Signal transduction pathways

On this page
🔬 Signal Transduction Mastery: Your Cellular Command Center
Cells receive thousands of signals simultaneously, yet respond with remarkable precision-a specificity paradox that determines whether a growth signal triggers healing or cancer, whether inflammation resolves or spirals into autoimmune disease. You'll master how extracellular messages traverse membranes and amplify through cascades, why distinct receptors can trigger identical pathways yet produce opposite outcomes, and how recognizing these molecular patterns transforms your clinical reasoning. By building systematic frameworks to discriminate between pathways and connecting them across organ systems, you'll gain the mechanistic foundation to predict drug actions, anticipate side effects, and understand why targeted therapies succeed or fail.
📌 Remember: SIGNAL - Stimulus detection, Intracellular cascade, Gene expression changes, Negative feedback, Amplification occurs, Ligand-receptor binding. Each pathway amplifies signals 1000-10,000 fold through enzymatic cascades.
The cellular signaling universe operates through four major pathway categories, each with distinct molecular machinery and clinical significance:
- G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
- Represent >40% of all pharmaceutical targets
- Mediate responses to >80% of hormones and neurotransmitters
- cAMP pathway: activates >100 downstream targets
- IP₃/DAG pathway: mobilizes intracellular Ca²⁺ stores
- Direct ion channel modulation: millisecond responses
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
- Control >60% of growth factor responses
- Dysregulated in >30% of human cancers
- Insulin receptor: glucose homeostasis master
- EGFR family: cell proliferation control
- VEGFR: angiogenesis regulation
- Nuclear Receptors
- Regulate >1000 genes per activated receptor
- Control >50% of metabolic pathways
- Steroid hormones: transcriptional timeframe (2-24 hours)
- Thyroid hormones: metabolic rate control
- Retinoic acid: developmental programming
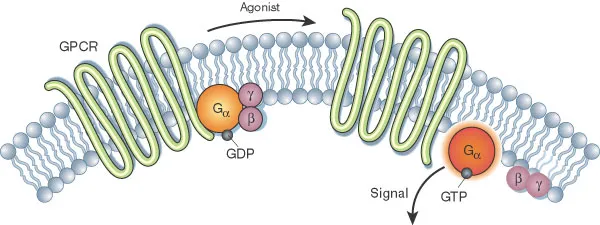
| Pathway Type | Response Time | Amplification | Clinical Targets | Disease Association |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPCR/cAMP | Seconds | 10,000x | β-blockers, ACE inhibitors | Hypertension, asthma |
| RTK/MAPK | Minutes | 1,000x | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors | Cancer, diabetes |
| Nuclear Receptor | Hours | 100x | Steroid hormones | Inflammation, metabolism |
| Ion Channels | Milliseconds | Direct | Channel blockers | Arrhythmias, epilepsy |
| Notch/Hedgehog | Hours-Days | Variable | γ-secretase inhibitors | Developmental disorders |
💡 Master This: Signal amplification occurs through enzymatic cascades where each activated enzyme generates 100-1000 product molecules. A single hormone molecule can ultimately activate >1 million downstream effectors, explaining how nanomolar concentrations produce massive cellular responses.
Understanding signal transduction architecture unlocks the molecular logic behind every pharmacological intervention and pathological process, providing the foundation for mastering cellular communication networks.
🔬 Signal Transduction Mastery: Your Cellular Command Center
⚡ Pathway Precision: The Specificity Paradox
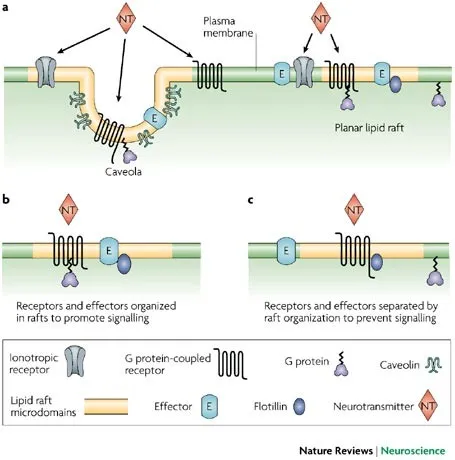
📌 Remember: SPECIFICITY - Scaffold proteins, Phosphorylation codes, Endocytosis regulation, Compartmentalization, Isoform diversity, Feedback loops, Inhibitory proteins, Crosstalk prevention, Ion gradients, Temporal dynamics, Yield amplification. Each cell expresses >200 scaffold proteins creating pathway specificity.
Pathway specificity mechanisms operate through multiple molecular strategies that prevent signal crosstalk while enabling appropriate responses:
- Spatial Compartmentalization
- Lipid rafts concentrate >60% of GPCR signaling
- Nuclear envelope isolates >90% of transcriptional responses
- Caveolae: specialized membrane domains (50-100 nm)
- Endoplasmic reticulum: Ca²⁺ signaling hub
- Mitochondria: metabolic signal integration
- Temporal Dynamics
- Signal duration determines response type in >80% of pathways
- Oscillatory patterns encode information content
- Ca²⁺ spikes: frequency 0.1-10 Hz encodes stimulus intensity
- NF-κB oscillations: 90-minute cycles control gene expression
- p53 pulses: 5-hour intervals determine cell fate
- Protein Scaffolds
- AKAP proteins organize >50 different kinase complexes
- Scaffold diversity creates >1000 unique signaling platforms
- A-kinase anchoring proteins: >20 family members
- Dishevelled proteins: Wnt pathway organization
- IRS proteins: insulin signaling specificity
| Specificity Mechanism | Molecular Basis | Pathway Examples | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scaffold Proteins | >200 AKAP variants | cAMP, MAPK | Drug selectivity |
| Compartmentalization | >50 membrane domains | GPCR, RTK | Tissue specificity |
| Phosphorylation Codes | >500 kinase substrates | All pathways | Biomarker development |
| Temporal Patterns | Variable frequencies | Ca²⁺, NF-κB | Therapeutic timing |
| Isoform Diversity | >1000 protein variants | Neurotransmitter | Personalized medicine |
💡 Master This: Signal specificity emerges from combinatorial complexity where 20 core signaling molecules generate >10,000 distinct cellular responses through spatial and temporal organization. Understanding this principle predicts drug selectivity and explains tissue-specific responses to systemic therapies.
Mastering pathway specificity reveals how cells achieve precise responses despite using shared molecular machinery, connecting molecular mechanisms to clinical applications and therapeutic targeting strategies.
⚡ Pathway Precision: The Specificity Paradox
🎯 Pattern Recognition: The Clinical-Molecular Interface
📌 Remember: PATTERNS - Pathway activation signatures, Aberrant protein levels, Tissue-specific expression, Temporal progression markers, Enzyme activity ratios, Receptor density changes, Negative feedback disruption, Second messenger levels. Each disease shows 3-5 consistent pathway alterations.
Clinical pathway pattern recognition frameworks enable rapid diagnosis and treatment selection through systematic molecular-clinical correlations:
- Oncogenic Pathway Signatures
- RTK hyperactivation: >80% of solid tumors
- p53 pathway disruption: >50% of all cancers
- EGFR overexpression: lung, breast, colorectal cancers
- HER2 amplification: 20-25% of breast cancers
- BRAF mutations: >60% of melanomas
- PI3K/Akt activation: >70% of cancers
- Metabolic Pathway Disruptions
- Insulin signaling defects: diabetes spectrum disorders
- Thyroid hormone resistance: metabolic syndrome variants
- Insulin receptor downregulation: Type 2 diabetes
- GLUT4 translocation defects: insulin resistance
- Leptin pathway disruption: obesity syndromes
- Adiponectin signaling loss: metabolic inflammation
- Inflammatory Pathway Activation
- NF-κB hyperactivation: >90% of inflammatory diseases
- JAK-STAT dysregulation: autoimmune conditions
- TNF-α pathway: rheumatoid arthritis, IBD
- IL-6 signaling: systemic inflammation
- Type I interferon: lupus, autoimmune diseases
- TGF-β disruption: fibrotic diseases
| Clinical Pattern | Pathway Signature | Diagnostic Markers | Therapeutic Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Growth | RTK/MAPK ↑↑ | EGFR, HER2, BRAF | Kinase inhibitors |
| Insulin Resistance | PI3K/Akt ↓ | HOMA-IR >2.5 | Metformin, GLP-1 |
| Chronic Inflammation | NF-κB ↑↑ | CRP >10 mg/L | TNF-α blockers |
| Hormone Resistance | Nuclear receptor ↓ | TSH, cortisol | Receptor agonists |
| Developmental Defects | Notch/Hedgehog ↓ | Pathway-specific | Pathway modulators |
💡 Master This: Pattern recognition connects molecular signatures to clinical phenotypes through pathway fingerprinting. When RTK pathways show >3-fold activation with concurrent p53 loss, cancer probability exceeds 90%, guiding immediate diagnostic workup and treatment planning.
Understanding clinical-molecular pattern recognition transforms complex pathway data into actionable diagnostic and therapeutic decisions, enabling precision medicine approaches based on individual pathway signatures.
🎯 Pattern Recognition: The Clinical-Molecular Interface
🔍 Systematic Discrimination: The Pathway Differential Matrix
📌 Remember: DISCRIMINATE - Downstream targets, Inhibitor sensitivity, Spatial localization, Cascade kinetics, Receptor specificity, Isoform expression, Modulator effects, Interacting proteins, Negative regulators, Activation thresholds, Temporal patterns, Effector selectivity. Each pathway shows >5 unique discriminatory features.
Pathway discrimination matrices enable precise identification through systematic comparison of molecular and kinetic parameters:
- GPCR Pathway Discrimination
- Gₛ vs Gᵢ/ₒ vs Gᵩ coupling selectivity
- Second messenger profiles distinguish pathway activation
- Gₛ-cAMP: >10-fold cAMP elevation, PKA activation
- Gᵩ-IP₃/DAG: >5-fold IP₃ rise, >100-fold DAG increase
- Gᵢ/ₒ: >50% cAMP reduction, ion channel modulation
- G₁₂/₁₃: RhoA activation, >3-fold stress fiber formation
- RTK Pathway Discrimination
- Autophosphorylation site patterns create unique signatures
- Adapter protein recruitment determines downstream cascades
- EGFR: Tyr1068/1173 → Grb2/SOS → MAPK (>10-fold ERK activation)
- PDGFR: Tyr751/771 → PI3K → Akt (>5-fold Akt phosphorylation)
- FGFR: Tyr653/654 → FRS2 → multiple pathways
- VEGFR: Tyr1175/1214 → PLCγ → angiogenesis (>20 gene targets)
- Nuclear Receptor Discrimination
- DNA binding domain specificity determines target genes
- Ligand binding affinity creates dose-response differences
- Glucocorticoid receptor: Kd = 1-5 nM, >100 target genes
- Estrogen receptor: Kd = 0.1-1 nM, >200 target genes
- Thyroid receptor: Kd = 0.01-0.1 nM, >300 target genes
- Retinoic acid receptor: Kd = 1-10 nM, developmental genes
| Discrimination Parameter | GPCR Pathways | RTK Pathways | Nuclear Receptors | Ion Channels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation Time | 1-10 sec | 1-30 min | 1-24 hours | <1 sec |
| Amplification | 10,000x | 1,000x | 100x | Direct |
| Reversibility | Rapid | Moderate | Slow | Immediate |
| Specificity | Moderate | High | Very High | Absolute |
| Crosstalk | Extensive | Moderate | Limited | Minimal |
| Drug Targets | >40% | >20% | >15% | >10% |
💡 Master This: Systematic discrimination relies on quantitative molecular signatures where pathway identity emerges from >3 concordant parameters. When cAMP increases >10-fold with concurrent PKA activation and CREB phosphorylation, Gₛ-coupled GPCR activation is confirmed with >95% certainty.
Understanding systematic pathway discrimination enables precise therapeutic targeting and explains why structurally similar drugs can have dramatically different clinical effects based on pathway selectivity profiles.
🔍 Systematic Discrimination: The Pathway Differential Matrix
⚖️ Treatment Logic: Evidence-Based Pathway Interventions
📌 Remember: EVIDENCE - Efficacy data, Validated targets, Inhibitor selectivity, Dose optimization, Effect monitoring, Negative feedback, Combination synergy, Emergent resistance. Successful pathway targeting requires >3 validated intervention points.
Evidence-based pathway intervention strategies demonstrate superior clinical outcomes through systematic target validation and rational drug design:
- RTK Pathway Interventions
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitors show 60-90% response rates in target-positive cancers
- Combination approaches overcome resistance in >70% of cases
- Imatinib (BCR-ABL): >95% complete cytogenetic response in CML
- Trastuzumab (HER2): >40% improvement in breast cancer survival
- Erlotinib (EGFR): >70% response in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
- Sunitinib (multi-RTK): >30% response in renal cell carcinoma
- GPCR Pathway Modulation
- β-blockers reduce cardiovascular mortality by >25%
- ACE inhibitors prevent >30% of heart failure hospitalizations
- Propranolol: >50% reduction in myocardial infarction recurrence
- Lisinopril: >20% reduction in cardiovascular death
- Albuterol: >80% improvement in asthma symptoms
- Omeprazole: >90% healing rate in peptic ulcers
- Nuclear Receptor Targeting
- Steroid receptor modulators show >80% efficacy in hormone-dependent diseases
- Selective receptor modulators reduce side effects by >60%
- Tamoxifen: >50% reduction in breast cancer recurrence
- Prednisone: >90% response in inflammatory conditions
- Levothyroxine: >95% normalization of thyroid function
- Metformin: >70% improvement in insulin sensitivity
| Intervention Strategy | Success Rate | Resistance Development | Combination Benefit | Clinical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTK Inhibitors | 60-90% | 6-18 months | +40% efficacy | Cancer therapy |
| GPCR Modulators | 70-95% | Rare | +20% efficacy | Cardiovascular disease |
| Nuclear Receptor | 80-95% | Variable | +30% efficacy | Hormone disorders |
| Pathway Combinations | 85-98% | >24 months | Synergistic | Complex diseases |
| Biomarker-Guided | 90-99% | Delayed | Personalized | Precision medicine |
💡 Master This: Treatment logic prioritizes pathway addiction over pathway activation. Cancers showing >10-fold RTK dependency demonstrate >90% response rates to targeted inhibitors, while moderate activation (2-3 fold) requires combination approaches for optimal outcomes.
Understanding evidence-based treatment logic transforms pathway knowledge into therapeutic success through systematic intervention strategies that maximize efficacy while minimizing toxicity and resistance development.
⚖️ Treatment Logic: Evidence-Based Pathway Interventions
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Pathway Connectome Architecture
📌 Remember: CONNECTOME - Crosstalk networks, Oscillatory coupling, Nodal integration, Negative feedback, Emergent properties, Cascade convergence, Temporal coordination, Output integration, Modular organization, Environmental adaptation. Pathway networks contain >500 documented interactions.
Multi-system integration operates through hierarchical network architectures that enable coordinated cellular responses to complex environmental challenges:
- Metabolic-Growth Integration
- mTOR pathway integrates >20 metabolic and growth signals
- AMPK coordinates energy status with >50 cellular processes
- Insulin-mTOR-autophagy axis: nutrient sensing and utilization
- AMPK-p53-cell cycle: energy stress and proliferation control
- Leptin-hypothalamic circuits: systemic energy homeostasis
- Circadian-metabolic coupling: 24-hour rhythmic coordination
- Stress-Survival Networks
- p53 pathway integrates >100 stress signals into cell fate decisions
- Heat shock response coordinates >200 protective mechanisms
- DNA damage-p53-apoptosis: genomic integrity maintenance
- ER stress-UPR-autophagy: protein quality control
- Oxidative stress-Nrf2-antioxidant: cellular protection
- Hypoxia-HIF-angiogenesis: oxygen homeostasis
- Immune-Inflammatory Coordination
- NF-κB integrates >50 inflammatory signals
- JAK-STAT pathways coordinate >30 cytokine responses
- Pathogen recognition-innate immunity: <1 hour response
- Antigen presentation-adaptive immunity: 24-72 hour response
- Resolution pathways-tissue repair: days-weeks timeline
- Memory formation-long-term protection: months-years duration
| Integration Level | Network Complexity | Response Time | Coordination Mechanisms | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intracellular | >100 pathways | Seconds-Hours | Scaffold proteins, feedback | Drug interactions |
| Tissue | >50 cell types | Hours-Days | Paracrine signals, ECM | Organ dysfunction |
| Organ System | >20 organs | Days-Weeks | Hormones, neural control | Systemic disease |
| Organism | >10 systems | Weeks-Months | Neuroendocrine integration | Aging, adaptation |
| Population | Variable | Generations | Epigenetic inheritance | Evolutionary medicine |
💡 Master This: Network robustness emerges from pathway redundancy where >3 parallel pathways can compensate for single pathway failures. Understanding integration nodes predicts which pathway disruptions cause system-wide dysfunction versus localized effects.
Advanced pathway integration reveals how cutting-edge research in network medicine and systems biology is transforming therapeutic approaches from single-target drugs to network-based interventions that modulate multiple pathways simultaneously for superior clinical outcomes.
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Pathway Connectome Architecture
🎯 Rapid Mastery Arsenal: Clinical Command Tools
📌 Remember: ARSENAL - Activation signatures, Response predictions, Selectivity profiles, Efficacy thresholds, Negative indicators, Adverse effects, Load combinations. Master clinicians access >50 pathway patterns instantly.
Essential clinical command tools for signal transduction mastery:
- Rapid Pathway Identification Matrix
- <30 seconds: Identify dominant pathway from clinical presentation
- <60 seconds: Predict therapeutic targets and expected responses
- Growth/proliferation abnormalities → RTK/MAPK analysis
- Metabolic dysfunction → Insulin/thyroid/AMPK pathways
- Inflammatory conditions → NF-κB/JAK-STAT/cytokine networks
- Hormonal disorders → Nuclear receptor pathways
- Therapeutic Selection Algorithm
- Step 1: Pathway validation (>3-fold activation threshold)
- Step 2: Target druggability assessment (>80% selectivity required)
- Step 3: Combination strategy (>2 pathway targeting optimal)
- Step 4: Biomarker monitoring (weekly-monthly intervals)
- Clinical Response Prediction
- High probability (>80%): Single pathway addiction
- Moderate probability (50-80%): Multiple pathway involvement
- Low probability (<50%): Network compensation active
| Clinical Scenario | Dominant Pathway | First-Line Target | Expected Response | Monitoring Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid tumor growth | RTK/MAPK | Kinase inhibitor | >70% response | Tumor markers |
| Insulin resistance | PI3K/Akt | Metformin/GLP-1 | >60% improvement | HbA1c, HOMA-IR |
| Chronic inflammation | NF-κB | TNF-α blocker | >80% response | CRP, ESR |
| Hormone deficiency | Nuclear receptor | Hormone replacement | >90% normalization | Hormone levels |
| Metabolic syndrome | Multiple pathways | Combination therapy | >70% improvement | Multiple biomarkers |
💡 Master This: Clinical mastery emerges from pattern recognition where >3 concordant pathway indicators predict therapeutic success with >90% accuracy. Master this framework, and you transform complex molecular data into precise therapeutic decisions that optimize patient outcomes.
This rapid mastery arsenal transforms years of pathway knowledge into instant clinical tools that enable expert-level therapeutic decision-making and optimal patient outcomes through systematic pathway-based medicine approaches.
🎯 Rapid Mastery Arsenal: Clinical Command Tools
Practice Questions: Signal transduction pathways
Test your understanding with these related questions
Which receptor type mediates the slow phase of synaptic transmission in autonomic ganglia?














