Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 1: Which receptor type mediates the slow phase of synaptic transmission in autonomic ganglia?
- A. Muscarinic (M3)
- B. Muscarinic (M2)
- C. Muscarinic (M1) (Correct Answer)
- D. Nicotinic (N2)
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***Muscarinic (M1)***
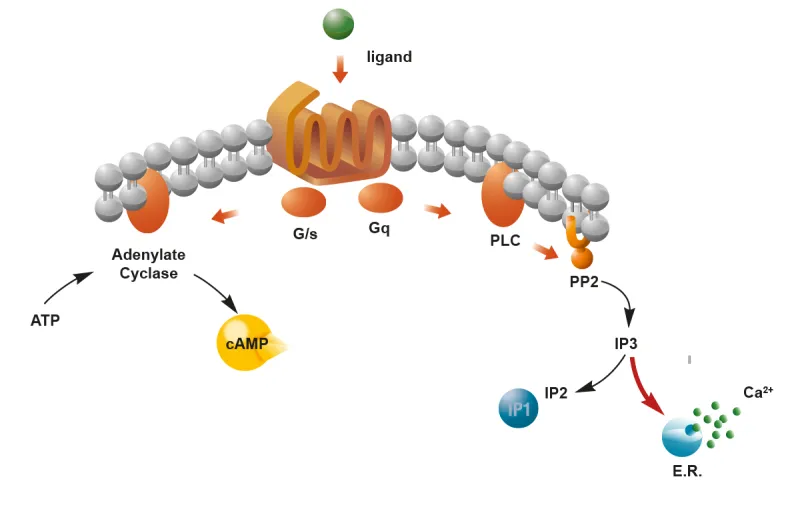
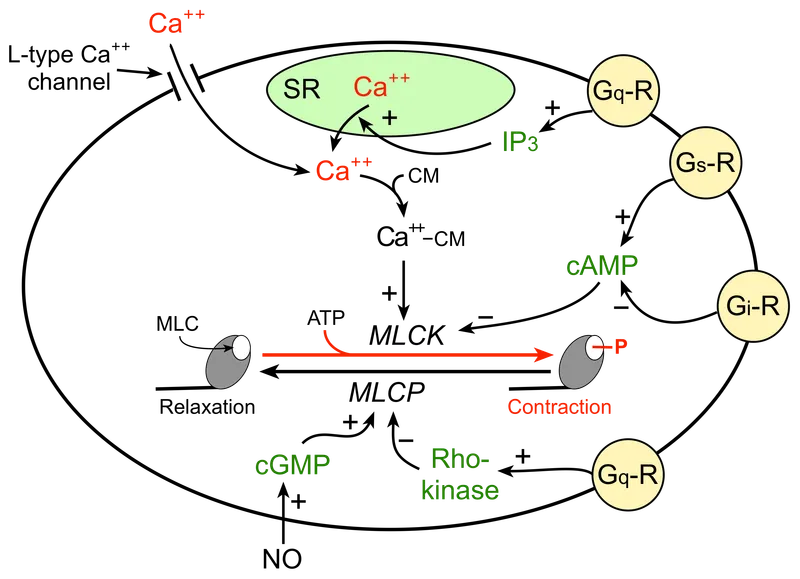
- **M1 receptors** are **Gq-protein coupled receptors** that activate phospholipase C, leading to increased intracellular calcium and diacylglycerol, which mediates the slow excitatory postsynaptic potential in autonomic ganglia.
- This activation results in a **slow depolarization** that prolongs the excitability of ganglionic neurons after the initial fast synaptic transmission.
*Muscarinic (M3)*
- **M3 receptors** are primarily found on **smooth muscle**, glands, and endothelium, mediating contraction, secretion, and vasodilation, respectively.
- While also **Gq-protein coupled**, their role in autonomic ganglia is not the main mediator of the slow phase of synaptic transmission.
*Muscarinic (M2)*
- **M2 receptors** are **Gi-protein coupled receptors** mainly found in the heart, mediating decreased heart rate and contractility.
- In autonomic ganglia, M2 receptors could have a modulatory role, but they are not responsible for the slow excitatory phase of synaptic transmission.
*Nicotinic (N2)*
- **Nicotinic N2 receptors** (also known as **NN or neuronal nicotinic receptors**) mediate the **fast excitatory postsynaptic potential** (EPSP) in autonomic ganglia by opening ion channels.
- This leads to rapid depolarization and action potential generation, which is distinct from the **slower, prolonged phase** of transmission.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator is studying a drug that acts on a G protein-coupled receptor in the pituitary gland. Binding of the drug to this receptor leads to increased production of inositol triphosphate (IP3) in the basophilic cells of the anterior pituitary. Administration of this drug every 90 minutes is most likely to be beneficial in the treatment of which of the following conditions?
- A. Prostate cancer
- B. Variceal bleeding
- C. Central diabetes insipidus
- D. Anovulatory infertility (Correct Answer)
- E. Hyperkalemia
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***Anovulatory infertility***
- The drug's action on a G protein-coupled receptor leading to increased **IP3 production** in pituitary basophils suggests activation of the **gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor**.
- **Pulsatile administration** (e.g., every 90 minutes) of GnRH or its agonists is crucial for stimulating the release of **FSH and LH**, which can induce ovulation in women with anovulatory infertility due to hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction.
*Prostate cancer*
- While GnRH agonists are used in prostate cancer, they are typically administered **continuously or in depot forms** to desensitize the GnRH receptor, thereby suppressing testosterone production.
- **Pulsatile administration** would rather stimulate testosterone release, which is detrimental in prostate cancer.
*Variceal bleeding*
- **Variceal bleeding** is primarily managed with vasoconstrictors like **octreotide** (a somatostatin analog) or **vasopressin**, which are unrelated to GnRH receptor activation.
- The mechanism of action described (increased IP3 in pituitary basophils) does not align with treatments for variceal bleeding.
*Central diabetes insipidus*
- **Central diabetes insipidus** is caused by a deficiency in **vasopressin (ADH)**, which regulates water balance in the kidneys.
- Treatment involves synthetic ADH (**desmopressin**), not drugs acting on GnRH receptors and affecting pituitary basophils.
*Hyperkalemia*
- **Hyperkalemia** is an electrolyte imbalance characterized by high potassium levels and is managed with medications that shift potassium intracellularly (e.g., insulin, beta-agonists) or promote its excretion (e.g., diuretics, potassium binders).
- The described drug action on pituitary GnRH receptors is unrelated to potassium homeostasis.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 3: A 59-year-old man is brought to the emergency department one hour after developing shortness of breath and “squeezing” chest pain that began while he was mowing the lawn. He has asthma, hypertension, and erectile dysfunction. Current medications include salmeterol, amlodipine, lisinopril, and vardenafil. His pulse is 110/min and blood pressure is 122/70 mm Hg. Physical examination shows diaphoresis. An ECG shows sinus tachycardia. Sublingual nitroglycerin is administered. Five minutes later, his pulse is 137/min and his blood pressure is 78/40 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of this patient's hypotension?
- A. Bradykinin accumulation
- B. Cyclic GMP elevation (Correct Answer)
- C. Decreased nitric oxide production
- D. Calcium channel antagonism
- E. Alpha-1 receptor antagonism
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***Cyclic GMP elevation***
- The patient's severe hypotension after nitroglycerin administration is likely due to an interaction with **vardenafil**, a **phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor**.
- Both nitroglycerin and vardenafil increase levels of **cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)**, leading to excessive systemic vasodilation and profound hypotension.
*Bradykinin accumulation*
- This is a well-known side effect of **ACE inhibitors (e.g., lisinopril)**, manifesting primarily as a dry cough or angioedema.
- While the patient is on lisinopril, bradykinin accumulation does not immediately cause severe hypotension following nitroglycerin administration in this manner.
*Decreased nitric oxide production*
- Nitric oxide (NO) is a **vasodilator**; decreased production would typically lead to vasoconstriction and *increased* blood pressure, not hypotension.
- Nitroglycerin, in fact, works by **increasing NO production** or release to induce vasodilation.
*Calcium channel antagonism*
- **Amlodipine** is a calcium channel blocker, which can cause vasodilation and lower blood pressure.
- However, the sudden and severe drop in blood pressure observed *after* nitroglycerin is not primarily due to an additive effect of amlodipine in the way PDE5 inhibitors interact.
*Alpha-1 receptor antagonism*
- Alpha-1 receptor antagonists (e.g., prazosin, doxazosin) cause **vasodilation** by blocking norepinephrine's action on blood vessels.
- While they can cause orthostatic hypotension, the patient is not on such a medication, and this mechanism does not explain the acute, severe drop seen after nitroglycerin.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 4: A 60-year-old man presents to the office for a scheduled follow-up visit. He has had hypertension for the past 30 years and his current anti-hypertensive medications include lisinopril (40 mg/day) and hydrochlorothiazide (50 mg/day). He follows most of the lifestyle modifications recommended by his physician, but is concerned about his occasional occipital headaches in the morning. His blood pressure is 160/98 mm Hg. The physician adds another drug to his regimen that acts centrally as an α2-adrenergic agonist. Which of the following second messengers is involved in the mechanism of action of this new drug?
- A. Calcium ions
- B. Inositol triphosphate
- C. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- D. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (Correct Answer)
- E. Diacylglycerol
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***Cyclic adenosine monophosphate***
- The physician likely added **clonidine or methyldopa**, both of which are **central α2-adrenergic agonists** used to treat hypertension.
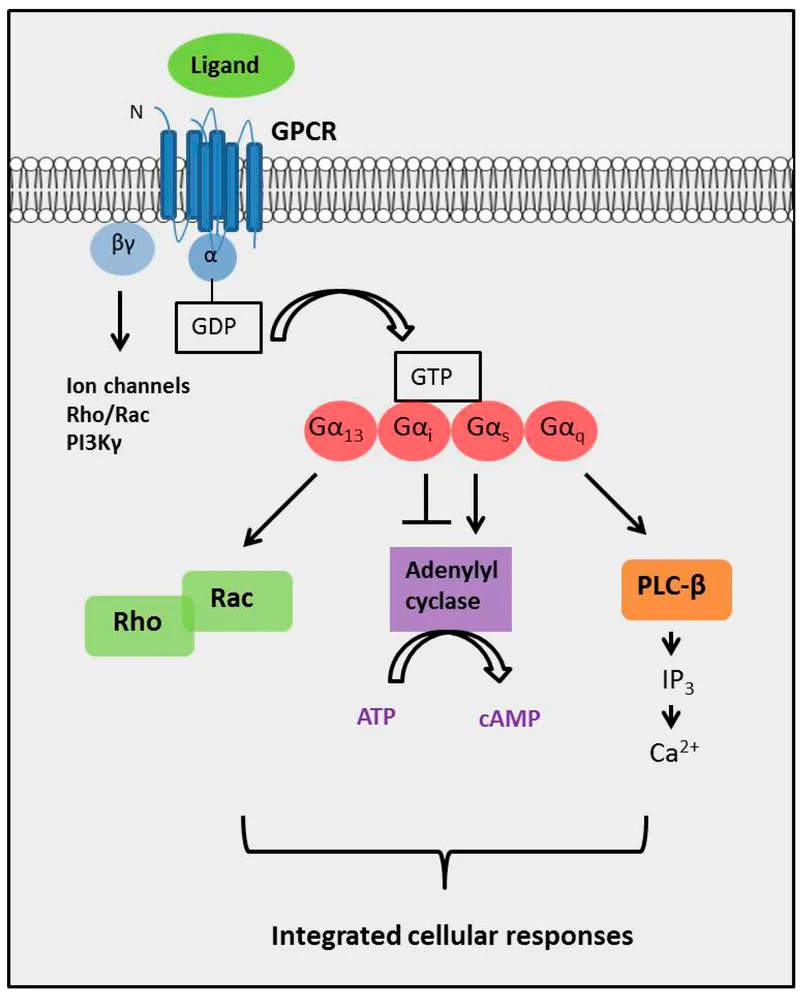
- Activation of **α2-adrenergic receptors** leads to the **inhibition of adenylyl cyclase** and a decrease in **intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels**, which is the second messenger.
*Calcium ions*
- While calcium ions are crucial second messengers in many cellular processes, they are primarily involved in the mechanism of action of **α1-adrenergic receptors** and **voltage-gated calcium channels**, not directly inhibited by α2-agonists.
- **α2-adrenergic agonism** primarily acts to *reduce* neuronal excitability, which can indirectly affect calcium flux but does not directly involve calcium as the primary second messenger.
*Inositol triphosphate*
- **Inositol triphosphate (IP3)** is a second messenger primarily associated with the activation of **Gq protein-coupled receptors**, leading to the release of intracellular calcium.
- This pathway is characteristic of **α1-adrenergic receptors**, which cause vasoconstriction, and is antagonistic to the α2-agonist mechanism.
*Cyclic guanosine monophosphate*
- **Cyclic GMP (cGMP)** is a key second messenger in processes such as **vasodilation mediated by nitric oxide** and the action of ANP/BNP.
- **α2-adrenergic agonists** do not directly modulate cGMP levels as their primary mechanism of action.
*Diacylglycerol*
- **Diacylglycerol (DAG)** is a second messenger, along with IP3, produced from the hydrolysis of **PIP2** by phospholipase C, following activation of **Gq protein-coupled receptors**.
- This pathway is associated with **α1-adrenergic receptor activation**, not the inhibitory pathway initiated by central α2-adrenergic agonists.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 5: A 70-year-old male presents to his primary care provider complaining of decreased sexual function. He reports that over the past several years, he has noted a gradual decline in his ability to sustain an erection. He used to wake up with erections but no longer does. His past medical history is notable for diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and a prior myocardial infarction. He takes metformin, glyburide, aspirin, and atorvastatin. He drinks 2-3 drinks per week and has a 25 pack-year smoking history. He has been happily married for 40 years. He retired from his job as a construction worker 5 years ago and has been enjoying retirement with his wife. His physician recommends starting a medication that is also used in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Which of the following is a downstream effect of this medication?
- A. Increase cGMP degradation
- B. Increase cAMP production
- C. Increase PDE5 activity
- D. Decrease nitric oxide production
- E. Decrease cGMP degradation (Correct Answer)
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***Decrease cGMP degradation***
- The medication described is likely a **phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor** (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil), used for erectile dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension.
- These drugs work by inhibiting the enzyme PDE5, which is responsible for the breakdown of **cyclic GMP (cGMP)**, thereby increasing cGMP levels.
*Increase cGMP degradation*
- This is the **opposite** of the medication's intended effect, as it would lead to reduced cGMP levels and worsen erectile dysfunction.
- An increase in cGMP degradation would diminish the **vasodilatory** effects necessary for erection.
*Increase cAMP production*
- This medication primarily affects the **cGMP pathway**, not directly boosting cyclic AMP (cAMP) production.
- While cAMP also plays a role in vasodilation, it's regulated by different enzymes and pathways, such as **adenylyl cyclase**.
*Increase PDE5 activity*
- This would lead to a more **rapid breakdown of cGMP**, counteracting the goal of the medication and exacerbating erectile dysfunction.
- The medication's mechanism is specifically designed to **inhibit PDE5 activity**.
*Decrease nitric oxide production*
- **Nitric oxide (NO)** production is a **precursor** to cGMP synthesis, as NO activates guanylate cyclase to produce cGMP.
- Decreasing NO production would **reduce cGMP levels**, which is contrary to the action of PDE5 inhibitors.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 6: A 59-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-year history of increased urinary frequency, weak urinary stream, and occasional straining to void urine. Rectal examination shows a large, nontender prostate without asymmetry or nodularity. His serum creatinine, prostate-specific antigen, and urinalysis are all within the reference range. A diagnosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia is made, and treatment with tamsulosin is begun. Which of the following changes in intracellular messaging is most likely to occur in response to this drug?
- A. Decreased activity of phospholipase C (Correct Answer)
- B. Increased activity of protein kinase C
- C. Increased production of diacylglycerol
- D. Decreased activity of protein kinase A
- E. Increased activity of adenylyl cyclase
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***Decreased activity of phospholipase C***
- **Tamsulosin** is an **alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist** that works by blocking alpha-1 receptors on the smooth muscle of the prostate and bladder neck, causing relaxation.
- Alpha-1 receptor activation normally utilizes the **Gq protein pathway**, which leads to the activation of phospholipase C, thus blocking these receptors decreases phospholipase C activity.
*Increased activity of protein kinase C*
- **Protein kinase C** is activated by **diacylglycerol (DAG)** and intracellular calcium, both of which are products of the phospholipase C pathway.
- Since tamsulosin decreases phospholipase C activity, it would subsequently lead to a *decrease*, not an increase, in protein kinase C activity.
*Increased production of diacylglycerol*
- **Diacylglycerol (DAG)** is a secondary messenger produced by the action of **phospholipase C** on **phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2)**.
- As tamsulosin inhibits the alpha-1 receptor and thus phospholipase C activity, it would *decrease* the production of DAG.
*Decreased activity of protein kinase A*
- **Protein kinase A (PKA)** is typically activated by **cyclic AMP (cAMP)**, which is produced by **adenylyl cyclase**.
- The alpha-1 receptor pathway (affected by tamsulosin) primarily involves phospholipase C, not adenylyl cyclase or protein kinase A.
*Increased activity of adenylyl cyclase*
- **Adenylyl cyclase** is responsible for converting **ATP to cAMP**, which is part of the Gs protein signaling pathway (beta-adrenergic receptors) or Gi protein pathway (alpha-2 adrenergic receptors).
- Tamsulosin specifically targets **alpha-1 adrenergic receptors** which are coupled to **Gq proteins**, not Gs or Gi proteins; therefore, it does not directly affect adenylyl cyclase activity.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old woman has a total thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma. She complains of tingling around the mouth 11 hours after the operation. Her condition rapidly deteriorates with difficulty breathing and chest tightness. Which of the following best represent the signaling pathway of the deficient hormone responsible for this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)
- B. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) (Correct Answer)
- C. Intracellular receptors
- D. Receptor tyrosine kinase
- E. Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)***
- The patient's symptoms of perioral tingling, difficulty breathing, and chest tightness after total thyroidectomy suggest **hypocalcemia**, likely due to accidental removal or damage to the **parathyroid glands** during surgery.
- The deficient **parathyroid hormone (PTH)** acts primarily through the **cAMP second messenger system** to increase serum calcium levels.
*Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)*
- **cGMP** is a second messenger system primarily involved in mediating the effects of hormones like **atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** and **nitric oxide**, which are unrelated to calcium homeostasis and parathyroid function.
- This pathway is not the primary mechanism of action for **PTH**.
*Intracellular receptors*
- **Intracellular receptors** are typically used by **steroid hormones** (e.g., cortisol, estrogen) and **thyroid hormones**, which are lipid-soluble and can cross the cell membrane.
- **PTH** is a peptide hormone and acts on cell surface receptors.
*Receptor tyrosine kinase*
- **Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)** are transmembrane receptors involved in signaling pathways for hormones like **insulin** and **growth factors**, promoting cell growth, differentiation, and metabolism.
- This is not the primary signaling pathway for **PTH**.
*Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)*
- The **IP3/DAG (diacylglycerol)** pathway is another common second messenger system used by various hormones (e.g., **vasopressin, oxytocin, TRH**), leading to the release of intracellular calcium.
- While it involves calcium signaling, it is not the primary or most characteristic pathway for **PTH** action, which predominantly utilizes **cAMP**.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 8: An investigator is studying the principles of cell-to-cell signaling of the autonomic nervous system. It is found that the adrenal medulla has receptors that, when activated, result in the immediate opening of Na+, Ca2+, and K+ channels, which subsequently leads to the secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine. These receptors are structurally most similar to which of the following receptors?
- A. Alpha 1 receptors of the bladder neck
- B. D2 receptors of the basal ganglia
- C. M2 receptors of heart
- D. NM receptors of the quadriceps femoris muscle (Correct Answer)
- E. H2 receptors of the stomach
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***NM receptors of the quadriceps femoris muscle***
- The adrenal medulla's chromaffin cells are modified **postganglionic sympathetic neurons** that release catecholamines upon stimulation by preganglionic neurons.
- The activation of **Na+, Ca2+, and K+ channels** leading to rapid depolarization and neurotransmitter release is characteristic of **nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (NM type)**, which are ligand-gated ion channels.
*Alpha 1 receptors of the bladder neck*
- **Alpha-1 receptors** are **G-protein coupled receptors** that primarily activate phospholipase C, leading to increased intracellular calcium and smooth muscle contraction.
- Their activation does not directly result in the immediate opening of Na+, Ca2+, and K+ channels.
*D2 receptors of the basal ganglia*
- **D2 receptors** are **G-protein coupled receptors**, specifically inhibitory (Gi-coupled), that decrease adenylyl cyclase activity and reduce intracellular cAMP.
- They do not function as direct ligand-gated ion channels.
*M2 receptors of heart*
- **M2 receptors** are **G-protein coupled receptors** (Gi-coupled) that decrease heart rate by inhibiting adenylyl cyclase and opening potassium channels indirectly via G-protein subunits.
- While they affect ion channels, this is an indirect G-protein mediated process, not a direct ligand-gated ion channel mechanism.
*H2 receptors of the stomach*
- **H2 receptors** are **G-protein coupled receptors** (Gs-coupled) that increase adenylyl cyclase activity, leading to increased cAMP and stimulation of gastric acid secretion.
- They are not ligand-gated ion channels and do not directly open Na+, K+, and Ca2+ channels.
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 9: An 11-month-old boy is brought to a pediatrician by his parents with a recurrent cough, which he has had since the age of 2 months. He has required 3 hospitalizations for severe wheezing episodes. His mother also mentions that he often has diarrhea. The boy’s detailed history reveals that he required hospitalization for meconium ileus during the neonatal period. Upon physical examination, his temperature is 37.0°C (98.6ºF), pulse rate is 104/min, respiratory rate is 40/min, and blood pressure is 55/33 mm Hg. An examination of the boy’s respiratory system reveals the presence of bilateral wheezing and scattered crepitations. An examination of his cardiovascular system does not reveal any abnormality. His length is 67.3 cm (26.5 in) and weight is 15 kg (33 lbs). His sweat chloride level is 74 mmol/L. His genetic evaluation confirms that he has an autosomal recessive disorder resulting in a dysfunctional membrane-bound protein. Which of the following best describes the mechanism associated with the most common mutation that causes this disorder?
- A. Decreased chloride transport through the protein
- B. Disordered regulation of the protein
- C. Decreased transcription of the protein due to splicing defect
- D. Complete absence of the protein
- E. Defective maturation and early degradation of the protein (Correct Answer)
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***Defective maturation and early degradation of the protein***
- The clinical picture (recurrent cough, wheezing, diarrhea, meconium ileus, elevated sweat chloride, autosomal recessive inheritance) strongly points to **cystic fibrosis (CF)**. The most common mutation in CF is **F508del**, which leads to misfolding of the **CFTR protein**, causing retention in the endoplasmic reticulum and subsequent degradation before reaching the cell membrane.
- This **defective processing and early degradation** result in a significant reduction or absence of functional CFTR protein at the cell surface, leading to impaired chloride transport.
*Decreased chloride transport through the protein*
- While **decreased chloride transport** is the ultimate functional consequence of cystic fibrosis, it is not the direct mechanism associated with the **F508del mutation's impact** on the CFTR protein itself.
- This option describes the **physiological result** of the protein defect, not the cellular/molecular mechanism of the most common mutation.
*Disordered regulation of the protein*
- **Disordered regulation** could be a potential mechanism for some CFTR mutations (Class IV mutations), affecting how the channel opens and closes or responds to signaling.
- However, for the **F508del mutation** (Class II mutation), the primary issue is the **lack of properly localized protein** due to misfolding and degradation, rather than a problem with the regulation or gating of the protein once it reaches the membrane.
*Decreased transcription of the protein due to splicing defect*
- **Decreased transcription** or **splicing defects** (Class I and V mutations) would result in reduced mRNA levels or incorrectly formed mRNA, leading to less protein synthesis.
- The **F508del mutation** involves a deletion of three nucleotides in exon 10, leading to a missing phenylalanine at position 508. Importantly, **transcription and splicing occur normally**; the mRNA is produced correctly. The problem arises at the **post-translational level** with protein folding, not at the transcriptional or splicing level.
*Complete absence of the protein*
- While functional CFTR protein is largely absent at the cell surface in F508del, the protein is **initially synthesized** in the endoplasmic reticulum.
- The problem is its **misfolding and rapid degradation**, preventing it from reaching the membrane, rather than a complete failure of protein synthesis from the outset (which would be seen in nonsense or frameshift mutations causing Class I defects).
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG Question 10: A research team discovers a novel bacterial toxin that causes severe hypotension in infected patients. In vitro studies show the toxin ADP-ribosylates a specific amino acid on Gq alpha subunits, preventing their activation by GPCRs. Patients develop hypotension despite elevated levels of vasopressin, angiotensin II, and endothelin-1. Synthesize the pathophysiological mechanism explaining why multiple vasopressor hormones fail to maintain blood pressure in these patients.
- A. The toxin depletes intracellular ATP preventing myosin-actin interaction
- B. The toxin prevents receptor binding of vasopressor hormones through allosteric inhibition
- C. ADP-ribosylation of Gq prevents PLC activation, blocking IP3-mediated calcium release and vascular smooth muscle contraction (Correct Answer)
- D. ADP-ribosylation increases cAMP levels causing smooth muscle relaxation
- E. The toxin activates Gi proteins causing excessive vasodilation that overwhelms vasoconstrictor signals
Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) Explanation: ***ADP-ribosylation of Gq prevents PLC activation, blocking IP3-mediated calcium release and vascular smooth muscle contraction***
- Vasopressor hormones like **Vasopressin**, **Angiotensin II**, and **Endothelin-1** signal through **Gq-coupled receptors** to trigger **vascular smooth muscle contraction**.
- By ADP-ribosylating the **Gq alpha subunit**, the toxin inhibits **Phospholipase C (PLC)**, preventing the generation of **IP3 and DAG**, which are essential for releasing **intracellular calcium**.
*The toxin prevents receptor binding of vasopressor hormones through allosteric inhibition*
- The toxin targets the **G-protein (intracellular)** rather than the **extracellular binding site** of the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs).
- Since binding still occurs but **signal transduction** is blocked, this describes a post-receptor defect rather than **allosteric inhibition** of the receptor itself.
*The toxin activates Gi proteins causing excessive vasodilation that overwhelms vasoconstrictor signals*
- The prompt explicitly states the toxin modifies the **Gq alpha subunit**, not the **Gi subunit**.
- **Gi protein** activation primarily lowers **cAMP**, whereas the failure of pressors in this case is linked to the lack of **calcium mobilization** via Gq.
*ADP-ribosylation increases cAMP levels causing smooth muscle relaxation*
- Increased **cAMP** (via Gs activation or Gi inhibition) does cause relaxation, but this mechanism is associated with toxins like **Cholera** or **Pertussis**.
- The modification of **Gq** specifically disrupts the **phosphoinositol pathway**, not the **adenylyl cyclase** pathway that regulates cAMP.
*The toxin depletes intracellular ATP preventing myosin-actin interaction*
- ADP-ribosylation is a specific **post-translational modification** using **NAD+** as a substrate, which does not result in systemic **ATP depletion**.
- The failure of contraction is due to a lack of **calcium-calmodulin** activation of **Myosin Light Chain Kinase (MLCK)**, not a lack of energy supply for the motor proteins.
More Second messenger systems (cAMP, cGMP, Ca2+) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.