Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Hedgehog signaling pathway. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 1: A 33-year-old woman comes to the physician 1 week after noticing a lump in her right breast. Fifteen years ago, she was diagnosed with osteosarcoma of her left distal femur. Her father died of an adrenocortical carcinoma at the age of 41 years. Examination shows a 2-cm, firm, immobile mass in the lower outer quadrant of the right breast. A core needle biopsy of the mass shows adenocarcinoma. Genetic analysis in this patient is most likely to show a defect in which of the following genes?
- A. BRCA1
- B. KRAS
- C. TP53 (Correct Answer)
- D. Rb
- E. PTEN
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***TP53***
- This patient's presentation with **early-onset breast cancer**, a history of **osteosarcoma** at a young age, and a father's death from **adrenocortical carcinoma** at 41 years strongly suggests **Li-Fraumeni syndrome**.
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a germline mutation in the **tumor suppressor gene TP53**, increasing the risk for multiple primary cancers at a young age.
*BRCA1*
- While **BRCA1 mutations** are associated with an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer, they are not typically linked to osteosarcoma or adrenocortical carcinoma.
- The constellation of cancers in this patient is more indicative of Li-Fraumeni syndrome than solely a BRCA1-related cancer syndrome.
*KRAS*
- **KRAS** is an oncogene commonly mutated in several cancers, including pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancer, but is not primarily associated with either Li-Fraumeni syndrome or the specific tumors seen in this family history.
- Mutations in KRAS are typically somatic mutations acquired during a person's lifetime, not germline mutations causing inherited cancer syndromes like the one suggested here.
*Rb*
- Mutations in the **retinoblastoma (Rb) gene** are associated with retinoblastoma and an increased risk of osteosarcoma, but not typically with adrenocortical carcinoma or breast cancer as part of a classic inherited syndrome.
- The combination of breast cancer, osteosarcoma, and adrenocortical carcinoma points more specifically to TP53.
*PTEN*
- **PTEN mutations** are associated with Cowden syndrome, which increases the risk for breast cancer, thyroid cancer, and endometrial cancer, along with benign growths.
- However, Cowden syndrome does not typically include osteosarcoma or adrenocortical carcinoma as prominent features, making PTEN less likely than TP53 for this specific family history.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 2: During the third week of development, the blastocyst undergoes a variety of differentiation processes responsible for the formation of the gastrula and, eventually, the embryo. This differentiation creates cell lineages that eventually become a variety of body systems. What cell lineage, present at this date, is responsible for the formation of the liver?
- A. Neuroectoderm
- B. Syncytiotrophoblasts
- C. Ectoderm
- D. Endoderm (Correct Answer)
- E. Mesoderm
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***Endoderm***
- The **endoderm** is one of the three primary germ layers that develops during gastrulation and is responsible for forming the lining of the **gastrointestinal tract** and associated organs, including the **liver** and pancreas.
- Liver development begins from an outgrowth of the **foregut endoderm**, which differentiates into hepatocytes and bile duct cells, forming the hepatic parenchyma.
*Neuroectoderm*
- **Neuroectoderm** is a specialized part of the ectoderm that gives rise to the entire **nervous system**, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
- It does not contribute to the formation of visceral organs like the liver.
*Syncytiotrophoblasts*
- **Syncytiotrophoblasts** are a layer of the **trophoblast** that form part of the placenta, specifically involved in hormone production and nutrient exchange between the mother and fetus.
- They are part of the supporting structures for pregnancy and do not contribute to the embryonic germ layers or organ formation within the embryo itself.
*Ectoderm*
- The **ectoderm** is the outermost germ layer and gives rise to the **epidermis of the skin**, hair, nails, nervous system, and sensory organs.
- While it forms the outer coverings and nervous system, it does not directly form internal organs like the liver.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** is the middle germ layer, responsible for forming **muscle**, **bone**, connective tissue, the circulatory system, kidneys, and gonads.
- While mesoderm contributes supporting structures to the liver (blood vessels, connective tissue, hematopoietic cells), the **hepatic parenchyma** (hepatocytes and bile ducts) is derived from the endoderm, making endoderm the primary cell lineage responsible for liver formation.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 3: A 67-year-old man is referred to a dermatologist after a reddish mole appears on his nose. The mole’s size has changed over the last 2 years, and occasional bleeding is noted. The man’s medical history is unremarkable, and he does not take any medications. He retired from his construction job 15 years ago. Physical examination of his nose reveals a 2-cm pink papule with a pearly appearance and overlying telangiectasia on the ala of the nose (see image). Which of the following would be the best treatment modality if surgery is not an option?
- A. Radiation therapy (Correct Answer)
- B. Imiquimod
- C. Interferon
- D. 5-fluorouracil
- E. Photodynamic therapy
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***Radiation therapy***
- This patient's presentation is highly suggestive of **basal cell carcinoma (BCC)**, given the reddish, pearly papule with telangiectasias on a sun-exposed area, a history of growth over two years, bleeding, and his prior occupation as a construction worker. **Radiation therapy** is an excellent option for **localized BCC** when surgery is contraindicated or not feasible due to patient preferences, tumor location (e.g., cosmetic areas), or medical comorbidities.
- **Definitive radiation therapy** can achieve high cure rates for BCC, comparable to Mohs surgery for appropriately selected superficial and nodular types, and is particularly useful in older patients.
*Imiquimod*
- **Imiquimod** is an **immune-response modifier** used topically for superficial BCCs, actinic keratoses, and external genital warts.
- While effective for **superficial BCCs**, its efficacy is lower for nodular or infiltrative BCCs, which appears more likely given the size (2 cm) and depth implied by chronic bleeding and growth over 2 years.
*Interferon*
- **Interferon** has been explored as an intralesional treatment for BCC, but it is **not a first-line or standard treatment option** due to variable response rates and the availability of more effective and reliable modalities.
- Its use is generally reserved for more advanced or difficult-to-treat cases, typically as part of clinical trials or for very specific indications, not as a primary treatment for a localized BCC where surgery or radiation is an option.
*5-fluorouracil*
- **5-fluorouracil (5-FU)** is a **topical chemotherapeutic agent** used primarily for **actinic keratoses** and **superficial BCCs**.
- Similar to imiquimod, its efficacy is limited to **superficial lesions** and is less effective for nodular, infiltrative, or larger BCCs due to insufficient penetration and risk of recurrence.
*Photodynamic therapy*
- **Photodynamic therapy (PDT)** involves applying a photosensitizing agent followed by exposure to specific wavelengths of light, primarily used for **actinic keratoses** and **superficial BCCs**.
- While effective for superficial lesions, its efficacy significantly decreases for **nodular BCCs** or those with deeper invasion, making it less suitable for a 2 cm lesion that has been growing and bleeding.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 4: A laboratory physician investigates the chromosomes of a fetus with a suspected chromosomal anomaly. She processes a cell culture obtained by amniocentesis. Prior to staining and microscopic examination of the fetal chromosomes, a drug that blocks cell division is added to the cell culture. In order to arrest chromosomes in metaphase, the physician most likely added a drug that is also used for the treatment of which of the following conditions?
- A. Trichomonas vaginitis
- B. Testicular cancer
- C. Herpes zoster
- D. Polycythemia vera
- E. Acute gouty arthritis (Correct Answer)
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***Acute gouty arthritis***
- The drug used to arrest chromosomes in metaphase is likely **colchicine**, which inhibits **microtubule polymerization** and spindle formation, thus arresting cells in metaphase.
- **Colchicine** is a well-established treatment for **acute gouty arthritis** due to its anti-inflammatory properties, primarily through disrupting neutrophil functions.
*Trichomonas vaginitis*
- This condition is typically treated with **metronidazole** or **tinidazole**, which are antibiotics targeting protozoa and anaerobic bacteria.
- These drugs do not inhibit microtubule assembly or arrest cells in metaphase.
*Testicular cancer*
- Testicular cancer is primarily treated with **BEP regimen** (bleomycin, etoposide, cisplatin), which does not include microtubule-inhibiting agents.
- While vinca alkaloids (vincristine, vinblastine) do arrest cells in metaphase via microtubule inhibition similar to colchicine, they are not standard first-line agents for testicular cancer.
- The question specifically asks about the primary clinical use of colchicine, which is gout, not cancer chemotherapy.
*Herpes zoster*
- Herpes zoster (shingles) is a viral infection treated with **antiviral medications** like acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir.
- These antivirals work by interfering with viral DNA replication and do not target microtubule formation or cell division.
*Polycythemia vera*
- Polycythemia vera is a myeloproliferative neoplasm often managed with **phlebotomy**, **hydroxyurea**, or ruxolitinib.
- These treatments aim to reduce blood cell counts or inhibit specific signaling pathways, none of which primarily involve arresting cells in metaphase by disrupting microtubules.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 5: A 13-year-old girl presents to an orthopedic surgeon for evaluation of a spinal curvature that was discovered during a school screening. She has otherwise been healthy and does not take any medications. On presentation, she is found to have significant asymmetry of her back and is sent for a spine radiograph. The radiograph reveals a unilateral rib attached to the left transverse process of the C7 vertebrae. Abnormal expression of which of the following genes is most likely responsible for this finding?
- A. WNT7
- B. FGF
- C. Homeobox (Correct Answer)
- D. PAX
- E. Sonic hedgehog
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***Homeobox***
- **Homeobox genes (HOX genes)** play a crucial role in specifying the identity of vertebral segments along the **craniocaudal axis** during embryonic development.
- An abnormal expression of these genes can lead to **skeletal malformations**, such as the formation of a **cervical rib**, by altering the segmental identity of the C7 vertebra.
*WNT7*
- **WNT7 genes** are involved in limb patterning and have a role in the formation of the **dorsoventral axis** of the limb and kidney development.
- They are not primarily associated with vertebral segmentation or the formation of cervical ribs.
*FGF*
- **Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) genes** are essential for various processes, including limb development, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis.
- While they are involved in numerous developmental pathways, they are not the primary genes responsible for specifying vertebral identity and thus cervical rib formation.
*PAX*
- **PAX genes** are a family of transcription factors critical for organ development, especially of the eye, brain, and kidney.
- While important for development, they are not directly implicated in the specification of vertebral segments or the pathogenesis of cervical ribs.
*Sonic hedgehog*
- **Sonic hedgehog (SHH)** signaling is a key pathway in embryonic development, particularly for pattern formation in the neural tube, limbs, and facial structures.
- While crucial for body axis development and segmentation, **HOX genes** have a more direct role in determining the specific identity of vertebral segments and causing cervical ribs.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 6: A 62-year-old woman presents to her oncologist to discuss the chemotherapy options for her newly diagnosed breast cancer. During the meeting, they discuss a drug that inhibits the breakdown of mitotic spindles in cells. Her oncologist explains that this will be more toxic to cancer cells because those cells are dividing more rapidly. Which of the following side effects is closely associated with the use of this chemotherapeutic agent?
- A. Photosensitivity
- B. Peripheral neuropathy (Correct Answer)
- C. Paralytic ileus
- D. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- E. Pulmonary fibrosis
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***Peripheral neuropathy***
- Drugs that inhibit the breakdown of **mitotic spindles** are **microtubule-targeting agents** (e.g., **taxanes** like paclitaxel/docetaxel, **vinca alkaloids** like vincristine/vinblastine).
- These agents interfere with **microtubule function** in neurons, leading to **axonal damage** and **peripheral neuropathy**.
- This is the **most characteristic and common dose-limiting toxicity** of microtubule inhibitors, affecting sensory and motor nerves (numbness, tingling, weakness in extremities).
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** is a common adverse effect associated with certain chemotherapeutic agents like **fluorouracil** (5-FU) or **methotrexate**, but is not linked to microtubule inhibitors.
- It involves an increased sensitivity to UV light, often manifesting as a rash or exaggerated sunburn.
*Paralytic ileus*
- **Paralytic ileus** can occur with **vinca alkaloids** (especially vincristine) due to autonomic neuropathy affecting the **enteric nervous system**.
- However, this is **less common** than peripheral neuropathy and occurs more specifically with vincristine rather than taxanes.
- **Peripheral neuropathy** is the more pervasive, dose-limiting, and universally characteristic side effect across all microtubule inhibitors.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a classic side effect of **alkylating agents** like **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, which produce the toxic metabolite **acrolein**.
- It is prevented/managed with **mesna**, which inactivates acrolein.
- Not associated with microtubule inhibitors.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a known side effect of certain chemotherapeutic drugs, most notably **bleomycin** and **busulfan**.
- This adverse effect is not associated with agents that target **mitotic spindle breakdown**.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 7: An investigator is studying the mechanism regulating pigment production in the skin. She has isolated a hormone produced by the anterior and intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland that stimulates neural crest-derived cells to produce pigments through the oxidation and polymerization of the amino acid tyrosine. This hormone is most likely cosecreted with a substance that acts on which of the following receptors?
- A. TSH receptor
- B. Glucocorticoid receptor
- C. Vasopressin receptor
- D. Dopamine receptor
- E. Mu receptor (Correct Answer)
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***Mu receptor***
- The hormone described, which stimulates pigment production in neural crest-derived cells, is **melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)**.
- **MSH** is derived from the pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) precursor, which also gives rise to **β-endorphin**, a potent opioid peptide that acts on **mu opioid receptors**.
*TSH receptor*
- The **TSH receptor** binds thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which primarily regulates thyroid hormone production and is not directly related to pigment production or opioid co-secretion from POMC.
- TSH is produced by the anterior pituitary but from a different lineage than POMC-derived hormones.
*Glucocorticoid receptor*
- The **glucocorticoid receptor** binds cortisol and other glucocorticoids, which are involved in stress response and metabolism.
- While ACTH (also derived from POMC) can stimulate adrenal glucocorticoid release, the question specifically refers to a substance *cosecreted* with MSH, not one that is *regulated* by MSH or its derivatives.
*Vasopressin receptor*
- **Vasopressin receptors** bind antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which regulates water balance and blood pressure.
- ADH is produced by the posterior pituitary (though synthesized in the hypothalamus) and is not cosecreted with MSH from the anterior/intermediate pituitary.
*Dopamine receptor*
- **Dopamine receptors** bind dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in various functions, including the inhibition of prolactin release from the pituitary.
- While dopamine can influence pituitary function, it is not cosecreted with MSH in the manner described, nor is it a direct product of POMC cleavage.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man with a history of sun exposure presents with a slowly growing, pearly nodule with telangiectasias on his nose. The lesion occasionally bleeds when traumatized. Biopsy shows basaloid cells arranged in palisading patterns. Which of the following mutations is most likely involved in the pathogenesis?
- A. P53 mutation
- B. PTCH1 gene mutation (Correct Answer)
- C. EGFR mutation
- D. KIT mutation
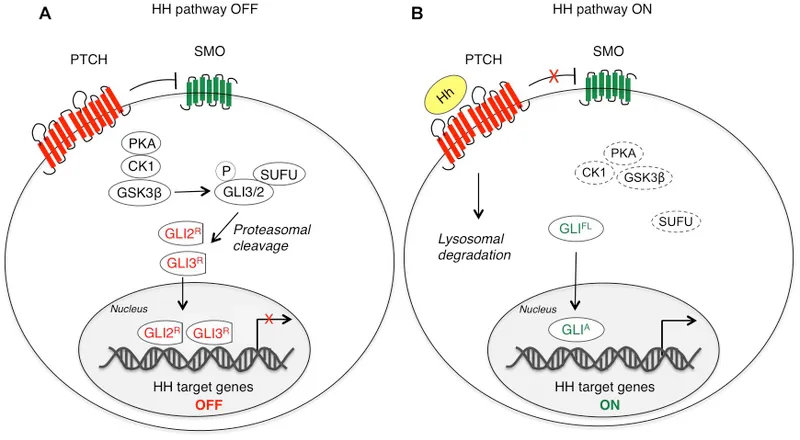
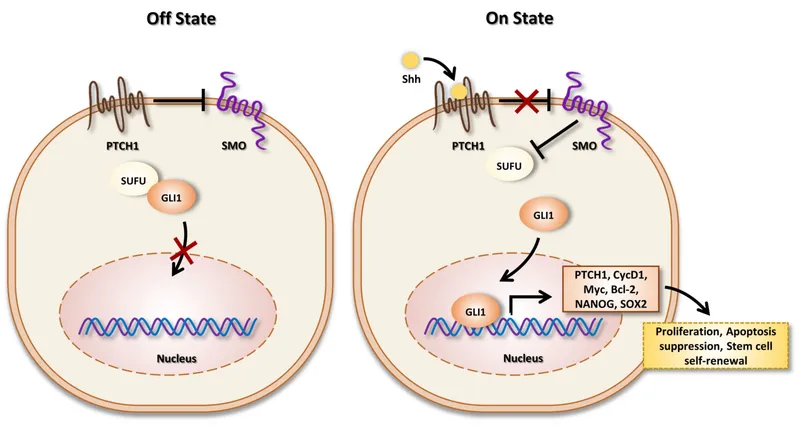
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: **PTCH1 gene mutation**
- The clinical presentation of a **pearly nodule with telangiectasias** on the **nose**, history of **sun exposure**, and **basaloid cells arranged in palisading patterns** on biopsy are classic for **basal cell carcinoma (BCC)** [1].
- Mutations in the **PTCH1 gene**, a tumor suppressor gene involved in the **Hedgehog signaling pathway**, are found in the majority of sporadic BCCs and are central to its pathogenesis [2,3].
*P53 mutation*
- While **P53 mutations** are common in many cancers, including **squamous cell carcinoma** [3], they are not the primary driver mutation for basal cell carcinoma in the way PTCH1 mutations are.
- Loss of P53 function typically leads to uncontrolled cell growth and reduced apoptosis, but it's a general cancer mechanism rather than a specific one for BCC.
*EGFR mutation*
- **EGFR mutations** are primarily associated with certain types of **lung adenocarcinoma** and **glioblastoma**, not basal cell carcinoma.
- These mutations lead to constitutive activation of the **epidermal growth factor receptor** signaling pathway, promoting cell proliferation and survival in those specific cancers.
*KIT mutation*
- **KIT mutations** are most commonly found in **gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST)** and certain types of **melanoma**.
- The KIT receptor tyrosine kinase plays a role in cell growth and differentiation in specific cell lineages, distinct from the epidermal cells involved in BCC.
**References:**
[1] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. The Skin, pp. 1158-1162.
[2] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. Neoplasia, pp. 306-307.
[3] Cross SS. Underwood's Pathology: A Clinical Approach. 6th ed. Disorders Involving Inflammatory And Haemopoietic Cells, pp. 643-644.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 9: An 8-year-old boy presents with a skin lesion on his back as shown in the picture. On physical examination, there are synchronous spasmodic movements of the neck, trunk, and extremities. The physician explains that this is likely due to a genetic condition, and further testing would be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Which of the following genes is involved in the development of this patient’s condition?
- A. NF2
- B. GNAQ
- C. TSC1 (Correct Answer)
- D. VHL
- E. NF1
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***TSC1***
- The image shows a **Shagreen patch**, a connective tissue nevus often described as having an "orange peel" or cobblestone texture, which is **pathognomonic for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)**.
- The description of **synchronous spasmodic movements** (seizures) in this 8-year-old boy is a common neurological manifestation of TSC. While TSC patients may present with **infantile spasms in early childhood**, older children typically develop other seizure types including **generalized tonic-clonic or myoclonic seizures**.
- Mutations in the **TSC1** (hamartin gene on chromosome 9q34) or **TSC2** (tuberin gene on chromosome 16p13.3) genes are responsible for this autosomal dominant condition affecting the mTOR pathway.
*NF2*
- Mutations in the *NF2* gene cause **Neurofibromatosis type 2**, characterized primarily by **bilateral vestibular schwannomas** (acoustic neuromas) leading to hearing loss.
- Dermatological manifestations include **cafe-au-lait spots** (fewer than NF1) and **cutaneous schwannomas**, not Shagreen patches.
*GNAQ*
- The *GNAQ* gene is associated with **Sturge-Weber syndrome**, which presents with a **port-wine stain (facial nevus flammeus)** typically in the trigeminal distribution and neurological symptoms such as seizures and developmental delays.
- This patient's Shagreen patch is not consistent with the vascular malformation seen in Sturge-Weber syndrome.
*VHL*
- Mutations in the *VHL* gene cause **Von Hippel-Lindau disease**, which predisposes individuals to various tumors including **cerebellar and retinal hemangioblastomas**, **renal cell carcinoma**, and **pheochromocytomas**.
- The clinical picture of a Shagreen patch and seizures is not characteristic of Von Hippel-Lindau disease.
*NF1*
- Mutations in the *NF1* gene cause **Neurofibromatosis type 1**, characterized by **multiple cafe-au-lait spots** (≥6), **axillary/inguinal freckling (Crowe's sign)**, cutaneous neurofibromas, **Lisch nodules** (iris hamartomas), and optic gliomas.
- While it is a neurocutaneous disorder, the skin lesion presented (Shagreen patch) is specific to TSC, not NF1.
Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG Question 10: A 55-year-old woman has a total thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma. She complains of tingling around the mouth 11 hours after the operation. Her condition rapidly deteriorates with difficulty breathing and chest tightness. Which of the following best represent the signaling pathway of the deficient hormone responsible for this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)
- B. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) (Correct Answer)
- C. Intracellular receptors
- D. Receptor tyrosine kinase
- E. Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)
Hedgehog signaling pathway Explanation: ***Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)***
- The patient's symptoms of perioral tingling, difficulty breathing, and chest tightness after total thyroidectomy suggest **hypocalcemia**, likely due to accidental removal or damage to the **parathyroid glands** during surgery.
- The deficient **parathyroid hormone (PTH)** acts primarily through the **cAMP second messenger system** to increase serum calcium levels.
*Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)*
- **cGMP** is a second messenger system primarily involved in mediating the effects of hormones like **atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** and **nitric oxide**, which are unrelated to calcium homeostasis and parathyroid function.
- This pathway is not the primary mechanism of action for **PTH**.
*Intracellular receptors*
- **Intracellular receptors** are typically used by **steroid hormones** (e.g., cortisol, estrogen) and **thyroid hormones**, which are lipid-soluble and can cross the cell membrane.
- **PTH** is a peptide hormone and acts on cell surface receptors.
*Receptor tyrosine kinase*
- **Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)** are transmembrane receptors involved in signaling pathways for hormones like **insulin** and **growth factors**, promoting cell growth, differentiation, and metabolism.
- This is not the primary signaling pathway for **PTH**.
*Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)*
- The **IP3/DAG (diacylglycerol)** pathway is another common second messenger system used by various hormones (e.g., **vasopressin, oxytocin, TRH**), leading to the release of intracellular calcium.
- While it involves calcium signaling, it is not the primary or most characteristic pathway for **PTH** action, which predominantly utilizes **cAMP**.
More Hedgehog signaling pathway US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.