosome. She finds that some of the organisms under investigation have mutations in a gene that encodes the enzyme required for synthesis of RNA from a DNA template. The mutations are most likely to reduce the therapeutic effect of which of the following drugs?
- A. Pyrazinamide
- B. Ethambutol
- C. Rifampin (Correct Answer)
- D. Streptomycin
- E. Levofloxacin
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: ***Rifampin***
- **Rifampin** specifically targets bacterial **DNA-dependent RNA polymerase**, inhibiting **RNA synthesis**. Mutations in the gene encoding this enzyme would directly reduce rifampin's binding and effectiveness.
- The description of the pathogen thriving within macrophages and using **sulfatide to evade lysosomal fusion** strongly suggests **Mycobacterium tuberculosis**, a bacterium for which rifampin is a cornerstone treatment.
*Pyrazinamide*
- **Pyrazinamide** is a prodrug that, once converted to **pyrazinoid acid**, disrupts **mycobacterial membrane potential** and metabolism. Its primary target is not RNA synthesis.
- Its efficacy is pH-dependent and it acts optimally in acidic environments, such as within macrophages, but mutations affecting RNA synthesis would not directly compromise its action.
*Ethambutol*
- **Ethambutol** inhibits **arabinosyl transferase**, an enzyme essential for the synthesis of the **mycobacterial cell wall component arabinogalactan**.
- Its mechanism of action is distinct from RNA synthesis, thus mutations affecting RNA polymerase would not impact its efficacy.
*Streptomycin*
- **Streptomycin** is an **aminoglycoside antibiotic** that binds to the **30S ribosomal subunit**, inhibiting bacterial **protein synthesis**.
- This mechanism is unrelated to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, so mutations in RNA synthesis enzymes would not affect streptomycin's action.
*Levofloxacin*
- **Levofloxacin** is a **fluoroquinolone antibiotic** that inhibits **bacterial DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II)** and **topoisomerase IV**, thereby blocking DNA replication and transcription.
- While it affects processes related to DNA, its direct target is not the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme itself, distinguishing it from rifampin's specific mechanism.
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 5: While performing a Western blot, a graduate student spilled a small amount of the radiolabeled antibody on her left forearm. Although very little harm was done to the skin, the radiation did cause minor damage to the DNA of the exposed skin by severing covalent bonds between the nitrogenous bases and the deoxyribose sugar, leaving several apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Damaged cells would most likely repair these sites by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Nucleotide excision repair
- B. Nonhomologous end joining repair
- C. Homologous recombination
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Base excision repair (Correct Answer)
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: **Base excision repair**
- This mechanism is specifically involved in correcting **single-base DNA damage** or **modified bases**, such as **apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites**.
- It involves removing the damaged base by a **DNA glycosylase**, creating an AP site, which is then processed by an **AP endonuclease** to cleave the phosphodiester backbone, followed by DNA polymerase and ligase.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- Primarily repairs **bulky DNA lesions**, such as **thymine dimers** caused by UV radiation, or damage from chemical adducts that distort the DNA helix.
- It involves excising a larger oligonucleotide containing the damage, not just a single base.
*Nonhomologous end joining repair*
- This pathway is used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks**, where both strands of the DNA molecule are broken.
- It is a "quick-and-dirty" repair mechanism that ligates the broken ends together, often leading to small insertions or deletions.
*Homologous recombination*
- A repair mechanism for **double-strand DNA breaks** that uses a homologous DNA template (e.g., sister chromatid) to accurately repair the break.
- This process is highly accurate but occurs only when a homologous template is available, typically during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
*Mismatch repair*
- Corrects **base-pair mismatches** and **small insertions/deletions** that occur during DNA replication, which were not corrected by DNA polymerase proofreading.
- It targets newly synthesized DNA strands based on methylation patterns in the parental strand.
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 6: DNA replication is a highly complex process where replication occurs on both strands of DNA. On the leading strand of DNA, replication occurs uninterrupted, but on the lagging strand, replication is interrupted and occurs in fragments called Okazaki fragments. These fragments need to be joined, which of the following enzymes is involved in the penultimate step before ligation can occur?
- A. DNA gyrase
- B. DNA ligase
- C. DNA helicase
- D. DNA polymerase I (Correct Answer)
- E. DNA polymerase III
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: **DNA polymerase I**
- **DNA polymerase I** plays a crucial role in removing the **RNA primers** from the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
- After primer removal, it fills the resulting gaps with **deoxyribonucleotides** before DNA ligase seals the nicks.
*DNA gyrase*
- **DNA gyrase** (a type of **topoisomerase**) is involved in relieving **supercoiling** ahead of the replication fork.
- It does not directly participate in the joining of Okazaki fragments, but rather in maintaining DNA topology during replication.
*DNA ligase*
- **DNA ligase** is responsible for the **final sealing** of the nicks between adjacent Okazaki fragments.
- It forms a **phosphodiester bond** between the 3'-hydroxyl end of one fragment and the 5'-phosphate end of the next, following primer removal and gap filling.
*DNA helicase*
- **DNA helicase** unwinds the double-stranded DNA helix, separating the two strands at the **replication fork**.
- This enzyme is essential for initiating replication but does not participate in processing Okazaki fragments.
*DNA polymerase III*
- **DNA polymerase III** is the primary enzyme responsible for the **elongation of new DNA strands** in both leading and lagging strand synthesis.
- It synthesizes the actual Okazaki fragments but does not directly remove primers or fill the gaps.
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 7: An investigator is studying the effects of zinc deprivation on cancer cell proliferation. It is hypothesized that because zinc is known to be a component of transcription factor motifs, zinc deprivation will result in slower tumor growth. To test this hypothesis, tumor cells are cultured on media containing low and high concentrations of zinc. During the experiment, a labeled oligonucleotide probe is used to identify the presence of a known transcription factor. The investigator most likely used which of the following laboratory techniques?
- A. ELISA
- B. PCR
- C. Western blot
- D. Northern blot
- E. Southwestern blot (Correct Answer)
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: ***Southwestern blot***
- A **Southwestern blot** specifically identifies **DNA-binding proteins** (such as transcription factors) by detecting their ability to bind to specific **labeled DNA oligonucleotide probes**
- The technique involves: protein separation by gel electrophoresis → transfer to membrane → probing with **labeled double-stranded DNA oligonucleotide**
- This directly answers the question: using a labeled oligonucleotide probe to identify a transcription factor
*ELISA*
- **ELISA** detects and quantifies proteins using **antibody-antigen interactions**, not DNA-binding activity
- While it could detect the presence of a transcription factor protein, it cannot assess the protein's ability to bind to specific DNA sequences
- Does not utilize oligonucleotide probes for detection
*PCR*
- **PCR** amplifies specific **DNA sequences** but does not detect or characterize proteins
- This technique would amplify DNA, not identify DNA-binding proteins
- Not applicable for detecting transcription factor presence or function
*Western blot*
- **Western blot** detects specific proteins using **antibodies**, not oligonucleotide probes
- While it could confirm transcription factor protein presence, it cannot assess DNA-binding capability
- Uses antibody-based detection, not nucleotide probe-based detection
*Northern blot*
- **Northern blot** detects specific **RNA molecules**, not DNA-binding proteins
- Uses labeled DNA or RNA probes to detect RNA, not to detect proteins that bind DNA
- Wrong target molecule (RNA vs. proteins)
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 8: An investigator is studying human genetics and cell division. A molecule is used to inhibit the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. Which of the following phases of the cell cycle does the molecule target?
- A. Prophase II
- B. Prophase I (Correct Answer)
- C. Metaphase II
- D. Telophase I
- E. Anaphase I
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: ***Prophase I***
- **Crossing over** (genetic recombination) occurs specifically during **Prophase I** of meiosis, particularly during the pachytene stage
- During this phase, homologous chromosomes pair up (synapsis) and exchange genetic material through recombination
- Inhibiting this exchange means targeting the phase where this critical genetic recombination takes place
*Prophase II*
- Prophase II is a stage in meiosis II where chromosomes condense again after a brief interkinesis
- **Crossing over does not occur** in Prophase II - genetic recombination has already been completed in Prophase I
- Homologous chromosomes are no longer paired at this stage
*Metaphase II*
- During Metaphase II, individual chromosomes (not homologous pairs) align along the metaphase plate
- There is **no exchange of genetic material** between homologous chromosomes at this stage
- This phase prepares for the separation of sister chromatids
*Telophase I*
- Telophase I involves decondensation of chromosomes and reformation of nuclear envelopes around the separated homologous chromosomes
- This marks the end of meiosis I, **after** genetic exchange has already occurred in Prophase I
- No crossing over occurs during this phase
*Anaphase I*
- In Anaphase I, **homologous chromosomes separate** and move to opposite poles of the cell
- This phase is characterized by segregation of chromosomes, **not genetic exchange**
- Crossing over has already been completed by this stage
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 9: A scientist wants to determine if a specific fragment is contained within genome X. She uses a restriction enzyme to digest the genome into smaller fragments to run on an agarose gel, with the goal of separating the resulting fragments. A nitrocellulose blotting paper is then used to transfer the fragments from the agarose gel. A radiolabeled probe containing a complementary sequence to the fragment she is searching for is incubated with the blotting paper. Which of the following is the RNA equivalent of this technique?
- A. RT-PCR
- B. Western blot
- C. qPCR
- D. Northern blot (Correct Answer)
- E. Southern blot
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: **Northern blot**
- The technique described in the question, involving **restriction enzyme digestion**, **agarose gel electrophoresis**, **blotting onto a membrane**, and **hybridization with a labeled probe**, is characteristic of a **Southern blot** for DNA
- The **Northern blot** is the analogous technique used to detect and quantify **RNA** sequences, following the same principles of separation by size and detection by hybridization with a complementary probe
- Both Southern and Northern blots use the same workflow: separate nucleic acids by size on gel → transfer to membrane → detect with complementary probe
*RT-PCR*
- **Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)** is used to amplify specific **RNA** sequences by first converting **RNA** into **complementary DNA (cDNA)** using reverse transcriptase, followed by standard PCR
- Unlike Northern blot, it is an **amplification technique** rather than a direct visualization method via blotting
*Western blot*
- **Western blot** is a technique used to detect and identify specific **proteins**, not nucleic acids
- It involves **gel electrophoresis** to separate proteins by size, followed by transfer to a membrane and detection using **antibodies** rather than nucleic acid probes
*qPCR*
- **Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)**, also known as real-time PCR, is a technique used to **quantify DNA or RNA** (after reverse transcription) in real-time
- It measures the accumulation of fluorescent signal during the PCR reaction, allowing for real-time monitoring and quantification, which is fundamentally different from a blotting technique
*Southern blot*
- The description in the question *is* a **Southern blot**, which is used for **DNA** detection, not RNA
- Since the question asks for the **RNA equivalent** of the described technique, and Southern blot detects DNA, Northern blot is the correct answer
RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG Question 10: A 12-year-old male presents to the emergency department following several days of facial edema. A urinalysis confirms proteinuria and hematuria. Once admitted, a kidney biopsy is viewed under an electron microscope to confirm the diagnosis of minimal change disease. In the following electron micrograph, what process occurs in the structure marked with an arrow?
- A. Podocyte foot process effacement (Correct Answer)
- B. Normal podocyte foot process interdigitation
- C. Mesangial cell proliferation
- D. Endothelial cell fenestration
- E. Glomerular basement membrane thickening
RNA interference and microRNAs Explanation: **Podocyte foot process effacement**
- Minimal change disease is characterized by the **effacement (flattening and fusion)** of podocyte foot processes, which are the structures indicated by the arrow in the image.
- This effacement leads to the loss of the **slit diaphragm barrier**, causing massive proteinuria.
*Normal podocyte foot process interdigitation*
- Normal podocyte foot processes exhibit a distinct, highly organized **interdigitating pattern**, which is clearly not observed in the image due to the flattening.
- This normal interdigitation is crucial for maintaining the **glomerular filtration barrier** and preventing protein leakage.
*Mesangial cell proliferation*
- **Mesangial cell proliferation** is characteristic of conditions like IgA nephropathy or mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis, and is not the primary feature of minimal change disease.
- The image illustrates changes in the podocytes, not the mesangial cells (labeled 'M').
*Endothelial cell fenestration*
- **Endothelial cell fenestrations** are normal pores in the glomerular endothelial cells that allow for filtration, and are not directly affected or effaced in minimal change disease.
- The arrow in the image points to the podocyte layer, not the endothelial cells.
*Glomerular basement membrane thickening*
- **Glomerular basement membrane (GBM) thickening** is seen in conditions like diabetic nephropathy or membranous nephropathy, but not typically in minimal change disease.
- In minimal change disease, the GBM typically appears normal under electron microscopy.
More RNA interference and microRNAs US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.