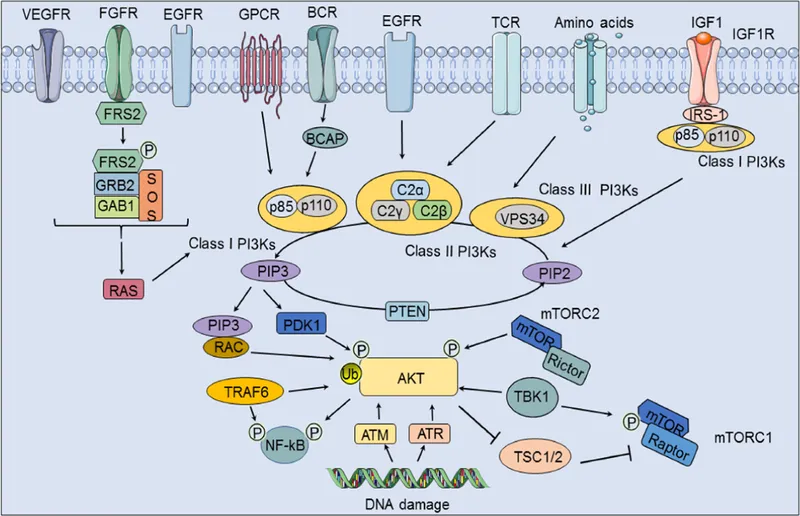
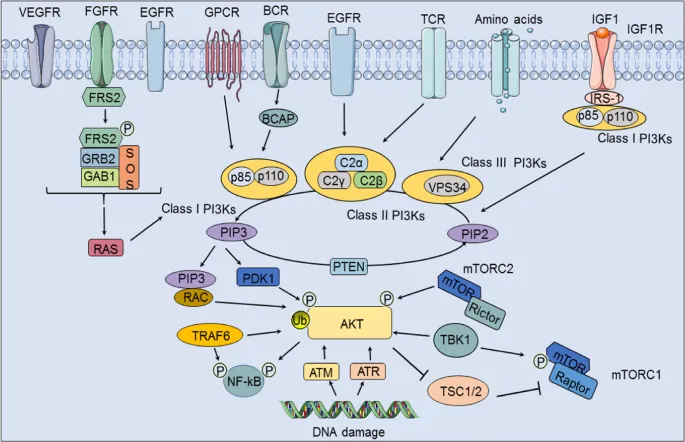
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for PI3K-Akt pathway. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 1: An investigator is studying a drug that acts on a G protein-coupled receptor in the pituitary gland. Binding of the drug to this receptor leads to increased production of inositol triphosphate (IP3) in the basophilic cells of the anterior pituitary. Administration of this drug every 90 minutes is most likely to be beneficial in the treatment of which of the following conditions?
- A. Prostate cancer
- B. Variceal bleeding
- C. Central diabetes insipidus
- D. Anovulatory infertility (Correct Answer)
- E. Hyperkalemia
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***Anovulatory infertility***
- The drug's action on a G protein-coupled receptor leading to increased **IP3 production** in pituitary basophils suggests activation of the **gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor**.
- **Pulsatile administration** (e.g., every 90 minutes) of GnRH or its agonists is crucial for stimulating the release of **FSH and LH**, which can induce ovulation in women with anovulatory infertility due to hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction.
*Prostate cancer*
- While GnRH agonists are used in prostate cancer, they are typically administered **continuously or in depot forms** to desensitize the GnRH receptor, thereby suppressing testosterone production.
- **Pulsatile administration** would rather stimulate testosterone release, which is detrimental in prostate cancer.
*Variceal bleeding*
- **Variceal bleeding** is primarily managed with vasoconstrictors like **octreotide** (a somatostatin analog) or **vasopressin**, which are unrelated to GnRH receptor activation.
- The mechanism of action described (increased IP3 in pituitary basophils) does not align with treatments for variceal bleeding.
*Central diabetes insipidus*
- **Central diabetes insipidus** is caused by a deficiency in **vasopressin (ADH)**, which regulates water balance in the kidneys.
- Treatment involves synthetic ADH (**desmopressin**), not drugs acting on GnRH receptors and affecting pituitary basophils.
*Hyperkalemia*
- **Hyperkalemia** is an electrolyte imbalance characterized by high potassium levels and is managed with medications that shift potassium intracellularly (e.g., insulin, beta-agonists) or promote its excretion (e.g., diuretics, potassium binders).
- The described drug action on pituitary GnRH receptors is unrelated to potassium homeostasis.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 2: A scientist is trying to design a drug to modulate cellular metabolism in the treatment of obesity. Specifically, he is interested in understanding how fats are processed in adipocytes in response to different energy states. His target is a protein within these cells that catalyzes catabolism of an energy source. The products of this reaction are subsequently used in gluconeogenesis or β-oxidation. Which of the following is true of the most likely protein that is being studied by this scientist?
- A. It is stimulated by epinephrine (Correct Answer)
- B. It is inhibited by glucagon
- C. It is inhibited by acetylcholine
- D. It is inhibited by cortisol
- E. It is stimulated by insulin
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***It is stimulated by epinephrine***
- The protein described is likely **hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL)**, which catabolizes **triglycerides** in adipocytes to **glycerol** and **fatty acids**.
- **Epinephrine** (and norepinephrine) stimulates HSL activity via a **cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)** pathway, leading to increased fatty acid release for energy.
*It is inhibited by glucagon*
- **Glucagon primarily acts on the liver** to promote gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, but it does **not directly inhibit HSL** in adipocytes.
- While glucagon has a lipolytic effect, it doesn't inhibit the enzyme that releases fatty acids.
*It is inhibited by acetylcholine*
- **Acetylcholine** is a neurotransmitter involved in the **parasympathetic nervous system**, which generally promotes energy storage.
- It does **not directly inhibit HSL**; its effects on lipid metabolism are indirect and typically involve other pathways.
*It is inhibited by cortisol*
- **Cortisol**, a glucocorticoid, generally **promotes lipolysis** (breakdown of fats) in certain contexts, particularly during stress to provide energy substrates.
- Therefore, it would **not inhibit HSL**; rather, it often enhances its activity or provides a permissive effect for other lipolytic hormones.
*It is stimulated by insulin*
- **Insulin** is an **anabolic hormone** that promotes energy storage, including **lipogenesis** (fat synthesis) and inhibits lipolysis.
- Insulin **inhibits HSL activity** by activating phosphodiesterase, which reduces cAMP levels, thus deactivating PKA and preventing HSL phosphorylation.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 3: A patient with HCC and a long history of alcohol dependence and chronic hepatitis C has been using the mTOR inhibitor sirolimus 100 mg for cancer treatment. Her cancer has shown a partial response. She also has a history of hypertension and poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by diabetic retinopathy. Current medications include enalapril and insulin. She asks her oncologist and hepatologist if she could try everolimus for its purported survival benefit in treating HCC. Based on clinical considerations, which of the following statements is most accurate?
- A. The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg
- B. The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of hypertension
- C. The patient should start everolimus 100 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg
- D. The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of her history of alcohol use disorder and hepatitis C
- E. The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of diabetes (Correct Answer)
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***The patient is not a good candidate for Noxbinle due to her history of diabetes***
- The current medication is sirolimus, an **mTOR inhibitor** and its successor everolimus, also an mTOR inhibitor, is not beneficial for this patient due to her **poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus**.
- mTOR inhibitors, including everolimus, are known to **worsen hyperglycemia** and **accelerate the progression of diabetes**, making it contraindicated in patients with already complicated diabetes.
*The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg*
- There is **no established evidence** that everolimus at any dose offers a superior survival benefit compared to sirolimus in HCC, particularly after a partial response to sirolimus.
- **Switching mTOR inhibitors** without a compelling clinical reason, especially with existing comorbidities, is not standard practice.
*The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of hypertension*
- While mTOR inhibitors can contribute to **hypertension**, this patient is already on **enalapril** for her existing hypertension.
- Her **poorly controlled diabetes** presents a more direct and severe contraindication due to the metabolic side effects of everolimus.
*The patient should start everolimus 100 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg*
- No clinical data supports a **superior survival benefit** of everolimus 100 mg over sirolimus 100 mg in HCC.
- Given the patient's existing **poorly controlled diabetes**, increasing the dose of an mTOR inhibitor or switching to an equivalent dose of another would heighten the risk of severe metabolic complications.
*The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of her history of alcohol use disorder and hepatitis C*
- The patient's history of alcohol dependence and chronic hepatitis C are **risk factors for HCC** but do not directly contraindicate a specific dose of everolimus more than her diabetes.
- While liver impairment due to these conditions might influence dosing of various medications, the **primary concern for everolimus** in this case remains the uncontrolled diabetes.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 4: A researcher is tracing the fate of C-peptide, a product of preproinsulin cleavage. Which of the following is a true statement regarding the fate of C-peptide?
- A. C-peptide exits the cells via a protein channel
- B. C-peptide is further cleaved into insulin
- C. C-peptide is packaged with insulin in secretory vesicles (Correct Answer)
- D. C-peptide is immediately degraded by the proteasome
- E. C-peptide activates an intracellular signaling cascade
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***C-peptide is packaged with insulin in secretory vesicles***
- Preproinsulin is cleaved in the **endoplasmic reticulum** to proinsulin (signal peptide removal), which is then transported to the **Golgi apparatus**.
- In the Golgi, proinsulin is cleaved by **prohormone convertases** into **insulin** and **C-peptide**, and both are stored together in **secretory vesicles** within the pancreatic beta cells.
- Upon stimulation, both insulin and C-peptide are **co-secreted** via exocytosis in equimolar amounts, making C-peptide a useful marker of endogenous insulin secretion.
*C-peptide exits the cells via a protein channel*
- C-peptide exits the beta cells via **exocytosis** of secretory granules, not through specific protein channels.
- It is **co-secreted with insulin** when secretory vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane.
- Its presence in the bloodstream in equimolar amounts with insulin makes it an indirect measure of **insulin secretion**.
*C-peptide is further cleaved into insulin*
- **C-peptide** is a product of proinsulin cleavage, alongside insulin; it is not further processed into insulin.
- Insulin itself is composed of two **peptide chains (A and B)** linked by disulfide bonds, formed after C-peptide is removed from proinsulin.
*C-peptide is immediately degraded by the proteasome*
- C-peptide is not immediately degraded by the **proteasome** upon synthesis.
- After secretion, it circulates in the blood with a **longer half-life** than insulin (approximately 30 minutes versus 4-6 minutes), allowing it to be a useful marker of endogenous insulin production.
- Its degradation occurs primarily in the **kidney**.
*C-peptide activates an intracellular signaling cascade*
- While there is some research suggesting C-peptide may have independent **biological activity** and activate certain signaling pathways extracellularly, its primary role in the context of the insulin synthesis pathway is as a **byproduct** of proinsulin processing.
- Its clinical utility is primarily as a **biomarker** of endogenous insulin secretion, particularly useful in distinguishing between endogenous and exogenous insulin in diabetic patients.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 5: A 33-year-old man with recently diagnosed testicular cancer visits his oncologist to discuss the treatment plan. His left testicle was removed after a thorough workup of a lump. A pelvic CT showed no enlarged lymph nodes and a simple orchiectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection was completed. The final diagnosis was stage IB non-seminoma testicular cancer (pT2N0M0). A combination of different chemotherapeutic medications is recommended including bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin. Each of the antineoplastic drugs has a different mechanism of action targeting cancer cells. What is the primary mechanism of action of bleomycin in cancer treatment?
- A. Direct DNA strand cleavage (Correct Answer)
- B. Ribonucleotide reductase inhibition
- C. RNA polymerase inhibition
- D. Topoisomerase II inhibition
- E. DNA polymerase inhibition
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***Direct DNA strand cleavage***
- Bleomycin is a **cytotoxic antibiotic** that induces DNA damage by generating **free radicals**, leading to **single and double-strand DNA breaks**.
- This mechanism primarily occurs in the **G2 and M phases** of the cell cycle, inhibiting DNA synthesis and cell division.
*Ribonucleotide reductase inhibition*
- This is the primary mechanism of action for drugs like **hydroxyurea**, which prevents the conversion of **ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides**, thereby impairing DNA synthesis.
- Bleomycin does not act by inhibiting this enzyme.
*RNA polymerase inhibition*
- This mechanism is associated with drugs such as **dactinomycin (actinomycin D)**, which intercalates into DNA and blocks RNA synthesis.
- Bleomycin's action is more direct in causing DNA damage rather than inhibiting RNA transcription.
*Topoisomerase II inhibition*
- Drugs like **etoposide** and **doxorubicin** are topoisomerase II inhibitors, which prevent DNA unwinding and re-ligation, leading to DNA breaks and cell death.
- While etoposide is used in the same regimen, this is not the mechanism of action for bleomycin.
*DNA polymerase inhibition*
- This is the mechanism of action for certain **antimetabolites** and **nucleoside analogs**, such as **cytarabine** or **gemcitabine**, which interfere with DNA replication by blocking DNA polymerase.
- Bleomycin's action is distinct, involving direct oxidative cleavage of DNA.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 6: A 43-year-old woman presents to your clinic for the evaluation of an abnormal skin lesion on her forearm. The patient is worried because her mother passed away from melanoma. You believe that the lesion warrants biopsy for further evaluation for possible melanoma. Your patient is concerned about her risk for malignant disease. What is the most important prognostic factor of melanoma?
- A. Depth of invasion of atypical cells (Correct Answer)
- B. S-100 tumor marker present
- C. Evolution of lesion over time
- D. Age at presentation
- E. Level of irregularity of the borders
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***Depth of invasion of atypical cells***
- The **Breslow depth**, which measures the vertical thickness of the melanoma from the granular layer of the epidermis to the deepest part of the tumor, is the **single most important prognostic factor** for localized melanoma.
- A greater depth of invasion correlates directly with a higher risk of **metastasis** and a poorer prognosis due to increased likelihood of reaching dermal lymphatics or blood vessels.
*S-100 tumor marker present*
- While **S-100 protein** is a marker expressed in melanoma cells and can be used to detect metastatic disease (e.g., in lymph nodes), its mere presence does not serve as the primary prognostic indicator for the primary lesion itself.
- S-100 reflects the presence of melanoma cells but does not provide information about the **depth or biological aggressiveness** of the initial tumor.
*Evolution of lesion over time*
- The **evolution or change** in a lesion (e.g., in size, shape, color, new symptoms) is a crucial diagnostic criterion for identifying suspicious lesions for biopsy.
- While important for diagnosis, it is not a direct prognostic factor once melanoma is confirmed; the **pathological features** after biopsy, particularly depth, determine prognosis.
*Age at presentation*
- **Age** can influence treatment decisions and overall health status, but it is not the most important independent prognostic factor for melanoma.
- Prognosis is primarily driven by tumor-specific characteristics rather than the patient's age.
*Level of irregularity of the borders*
- **Border irregularity** is one of the ABCDE criteria (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter >6mm, Evolving) used to identify suspicious pigmented lesions.
- It is a diagnostic indicator that warrants further investigation but does not independently determine **prognosis** as definitively as the Breslow depth after biopsy.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old woman has a total thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma. She complains of tingling around the mouth 11 hours after the operation. Her condition rapidly deteriorates with difficulty breathing and chest tightness. Which of the following best represent the signaling pathway of the deficient hormone responsible for this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)
- B. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) (Correct Answer)
- C. Intracellular receptors
- D. Receptor tyrosine kinase
- E. Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)***
- The patient's symptoms of perioral tingling, difficulty breathing, and chest tightness after total thyroidectomy suggest **hypocalcemia**, likely due to accidental removal or damage to the **parathyroid glands** during surgery.
- The deficient **parathyroid hormone (PTH)** acts primarily through the **cAMP second messenger system** to increase serum calcium levels.
*Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)*
- **cGMP** is a second messenger system primarily involved in mediating the effects of hormones like **atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** and **nitric oxide**, which are unrelated to calcium homeostasis and parathyroid function.
- This pathway is not the primary mechanism of action for **PTH**.
*Intracellular receptors*
- **Intracellular receptors** are typically used by **steroid hormones** (e.g., cortisol, estrogen) and **thyroid hormones**, which are lipid-soluble and can cross the cell membrane.
- **PTH** is a peptide hormone and acts on cell surface receptors.
*Receptor tyrosine kinase*
- **Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)** are transmembrane receptors involved in signaling pathways for hormones like **insulin** and **growth factors**, promoting cell growth, differentiation, and metabolism.
- This is not the primary signaling pathway for **PTH**.
*Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)*
- The **IP3/DAG (diacylglycerol)** pathway is another common second messenger system used by various hormones (e.g., **vasopressin, oxytocin, TRH**), leading to the release of intracellular calcium.
- While it involves calcium signaling, it is not the primary or most characteristic pathway for **PTH** action, which predominantly utilizes **cAMP**.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 8: A 66-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of constipation and streaks of blood in his stool. He has had a 10-kg (22-lb) weight loss during this period. Colonoscopy shows an exophytic tumor in the sigmoid colon. A CT scan of the abdomen shows liver metastases and enlarged mesenteric and para-aortic lymph nodes. A diagnosis of stage IV colorectal cancer is made, and palliative chemotherapy is initiated. The chemotherapy regimen includes a monoclonal antibody that inhibits tumor growth by preventing ligand binding to a protein directly responsible for epithelial cell proliferation and organogenesis. Which of the following proteins is most likely inhibited by this drug?
- A. VEGF
- B. TNF-α
- C. EGFR (Correct Answer)
- D. ALK
- E. CD52
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***EGFR***
- The description of a monoclonal antibody preventing ligand binding to a protein responsible for **epithelial cell proliferation** and organogenesis strongly points to the **epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)**.
- EGFR is highly expressed in many colorectal cancers and its activation by ligands like EGF promotes cell growth, survival, and metastasis. Inhibiting it reduces tumor progression.
*VEGF*
- **Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)** is primarily involved in **angiogenesis**, the formation of new blood vessels.
- While anti-VEGF therapies (e.g., bevacizumab) are used in colorectal cancer, their mechanism is inhibiting blood supply to the tumor, not directly blocking a receptor responsible for epithelial cell proliferation as described.
*TNF-α*
- **Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)** is a **cytokine** primarily involved in inflammation and immune responses.
- Antibodies against TNF-α (e.g., infliximab) are used in inflammatory conditions like Crohn's disease, not typically as targeted therapy for colorectal cancer directly inhibiting epithelial proliferation.
*ALK*
- **Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)** is a **receptor tyrosine kinase** often implicated in lung cancer and lymphomas.
- ALK rearrangements lead to oncogenic fusion proteins, but it is not a primary target for widespread epithelial cell proliferation in colorectal cancer.
*CD52*
- **CD52** is a glycoprotein found on the surface of various immune cells, including lymphocytes.
- Antibodies targeting CD52 (e.g., alemtuzumab) are used in certain leukemias and lymphomas to deplete these cells, not for inhibiting epithelial cell proliferation in solid tumors.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 9: A 78-year-old man receives chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Despite appropriate therapy, he dies 4 months later. Histopathological examination of the cancer cells shows the presence of a transmembrane efflux pump protein that is known to cause decreased intracellular concentrations of chemotherapeutic drugs. Which of the following best describes this membrane protein?
- A. G protein
- B. Cadherin
- C. P-glycoprotein (Correct Answer)
- D. Tyrosine receptor
- E. Channel protein
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: **P-glycoprotein**
- **P-glycoprotein** (also known as **MDR1**) is a well-known **efflux pump** that actively transports many chemotherapy drugs out of cancer cells, leading to **multidrug resistance**.
- Its presence explains the **decreased intracellular concentrations** of chemotherapy drugs and the poor response to treatment in this patient.
*G protein*
- **G proteins** are intracellular signaling molecules that mediate responses to various extracellular stimuli, not primarily involved in drug efflux.
- They are typically associated with **G protein-coupled receptors** and downstream signaling pathways, not direct drug transport.
*Cadherin*
- **Cadherins** are cell adhesion molecules that play a crucial role in cell-cell binding and maintaining tissue structure.
- They are not involved in the active transport of drugs across the cell membrane.
*Tyrosine receptor*
- **Tyrosine kinase receptors** are transmembrane proteins that bind to growth factors and initiate intracellular signaling cascades, promoting cell growth and differentiation.
- They are involved in signaling, not in the active transport of chemotherapy drugs out of the cell.
*Channel protein*
- **Channel proteins** facilitate the passive diffusion of ions or small molecules across the cell membrane, typically down their electrochemical gradient.
- While they are transmembrane proteins, they do not actively pump drugs out against a concentration gradient, which is characteristic of multidrug resistance.
PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG Question 10: A 14-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of a 12-hour history of abdominal pain and dark urine. Three days ago, he developed a cough, sore throat, and rhinorrhea. Examination shows conjunctival pallor, scleral icterus, and mild splenomegaly. A peripheral blood smear shows small round inclusions within erythrocytes and several erythrocytes with semicircular indentations. The underlying cause of this patient's condition is most likely to also affect which of the following processes?
- A. Anchoring proteins to cell surface
- B. Function of myeloperoxidase
- C. Biosynthesis of glutathione
- D. Generation of superoxide (Correct Answer)
- E. Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate
PI3K-Akt pathway Explanation: ***Generation of superoxide***
- This patient presents with signs of **hemolytic anemia** (abdominal pain, dark urine, conjunctival pallor, scleral icterus), likely triggered by an infection (cough, sore throat, rhinorrhea), and a peripheral blood smear showing **Heinz bodies** (small round inclusions) and **bite cells** (semicircular indentations). These findings are classic for **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**.
- **G6PD deficiency** impairs the **pentose phosphate pathway**, which is essential for producing **NADPH**. NADPH is required by **NADPH oxidase** for the **generation of superoxide** in phagocytes through the **respiratory burst** to kill bacteria.
*Anchoring proteins to cell surface*
- This process is primarily affected in diseases like **paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria** (PNH), where there is a defect in the **PIG-A gene** leading to deficient synthesis of **GPI anchors**.
- PNH presents with hemolytic anemia but lacks the characteristic Heinz bodies and bite cells seen in G6PD deficiency and is not typically triggered by infection in this acute manner.
*Function of myeloperoxidase*
- **Myeloperoxidase deficiency** leads to impaired killing of bacteria and fungi within phagocytes, increasing susceptibility to recurrent infections.
- While patients with myeloperoxidase deficiency have a normal respiratory burst, they do not present with hemolytic anemia or the specific red blood cell findings of G6PD deficiency.
*Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate*
- **Pyruvate kinase deficiency** affects the final step in **glycolysis**, causing a buildup of **2,3-BPG** and impaired ATP production in red blood cells.
- This leads to chronic hemolytic anemia but does not present with Heinz bodies or bite cells, nor is it acutely triggered by infection in the same way as G6PD deficiency.
*Biosynthesis of glutathione*
- While G6PD deficiency impacts the **reduction of oxidized glutathione** (GSSG) back to **reduced glutathione** (GSH), it does not directly affect the *biosynthesis* of glutathione.
- The problem in G6PD deficiency is G6PD's inability to produce sufficient NADPH, which is a cofactor for **glutathione reductase**, thereby impairing the regeneration of GSH necessary to protect red blood cells from oxidative stress.
More PI3K-Akt pathway US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.