Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Non-Mendelian inheritance. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 1: A 4-year-old boy presents to his pediatrician for severe developmental delay. On exam he is noted to have macroorchidism, hypertelorism, large protruding ears, a large jaw, and a long thin face. Suspicious of what the diagnosis may be, the pediatrician orders a PCR and DNA sequencing. The results reveal an expansion of 250 repeats of CGG. What is the diagnosis of the boy?
- A. Huntington's disease
- B. Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
- C. Myotonic dystrophy type 1
- D. Fragile X syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Friedreich ataxia
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***Fragile X syndrome***
- The combination of **developmental delay**, characteristic physical features (**macroorchidism, large protruding ears, long thin face, large jaw**), and a **CGG repeat expansion** (250 repeats) is pathognomonic for Fragile X syndrome.
- This is an **X-linked disorder** caused by an expansion of CGG trinucleotide repeats in the *FMR1* gene, leading to reduced or absent fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP).
*Huntington's disease*
- Characterized by **chorea**, psychiatric symptoms, and cognitive decline, typically manifesting in adulthood, not early childhood developmental delay.
- Caused by a **CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion** in the *HTT* gene, not CGG.
*Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy*
- This is an **X-linked recessive** neurodegenerative disorder leading to muscle weakness and atrophy, which usually presents in adulthood.
- It is caused by a **CAG repeat expansion** in the androgen receptor gene.
*Myotonic dystrophy type 1*
- Presents with progressive **muscle wasting and weakness**, myotonia, cataracts, and cardiac conduction defects, typically later in childhood or adulthood.
- Caused by a **CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion** in the *DMPK* gene.
*Friedreich ataxia*
- Characterized by progressive **ataxia**, dysarthria, and loss of vibration/proprioception, usually beginning in childhood or adolescence.
- Caused by a **GAA trinucleotide repeat expansion** in the *FXN* gene.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 2: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician because his mother is concerned about recent behavioral changes. His mother states that she has started to notice that he is slurring his speech and seems to be falling more than normal. On exam, the pediatrician observes the boy has pes cavus, hammer toes, and kyphoscoliosis. Based on these findings, the pediatrician is concerned the child has a trinucleotide repeat disease. Which of the following trinucleotide repeats is this child most likely to possess?
- A. CTG
- B. GAA (Correct Answer)
- C. CGG
- D. CAG
- E. GCC
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***GAA***
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **Friedreich's ataxia**, an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder.
- The presented symptoms of **ataxia** (slurred speech, falling), **pes cavus**, **hammer toes**, and **kyphoscoliosis** are classic features of Friedreich's ataxia.
*CTG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **myotonic dystrophy type 1**, an autosomal dominant disorder.
- While it causes muscle weakness, it is characterized by **myotonia** (delayed muscle relaxation), cataracts, and frontal baldness, which are not described here.
*CGG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **fragile X syndrome**, an X-linked dominant disorder.
- Fragile X syndrome primarily causes intellectual disability, behavioral issues (e.g., autism spectrum disorder), and characteristic facial features, but not the specific neurological and orthopedic findings seen in this patient.
*CAG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with several neurodegenerative diseases, including **Huntington's disease**, spinocerebellar ataxias, and **dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy**.
- Huntington's disease, for example, presents with chorea, cognitive decline, and psychiatric symptoms, differing from the patient's presentation.
*GCC*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS)**.
- FXTAS typically affects older adult carriers of premutation alleles for fragile X, presenting with intention tremor and gait ataxia, not the early childhood onset and specific orthopedic deformities seen here.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 3: A healthy 30-year-old woman comes to the physician with her husband for preconception counseling. Her husband is healthy but she is concerned because her brother was recently diagnosed with a genetic liver condition for which he takes penicillamine. Her father-in-law has liver cirrhosis and a tremor. The results of genetic testing show that both the patient and her husband are carriers of a mutation in the ATP7B gene. Which of the following is the chance that this patient’s offspring will eventually develop the hereditary condition?
- A. 0%
- B. 25% (Correct Answer)
- C. 100%
- D. 50%
- E. 75%
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***25%***
- The familial history (brother with a genetic liver condition, father-in-law with cirrhosis and tremor) and the **ATP7B gene mutation** indicate **Wilson's disease**, which is typically inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- If both parents are carriers (heterozygous for the mutation), the probability that their offspring will inherit two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) and, therefore, develop the condition is **25%** as per Mendelian inheritance.
*0%*
- This is incorrect because both parents are identified as carriers, meaning there is a definite risk of passing on the mutated genes to their offspring.
- For the risk to be 0%, at least one parent would need to be completely free of the mutation or the inheritance pattern would need to be dominant with no penetrance.
*100%*
- This would only be the case if both parents had the disease (were homozygous for the mutation) or if the condition were dominant and at least one parent had the disease and passed on the dominant allele.
- Since both are carriers, the chance of inheriting two mutated alleles is not 100%.
*50%*
- A 50% chance would apply if one parent had the disease (homozygous recessive) and the other was a carrier, or if it were an autosomal dominant condition with one affected heterozygous parent.
- This does not reflect the inheritance pattern for two carrier parents in an autosomal recessive condition.
*75%*
- A 75% chance is not typical for a single genetic outcome in standard Mendelian inheritance patterns from carrier parents.
- In the context of two carriers for an autosomal recessive trait, 75% represents the chance of the offspring either being a carrier (50%) or being completely unaffected (25%), but not the chance of developing the condition.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 4: A 5-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of behavioral problems. His mother says that he has frequent angry outbursts and gets into fights with his classmates. He constantly complains of feeling hungry, even after eating a full meal. He has no siblings, and both of his parents are healthy. He is at the 25th percentile for height and is above the 95th percentile for weight. Physical examination shows central obesity, undescended testes, almond-shaped eyes, and a thin upper lip. Which of the following genetic changes is most likely associated with this patient's condition?
- A. Mitotic nondisjunction of chromosome 21
- B. Mutation of FBN-1 gene on chromosome 15
- C. Microdeletion of long arm of chromosome 7
- D. Loss of paternal gene expression on chromosome 15 (Correct Answer)
- E. Deletion of Phe508 on chromosome 7
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***Loss of paternal gene expression on chromosome 15***
- The patient's symptoms, including **hyperphagia**, **obesity**, behavioral issues, short stature, and **hypogonadism** (undescended testes), are characteristic of **Prader-Willi syndrome**.
- Prader-Willi syndrome is most commonly caused by the **loss of paternal gene expression** from the **q11-q13 region of chromosome 15**, either due to a paternal deletion, maternal uniparental disomy, or a defect in the imprinting center.
*Microdeletion of long arm of chromosome 7*
- A microdeletion on the long arm of chromosome 7 (7q11.23) is associated with **Williams syndrome**, characterized by an **elfin facial appearance**, supravalvular aortic stenosis, and intellectual disability.
- This does not match the patient's symptoms of obesity, hyperphagia, or hypogonadism.
*Deletion of Phe508 on chromosome 7*
- A deletion of phenylalanine at position 508 (**ΔF508**) on chromosome 7 is the most common mutation in the **cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)** gene, causing **cystic fibrosis**.
- Cystic fibrosis is an **autosomal recessive disorder** requiring mutations in both alleles (inherited from both parents), and primarily affects the exocrine glands, leading to lung disease, pancreatic insufficiency, and infertility, which are unrelated to the patient's presentation.
*Mutation of FBN-1 gene on chromosome 15*
- A mutation in the **FBN1 gene** on chromosome 15 (15q21.1) causes **Marfan syndrome**, which is a connective tissue disorder.
- Marfan syndrome presents with tall stature, long limbs (**arachnodactyly**), lens dislocation, and aortic root dilation, none of which are described in this patient.
*Mitotic nondisjunction of chromosome 21*
- Mitotic nondisjunction of chromosome 21 can lead to **mosaic Down syndrome**, but **trisomy 21** (due to meiotic nondisjunction) is the most common cause of Down syndrome.
- Down syndrome is associated with characteristic facial features, intellectual disability, and congenital heart defects, which are distinct from the symptoms presented.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 5: A deficiency in which of the following lysosomal enzymes is inherited in a pattern similar to a deficiency of iduronate sulfatase (Hunter syndrome)?
- A. Sphingomyelinase
- B. Glucocerebrosidase
- C. Galactocerebrosidase
- D. Alpha-L-iduronidase
- E. Alpha-galactosidase A (Correct Answer)
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***Alpha-galactosidase A***
- A deficiency in **alpha-galactosidase A** causes **Fabry disease**, which, like Hunter syndrome (iduronate sulfatase deficiency), is inherited in an **X-linked recessive** pattern.
- Both conditions primarily affect males, with carrier females potentially exhibiting milder symptoms.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- A deficiency in sphingomyelinase leads to **Niemann-Pick disease types A and B**, which are inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- This mode of inheritance differs from the X-linked pattern of Hunter syndrome.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in glucocerebrosidase causes **Gaucher disease**, inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- This is a common lysosomal storage disorder, but its inheritance pattern is distinct from X-linked disorders.
*Galactocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in galactocerebrosidase causes **Krabbe disease (globoid cell leukodystrophy)**, which is inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- Krabbe disease is a severe neurodegenerative disorder, but its genetic transmission is not X-linked.
*Alpha-L-iduronidase*
- A deficiency in **alpha-L-iduronidase** causes **Hurler syndrome (MPS I)**, which is inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- While both Hunter and Hurler syndromes are mucopolysaccharidoses, their genetic inheritance patterns are different.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 6: A 13-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 1-month history of abnormal movements of her muscles that she cannot control. She has a younger brother with cognitive disabilities and epilepsy. Examination shows frequent, brief, involuntary contractions of the muscle groups of the upper arms, legs, and face that can be triggered by touch. An EEG shows generalized epileptiform activity. A trichrome stain of a skeletal muscle biopsy specimen shows muscle fibers with peripheral red inclusions that disrupt the normal fiber contour. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of the patient's symptoms?
- A. CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion
- B. Mutation of the methyl-CpG binding protein 2 gene
- C. Truncated dystrophin protein
- D. Autoimmune endomysial destruction
- E. Defective oxidative phosphorylation (Correct Answer)
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***Defective oxidative phosphorylation***
- The constellation of **uncontrolled muscle movements (myoclonus)**, **epilepsy**, and the brother's **cognitive disabilities** strongly suggests a **mitochondrial disorder**.
- **Ragged red fibers** on trichrome stain of skeletal muscle biopsy are pathognomonic for **mitochondrial myopathies**, indicating defective oxidative phosphorylation due to abnormal mitochondrial aggregates.
*CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion*
- This is characteristic of **Myotonic Dystrophy**, which primarily presents with **myotonia** (delayed muscle relaxation), progressive muscle weakness, and often cataracts, rather than prominent myoclonus and seizures.
- While muscle weakness can occur, the specific biopsy findings and prominent myoclonus point away from this diagnosis.
*Mutation of the methyl-CpG binding protein 2 gene*
- A mutation in the **MECP2 gene** causes **Rett Syndrome**, an X-linked dominant disorder seen almost exclusively in girls.
- It involves normal development for 6-18 months followed by regression, loss of purposeful hand movements, **stereotypical hand-wringing**, and microcephaly, which are not described here.
*Truncated dystrophin protein*
- A truncated dystrophin protein causes **Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy**, an X-linked recessive disorder leading to progressive muscle weakness, **Gowers' sign**, and elevated creatine kinase.
- This condition does not typically present with myoclonus or the characteristic ragged red fibers, nor does it typically involve the sibling's intellectual disability and epilepsy in this manner.
*Autoimmune endomysial destruction*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **celiac disease**, which can have neurological symptoms like ataxia or peripheral neuropathy, but not typically the severe myoclonus, epilepsy, or muscle biopsy findings seen here.
- **Inflammatory myopathies** like polymyositis may show endomysial inflammation, but the clinical picture and specific biopsy findings (ragged red fibers) are not consistent.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 7: A 6-year-old male presents to the pediatrician with seizures. His mother reports that the patient has had two seizures lasting about 30 seconds each over the last three days. She reports that the patient has previously had seizures a few times per year since he was 12 months of age. The patient’s past medical history is otherwise notable for intellectual disability. He rolled over at 14 months of age and walked at 24 months of age. The patient’s mother denies any family history of epilepsy or other neurologic diseases. The patient is in the 3rd percentile for height and the 15th percentile for weight. On physical exam, he has a happy demeanor with frequent smiling. The patient has strabismus and an ataxic gait accompanied by flapping of the hands. He responds intermittently to questions with one-word answers. This patient is most likely to have which of the following genetic abnormalities?
- A. Chromosomal macrodeletion on chromosome 5
- B. Maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 15
- C. Imprinting defect on chromosome 11
- D. Trinucleotide repeat disorder
- E. Paternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 15 (Correct Answer)
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***Paternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 15***
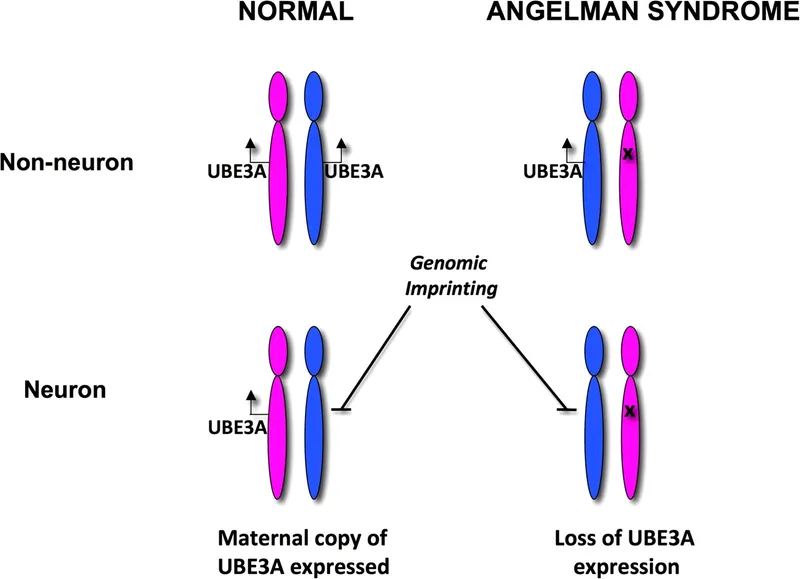
- The patient's presentation with **intellectual disability**, **seizures**, developmental delay (rolling over at 14 months, walking at 24 months), **ataxic gait**, **happy demeanor** with frequent smiling, and hand flapping are classic features of **Angelman syndrome**.
- **Angelman syndrome** requires loss of function of the maternal UBE3A gene on chromosome 15, which is paternally imprinted (meaning only the maternal copy is active).
- **Paternal uniparental disomy** means both copies of chromosome 15 come from the father, resulting in no functional maternal UBE3A gene, causing Angelman syndrome.
- Other causes include maternal deletion of 15q11-q13 (most common), imprinting defects, and UBE3A mutations.
*Maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 15*
- This causes **Prader-Willi syndrome**, not Angelman syndrome.
- When both chromosome 15s come from the mother, there is no paternal contribution, and paternally expressed genes are lost.
- Prader-Willi presents with **neonatal hypotonia**, **feeding difficulties**, later **hyperphagia** and **obesity**, which are not seen in this patient.
*Imprinting defect on chromosome 11*
- This is associated with **Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome**, which presents with **macroglossia**, **omphalocele**, **hemihyperplasia**, and increased tumor risk.
- The clinical presentation is distinctly different from this patient's features.
*Trinucleotide repeat disorder*
- Includes conditions such as **Fragile X syndrome**, **Huntington's disease**, and **Myotonic dystrophy**.
- Fragile X syndrome can cause intellectual disability and seizures but typically presents with **macroorchidism** (in post-pubertal males), long face, large ears, and **autistic features** rather than the happy demeanor seen here.
*Chromosomal macrodeletion on chromosome 5*
- This is characteristic of **Cri du Chat syndrome** (5p deletion).
- Presents with a distinctive **cat-like cry**, **microcephaly**, widely spaced eyes, and severe intellectual disability, which do not match this patient's presentation.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 8: A Caucasian 32-year-old woman has an uncomplicated vaginal delivery, giving birth to male and female fraternal twins at term. At 2 days of life, the twin sister develops abdominal distension without emesis, and the mother states that she has not noticed the passage of stool for this infant. Genetic testing identifies deletion of an amino acid in a membrane channel for the girl. Both parents are healthy. Assuming that twin brother's disease status/symptomatology is unclear, which of the following best approximates the probability that the twin brother is a carrier of the disease allele?
- A. 100%
- B. 67% (Correct Answer)
- C. 0%
- D. 50%
- E. 25%
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***67%***
- The sister's symptoms of **abdominal distension** without emesis and lack of stool passage, along with genetic testing identifying a **deletion of an amino acid in a membrane channel**, strongly suggest **Cystic Fibrosis (CF)**. CF is an **autosomal recessive disorder**.
- Since the affected twin sister has CF (genotype **aa**), and both parents are healthy, both parents must be **heterozygous carriers (Aa)**. When two carriers (Aa x Aa) have offspring, the probability of any child being a carrier (Aa) is **2/3** among the unaffected offspring. The twin brother is currently unaffected (phenotypically healthy), so the probability of him being a carrier is 2/3, or approximately 67%.
*100%*
- This would only be true if one or both parents were **homozygous affected (aa)**, or if the disease inheritance was **dominant** and the parents were carriers, which is not the case for this autosomal recessive disorder where the parents are healthy carriers and the brother is phenotypically unaffected.
- While both parents *are* carriers, the brother, being unaffected, has a chance of being **homozygous dominant (AA)**, meaning he is not a carrier.
*0%*
- This is incorrect because we know both parents are **obligate carriers** (heterozygous, Aa) for the recessive allele, given their affected child (aa). Therefore, their children have a 75% chance of inheriting at least one disease allele (50% carrier, 25% affected).
- The twin brother being unaffected means he has a 2/3 chance of being a carrier, not 0%.
*50%*
- This probability (1/2) is the chance of a child inheriting a specific allele from one parent, or the chance of being a carrier if one parent is affected and the other is homozygous dominant.
- In an **autosomal recessive** inheritance pattern where both parents are carriers (Aa x Aa) and the offspring is unaffected, the probability of being a carrier is **2/3**, not 1/2.
*25%*
- This is the probability of a child being **homozygous dominant (AA)** from two carrier parents (Aa x Aa), meaning they would neither have the disease nor be carriers.
- It is also the probability of a child being affected (aa) if both parents are carriers. Neither of these scenarios matches the question asking for the probability of the *unaffected* twin brother being a carrier.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 9: Given the pattern of inheritance shown in the pedigree, where might you find the disease gene in question?
- A. On helical RNA in the cytoplasm
- B. On circular DNA in the mitochondrion (Correct Answer)
- C. On double stranded DNA in the nucleus
- D. On single-stranded DNA in the cytoplasm
- E. On linear DNA in the mitochondrion
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***On circular DNA in the mitochondrion***
- The pedigree shows a pattern of **maternal inheritance**, where all offspring of an affected mother are affected, but none of the offspring of an affected father are affected. This is characteristic of **mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)** inheritance, which is exclusively passed down from the mother.
- Mitochondrial DNA is typically **circular** and found in the mitochondria within the cytoplasm.
*On helical RNA in the cytoplasm*
- **RNA** is not the primary carrier of genetic information for inherited diseases in humans; **DNA** serves this role.
- While some viruses use RNA as their genetic material, human inheritance patterns are based on DNA.
*On double-stranded DNA in the nucleus*
- This describes **nuclear DNA**, which follows Mendelian patterns of inheritance (autosomal dominant, recessive, X-linked) and involves contributions from both parents.
- The observed maternal-only inheritance pattern rules out nuclear DNA as the sole location for this disease gene.
*On single-stranded DNA in the cytoplasm*
- Human genetic material is generally **double-stranded DNA**, except in some viral contexts.
- The cytoplasm contains mitochondria, but the primary form of DNA there is circular and double-stranded, not single-stranded.
*On linear DNA in the mitochondrion*
- **Mitochondrial DNA** is characteristically **circular**, not linear, in most eukaryotic organisms, including humans.
- While located in the mitochondrion, the specific structure (linear vs. circular) is important for its proper function and replication.
Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG Question 10: A 13-year-old girl is brought to the outpatient clinic by her parents with a complaint of episodic spasm in her fingers for the past few months. Upon further questioning, her mother notes that the girl has not been doing well at school. She also believes that the girl is shorter than the other children in her class. On examination, her pulse is 72/min, temperature 37.6°C (99.7°F), respiratory rate 16/min, and blood pressure 120/88 mm Hg. The girl has short 4th and 5th fingers on both hands, a round face, and discolored teeth. Her height is 135 cm (4 ft 5 in) and she weighs 60 kg (132 lb). Investigation reports show the following values:
Hemoglobin (Hb%) 12.5 g/dL
White blood cell total count 10,000/mm3
Platelets 260,000/mm3
Calcium, serum (Ca2+) 4.0 mg/dL
Serum albumin 4.0 g/dL
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), serum 15 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum 8 U/L
Serum creatinine 0.5 mg/dL
Urea 27 mg/dL
Sodium 137 mEq/L
Potassium 4.5 mEq/L
Magnesium 2.5 mEq/L
Parathyroid hormone, serum, N-terminal 930 pg/mL (normal: 230-630 pg/mL)
Serum vitamin D 45 ng/dL
Which of the following is the mode of inheritance of the disease this patient has?
- A. X-linked recessive
- B. Mitochondrial inheritance
- C. X linked dominant
- D. Autosomal recessive
- E. Autosomal dominant (Correct Answer)
Non-Mendelian inheritance Explanation: ***Autosomal dominant***
- The clinical presentation with **short 4th and 5th fingers**, **round face**, **short stature** (height 135 cm, which is below average for a 13-year-old girl), **hypocalcemia** (4.0 mg/dL), and **elevated PTH** (930 pg/mL) is characteristic of **pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP)**, specifically **Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO)**.
- PHP type 1A (AHO) is typically inherited in an **autosomal dominant** pattern, often due to mutations in the **GNAS gene**.
*X-linked recessive*
- This mode of inheritance primarily affects males, with females usually being asymptomatic carriers. The patient is a female, making X-linked recessive less likely for a symptomatic presentation like this.
- Conditions like **Duchenne muscular dystrophy** or **fragile X syndrome** are X-linked recessive and have different clinical features.
*Mitochondrial inheritance*
- This inheritance pattern involves genes located in the mitochondria and is passed down from the mother to all her children; however, the clinical picture here does not align with typical mitochondrial disorders such as **MELAS syndrome** or **Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy**.
- Mitochondrial disorders often present with neurological or muscular symptoms that are progressive and distinct from the endocrine and skeletal features seen in this patient.
*X linked dominant*
- X-linked dominant inheritance would typically cause affected fathers to pass the trait to all their daughters, but not to their sons. Affected mothers have a 50% chance of passing it to each child. While females can be affected, the specific constellation of symptoms (PHP type 1A with AHO features) does not primarily follow an X-linked dominant pattern.
- Examples include **Rett syndrome** and **vitamin D-resistant rickets**, which have different clinical manifestations.
*Autosomal recessive*
- Autosomal recessive conditions require two copies of a mutated gene for the disease to manifest, meaning both parents are usually carriers. This mode of inheritance is seen in conditions like **cystic fibrosis** or **sickle cell anemia**, which have distinct presentations and are not consistent with the patient's symptoms of AHO and PHP.
- While some forms of hypoparathyroidism can be autosomal recessive, the classic features of AHO with brachydactyly and osteodystrophy strongly point away from autosomal recessive inheritance for this specific syndrome.
More Non-Mendelian inheritance US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.