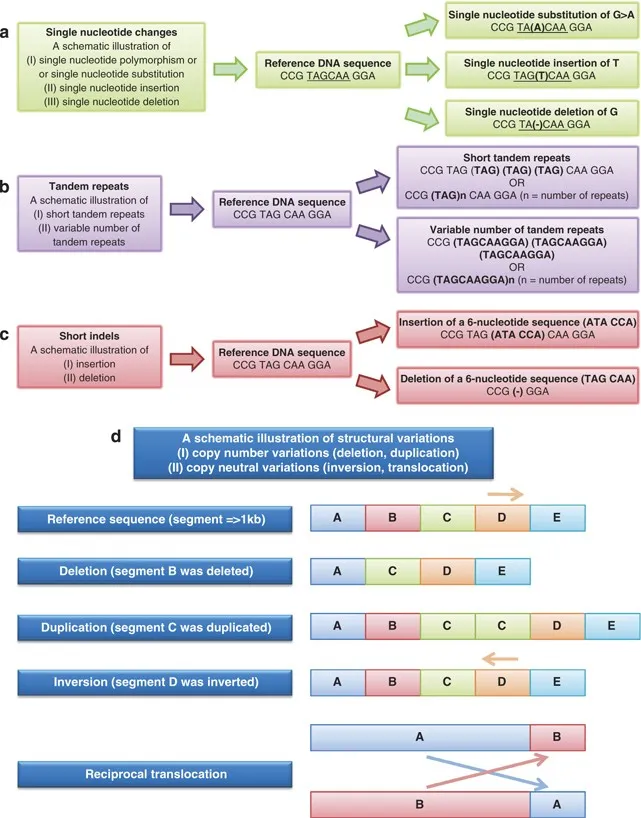
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Genetic polymorphisms. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 1: An investigator is studying genetic mutations of coagulation factors from patient samples. Genetic sequencing of one patient's coagulation factors shows a DNA point mutation that substitutes guanine for adenine. The corresponding mRNA codon forms a glutamine in place of arginine on position 506 at the polypeptide cleavage site. This patient's disorder is most likely to cause which of the following?
- A. Iron deficiency
- B. Ischemic stroke
- C. Cerebral vein thrombosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Petechiae
- E. Hemarthrosis
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***Cerebral vein thrombosis***
- The description of a DNA point mutation leading to a **glutamine in place of arginine at position 506** in a coagulation factor is characteristic of **Factor V Leiden mutation**.
- **Factor V Leiden** causes resistance to inactivation by activated protein C, leading to a **hypercoagulable state** and an increased risk of venous thromboses, including **cerebral vein thrombosis**.
*Iron deficiency*
- This condition is typically caused by **chronic blood loss**, inadequate dietary iron intake, or **impaired iron absorption**, not by a coagulation factor mutation that promotes clotting.
- Iron deficiency is associated with **anemia** and unrelated to thrombotic disorders like Factor V Leiden.
*Ischemic stroke*
- While Factor V Leiden increases the risk of **venous thrombosis**, its association with arterial thrombosis (the most common cause of ischemic stroke) is **less direct** and less pronounced than its link to venous clots.
- Ischemic stroke is more commonly associated with conditions like **atherosclerosis**, atrial fibrillation, or vasculitis.
*Petechiae*
- **Petechiae** are small, pinpoint hemorrhages under the skin, usually indicative of **platelet dysfunction** (e.g., thrombocytopenia) or **capillary fragility**.
- A hypercoagulable state like Factor V Leiden leads to excessive clotting, not bleeding disorders.
*Hemarthrosis*
- **Hemarthrosis**, or bleeding into joints, is a classic symptom of **severe bleeding disorders**, such as classic **hemophilia (Factor VIII or IX deficiency)**.
- Factor V Leiden causes a predisposition to clotting, which is the opposite of conditions that cause hemarthrosis.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 2: A newlywed couple comes to your office for genetic counseling. Both potential parents are known to be carriers of the same Cystic Fibrosis (CF) mutation. What is the probability that at least one of their next three children will have CF if they are all single births?
- A. 37/64 (Correct Answer)
- B. 0
- C. 1/64
- D. 1
- E. 27/64
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***37/64***
- The probability of a child having CF from two carrier parents is **1/4** (recessive inheritance), and the probability of a child not having CF is **3/4**.
- The probability that *none* of the three children will have CF is (3/4)³ = **27/64**. Therefore, the probability that *at least one* child will have CF is 1 - 27/64 = **37/64**.
*0*
- This option is incorrect because there is a **definite statistical probability** for a child to inherit CF when both parents are carriers.
- CF is an **autosomal recessive disorder**, meaning there is a 25% chance per child, not a 0% chance.
*1/64*
- This represents the probability that ***all three children*** would have CF: (1/4)³ = 1/64.
- This is an **underestimation** of the probability for at least one child to be affected, as the question asks about "at least one" not "all three."
*1*
- This would imply that it's an **absolute certainty** that at least one child will have CF, which is incorrect.
- Each child's outcome is independent, and there is always a chance (27/64) that none of the three children will have the disease.
*27/64*
- This calculation represents the probability that **none of the three children will have CF**: (3/4)³ = 27/64.
- This is the **complementary probability** to "at least one child having CF", not the actual answer to the question asked.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 3: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician because his mother is concerned about recent behavioral changes. His mother states that she has started to notice that he is slurring his speech and seems to be falling more than normal. On exam, the pediatrician observes the boy has pes cavus, hammer toes, and kyphoscoliosis. Based on these findings, the pediatrician is concerned the child has a trinucleotide repeat disease. Which of the following trinucleotide repeats is this child most likely to possess?
- A. CTG
- B. GAA (Correct Answer)
- C. CGG
- D. CAG
- E. GCC
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***GAA***
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **Friedreich's ataxia**, an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder.
- The presented symptoms of **ataxia** (slurred speech, falling), **pes cavus**, **hammer toes**, and **kyphoscoliosis** are classic features of Friedreich's ataxia.
*CTG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **myotonic dystrophy type 1**, an autosomal dominant disorder.
- While it causes muscle weakness, it is characterized by **myotonia** (delayed muscle relaxation), cataracts, and frontal baldness, which are not described here.
*CGG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **fragile X syndrome**, an X-linked dominant disorder.
- Fragile X syndrome primarily causes intellectual disability, behavioral issues (e.g., autism spectrum disorder), and characteristic facial features, but not the specific neurological and orthopedic findings seen in this patient.
*CAG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with several neurodegenerative diseases, including **Huntington's disease**, spinocerebellar ataxias, and **dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy**.
- Huntington's disease, for example, presents with chorea, cognitive decline, and psychiatric symptoms, differing from the patient's presentation.
*GCC*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS)**.
- FXTAS typically affects older adult carriers of premutation alleles for fragile X, presenting with intention tremor and gait ataxia, not the early childhood onset and specific orthopedic deformities seen here.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 4: A 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of severe muscle aches and fatigue for 3 days. Last week he was diagnosed with atypical pneumonia and treated with clarithromycin. He has hyperlipidemia for which he takes lovastatin. Physical examination shows generalized tenderness of the proximal muscles in the upper and lower extremities. Serum studies show an elevated creatine kinase concentration. This patient's current symptoms are most likely caused by inhibition of which of the following hepatic enzymes?
- A. CYP2E1
- B. CYP3A4 (Correct Answer)
- C. CYP2C9
- D. CYP1A2
- E. CYP2C19
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***CYP3A4***
- The patient is taking **lovastatin**, which is metabolized by **CYP3A4**. **Clarithromycin** is a potent **CYP3A4 inhibitor**.
- Inhibition of **CYP3A4** by clarithromycin leads to increased lovastatin levels, causing statin-induced **myopathy** (muscle aches, fatigue, and elevated creatine kinase).
*CYP2E1*
- This enzyme is primarily involved in the metabolism of compounds like **ethanol** and **acetaminophen**, not lovastatin.
- Its inhibition would not explain the interaction between clarithromycin and lovastatin.
*CYP2C9*
- This enzyme metabolizes drugs such as **warfarin** and **NSAIDs**, but it is not the primary enzyme responsible for lovastatin metabolism or its interaction with clarithromycin.
- Inhibition of **CYP2C9** would not lead to the described myopathy in this context.
*CYP1A2*
- **CYP1A2** is involved in the metabolism of drugs like **caffeine** and **theophylline**.
- It does not play a significant role in the metabolism of lovastatin, and its inhibition would not cause the observed symptoms.
*CYP2C19*
- **CYP2C19** metabolizes drugs such as **clopidogrel** and **omeprazole**.
- It is not the target enzyme for the interaction between lovastatin and clarithromycin.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 5: A 30-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a routine check-up. During the appointment, he remarks that he has started noticing some thinning and hair loss without other symptoms. The physician reassures him that he is likely experiencing male-pattern baldness and explains that the condition is largely inherited. Specifically he notes that there are multiple genes that are responsible for the condition so it is difficult to predict the timing and development of hair loss. What genetic principle is being illustrated by this scenario?
- A. Uniparental disomy
- B. Polygenic inheritance (Correct Answer)
- C. Pleiotropy
- D. Anticipation
- E. Heteroplasmy
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***Polygenic inheritance***
- This scenario describes male-pattern baldness as being influenced by **multiple genes**, which is the definition of polygenic inheritance.
- The difficulty in predicting the timing and development of hair loss further supports polygenic inheritance, as the combined effect of several genes and environmental factors can lead to a **continuous variation** in phenotypic expression.
*Uniparental disomy*
- This refers to the inheritance of **two copies of a chromosome** or part of a chromosome from **one parent** and no copies from the other parent.
- It is typically associated with specific genetic disorders like Prader-Willi or Angelman syndromes and does not explain the general inheritance pattern of male-pattern baldness.
*Pleiotropy*
- **Pleiotropy** occurs when a **single gene** affects **multiple seemingly unrelated phenotypic traits**.
- This principle is incorrect because the scenario explicitly states that male-pattern baldness is influenced by "multiple genes," not a single gene affecting multiple traits.
*Anticipation*
- **Anticipation** is a phenomenon where the symptoms of a genetic disorder become more severe or appear earlier with each successive generation.
- This phenomenon is observed in conditions like Huntington's disease or myotonic dystrophy and is not the genetic principle described for male-pattern baldness.
*Heteroplasmy*
- **Heteroplasmy** refers to the presence of **more than one type of mitochondrial DNA** (mtDNA) within a single cell or individual.
- This principle is exclusive to mitochondrial inheritance and is not relevant to the inheritance pattern of male-pattern baldness, which is generally considered to be affected by nuclear genes.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 6: A 34-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 18 weeks' gestation, comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She recently read about a genetic disorder that manifests with gait ataxia, kyphoscoliosis, and arrhythmia and is concerned about the possibility of her child inheriting the disease. There is no personal or family history of this disorder. The frequency of unaffected carriers in the general population is 1/100. Assuming the population is in a steady state without selection, what is the probability that her child will develop this disease?
- A. 1/10,000
- B. 1/20,000
- C. 1/40,000 (Correct Answer)
- D. 1/200
- E. 1/400
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***1/40,000***
- This disorder (Friedreich's ataxia) follows **autosomal recessive** inheritance, meaning both parents must be carriers for the child to be affected.
- Since there is no family history, we treat both parents as random individuals from the general population with carrier frequency 1/100.
- **Calculation**: Probability mother is carrier (1/100) × Probability father is carrier (1/100) × Probability child is affected given both parents are carriers (1/4) = **1/40,000**.
- This applies Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium principles for a steady-state population.
*1/10,000*
- This calculation (1/100 × 1/100 = 1/10,000) represents only the probability that both parents are carriers.
- It fails to account for the **1/4 chance** of an affected child when two carriers of an **autosomal recessive** condition conceive.
- This would be the answer if both parents being carriers automatically meant the child would be affected, which is incorrect.
*1/20,000*
- This result would occur if the probability of the child inheriting the disease from carrier parents was 1/2 instead of 1/4 (1/100 × 1/100 × 1/2 = 1/20,000).
- A 1/2 probability would apply to **autosomal dominant** conditions where one affected parent passes the disease, not for **autosomal recessive** inheritance.
- For autosomal recessive disorders, two carrier parents have a 1/4 (not 1/2) chance of an affected child.
*1/200*
- This probability (1/100 × 1/2 = 1/200) would suggest only one parent needed to be a carrier with a 1/2 transmission probability.
- This does not account for the requirement that **both parents must be carriers** for an **autosomal recessive** disorder.
- It represents a fundamental misunderstanding of recessive inheritance patterns.
*1/400*
- This calculation (1/100 × 1/4 = 1/400) incorrectly assumes only one parent needs to be a carrier.
- For **autosomal recessive** inheritance, **both parents must be carriers**, so both their carrier probabilities (1/100 each) must be included in the calculation.
- It omits the second parent's carrier probability entirely.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 7: A 23-year-old woman and her husband come to a genetic counselor because she is concerned about the chance of having an inherited defect if they had a child. Family history reveals no significant family history in her husband; however, her sister had a son who has seizures, failure to thrive, and neurodegeneration. She does not remember the name of the disease but remembers that her nephew had sparse, brittle hair that kinked in odd directions. She does not think that any other members of her family including her sister's husband have had this disorder. If this couple had a son, what is the most likely chance that he would have the same disorder that affected the patient's nephew?
- A. 100%
- B. 12.5%
- C. 25% (Correct Answer)
- D. 50%
- E. Close to 0%
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***25%***
- The nephew's symptoms of **seizures, failure to thrive, neurodegeneration**, and **sparse, brittle, kinky hair** are highly indicative of **Menkes disease**, an **X-linked recessive** disorder.
- Since the patient's sister had an affected son, the sister is an **obligate carrier** of the mutation.
- The patient and her sister share the same parents, so their mother must be a carrier (or have the mutation).
- The patient herself has a **50% chance of being a carrier**.
- **If the patient is a carrier**, each son has a **50% chance** of being affected.
- **Overall probability**: 0.5 (chance patient is carrier) × 0.5 (chance son inherits mutation) = **0.25 = 25%**.
*Close to 0%*
- This would only be correct if the patient had no chance of being a carrier, which is not the case given her family history.
- Her sister's affected son confirms the mutation is present in the maternal lineage.
*100%*
- This would only occur if the patient were definitely a carrier AND all male offspring inherited the mutation, or if the disorder were autosomal dominant with complete penetrance.
- For **X-linked recessive** disorders, even carrier mothers only pass the mutation to 50% of sons on average.
*12.5%*
- This percentage might represent additional generational steps or compound probabilities not relevant to this direct parent-child scenario.
- The correct calculation for this scenario is 50% × 50% = 25%.
*50%*
- This would be correct if we knew with certainty that the patient is a carrier.
- However, since we only know her sister is a carrier, the patient has a 50% chance of being a carrier herself, making the overall risk 25%.
- This is a common error in genetic counseling calculations—forgetting to account for the uncertain carrier status of the at-risk individual.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 8: A healthy 29-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the physician for genetic counseling prior to conception. Her brother has a disease that has resulted in infertility, a right-sided heart, and frequent sinus and ear infections. No other family members are affected. The intended father has no history of this disease. The population prevalence of this disease is 1 in 40,000. Which of the following best represents the chance that this patient’s offspring will develop her brother's disease?
- A. 25%
- B. 66%
- C. 0.2% (Correct Answer)
- D. 0.7%
- E. 1%
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***0.2%***
- The brother's symptoms (infertility, right-sided heart, frequent infections) are characteristic of **Kartagener syndrome**, a form of **primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD)**, which has an **autosomal recessive** inheritance pattern.
- Since the patient's parents are obligate heterozygotes (carriers), the patient has a 2/3 chance of being a carrier. Given the population prevalence of 1/40,000 for an autosomal recessive disease, the carrier frequency (2pq) is approximately **2 x sqrt(1/40,000) = 2 x 1/200 = 1/100**. The chance of her child inheriting the disease is (2/3 chance of patient being carrier) x (1/100 chance of partner being carrier) x (1/4 chance of affected offspring) = 2/1200 ≈ **0.00166 or 0.166%**, which is closest to 0.2%.
*25%*
- This would be the risk if both parents were known carriers, and it represents the chance of an affected offspring from two heterozygotes.
- In this scenario, the woman's partner's carrier status is unknown and based on population prevalence, making the overall risk much lower.
*66%*
- This is the probability that the patient (the healthy sister of an affected individual with an autosomal recessive disease) is a **carrier**.
- This value alone does not account for the partner's carrier status or the final Mendelian inheritance probability (1/4) for an affected child.
*0.7%*
- This percentage is too high; it might result from incorrect calculation of the population carrier frequency or misapplication of probabilities.
- The correct carrier frequency for the partner is 1/100, which is significantly lower than what would lead to a 0.7% final risk.
*1%*
- This value is also too high and likely results from a miscalculation of either the carrier frequency or the overall probability.
- A 1% chance would suggest a much higher population carrier frequency or a different inheritance scenario.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 9: Drug A is an experimental compound being investigated for potential use as a protectant against venous thrombosis. Binding assays reveal that the drug’s primary mechanism of action is to block carboxylation of glutamic acid residues in certain serum proteins. Drug A is most similar to which of the following:
- A. Streptokinase
- B. Bivalirudin
- C. Warfarin (Correct Answer)
- D. Heparin
- E. Rivaroxaban
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***Warfarin***
- Warfarin inhibits **vitamin K epoxide reductase**, enzyme responsible for regenerating active vitamin K.
- Active vitamin K is a cofactor for the **gamma-carboxylation of glutamic acid residues** on factors II, VII, IX, X and protein C and S. Thus, warfarin blocks their activation, inhibiting coagulation.
*Steptokinase*
- **Streptokinase** is a **thrombolytic drug** that catalyzes the conversion of **plasminogen to plasmin**, an enzyme that degrades fibrin clots.
- Its mechanism of action is focused on **breaking down existing clots**, rather than preventing their formation by affecting coagulation factor synthesis.
*Bivalirudin*
- **Bivalirudin** is a direct **thrombin inhibitor**, binding directly to the active site and exosite I of thrombin to prevent its action.
- It does not interfere with the **carboxylation of glutamic acid residues** but rather directly inhibits the final common pathway of coagulation.
*Heparin*
- **Heparin** works by potentiating the action of **antithrombin III**, which in turn inactivates thrombin and factor Xa.
- Its mechanism involves accelerating the natural anticoagulant system, rather than inhibiting the **synthesis or activation of coagulation factors** through carboxylation.
*Rivaroxaban*
- **Rivaroxaban** is a **direct factor Xa inhibitor**, which blocks the activity of free and clot-bound factor Xa.
- It directly interferes with the coagulation cascade downstream of the carboxylation step, and does not affect the **vitamin K-dependent carboxylation process**.
Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG Question 10: A 31-year-old man and his wife were referred to a genetic counselor. They are concerned about the chance that their children are likely to inherit certain conditions that run in their families. The wife's father and grandfather are both healthy, but her grandfather cannot see the color red. The husband is unaware if any member of his family has the same condition. The geneticist provides some details about genetic diseases and inheritance patterns, then orders lab tests to analyze the gene mutations carried by both partners. Which of the following are the correct terms regarding the genotype and phenotype of males affected by the condition described?
- A. Homozygote; reduced or incomplete penetrance
- B. Heterozygotes; reduced or incomplete penetrance
- C. Hemizygous; reduced or incomplete penetrance
- D. Heterozygotes; full penetrance
- E. Hemizygous; full penetrance (Correct Answer)
Genetic polymorphisms Explanation: ***Hemizygous; full penetrance***
- The condition described (**red color blindness**) is an **X-linked recessive** trait, meaning males have only one X chromosome and are thus **hemizygous** for genes on the X chromosome.
- **Full penetrance** in X-linked recessive traits means that if a male inherits the affected X chromosome, he will express the phenotype of the condition.
*Homozygote; reduced or incomplete penetrance*
- **Homozygous** refers to having two identical alleles for a particular gene, which is not applicable to an X-linked gene in males as they only have one X chromosome.
- **Reduced or incomplete penetrance** means that a person with the genotype may or may not express the phenotype, which is typically not the case for males with X-linked recessive color blindness.
*Heterozygotes; reduced or incomplete penetrance*
- **Heterozygous** means having two different alleles for a gene; this term is not applicable to males regarding X-linked genes.
- Males are **hemizygous** for X-linked genes, meaning they only have one allele, not two different ones.
*Hemizygous; reduced or incomplete penetrance*
- While males are indeed **hemizygous** for X-linked genes like color blindness, the penetrance for red-green color blindness in males is generally considered to be **full**, meaning if they carry the mutated gene, they will express the trait.
- **Reduced penetrance** would imply that some males with the genotype might not exhibit color blindness, which is rare for this condition.
*Heterozygotes; full penetrance*
- The term **heterozygous** applies to individuals with two different alleles for a gene, which is not the genetic state of males for X-linked genes.
- While penetrance is full, the term **heterozygotes** is incorrect for defining the male genotype in this context.
More Genetic polymorphisms US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.