Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Dysregulation in disease states. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 1: Researchers are investigating oncogenes, specifically the KRAS gene that is associated with colon, lung, and pancreatic cancer. They have established that the gain-of-function mutation in this gene increases the chance of cancer development. They are also working to advance the research further to study tumor suppressor genes. Which of the genes below is considered a tumor suppressor gene?
- A. Her2/neu
- B. BRAF
- C. BCL-2
- D. JAK2
- E. Rb (Correct Answer)
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Rb***
- The **retinoblastoma (Rb)** gene is a classic example of a **tumor suppressor gene**. Its protein product, Rb, plays a critical role in regulating the **cell cycle** by preventing uncontrolled cell division.
- When **Rb is mutated or inactivated**, cells can divide without proper checks, leading to tumor formation, particularly in cases like retinoblastoma.
*Her2/neu*
- **Her2/neu** (also known as ERBB2) is an **oncogene** that encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase involved in cell growth and differentiation.
- Its overexpression or amplification is associated with certain cancers, notably **breast cancer**, but it is not a tumor suppressor.
*BRAF*
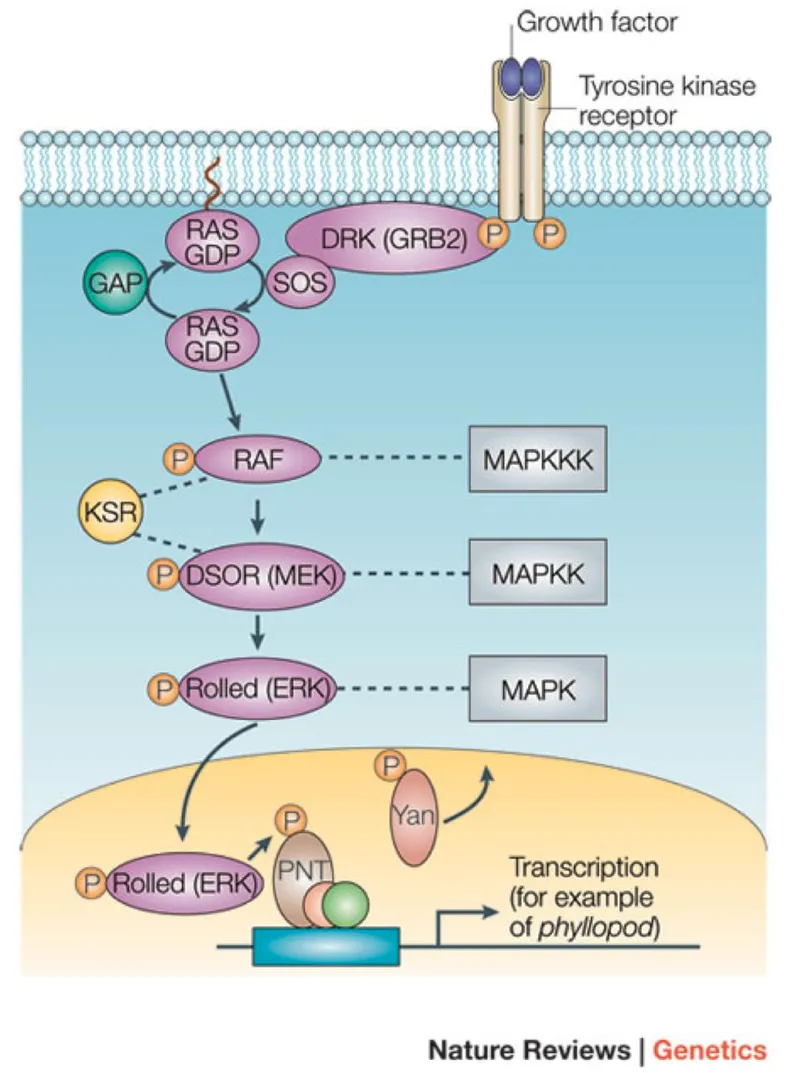
- **BRAF** is an **oncogene** that codes for a serine/threonine kinase involved in the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway, which regulates cell growth.
- **Gain-of-function mutations** in BRAF are frequently found in melanoma, thyroid cancer, and colorectal cancer, promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation.
*BCL-2*
- **BCL-2** is an **anti-apoptotic gene**, meaning it prevents programmed cell death. While its overexpression can contribute to cancer by allowing abnormal cells to survive, it is not classified as a tumor suppressor gene.
- Instead, BCL-2 is considered an **oncogene** because mutations or overexpression promote cell survival and inhibit apoptosis.
*JAK2*
- **JAK2** (Janus Kinase 2) is a **proto-oncogene** encoding a tyrosine kinase involved in cytokine receptor signaling, which regulates hematopoiesis.
- **Gain-of-function mutations**, such as JAK2 V617F, are frequently found in **myeloproliferative neoplasms** (e.g., polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, myelofibrosis), leading to uncontrolled blood cell production.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 2: A scientist is studying the anatomy and function of bone growth. He is able to create a cell line of osteocytes with a mutation that prevents the osteocytes from exchanging nutrients and waste products within neighboring lamellae. This mutation most likely affected which of the following cell structures?
- A. Dynein
- B. Gap junctions (Correct Answer)
- C. Endoplasmic reticulum
- D. Plasma membrane
- E. Kinesin
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Gap junctions***
- **Gap junctions** are specialized intercellular connections that permit direct communication and exchange of small molecules and ions between adjacent cells.
- In osteocytes, **gap junctions** located in the **canaliculi** are crucial for the exchange of nutrients, waste, and signaling molecules within and between lamellae, allowing for synchronous activity and maintaining bone health.
- These connexin-based channels physically connect the cytoplasm of neighboring osteocytes embedded in bone matrix.
*Dynein*
- **Dynein** is a motor protein involved in intracellular transport towards the minus end of **microtubules**, playing a role in moving organelles and vesicles.
- It is not directly responsible for the intercellular exchange of nutrients and waste products between cells.
*Endoplasmic reticulum*
- The **endoplasmic reticulum** is an organelle involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism, playing a critical role in cellular function.
- It does not directly mediate the exchange of nutrients and waste products between adjacent cells.
*Plasma membrane*
- While **gap junctions** are embedded within the **plasma membrane**, the membrane itself does not facilitate direct cytoplasmic continuity between cells.
- The question specifically refers to structures that enable direct cell-to-cell exchange; the mutation affects the gap junction channels themselves (connexins), not the general plasma membrane structure.
- Without functional gap junctions, the plasma membrane alone cannot support the intercellular communication required for osteocyte networks.
*Kinesin*
- **Kinesin** is a motor protein that moves cargo along **microtubules** towards the plus end, involved in fundamental cellular processes like cell division and organelle transport.
- It is not involved in direct intercellular communication for nutrient and waste exchange but rather internal cellular trafficking.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 3: A 26-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his friends because of blurred vision and slurred speech for the past 6 hours. He had some difficulty swallowing his food during lunch and has weakness in both arms. Two weeks ago, he had an upper respiratory infection that resolved spontaneously. He lives independently and returned from his grandparents' farm 2 days ago. He commonly consumes canned vegetables and fruits. He is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 88/min, respirations are 10/min and labored, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Examination shows bilateral nystagmus and ptosis. The pupils are dilated and not reactive to light. Muscle strength of the facial muscles and bilateral upper extremities is decreased. Upper extremity deep tendon reflexes are 1+ bilaterally. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Autoantibodies against myelin
- B. Chemical that inhibits acetylcholinesterase
- C. Autoantibodies against ACh receptors
- D. Toxin that inhibits ACh release (Correct Answer)
- E. Cell-mediated focal demyelination
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: **Toxin that inhibits ACh release**
- The patient's symptoms, including **blurred vision, ptosis, fixed dilated pupils, slurred speech, dysphagia, and descending flaccid paralysis** (weakness in arms before legs, with reduced reflexes), are highly characteristic of **botulism**.
- **Clostridium botulinum toxin** inhibits the release of **acetylcholine (ACh)** at the neuromuscular junction and parasympathetic synapses, leading to these symptoms. The history of consuming **canned foods** and returning from a farm suggests a potential exposure source.
*Autoantibodies against myelin*
- This mechanism describes **Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS)**, which typically presents with **ascending paralysis** and areflexia, often following an infection.
- While GBS can cause some cranial nerve involvement, the prominent **fixed dilated pupils (pupil-sparing paralysis is typical in GBS)** and the **descending pattern of weakness** in this patient are inconsistent with GBS.
*Chemical that inhibits acetylcholinesterase*
- This mechanism is associated with **organophosphate poisoning**, which presents with a **cholinergic crisis**.
- Symptoms include **miosis**, increased salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, gastrointestinal upset, emesis (**SLUDGE** syndrome), bradycardia, and muscle fasciculations, none of which are noted in this patient.
*Autoantibodies against ACh receptors*
- This is the underlying mechanism of **myasthenia gravis**, an autoimmune disorder characterized by **fluctuating muscle weakness** that worsens with activity and improves with rest.
- Key features often include **ptosis and diplopia**, but pupils are typically **spared**. The weakness in myasthenia gravis is not typically descending with fixed dilated pupils, and it does not usually present acutely with such severe widespread involvement.
*Cell-mediated focal demyelination*
- This describes the pathology of **multiple sclerosis (MS)**, a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system.
- MS typically presents with **diverse neurological symptoms** that can be relapsing-remitting or progressive, often including sensory disturbances, motor weakness, visual changes (e.g., optic neuritis), and bladder dysfunction. It does not typically cause acute, rapidly progressive flaccid paralysis with fixed dilated pupils and bulbar symptoms as seen here.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 4: A 40-year-old man is brought to an urgent care clinic by his wife with complaints of dizziness and blurring of vision for several hours. His wife adds that he has had slurred speech since this morning and complained of difficulty swallowing last night. His wife mentions that her husband was working outdoors and ate stew with roasted beef and potatoes that had been sitting on the stove for the past 3 days. The patient's past medical history is unremarkable. A physical examination reveals right eye ptosis and palatal weakness with an impaired gag reflex. Cranial nerve examination reveals findings suggestive of multiple cranial nerve involvement. What is the mechanism of action of the toxin that is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Ribosylation of the Gs protein
- B. Inhibition of glycine and GABA
- C. Expression of superantigen
- D. Inhibition of the release of acetylcholine (Correct Answer)
- E. Ribosylation of eukaryotic elongation factor-2
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Inhibition of the release of acetylcholine***
- The patient's symptoms (dizziness, blurred vision, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing, ptosis, palatal weakness, impaired gag reflex, CN V and VII lesions) are consistent with **botulism**, caused by *Clostridium botulinum* toxin.
- **Botulinum toxin** acts by cleaving SNARE proteins (syntaxin, SNAP-25, and synaptobrevin) at the neuromuscular junction, thereby **inhibiting acetylcholine (ACh) release** from presynaptic terminals and causing flaccid paralysis.
*Ribosylation of the Gs protein*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **cholera toxin** and **heat-labile enterotoxin** of *E. coli*.
- It leads to persistent activation of adenylate cyclase, resulting in increased cyclic AMP and causing **secretory diarrhea**, which is not seen here.
*Inhibition of glycine and GABA*
- This mechanism is associated with **tetanus toxin**, produced by *Clostridium tetani*.
- Tetanus toxin acts by blocking the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters **glycine** and **GABA** in the spinal cord, leading to spastic paralysis and muscle rigidity.
*Expression of superantigen*
- **Superantigens** are toxins produced by bacteria like *Staphylococcus aureus* (e.g., toxic shock syndrome toxin-1) and *Streptococcus pyogenes*.
- They cause widespread activation of T cells, leading to a massive inflammatory response and symptoms like **fever, rash, and hypotension**, rather than neurological deficits.
*Ribosylation of eukaryotic elongation factor-2*
- This is the mechanism of action of **diphtheria toxin**, produced by *Corynebacterium diphtheriae*.
- It inhibits protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells, leading to **cell death** and symptoms like pharyngitis, pseudomembrane formation, and myocarditis, not the paralytic symptoms described.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 5: A 30-year-old woman presents to her physician for her annual checkup. She has diabetes mellitus, type 1 and takes insulin regularly. She reports no incidents of elevated or low blood sugar and that she is feeling energetic and ready to face the morning every day. Her vital signs and physical are normal. On the way home from her checkup she stops by the pharmacy and picks up her prescription of insulin. Later that night she takes a dose. What is the signaling mechanism associated with this medication?
- A. Increased concentration intracellular cAMP
- B. Increased permeability of the cell membrane to negatively charged molecules
- C. Activation of tyrosine kinase (Correct Answer)
- D. Rapid and direct upregulation of enzyme transcription
- E. Increased permeability of the cell membrane to positively charged molecules
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Activation of tyrosine kinase***
- **Insulin** primarily binds to the **insulin receptor**, which is a **receptor tyrosine kinase**.
- Upon insulin binding, the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor is activated, leading to **autophosphorylation** and phosphorylation of downstream signaling proteins like **IRS-1**.
*Increased concentration intracellular cAMP*
- This mechanism is characteristic of signaling pathways involving **G protein-coupled receptors** that activate adenylyl cyclase, such as those for **glucagon** or **catecholamines**.
- Insulin does not primarily signal through **cAMP** as a second messenger.
*Increased permeability of the cell membrane to negatively charged molecules*
- Changes in membrane permeability to negatively charged molecules are usually associated with **GABAergic** or **glycinergic neurotransmission**, leading to inhibitory postsynaptic potentials.
- This is not a primary mechanism for **insulin signaling**.
*Rapid and direct upregulation of enzyme transcription*
- While insulin does influence gene expression over longer periods, its immediate effects involve **protein phosphorylation** and translocation, not direct, rapid transcriptional changes at the moment of receptor binding.
- Steroid hormones typically mediate more direct transcriptional regulation.
*Increased permeability of the cell membrane to positively charged molecules*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **ligand-gated ion channels** that allow influx of ions like **Na+** or **Ca2+**, important in neuronal excitation or muscle contraction.
- Insulin signaling primarily involves **kinase cascades** and not direct changes in membrane permeability to positive ions.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 6: A 46-year-old premenopausal woman undergoes lumpectomy after a diagnosis of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast is made. Pathologic examination of the surgical specimen shows that the breast cancer cells stain positive for estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor, and negative for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. Which of the following characteristics applies to the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient's condition?
- A. Monoclonal antibody against tyrosine kinase receptor
- B. Monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor
- C. Selective agonist at progesterone receptors in mammary tissue
- D. Selective agonist at estrogen receptors in bone tissue
- E. Selective antagonist at estrogen receptors in mammary tissue (Correct Answer)
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Selective antagonist at estrogen receptors in mammary tissue***
- The patient's tumor is **estrogen receptor (ER) positive** and **progesterone receptor (PR) positive**. This indicates a **hormone-sensitive cancer**, making endocrine therapy the most appropriate pharmacotherapy.
- A **selective antagonist at estrogen receptors** in mammary tissue, such as **tamoxifen** (a selective estrogen receptor modulator, SERM), is effective in blocking estrogen-mediated tumor growth in premenopausal patients.
*Monoclonal antibody against tyrosine kinase receptor*
- This therapy, typically targeting **HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2)**, would be appropriate if the tumor was **HER2-positive**.
- The patient's tumor is **HER2-negative**, meaning this type of targeted therapy would not be beneficial.
*Monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor*
- This class of drugs, like **bevacizumab**, targets **angiogenesis** by inhibiting VEGF, which is crucial for tumor blood supply.
- While used in some cancers, it is not the primary or most appropriate pharmacotherapy based on the specific receptor status of this patient's breast cancer.
*Selective agonist at progesterone receptors in mammary tissue*
- An **agonist** at progesterone receptors would **promote growth** if the tumor is progesterone receptor-positive, which would be counterproductive for cancer treatment.
- The goal of endocrine therapy for PR-positive tumors is to inhibit the effects of progesterone.
*Selective agonist at estrogen receptors in bone tissue*
- An agonist at estrogen receptors in bone tissue would **mimic estrogen's effects**, which is undesirable given the estrogen-sensitive nature of the breast cancer.
- While some SERMs (like tamoxifen) can have agonist effects in bone (which can be beneficial for bone density), the primary therapeutic action for breast cancer is antagonism in mammary tissue.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 7: A stool sample was taken from a 19-year-old male who presented with profuse watery diarrhea. He recently returned from a trip to Central America. A microbiologist identified the causative agent as a gram-negative, oxidase-positive, comma-shaped bacteria that is able to grow well in a pH > 8. Which of the following is a mechanism of action of the toxin produced by this bacteria?
- A. Overactivation of adenylate cyclase by inhibition of Gi subunit by ADP-ribosylation
- B. Inactivation of the 60S ribosomal subunit by cleaving an adenine from the 28S rRNA
- C. Overactivation of guanylate cyclase
- D. Overactivation of adenylate cyclase by activation of Gs subunit by ADP-ribosylation (Correct Answer)
- E. Degradation of cell membranes by hydrolysis of the phospholipids
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Overactivation of adenylate cyclase by activation of Gs subunit by ADP-ribosylation***
- The description of the bacterium as **gram-negative, oxidase-positive, comma-shaped, growing well in pH > 8**, and causing **profuse watery diarrhea** after travel to Central America points to *Vibrio cholerae*.
- **Cholera toxin** (CTX) produced by *V. cholerae* is an A-B toxin that **ADP-ribosylates the Gs α-subunit**, permanently activating **adenylate cyclase**. This leads to increased cAMP levels, causing secretion of water and electrolytes into the intestinal lumen.
*Overactivation of adenylate cyclase by inhibition of Gi subunit by ADP-ribosylation*
- This mechanism describes the action of **pertussis toxin** from *Bordetella pertussis*, which ADP-ribosylates and **inhibits the Gi subunit**, preventing adenylate cyclase inhibition.
- While both ultimately increase cAMP, the specific target and mechanism (inhibition of Gi vs. activation of Gs) differ from cholera toxin.
*Inactivation of the 60S ribosomal subunit by cleaving an adenine from the 28S rRNA*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **Shiga toxin** produced by *Shigella dysenteriae* and Shiga-like toxins (verotoxins) produced by **enterohemorrhagic *E. coli*** (EHEC).
- These toxins inhibit protein synthesis, leading to cell death and often bloody diarrhea and hemolytic uremic syndrome, which is not described here.
*Overactivation of guanylate cyclase*
- **Heat-stable enterotoxins (ST)** produced by **enterotoxigenic *E. coli*** (ETEC) activate **guanylate cyclase**, leading to increased cGMP and subsequent fluid secretion.
- While ETEC can cause watery diarrhea, the bacterial characteristics provided (oxidase-positive, comma-shaped) do not fit *E. coli*.
*Degradation of cell membranes by hydrolysis of the phospholipids*
- This mechanism is associated with toxins like **phospholipases** or **lecithinases** (e.g., alpha-toxin of *Clostridium perfringens*).
- These toxins cause direct cell lysis and tissue damage, which is not the primary mechanism of action for the watery diarrhea seen in cholera.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 8: A group of scientists is studying the mechanism of action of various pancreatic hormones in rats. The scientists studied hormone A, which is secreted by the β-cells of the pancreas, and found that hormone A binds to a complex dimeric receptor on the cell membrane and exerts its effects via phosphorylation and subsequent downstream signaling that includes dephosphorylation of different intracellular proteins. Now they are studying hormone B, which is secreted by the α-cells and antagonizes the actions of hormone A. Which 2nd messenger system would hormone B utilize to exert its cellular effects?
- A. Direct cytoplasmic receptor binding
- B. Phospholipase C
- C. Tyrosine kinase
- D. Direct nuclear receptor binding
- E. Adenylyl cyclase-cyclic AMP (Correct Answer)
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Adenylyl cyclase-cyclic AMP***
- Hormone B is **glucagon**, secreted by pancreatic α-cells, which antagonizes the effects of insulin (hormone A). Glucagon primarily acts through a **G protein-coupled receptor** that activates **adenylyl cyclase**, leading to an increase in intracellular **cyclic AMP (cAMP)**.
- Increased cAMP then activates **protein kinase A (PKA)**, which phosphorylates various intracellular proteins to promote **glycogenolysis** and **gluconeogenesis**, thereby raising blood glucose levels.
*Direct cytoplasmic receptor binding*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **steroid hormones**, which are lipid-soluble and can diffuse across the cell membrane to bind to receptors in the cytoplasm.
- Pancreatic hormones like glucagon are **peptide hormones**, which are water-soluble and typically bind to cell surface receptors.
*Phospholipase C*
- Activation of **phospholipase C (PLC)** leads to the production of **inositol triphosphate (IP3)** and **diacylglycerol (DAG)**, which mobilize intracellular calcium and activate protein kinase C, respectively.
- While some G protein-coupled receptors activate PLC, **glucagon's primary signaling pathway** involves adenylyl cyclase.
*Tyrosine kinase*
- **Tyrosine kinase receptors** are often associated with growth factors and insulin (hormone A) signaling, leading to phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on target proteins.
- Glucagon's receptor is a **G protein-coupled receptor**, not a receptor tyrosine kinase, and its actions are mediated through serine/threonine phosphorylation via PKA.
*Direct nuclear receptor binding*
- This mechanism is typical for **steroid hormones** and **thyroid hormones**, which are lipid-soluble and bind to receptors in the nucleus to directly influence gene transcription.
- As a peptide hormone, glucagon binds to cell surface receptors and does not directly interact with nuclear receptors.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 9: A 64-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 7-month history of abdominal discomfort, fatigue, and a 6.8-kg (15-lb) weight loss. Physical examination shows generalized pallor and splenomegaly. Laboratory studies show anemia with pronounced leukocytosis and thrombocytosis. Cytogenetic analysis shows a BCR-ABL fusion gene. A drug with which of the following mechanisms of action is most appropriate for this patient?
- A. Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor
- B. Monoclonal anti-HER-2 antibody
- C. Topoisomerase II inhibitor
- D. Monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody
- E. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Correct Answer)
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Tyrosine kinase inhibitor***
- The patient's symptoms (abdominal discomfort, fatigue, weight loss, pallor, splenomegaly), laboratory findings (**anemia with pronounced leukocytosis and thrombocytosis**), and the presence of a **BCR-ABL fusion gene** are highly characteristic of **Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)**.
- The **BCR-ABL fusion gene** encodes a constitutively active **tyrosine kinase**, which is the hallmark of CML and the primary therapeutic target for **tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs)** like imatinib.
*Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor*
- **Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors** (e.g., hydroxyurea) block DNA synthesis and are used in myeloproliferative disorders to reduce cell counts, but they are not specific to the **BCR-ABL fusion gene** and are not the most appropriate first-line targeted therapy for CML.
- While they can control symptoms, they do not target the underlying molecular defect in CML as effectively as TKIs.
*Monoclonal anti-HER-2 antibody*
- **Monoclonal anti-HER-2 antibodies** (e.g., trastuzumab) are used to treat **HER-2 positive breast cancer** and some gastric cancers.
- They are not relevant to the treatment of CML, which is characterized by the **BCR-ABL fusion gene**.
*Topoisomerase II inhibitor*
- **Topoisomerase II inhibitors** (e.g., etoposide, doxorubicin) prevent DNA unwinding and replication, leading to cell death, and are used in various hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
- These drugs are broad-spectrum chemotherapeutic agents not specifically targeted to the **BCR-ABL fusion protein** in CML and are not first-line therapy for this condition.
*Monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody*
- **Monoclonal anti-CD20 antibodies** (e.g., rituximab) target the CD20 protein on B lymphocytes and are primarily used to treat **B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma** and some autoimmune diseases.
- They have no role in the direct treatment of CML, which is a myeloid malignancy.
Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG Question 10: An 11-month-old boy is brought to a pediatrician by his parents with a recurrent cough, which he has had since the age of 2 months. He has required 3 hospitalizations for severe wheezing episodes. His mother also mentions that he often has diarrhea. The boy’s detailed history reveals that he required hospitalization for meconium ileus during the neonatal period. Upon physical examination, his temperature is 37.0°C (98.6ºF), pulse rate is 104/min, respiratory rate is 40/min, and blood pressure is 55/33 mm Hg. An examination of the boy’s respiratory system reveals the presence of bilateral wheezing and scattered crepitations. An examination of his cardiovascular system does not reveal any abnormality. His length is 67.3 cm (26.5 in) and weight is 15 kg (33 lbs). His sweat chloride level is 74 mmol/L. His genetic evaluation confirms that he has an autosomal recessive disorder resulting in a dysfunctional membrane-bound protein. Which of the following best describes the mechanism associated with the most common mutation that causes this disorder?
- A. Decreased chloride transport through the protein
- B. Disordered regulation of the protein
- C. Decreased transcription of the protein due to splicing defect
- D. Complete absence of the protein
- E. Defective maturation and early degradation of the protein (Correct Answer)
Dysregulation in disease states Explanation: ***Defective maturation and early degradation of the protein***
- The clinical picture (recurrent cough, wheezing, diarrhea, meconium ileus, elevated sweat chloride, autosomal recessive inheritance) strongly points to **cystic fibrosis (CF)**. The most common mutation in CF is **F508del**, which leads to misfolding of the **CFTR protein**, causing retention in the endoplasmic reticulum and subsequent degradation before reaching the cell membrane.
- This **defective processing and early degradation** result in a significant reduction or absence of functional CFTR protein at the cell surface, leading to impaired chloride transport.
*Decreased chloride transport through the protein*
- While **decreased chloride transport** is the ultimate functional consequence of cystic fibrosis, it is not the direct mechanism associated with the **F508del mutation's impact** on the CFTR protein itself.
- This option describes the **physiological result** of the protein defect, not the cellular/molecular mechanism of the most common mutation.
*Disordered regulation of the protein*
- **Disordered regulation** could be a potential mechanism for some CFTR mutations (Class IV mutations), affecting how the channel opens and closes or responds to signaling.
- However, for the **F508del mutation** (Class II mutation), the primary issue is the **lack of properly localized protein** due to misfolding and degradation, rather than a problem with the regulation or gating of the protein once it reaches the membrane.
*Decreased transcription of the protein due to splicing defect*
- **Decreased transcription** or **splicing defects** (Class I and V mutations) would result in reduced mRNA levels or incorrectly formed mRNA, leading to less protein synthesis.
- The **F508del mutation** involves a deletion of three nucleotides in exon 10, leading to a missing phenylalanine at position 508. Importantly, **transcription and splicing occur normally**; the mRNA is produced correctly. The problem arises at the **post-translational level** with protein folding, not at the transcriptional or splicing level.
*Complete absence of the protein*
- While functional CFTR protein is largely absent at the cell surface in F508del, the protein is **initially synthesized** in the endoplasmic reticulum.
- The problem is its **misfolding and rapid degradation**, preventing it from reaching the membrane, rather than a complete failure of protein synthesis from the outset (which would be seen in nonsense or frameshift mutations causing Class I defects).
More Dysregulation in disease states US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.