MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for MAP kinase pathways. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 1: A 38-year-old man presents with concerns after finding out that his father was recently diagnosed with colon cancer. Family history is only significant for his paternal grandfather who also had colon cancer. A screening colonoscopy is performed, and a polyp is found in the ascending (proximal) colon, which on biopsy shows adenocarcinoma. A mutation in a gene that is responsible for which of the following cellular functions is the most likely etiology of this patient’s cancer?
- A. DNA mismatch repair (Correct Answer)
- B. Signal transduction
- C. Cytoskeletal stability
- D. Inhibits progression from G1 to S phase
- E. Inhibitor of apoptosis
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: ***DNA mismatch repair***
- The patient's presentation with **early-onset colon cancer** (38 years old), location in the **proximal colon** (ascending colon), and a **strong family history** of colon cancer in his father and paternal grandfather are highly suggestive of **Lynch syndrome (hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer or HNPCC)**.
- Lynch syndrome is caused by inherited mutations in **DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes**, such as *MLH1, MSH2, MSH6*, and *PMS2*, leading to microsatellite instability and an increased risk of various cancers, particularly colorectal and endometrial.
*Signal transduction*
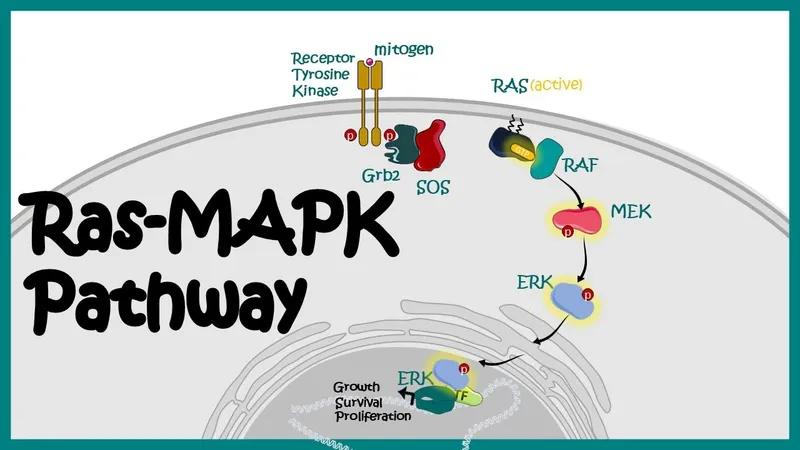
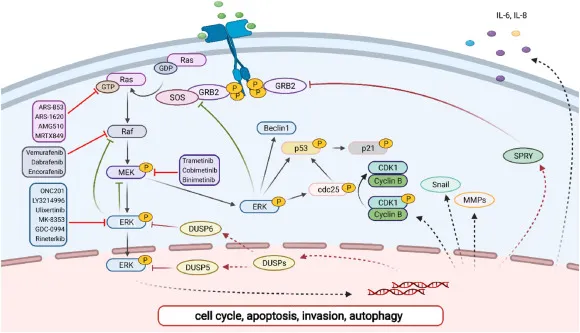
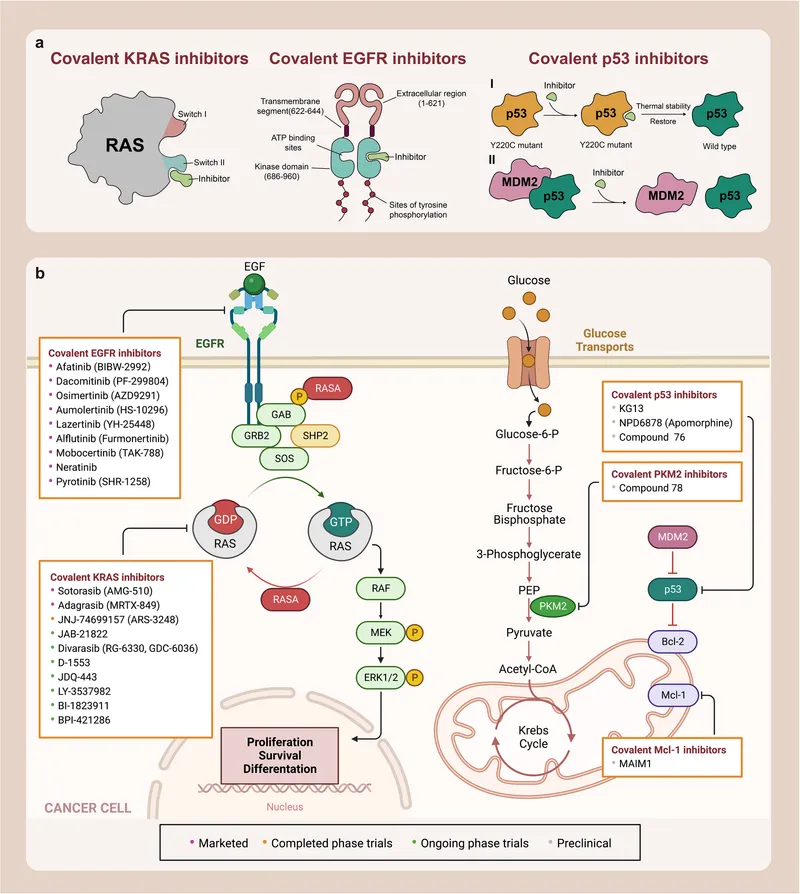
- Mutations in **signal transduction genes (e.g., *KRAS*, *BRAF*)** are common in sporadic colorectal cancer and lead to constitutive activation of cell growth pathways through the RAS/MAPK signaling cascade.
- While mutations in these genes are important in colorectal cancer pathogenesis, they typically do not explain the **familial aggregation, early onset, and proximal location** seen in this patient, which are hallmarks of Lynch syndrome.
*Cytoskeletal stability*
- Genes involved in cytoskeletal stability are crucial for cell structure and migration, but their primary dysfunction is not the direct cause of inherited colorectal cancer syndromes like Lynch syndrome.
- While some advanced cancers may show changes in cytoskeletal proteins, this is not the fundamental genetic defect underlying this specific familial cancer presentation.
*Inhibits progression from G1 to S phase*
- Proteins that inhibit progression from G1 to S phase are typically **tumor suppressor genes**, such as **retinoblastoma protein (Rb)** or **p53**.
- Loss of function in these genes promotes uncontrolled cell division, but mutations in *Rb* or *p53* are not the primary cause of Lynch syndrome; rather, it is characterized by defects in **DNA repair**.
*Inhibitor of apoptosis*
- Genes that inhibit apoptosis (programmed cell death) are often **oncogenes** (e.g., *BCL-2*) or genes that, when mutated, lead to resistance to apoptotic signals.
- While resistance to apoptosis is a hallmark of cancer, the fundamental defect in Lynch syndrome is impaired **DNA repair**, not primarily a direct inhibition of apoptosis.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 2: A 62-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of a mole on her forearm that has increased in size over the last several months. Physical examination shows a 9-mm skin lesion on the right forearm with irregular borders. An excisional biopsy is performed, and genetic analysis shows a mutation in the gene that encodes B-Raf. Which of the following cellular events most likely predisposed this patient to developing this skin lesion?
- A. Deamination of cytosine, guanine, and adenine nucleotides
- B. Relocation of a chromosomal segment onto a nonhomologous chromosome
- C. Formation of covalent bonds between adjacent pyrimidine bases (Correct Answer)
- D. Insufficient phosphorylation of p53
- E. Double-strand breaks in DNA molecules
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: ***Formation of covalent bonds between adjacent pyrimidine bases***
- This describes **pyrimidine dimers**, typically **thymine dimers**, which are formed due to **UV radiation exposure**.
- UV radiation is the primary environmental risk factor for **melanoma**, and the **B-Raf mutation** (common in melanoma) is often linked to these UV-induced DNA lesions.
*Deamination of cytosine, guanine, and adenine nucleotides*
- **Deamination** is a chemical alteration of DNA bases that can lead to mutations, but it is not the most direct or common mechanism for UV-induced melanoma.
- While deamination can occur spontaneously or be induced by certain chemicals, it is not the primary event linked to **UV radiation** and **B-Raf mutations** in melanoma.
*Relocation of a chromosomal segment onto a nonhomologous chromosome*
- This describes a **translocation**, a type of chromosomal rearrangement.
- While translocations can be associated with some cancers (e.g., leukemias, sarcomas), they are not the typical mechanism for initiating **melanoma** or directly causing **B-Raf mutations**.
*Insufficient phosphorylation of p53*
- **p53 phosphorylation** is crucial for its activation as a tumor suppressor protein, and insufficient phosphorylation would impair its function.
- However, the direct cause of this specific melanoma with a **B-Raf mutation** is usually DNA damage (like pyrimidine dimers) rather than a primary defect in p53 phosphorylation.
*Double-strand breaks in DNA molecules*
- **Double-strand breaks (DSBs)** are highly deleterious DNA lesions that can lead to chromosomal rearrangements or cell death if not repaired.
- While DSBs can be caused by various factors, including high-energy radiation, they are not the most common or characteristic DNA lesion specifically implicated in the initiation of **melanoma** due to UV exposure and subsequent **B-Raf mutation**.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 3: A 28-year-old patient presents to a medical office for a consultation regarding a mole on her nose that is increasing in size. She also complains of frequent headaches, which she associates with stress on the job. She works as a civil engineer and spends much of her time outside. Her past medical history is positive for bronchial asthma; nevertheless, her vitals are stable. The mole is 8 mm in diameter, has irregular borders, and is brown in color. A biopsy is performed and sent for genetic analysis. A mutation is found. A mutation in which gene is characteristic of this patient’s main diagnosis?
- A. DCC
- B. APC
- C. BRAF (Correct Answer)
- D. c-MYC
- E. BCL-2
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: ***BRAF***
- The patient's presentation with an **enlarging mole** on the nose with **irregular borders** and significant sun exposure strongly suggests **melanoma**.
- **BRAF mutations** are found in approximately 50% of melanomas and are a key target for therapy.
*DCC*
- The DCC (Deleted in Colorectal Carcinoma) gene is primarily associated with **colorectal cancer**.
- While it plays a role in apoptosis and cellular differentiation, it is not a characteristic mutation for melanoma.
*APC*
- The APC (Adenomatous Polyposis Coli) gene is a **tumor suppressor gene** most famously linked to **familial adenomatous polyposis** and **colorectal cancer**.
- Mutations in APC are not characteristic of melanoma.
*c-MYC*
- The c-MYC gene is an **oncogene** involved in cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis, commonly amplified or mutated in various cancers like lymphomas and some solid tumors.
- While important in cancer biology, c-MYC mutations are not a primary driver or characteristic mutation for melanoma.
*BCL-2*
- BCL-2 is an **anti-apoptotic gene** known for its role in preventing programmed cell death, and its overexpression is common in lymphomas (especially follicular lymphoma).
- It is not a characteristic mutation associated with melanoma development or progression.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 4: A 55-year-old man with a history of sun exposure presents with a slowly growing, pearly nodule with telangiectasias on his nose. The lesion occasionally bleeds when traumatized. Biopsy shows basaloid cells arranged in palisading patterns. Which of the following mutations is most likely involved in the pathogenesis?
- A. P53 mutation
- B. PTCH1 gene mutation (Correct Answer)
- C. EGFR mutation
- D. KIT mutation
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: **PTCH1 gene mutation**
- The clinical presentation of a **pearly nodule with telangiectasias** on the **nose**, history of **sun exposure**, and **basaloid cells arranged in palisading patterns** on biopsy are classic for **basal cell carcinoma (BCC)** [1].
- Mutations in the **PTCH1 gene**, a tumor suppressor gene involved in the **Hedgehog signaling pathway**, are found in the majority of sporadic BCCs and are central to its pathogenesis [2,3].
*P53 mutation*
- While **P53 mutations** are common in many cancers, including **squamous cell carcinoma** [3], they are not the primary driver mutation for basal cell carcinoma in the way PTCH1 mutations are.
- Loss of P53 function typically leads to uncontrolled cell growth and reduced apoptosis, but it's a general cancer mechanism rather than a specific one for BCC.
*EGFR mutation*
- **EGFR mutations** are primarily associated with certain types of **lung adenocarcinoma** and **glioblastoma**, not basal cell carcinoma.
- These mutations lead to constitutive activation of the **epidermal growth factor receptor** signaling pathway, promoting cell proliferation and survival in those specific cancers.
*KIT mutation*
- **KIT mutations** are most commonly found in **gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST)** and certain types of **melanoma**.
- The KIT receptor tyrosine kinase plays a role in cell growth and differentiation in specific cell lineages, distinct from the epidermal cells involved in BCC.
**References:**
[1] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. The Skin, pp. 1158-1162.
[2] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. Neoplasia, pp. 306-307.
[3] Cross SS. Underwood's Pathology: A Clinical Approach. 6th ed. Disorders Involving Inflammatory And Haemopoietic Cells, pp. 643-644.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 5: A 16-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a lesion that has been growing on his jaw over the past several months. He recently immigrated to the USA from Kenya with his family. Physical examination shows a 3-cm solid mass located above the left mandible. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. Biopsy of the mass shows sheets of lymphocytes and interspersed reactive histiocytes with abundant, clear cytoplasm and phagocytosed debris. Which of the following mechanisms is most likely directly responsible for the malignant transformation of this patient's cells?
- A. Defect in DNA repair
- B. Impairment of receptor function
- C. Inhibition of cell cycle arrest
- D. Integration of viral DNA (Correct Answer)
- E. Activation of transcription
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: **Integration of viral DNA**
- The clinical presentation (rapidly growing jaw mass in a young boy from Kenya) and histological findings (sheets of lymphocytes, "starry sky" appearance due to macrophages) are classic for **endemic Burkitt lymphoma**.
- Endemic Burkitt lymphoma is strongly associated with **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)** infection. EBV DNA integrates into the host cell genome, promoting the characteristic **t(8;14) translocation** of *MYC* oncogene, leading to its overexpression and uncontrolled cell proliferation.
*Defect in DNA repair*
- While defects in DNA repair can lead to malignancy (e.g., in Lynch syndrome, xeroderma pigmentosum), it is not the primary mechanism of oncogenesis in Burkitt lymphoma.
- The hallmark of Burkitt lymphoma is a specific chromosomal translocation, not a generalized DNA repair defect.
*Impairment of receptor function*
- Impaired receptor function is associated with certain diseases (e.g., some autoimmune conditions, diabetes insipidus) but is not a direct mechanism for malignant transformation in Burkitt lymphoma.
- Malignancy typically arises from uncontrolled cell growth and division, not directly from receptor dysfunction.
*Inhibition of cell cycle arrest*
- While Burkitt lymphoma cells do evade cell cycle arrest, this is a **consequence** of the *MYC* oncogene overexpression, not the primary mechanism of malignant transformation itself.
- The **integration of viral DNA** leading to the *MYC* translocation is the upstream event that *causes* the inhibition of cell cycle arrest.
*Activation of transcription*
- **Activation of transcription** (specifically of the *MYC* oncogene) is a crucial step in the pathogenesis of Burkitt lymphoma, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
- However, the direct cause of this dysregulated transcriptional activation is the **chromosomal translocation** resulting from viral DNA integration.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 6: A 51-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a persistent cough and a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss over the past 2 months. Yesterday, she coughed up bloody sputum. She does not smoke. Pulmonary examination shows decreased breath sounds over the right upper lobe. A CT scan of the chest shows a mass in the periphery of the right upper lobe. Histopathologic examination of a specimen obtained on CT-guided biopsy shows glandular cells with papillary components and signet ring cells that stain positive for mucin. An alteration in which of the following genes is most likely to have occurred in this patient?
- A. TP53
- B. SMAD4 (DPC4)
- C. APC
- D. MYCL1
- E. ALK (Correct Answer)
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: ***ALK***
- The patient's presentation with **adenocarcinoma** (glandular cells, mucin, peripheral location) in a **non-smoker** suggests a higher likelihood of specific driver mutations, such as **ALK rearrangements**.
- **ALK gene rearrangements** are characteristic oncogenic drivers in a subset of lung adenocarcinomas, particularly in younger patients and non-smokers.
*TP53*
- **TP53** is a tumor suppressor gene frequently mutated in many cancers, including lung cancer, but its mutation is not as specific to the clinical and histopathological findings of this patient's adenocarcinoma presenting in a non-smoker.
- While common in lung cancer overall, **TP53 mutations** are more strongly associated with squamous cell carcinoma or small cell lung cancer, or with smoking-related adenocarcinoma.
*SMAD4 (DPC4)*
- **SMAD4** is a tumor suppressor gene primarily associated with **pancreatic cancer** and **colorectal cancer**, playing a key role in the TGF-β signaling pathway.
- Its mutation is not a common or characteristic driver in lung adenocarcinoma, especially with the features described.
*APC*
- The **APC gene** is a tumor suppressor gene centrally involved in the **Wnt signaling pathway** and is primarily associated with **colorectal cancer**, particularly **familial adenomatous polyposis**.
- APC mutations are not typically found as primary drivers in lung adenocarcinoma.
*MYCL1*
- **MYCL1 (L-MYC)** is an oncogene belonging to the MYC family, implicated in cell proliferation and apoptosis.
- While MYC family genes can be amplified in various cancers, **MYCL1 amplification** is more characteristic of **small cell lung cancer**, not adenocarcinoma, and does not align with the glandular and papillary features described.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 7: A 13-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician for evaluation of leg pain. Specifically, he has been having pain around his right knee that has gotten progressively worse over the last several months. On presentation, he has swelling and tenderness over his right distal femur. Radiographs are obtained and the results are shown in figure A. His family history is significant in that several family members also had this disorder and others had pathology in the eye near birth. The patient is referred for a genetic consult, and a mutation is found on a certain chromosome. The chromosome that is most likely affected also contains a gene that is associated with which of the following pathologies?
- A. Pancreatic cancers
- B. Colorectal cancer
- C. Soft tissue sarcomas
- D. Neurofibromas
- E. Breast cancer (Correct Answer)
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: ***Breast cancer***
- This clinical scenario describes hereditary retinoblastoma, characterized by **osteosarcoma** (leg pain, distal femur swelling, and tenderness in a young boy), **retinoblastoma** (eye pathology near birth), and a family history.
- The gene mutated in hereditary retinoblastoma is the **RB1 gene**, located on **chromosome 13**. This chromosome also contains the **BRCA2 gene**, which is associated with an increased risk of **breast cancer**.
*Pancreatic cancers*
- While certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of pancreatic cancer (e.g., **BRCA1/2**, PALB2, ATM), the specific gene and chromosome linked to the described primary condition (hereditary retinoblastoma/osteosarcoma) do not directly point to pancreatic cancer as the most strongly associated co-pathology on that same chromosome in the context of the given options.
- The RB1 gene is on chromosome 13, and while BRCA2 (also on chromosome 13) can be associated with pancreatic cancer, breast cancer is a more prominent association for BRCA2.
*Colorectal cancer*
- Colorectal cancer is often associated with mutations in genes like **APC** (familial adenomatous polyposis) on chromosome 5 or **MLH1**, **MSH2** (Lynch syndrome) on other chromosomes, not primarily chromosome 13 in the context of retinoblastoma.
- There is no direct strong link between the RB1 gene/chromosome 13 and colorectal cancer that would make it the most likely answer among the choices.
*Soft tissue sarcomas*
- While retinoblastoma patients have an increased risk of subsequent cancers, including soft tissue sarcomas, the question asks about a pathology associated with a gene on the **same chromosome** as RB1.
- No major gene causing soft tissue sarcomas is primarily located on chromosome 13 and as prominently linked as BRCA2 to breast cancer.
*Neurofibromas*
- Neurofibromas are characteristic of **neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)**, caused by a mutation in the **NF1 gene** located on chromosome 17.
- This is a different chromosome and gene entirely from the RB1 gene on chromosome 13.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old man is brought in by ambulance to the ER, barely conscious, after feeling drowsy and falling to the floor during a presentation several hours ago. His colleague who accompanied him says he has had similar episodes 5 times in the past 3 months. No significant past medical history. His blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg and pulse is 114/min. His capillary blood glucose is 15 mg/dL. Immediate IV dextrose with thiamine is started, and he rapidly regains consciousness. A contrast CT of the abdomen is performed which reveals a tumor in the pancreas. Which of the following relative laboratory findings would you most likely expect to find in this patient?
- A. Glucose: ↑, Insulin: ↓, C-Peptide: ↓, Ketoacidosis: Present
- B. Glucose: Normal, Insulin: Normal, C-Peptide: Normal, Ketoacidosis: Absent
- C. Glucose: ↓, Insulin: ↑, C-Peptide: ↑, Ketoacidosis: Absent (Correct Answer)
- D. Glucose: ↓, Insulin: ↑, C-Peptide: ↓, Ketoacidosis: Absent
- E. Glucose: ↑, Insulin: ↑/Normal, C-Peptide: ↑/Normal, Ketoacidosis: Absent
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: ***Glucose: ↓, Insulin: ↑, C-Peptide: ↑, Ketoacidosis: Absent***
- The patient's **hypoglycemia (15 mg/dL)**, coupled with a pancreatic tumor and recurrent episodes, strongly suggests an **insulinoma**.
- An **insulinoma** is an insulin-secreting tumor, leading to **high insulin** and **C-peptide** levels in the presence of low glucose, and typically no ketoacidosis because insulin inhibits ketogenesis.
*Glucose: ↑, Insulin: ↓, C-Peptide: ↓, Ketoacidosis: Present*
- This profile describes **Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus** or severe insulin deficiency, where high glucose is due to lack of insulin production and subsequent diabetic ketoacidosis.
- The patient's symptoms (hypoglycemia) and the presence of a pancreatic tumor producing insulin are contradictory to this profile.
*Glucose: Normal, Insulin: Normal, C-Peptide: Normal, Ketoacidosis: Absent*
- This profile represents a **healthy individual** with normal metabolic function, which is inconsistent with the patient's severe hypoglycemia and recurrent collapses.
- It would not explain the patient's symptoms or the pancreatic tumor's function.
*Glucose: ↓, Insulin: ↑, C-Peptide: ↓, Ketoacidosis: Absent*
- This finding would be typical of **exogenous insulin administration** (e.g., insulin overdose) where insulin levels are high, but C-peptide (which is co-secreted with endogenous insulin) is low.
- While hypoglycemia is present, the low C-peptide contradicts the presence of an endogenous insulin-secreting pancreatic tumor.
*Glucose: ↑, Insulin: ↑/Normal, C-Peptide: ↑/Normal, Ketoacidosis: Absent*
- These findings could be seen in conditions like **Type 2 Diabetes** with **insulin resistance** or Cushing's syndrome where glucose and insulin might be elevated, but the patient's primary presentation is severe hypoglycemia.
- This profile does not align with the patient's profound hypoglycemia and clinical picture of an insulinoma.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 9: A research team discovers a novel bacterial toxin that causes severe hypotension in infected patients. In vitro studies show the toxin ADP-ribosylates a specific amino acid on Gq alpha subunits, preventing their activation by GPCRs. Patients develop hypotension despite elevated levels of vasopressin, angiotensin II, and endothelin-1. Synthesize the pathophysiological mechanism explaining why multiple vasopressor hormones fail to maintain blood pressure in these patients.
- A. The toxin depletes intracellular ATP preventing myosin-actin interaction
- B. The toxin prevents receptor binding of vasopressor hormones through allosteric inhibition
- C. ADP-ribosylation of Gq prevents PLC activation, blocking IP3-mediated calcium release and vascular smooth muscle contraction (Correct Answer)
- D. ADP-ribosylation increases cAMP levels causing smooth muscle relaxation
- E. The toxin activates Gi proteins causing excessive vasodilation that overwhelms vasoconstrictor signals
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: ***ADP-ribosylation of Gq prevents PLC activation, blocking IP3-mediated calcium release and vascular smooth muscle contraction***
- Vasopressor hormones like **Vasopressin**, **Angiotensin II**, and **Endothelin-1** signal through **Gq-coupled receptors** to trigger **vascular smooth muscle contraction**.
- By ADP-ribosylating the **Gq alpha subunit**, the toxin inhibits **Phospholipase C (PLC)**, preventing the generation of **IP3 and DAG**, which are essential for releasing **intracellular calcium**.
*The toxin prevents receptor binding of vasopressor hormones through allosteric inhibition*
- The toxin targets the **G-protein (intracellular)** rather than the **extracellular binding site** of the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs).
- Since binding still occurs but **signal transduction** is blocked, this describes a post-receptor defect rather than **allosteric inhibition** of the receptor itself.
*The toxin activates Gi proteins causing excessive vasodilation that overwhelms vasoconstrictor signals*
- The prompt explicitly states the toxin modifies the **Gq alpha subunit**, not the **Gi subunit**.
- **Gi protein** activation primarily lowers **cAMP**, whereas the failure of pressors in this case is linked to the lack of **calcium mobilization** via Gq.
*ADP-ribosylation increases cAMP levels causing smooth muscle relaxation*
- Increased **cAMP** (via Gs activation or Gi inhibition) does cause relaxation, but this mechanism is associated with toxins like **Cholera** or **Pertussis**.
- The modification of **Gq** specifically disrupts the **phosphoinositol pathway**, not the **adenylyl cyclase** pathway that regulates cAMP.
*The toxin depletes intracellular ATP preventing myosin-actin interaction*
- ADP-ribosylation is a specific **post-translational modification** using **NAD+** as a substrate, which does not result in systemic **ATP depletion**.
- The failure of contraction is due to a lack of **calcium-calmodulin** activation of **Myosin Light Chain Kinase (MLCK)**, not a lack of energy supply for the motor proteins.
MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG Question 10: A 42-year-old woman with metastatic melanoma develops severe colitis while being treated with ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4 antibody) and nivolumab (anti-PD-1 antibody). Her oncologist must decide whether to continue immunotherapy or treat the colitis with immunosuppression. Tumor analysis shows high PD-L1 expression and BRAF wild-type status. Previous conventional chemotherapy failed. Evaluate the optimal management strategy considering signal transduction implications.
- A. Stop both drugs permanently as immune-related adverse events indicate loss of self-tolerance mechanisms
- B. Continue both checkpoint inhibitors as tumor response depends on sustained T-cell receptor co-stimulation blockade
- C. Discontinue ipilimumab, continue nivolumab with corticosteroids, as PD-1 pathway blockade may be sufficient given high PD-L1 expression (Correct Answer)
- D. Continue both drugs but add TNF-alpha inhibitor to block inflammatory signaling without affecting anti-tumor immunity
- E. Stop all immunotherapy and switch to targeted therapy despite BRAF wild-type status
MAP kinase pathways Explanation: ***Discontinue ipilimumab, continue nivolumab with corticosteroids, as PD-1 pathway blockade may be sufficient given high PD-L1 expression***
- Severe colitis is a significant **immune-related adverse event (irAE)**; managing it requires **corticosteroids** to suppress the excessive T-cell response while balancing anti-tumor efficacy.
- In patients with **high PD-L1 expression**, the **PD-1 inhibitor (Nivolumab)** may provide sufficient anti-tumor signal transduction blockade alone, allowing for the discontinuation of the more toxic **anti-CTLA-4** agent.
*Continue both checkpoint inhibitors as tumor response depends on sustained T-cell receptor co-stimulation blockade*
- Sustaining treatment during severe colitis poses a high risk of **colon perforation** and death due to uncontrolled lymphocytic infiltration.
- **CTLA-4** blockade affects the priming phase in lymph nodes, and continuing it during high-grade toxicity is contraindicated by clinical safety guidelines.
*Stop all immunotherapy and switch to targeted therapy despite BRAF wild-type status*
- Targeted therapies like **BRAF and MEK inhibitors** require the **BRAF V600 mutation** to function; they are ineffective in **BRAF wild-type** status.
- Switching to these agents would leave the patient with no effective treatment for the underlying **metastatic melanoma**.
*Continue both drugs but add TNF-alpha inhibitor to block inflammatory signaling without affecting anti-tumor immunity*
- While **TNF-alpha inhibitors** like infliximab are used for refractory colitis, they are typically added only after **corticosteroids** fail to control symptoms.
- Clinical protocols mandate the suspension of the offending agents during **Grade 3/4 toxicity** to prevent further immune-mediated tissue damage.
*Stop both drugs permanently as immune-related adverse events indicate loss of self-tolerance mechanisms*
- Benefit-risk assessment often allows for the resumption of **PD-1 inhibitors** once toxicity resolves, especially if the tumor shows evidence of responding.
- **Permanent discontinuation** of all life-saving immunotherapy may not be necessary if the toxicity is managed and the clinical benefit of the **PD-1 pathway** blockade is high.
More MAP kinase pathways US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.