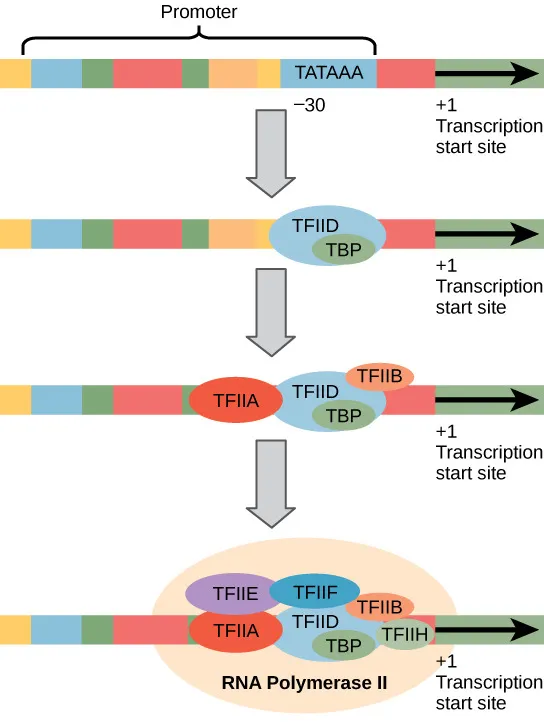
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Initiation of transcription. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old man presents with a hereditary condition affecting iron metabolism. The condition is caused by mutations in a gene that normally stimulates hepatic production of hepcidin, a hormone that downregulates iron absorption by inhibiting ferroportin (an iron transporter) on enterocytes. Due to this genetic defect, the patient has developed iron overload. He presents with skin hyperpigmentation, fatigue, joint pain, and diabetes mellitus. Laboratory studies show elevated serum ferritin and transferrin saturation. The patient is also developing early signs of cardiovascular complications from iron deposition. What would be the first cardiac manifestation in this patient?
- A. Preload: decreased, cardiac contractility: unchanged, afterload: increased (Correct Answer)
- B. Preload: decreased, cardiac contractility: decreased, afterload: decreased
- C. Preload: increased, cardiac contractility: increased, afterload: increased
- D. Preload: increased, cardiac contractility: decreased, afterload: increased
- E. Preload: increased, cardiac contractility: increased, afterload: decreased
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***Preload: decreased, cardiac contractility: unchanged, afterload: increased***
- The first cardiac manifestation of **hereditary hemochromatosis** is typically **restrictive cardiomyopathy**, where iron deposition causes myocardial stiffening and impaired diastolic relaxation.
- In early restrictive disease, the stiff ventricle has **impaired filling**, leading to **reduced end-diastolic volume (decreased preload)** despite elevated filling pressures.
- **Systolic contractility remains initially unchanged** as the primary defect is diastolic dysfunction, not systolic failure.
- **Afterload is increased** due to compensatory peripheral vasoconstriction and reduced stroke volume triggering baroreceptor responses.
- This pattern reflects pure diastolic dysfunction with preserved systolic function (HFpEF pattern).
*Preload: decreased, cardiac contractility: decreased, afterload: decreased*
- While preload may be decreased, **reduced afterload** is inconsistent with restrictive cardiomyopathy, which typically shows compensatory vasoconstriction, not vasodilation.
- **Decreased contractility** occurs in later stages when iron toxicity directly damages myofibrils, progressing to dilated cardiomyopathy, but is not the initial presentation.
*Preload: increased, cardiac contractility: increased, afterload: increased*
- **Increased contractility** is not seen in iron-induced cardiac disease; iron deposition impairs, rather than enhances, myocardial function.
- This pattern would suggest a hyperdynamic state (e.g., sepsis, hyperthyroidism) which is unrelated to hemochromatosis.
*Preload: increased, cardiac contractility: decreased, afterload: increased*
- This combination describes **advanced or dilated cardiomyopathy** where the heart fails to pump effectively, causing volume overload and elevated preload.
- While this can occur in later stages of hemochromatosis, the **first cardiac manifestation** is restrictive (diastolic) dysfunction, not dilated (systolic) dysfunction.
- Decreased contractility develops after prolonged iron exposure damages contractile proteins.
*Preload: increased, cardiac contractility: increased, afterload: decreased*
- This pattern describes hyperdynamic circulation with reduced systemic vascular resistance, which does not occur in iron overload cardiomyopathy.
- Iron deposition causes myocardial stiffness and eventual contractile dysfunction, never enhanced contractility.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 2: Researchers are investigating oncogenes, specifically the KRAS gene that is associated with colon, lung, and pancreatic cancer. They have established that the gain-of-function mutation in this gene increases the chance of cancer development. They are also working to advance the research further to study tumor suppressor genes. Which of the genes below is considered a tumor suppressor gene?
- A. Her2/neu
- B. BRAF
- C. BCL-2
- D. JAK2
- E. Rb (Correct Answer)
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***Rb***
- The **retinoblastoma (Rb)** gene is a classic example of a **tumor suppressor gene**. Its protein product, Rb, plays a critical role in regulating the **cell cycle** by preventing uncontrolled cell division.
- When **Rb is mutated or inactivated**, cells can divide without proper checks, leading to tumor formation, particularly in cases like retinoblastoma.
*Her2/neu*
- **Her2/neu** (also known as ERBB2) is an **oncogene** that encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase involved in cell growth and differentiation.
- Its overexpression or amplification is associated with certain cancers, notably **breast cancer**, but it is not a tumor suppressor.
*BRAF*
- **BRAF** is an **oncogene** that codes for a serine/threonine kinase involved in the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway, which regulates cell growth.
- **Gain-of-function mutations** in BRAF are frequently found in melanoma, thyroid cancer, and colorectal cancer, promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation.
*BCL-2*
- **BCL-2** is an **anti-apoptotic gene**, meaning it prevents programmed cell death. While its overexpression can contribute to cancer by allowing abnormal cells to survive, it is not classified as a tumor suppressor gene.
- Instead, BCL-2 is considered an **oncogene** because mutations or overexpression promote cell survival and inhibit apoptosis.
*JAK2*
- **JAK2** (Janus Kinase 2) is a **proto-oncogene** encoding a tyrosine kinase involved in cytokine receptor signaling, which regulates hematopoiesis.
- **Gain-of-function mutations**, such as JAK2 V617F, are frequently found in **myeloproliferative neoplasms** (e.g., polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, myelofibrosis), leading to uncontrolled blood cell production.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by his friends after a camping trip. He and his friends were in the woods camping when the patient started experiencing severe right upper quadrant abdominal pain after foraging and ingesting some wild mushrooms about 3 hours earlier. The patient is lethargic on exam and appears jaundiced. He has scleral icterus and is severely tender to palpation in the right upper quadrant. He has scattered petechiae on his extremities. Liver function tests are:
Serum:
Na+: 134 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 4.2 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 50 mg/dL
Glucose: 100 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.4 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase: 400 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, GOT): 3278 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, GPT): 3045 U/L
gamma-Glutamyltransferase (GGT): 100 U/L
The most likely cause of this patient’s clinical presentation acts by inhibiting which of the following molecules?
- A. RNA polymerase II (Correct Answer)
- B. RNA polymerase III
- C. Topoisomerase
- D. RNA polymerase I
- E. Prokaryote RNA polymerase
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***RNA polymerase II***
- The clinical presentation with severe hepatotoxicity (jaundice, elevated AST/ALT, RUQ pain, petechiae, lethargy) following wild mushroom ingestion is highly suggestive of poisoning by **Amanita phalloides** (death cap mushroom).
- The primary toxin in *Amanita phalloides* is **alpha-amanitin**, which specifically inhibits **RNA polymerase II**, thereby halting mRNA synthesis and leading to cellular death, particularly in rapidly dividing cells and hepatocytes.
*RNA polymerase III*
- **RNA polymerase III** is responsible for synthesizing **tRNA** and **5S ribosomal RNA**.
- While essential for cell function, it is not the primary target of amanitin toxins, and its inhibition would not directly cause the severe hepatotoxicity observed.
*Topoisomerase*
- **Topoisomerases** are enzymes that regulate the supercoiling of **DNA** during replication, transcription, and repair.
- While critical for cell survival, they are not the target of the toxins found in *Amanita phalloides* mushrooms.
*RNA polymerase I*
- **RNA polymerase I** is responsible for synthesizing most **ribosomal RNA (rRNA)**.
- While also essential, it is less sensitive to **alpha-amanitin** than RNA polymerase II, requiring much higher concentrations for inhibition.
*Prokaryote RNA polymerase*
- **Prokaryote RNA polymerase** is fundamentally different in structure and function from eukaryotic RNA polymerases.
- **Alpha-amanitin** specifically targets eukaryotic RNA polymerases and has no significant inhibitory effect on prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 4: E. coli has the ability to regulate its enzymes to break down various sources of energy when available. It prevents waste by the use of the lac operon, which encodes a polycistronic transcript. At a low concentration of glucose and absence of lactose, which of the following occurs?
- A. Decreased cAMP levels result in poor binding to the catabolite activator protein
- B. Increased cAMP levels result in binding to the catabolite activator protein (Correct Answer)
- C. Increased allolactose levels bind to the repressor
- D. Repressor releases from lac operator
- E. Transcription of the lac Z, Y, and A genes increase
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***Increased cAMP levels result in binding to the catabolite activator protein***
- In the absence of glucose, **adenylate cyclase** activity increases, leading to higher levels of **cAMP**.
- **cAMP** then binds to the **catabolite activator protein (CAP)**, forming the **cAMP-CAP complex**, which is crucial for activating lac operon transcription in the absence of glucose.
*Decreased cAMP levels result in poor binding to the catabolite activator protein*
- **Decreased glucose levels** actually lead to **increased cAMP** synthesis, not decreased.
- High **cAMP** levels enhance, not hinder, its binding to **CAP**.
*Increased allolactose levels bind to the repressor*
- **Allolactose** is an inducer that forms in the presence of **lactose**, which is stated to be absent in this scenario.
- Therefore, **allolactose levels** would be low, and it would not bind to the **repressor**.
*Repressor releases from lac operator*
- The **repressor protein** is bound to the **lac operator** in the absence of lactose.
- For the **repressor to be released**, **allolactose** (formed from lactose) must be present to bind to it.
*Transcription of the lac Z, Y, and A genes increase*
- While **cAMP-CAP binding** would promote transcription, the **absence of lactose** means the **repressor remains bound** to the operator.
- This binding effectively blocks RNA polymerase, preventing significant transcription of the **lac Z, Y, and A genes**, regardless of high **cAMP** levels.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 5: A 55-year-old man, who was recently diagnosed with tuberculosis, presents to his primary care provider as part of his routine follow-up visit every month. He is currently in the initial phase of anti-tubercular therapy. His personal and medical histories are relevant for multiple trips to Southeast Asia as part of volunteer activities and diabetes of 5 years duration, respectively. A physical examination is unremarkable except for a visual abnormality on a color chart; he is unable to differentiate red from green. The physician suspects the visual irregularity as a sign of toxicity due to one of the drugs in the treatment regimen. Which of the following is the mechanism by which this medication acts in the treatment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
- A. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- B. Inhibition of arabinosyltransferase (Correct Answer)
- C. Inhibition of protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit
- D. Inhibition of mycolic acid synthesis
- E. Induction of free radical metabolites
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***Inhibition of arabinosyltransferase***
- The patient's inability to differentiate red from green is a classic symptom of **optic neuritis** (specifically retrobulbar neuritis), a known side effect of **ethambutol**.
- **Ethambutol** works by inhibiting **arabinosyltransferase**, an enzyme essential for the synthesis of the mycobacterial cell wall component **arabinogalactan**.
*Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **rifampin**, another first-line anti-TB drug.
- While rifampin has various side effects (e.g., **hepatotoxicity**, **red-orange discoloration of bodily fluids**), **optic neuritis** is not its primary or common adverse effect.
*Inhibition of protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **aminoglycosides** (e.g., streptomycin, amikacin) and **tetracyclines**, which are used in certain TB regimens, especially for **drug-resistant cases**.
- Common side effects include **ototoxicity** and **nephrotoxicity**, not optic neuritis.
*Inhibition of mycolic acid synthesis*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **isoniazid**, a cornerstone anti-TB drug.
- Isoniazid's main side effects are **hepatotoxicity** and **peripheral neuropathy**, which is often prevented by **pyridoxine (vitamin B6) supplementation**.
*Induction of free radical metabolites*
- This is the mechanism by which **pyrazinamide** is thought to act, although its precise mechanism is not fully understood.
- Pyrazinamide is primarily associated with **hepatotoxicity** and **hyperuricemia** leading to **gout**, not optic neuritis.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 6: A 37-year-old man previously treated with monotherapy for latent tuberculosis develops new-onset cough, night sweats and fever. He produces a sputum sample that is positive for acid-fast bacilli. Resistance testing of his isolated bacteria finds a mutation in the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. To which of the following antibiotics might this patient's infection be resistant?
- A. Isoniazid
- B. Rifampin (Correct Answer)
- C. Pyrazinamide
- D. Streptomycin
- E. Ethambutol
Initiation of transcription Explanation: **Rifampin is correct**
- A mutation in the **DNA-dependent RNA polymerase** gene (*rpoB*) is the primary mechanism of resistance to **rifampin**.
- **Rifampin** specifically targets bacterial **RNA polymerase**, inhibiting RNA synthesis.
*Isoniazid is incorrect*
- Resistance to **isoniazid** is typically associated with mutations in the **katG** gene (encoding catalase-peroxidase) or the **inhA** gene (involved in mycolic acid synthesis).
- It does not directly affect **DNA-dependent RNA polymerase**.
*Pyrazinamide is incorrect*
- Resistance to **pyrazinamide** is primarily linked to mutations in the **pncA** gene, which encodes pyrazinamidase, an enzyme required to activate pyrazinamide.
- This drug's mechanism of action and resistance pathways are unrelated to **RNA polymerase**.
*Streptomycin is incorrect*
- Resistance to **streptomycin**, an aminoglycoside, primarily involves mutations in the **rrs** gene (16S rRNA) or the **rpsL** gene (ribosomal protein S12).
- It works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis and is not directly related to **RNA polymerase**.
*Ethambutol is incorrect*
- Resistance to **ethambutol** is mainly due to mutations in the **embB** gene, which encodes arabinosyl transferases involved in arabinogalactan synthesis in the cell wall.
- Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting cell wall synthesis, not **RNA polymerase**.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 7: Although nucleotide addition during DNA replication in prokaryotes proceeds approximately 20-times faster than in eukaryotes, why can much larger amounts of DNA be replicated in eukaryotes in a time-effective manner?
- A. Eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication (Correct Answer)
- B. Eukaryotes have helicase which can more easily unwind DNA strands
- C. Eukaryotes have fewer polymerase types
- D. Eukaryotes have less genetic material to replicate
- E. Eukaryotes have a single, circular chromosome
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***Eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication***
- Eukaryotic chromosomes are much larger than prokaryotic chromosomes and require multiple origins of replication to complete DNA synthesis within a reasonable timeframe.
- Each origin of replication initiates simultaneously, allowing DNA synthesis to occur at many sites along the chromosome, effectively increasing the overall speed of replication.
- This compensates for the slower rate of nucleotide addition by DNA polymerase in eukaryotes compared to prokaryotes.
*Eukaryotes have helicase which can more easily unwind DNA strands*
- While helicase activity is crucial for unwinding DNA, there is no evidence to suggest that eukaryotic helicases are significantly more efficient or faster at unwinding DNA compared to prokaryotic helicases in a way that would account for the large difference in overall replication time.
- The rate of DNA unwinding by helicase is a factor in replication speed, but it does not overcome the fundamental limitation of a single origin of replication in prokaryotes.
*Eukaryotes have fewer polymerase types*
- Eukaryotic cells actually have **more** types of DNA polymerases than prokaryotic cells, each specialized for different functions like replication, repair, and mitochondrial DNA synthesis.
- The number of polymerase types does not directly relate to the speed or efficiency of overall DNA replication in terms of replicating large amounts of DNA.
*Eukaryotes have less genetic material to replicate*
- Eukaryotic organisms typically have significantly **more** genetic material (a larger genome size) than prokaryotic organisms, not less.
- If eukaryotes had less genetic material, the question itself about effective replication of "much larger amounts of DNA" would be contradictory.
*Eukaryotes have a single, circular chromosome*
- Eukaryotic cells have **multiple, linear chromosomes** within a membrane-bound nucleus, not a single circular chromosome.
- Prokaryotic cells typically have a single, circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region.
- The linear structure of eukaryotic chromosomes with multiple origins is actually what enables efficient replication of large genomes, making this statement both factually incorrect and contradictory to the mechanism in question.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 8: You are culturing bacteria on lactose-rich and glucose-free media. These bacteria regulate gene expression via the lac operon to ferment lactose into glucose and galactose for their metabolic needs. You add free glucose to the media. The addition of glucose reduces lactose fermentation secondary to which of the following changes?
- A. Increased level of cAMP
- B. Increased binding by the repressor to the operator
- C. Decreased binding by the repressor to the operator
- D. Decreased level of cAMP (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased binding of CAP to DNA
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***Decreased level of cAMP***
- The addition of **glucose** leads to a **decrease in intracellular cAMP levels**, which is a key component in catabolite repression.
- Reduced cAMP means less cAMP-CAP complex formation, thus **decreasing the positive regulation** of the *lac* operon.
*Increased level of cAMP*
- An **increased level of cAMP** would occur in the **absence of glucose**, which would then promote the formation of the **cAMP-CAP complex** necessary for *lac* operon activation.
- This would lead to **increased lactose fermentation**, which is the opposite of the scenario described.
*Increased binding by the repressor to the operator*
- The **repressor protein** binds to the operator in the **absence of lactose** to inhibit transcription.
- Lactose's presence (even with glucose) would lead to the conversion into **allolactose**, which binds to the repressor and *prevents* its binding to the operator.
*Decreased binding by the repressor to the operator*
- This scenario would happen in the **presence of lactose**, as **allolactose** would bind to the repressor and cause it to dissociate from the operator.
- While lactose is present in the initial setup, the question focuses on the *inhibitory effect of glucose*, which is independent of repressor binding related to lactose.
*Increased binding of CAP to DNA*
- **CAP (catabolite activator protein)** binding to DNA is *stimulated* by its association with **cAMP**.
- Since glucose leads to decreased cAMP, it would result in **decreased CAP binding to DNA**, thereby reducing *lac* operon transcription.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is studying the genotypes of wingless fruit flies using full exome sequencing. Compared to wild-type winged fruit flies, the wingless fruit flies are found to have a point mutation in the gene encoding wing bud formation during embryogenesis. The point mutation in the gene causes the mRNA transcript to have a 'UUG' segment instead of an 'AUG' segment. Which of the following processes is most likely affected by this mutation?
- A. Cleavage of 5' intron
- B. Binding of met-tRNA to 40S complex (Correct Answer)
- C. Catalyzation of peptide bond formation
- D. Dissociation of mRNA from ribosome complex
- E. Shift of peptidyl-tRNA from A to P site
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***Binding of met-tRNA to 40S complex***
- The **start codon AUG** is essential for the initiation of translation, as it signals where the ribosome should begin synthesizing the polypeptide chain and recruits the initiator tRNA carrying **methionine (met-tRNA)** to the 40S ribosomal subunit.
- A mutation from **AUG to UUG** means the ribosome will not recognize the correct start site, preventing the initial binding of met-tRNA and the formation of the **initiation complex**.
*Cleavage of 5' intron*
- This process is part of **RNA splicing**, which occurs after transcription in the nucleus, where introns are removed from the **pre-mRNA**.
- The described mutation affects a **codon sequence** in the mRNA, which is a post-splicing event related to translation, not intron cleavage.
*Catalyzation of peptide bond formation*
- This occurs during the **elongation phase of translation**, where the peptidyl transferase activity of the ribosome forms peptide bonds between amino acids.
- The mutation prevents the **initiation of translation** altogether, meaning elongation and peptide bond formation will not even begin.
*Dissociation of mRNA from ribosome complex*
- This event happens at the **termination phase of translation**, when a stop codon is reached, and release factors cause the ribosome to dissociate from the mRNA and the newly synthesized polypeptide.
- The mutation prevents the **start of translation**, so the ribosome will not reach the stage where it would dissociate from the mRNA.
*Shift of peptidyl-tRNA from A to P site*
- This is a step in the **elongation phase of translation**, specifically the **translocation process**, where the ribosome moves along the mRNA, shifting the peptidyl-tRNA from the A (aminoacyl) site to the P (peptidyl) site.
- Since the **initiation of translation** is blocked by the mutated start codon, the ribosome cannot begin polypeptide synthesis, and thus, elongation steps like translocation cannot occur.
Initiation of transcription US Medical PG Question 10: A 82-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from a retirement community after she was found down during the evening. On presentation, she complains that she experienced several hours of nausea, vomiting, crampy abdominal pain, and diarrhea prior to blacking out. She said that she cannot recall any factors that may have triggered her symptoms; however, she recalls that some of her friends with whom she eats also had similar symptoms earlier in the day and were brought to the hospital. They often go for walks and occasionally cook for themselves from a garden that they keep in the woods behind the facility. One of the residents on the team recalls seeing other patients from this facility earlier today, one of whom presented with kidney failure and scleral icterus prior to passing away. The enzyme most likely affected in this case has which of the following functions?
- A. Synthesis of large ribosomal RNA
- B. Synthesis of messenger RNA (Correct Answer)
- C. Synthesis of small nucleolar RNA
- D. Synthesis of 5S ribosomal RNA
- E. Synthesis of transfer RNA
Initiation of transcription Explanation: ***Synthesis of messenger RNA***
- The clinical presentation (nausea, vomiting, crampy abdominal pain, diarrhea, hepatotoxicity with scleral icterus, acute kidney injury, and death), combined with the history of eating from a **garden in the woods**, is highly suggestive of **Amanita phalloides (death cap mushroom)** poisoning.
- The primary toxin is **alpha-amanitin**, which specifically and potently inhibits **RNA polymerase II**.
- **RNA polymerase II** is responsible for transcribing all **messenger RNA (mRNA)** in eukaryotic cells, which is essential for protein synthesis.
- Inhibition of mRNA synthesis leads to **inability to produce new proteins**, causing hepatocyte and renal tubular cell death, explaining the liver failure (jaundice, scleral icterus) and kidney failure seen in severe cases.
- This is the **classic biochemical mechanism** tested in alpha-amanitin poisoning questions.
*Synthesis of large ribosomal RNA*
- Large ribosomal RNAs (28S, 18S, 5.8S rRNA) are synthesized by **RNA polymerase I**, not RNA polymerase II.
- Alpha-amanitin has **minimal effect** on RNA polymerase I, even at high concentrations.
- This enzyme is not the primary target in mushroom poisoning.
*Synthesis of 5S ribosomal RNA*
- The 5S ribosomal RNA is synthesized by **RNA polymerase III**, not RNA polymerase II.
- RNA polymerase III is relatively **resistant** to alpha-amanitin compared to RNA polymerase II.
- While very high concentrations may affect it, this is not the primary mechanism of toxicity.
*Synthesis of transfer RNA*
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) is synthesized by **RNA polymerase III**, not RNA polymerase II.
- Like 5S rRNA, RNA polymerase III is much less sensitive to alpha-amanitin inhibition.
- This is not the primary target explaining the clinical toxicity.
*Synthesis of small nucleolar RNA*
- While **RNA polymerase II** does transcribe some small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), this is **not its primary or most clinically relevant function**.
- Most snoRNAs are encoded within introns of host genes and processed from pre-mRNA transcripts.
- The critical toxicity of alpha-amanitin results from inhibition of **mRNA synthesis**, not snoRNA synthesis.
- In medical education and board examinations, RNA polymerase II inhibition by alpha-amanitin is tested in the context of **mRNA synthesis**.
More Initiation of transcription US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.