Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Gene therapy approaches. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 1: A 6-year-old child presents for evaluation of a medical condition associated with recurrent infections. After reviewing all of the medical history, gene therapy is offered to treat a deficiency in adenosine deaminase (ADA). ADA deficiency is the most common autosomal recessive mutation in which of the following diseases?
- A. Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
- B. Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia
- C. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (Correct Answer)
- D. DiGeorge Syndrome
- E. Hyper-IgM Syndrome
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***Severe Combined Immunodeficiency***
- **Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency** leads to the accumulation of toxic metabolites that impair lymphocyte development and function, primarily affecting **T and B cells**, which is a common cause of SCID.
- Patients with SCID present with **recurrent, severe infections** due to profound immunodeficiency, making them candidates for treatments like gene therapy.
*Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome*
- This is an **X-linked recessive disorder** characterized by eczema, thrombocytopenia, and immunodeficiency, but it is caused by a mutation in the **WASP gene**, not ADA deficiency.
- While it involves immunodeficiency and recurrent infections, the underlying genetic defect and specific clinical triad are distinct from ADA deficiency.
*Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia*
- This is an **X-linked recessive disorder** caused by a defect in the **BTK gene**, leading to a lack of mature B cells and hence very low levels of immunoglobulins.
- While it results in recurrent bacterial infections due to absent antibodies, its genetic cause and primary immunological defect (B cell specific) differ from ADA deficiency.
*DiGeorge Syndrome*
- This is a developmental disorder caused by a **microdeletion on chromosome 22q11.2**, leading to abnormal development of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches.
- It results in **T-cell deficiency** due to thymic aplasia/hypoplasia, hypocalcemia due to parathyroid hypoplasia, and congenital heart defects, but not ADA deficiency.
*Hyper-IgM Syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by normal or elevated IgM levels and deficiencies in other immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgE), largely due to defects in **CD40-CD40L interaction** or other genes involved in isotype switching.
- Patients suffer from recurrent infections and opportunistic infections but the genetic basis and specific immunological defect are distinct from ADA deficiency.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 2: A virology student is asked to identify a sample of virus. When subjected to a nonionic detergent, which disrupts lipid membranes, the virus was shown to lose infectivity. The student then purified the genetic material from the virus and subjected it to treatment with RNase, an enzyme that cleaves the phosphodiester linkages in the RNA backbone. A minute amount of the sample was then injected into a human cell line and was found to produce viral particles a few days later. Which of the following viruses was in the unknown sample?
- A. Togavirus
- B. Hepevirus
- C. Calicivirus
- D. Adenovirus
- E. Herpesvirus (Correct Answer)
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***Herpesvirus***
- The loss of infectivity with nonionic detergents indicates the presence of a **lipid envelope**, a characteristic of herpesviruses.
- The genetic material survived **RNase treatment**, indicating it is **DNA** (not RNA), which is consistent with herpesviruses being DNA viruses.
- Under experimental conditions with **direct intracellular injection**, purified herpesvirus DNA can initiate viral replication by utilizing host cell transcription machinery, ultimately producing viral particles.
*Togavirus*
- Togaviruses are **enveloped RNA viruses**; they would lose infectivity with detergent treatment.
- However, their **RNA genome** would have been destroyed by RNase treatment, preventing any subsequent viral particle production.
*Hepevirus*
- Hepeviruses are **non-enveloped RNA viruses**; they would **not** lose infectivity with nonionic detergent, which contradicts the experimental observation.
- Additionally, their **RNA genome** would be destroyed by RNase, preventing viral replication.
*Calicivirus*
- Caliciviruses are **non-enveloped RNA viruses**, so they would not be inactivated by nonionic detergents.
- Their **RNA genome** would be susceptible to degradation by RNase, precluding viral production.
*Adenovirus*
- Adenoviruses are **non-enveloped DNA viruses**, meaning they would **not lose infectivity** when treated with nonionic detergent, which contradicts the first experimental result.
- Although they have a DNA genome that would survive RNase treatment, the lack of envelope rules them out.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 3: A 13-year-old Caucasian male presents with his father to the pediatrician’s office complaining of left lower thigh pain. He reports slowly progressive pain over the distal aspect of his left thigh over the past three months. He denies any recent trauma to the area. His temperature is 100.9°F (38.3°C). On exam, there is swelling and tenderness overlying the inferior aspect of the left femoral diaphysis. Laboratory evaluation is notable for an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Biopsy of the lesion demonstrates sheets of monotonous small round blue cells with minimal cytoplasm. He is diagnosed and started on a medication that inhibits transcription by intercalating into DNA at the transcription initiation complex. Which of the following adverse events will this patient be at highest risk for following initiation of this medication?
- A. Peripheral neuropathy
- B. Bone marrow suppression (Correct Answer)
- C. Gingival hyperplasia
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Hemorrhagic cystitis
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***Bone marrow suppression***
- The medication described, which inhibits transcription by intercalating into DNA at the transcription initiation complex, is likely **dactinomycin (actinomycin D)**.
- **Bone marrow suppression** is a common and severe adverse effect of dactinomycin, leading to issues like **neutropenia** and **thrombocytopenia**.
*Peripheral neuropathy*
- This is a common side effect of **vinca alkaloids** (e.g., vincristine, vinblastine) and **taxanes**, which are not described by the mechanism of action given.
- Dactinomycin does not typically cause significant peripheral neuropathy.
*Gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** is a known side effect of medications such as **cyclosporine**, **phenytoin**, and **calcium channel blockers** like nifedipine.
- It is not associated with dactinomycin.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- This is a serious adverse effect of certain chemotherapeutic agents like **bleomycin** and **busulfan**, and other drugs like **amiodarone** and **methotrexate**.
- Dactinomycin is not primarily associated with pulmonary fibrosis.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a classic adverse effect of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, caused by the metabolite **acrolein**.
- This adverse event is prevented by co-administration of **MESNA**, and is not a common side effect of dactinomycin.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 4: A group of scientists is conducting an experiment on the human cells involved in the immune response. They genetically modify B cells so they do not express the cluster of differentiation 21 (CD21) on their cell surfaces. The pathogenesis of which of the following organisms would most likely be affected by this genetic modification?
- A. Human papillomavirus
- B. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- C. Parvovirus B19
- D. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) (Correct Answer)
- E. Measles virus
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)***
- EBV primarily infects B cells by binding to **CD21**, also known as the **C3d receptor** or CR2.
- Absence of CD21 would prevent EBV from entering B cells, thereby disrupting its **pathogenesis** and replication cycle.
*Human papillomavirus*
- HPV primarily infects **epithelial cells** and uses entry receptors other than CD21, such as alpha-6 integrins and heparan sulfate proteoglycans.
- Its pathogenesis is not directly dependent on B cell CD21 expression.
*Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)*
- HIV primarily infects **CD4+ T cells and macrophages** by binding to CD4 and chemokine co-receptors (CCR5 or CXCR4).
- CD21 on B cells is not a primary receptor for HIV entry or infection.
*Parvovirus B19*
- Parvovirus B19 primarily targets **erythroid progenitor cells** by binding to the **P antigen** (globoside) on their surface.
- Its infection pathway does not involve CD21 on B cells.
*Measles virus*
- Measles virus primarily uses **CD150 (SLAM)** as its receptor on immune cells (including B cells and T cells) and nectin-4 on epithelial cells.
- While B cells can be infected, CD21 is not the primary receptor for measles virus entry.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 5: A 35-year-old female presents to the emergency room complaining of diarrhea and dehydration. She has been experiencing severe watery diarrhea for the past 3 days. She reports that she has been unable to leave the bathroom for more than a few minutes at a time. The diarrhea is profuse and watery without visible blood or mucus. She recently returned from a volunteer trip to Yemen where she worked at an orphanage. Her past medical history is notable for psoriasis for which she takes sulfasalazine. The patient drinks socially and does not smoke. Her temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 100/55 mmHg, pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 20/min. Mucous membranes are dry. Her eyes appear sunken. Capillary refill is 4 seconds. The patient is started on intravenous fluid resuscitation. Which of the following processes is capable of transmitting the genetic material for the toxin responsible for this patient's condition?
- A. Transposition
- B. Conjugation
- C. Endospore formation
- D. Transduction (Correct Answer)
- E. Transformation
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***Transduction***
- The patient's symptoms are highly suggestive of **cholera**, caused by *Vibrio cholerae*, which produces **cholera toxin**.
- The genes for cholera toxin are carried on a **bacteriophage (CTXφ)**, and their transfer between bacteria occurs via **transduction**.
*Transposition*
- **Transposition** involves the movement of **transposons ("jumping genes")** within a genome or between DNA molecules.
- While transposons can carry antimicrobial resistance genes or virulence factors, this mechanism is not typically associated with the transfer of the primary cholera toxin genes.
*Conjugation*
- **Conjugation** is the transfer of genetic material between bacteria through direct cell-to-cell contact, often involving a **pilus** and the transfer of **plasmids**.
- While *Vibrio cholerae* can engage in conjugation, the cholera toxin genes are predominantly acquired via specialized transduction with the CTXφ phage, not typically plasmid-mediated conjugation.
*Endospore formation*
- **Endospore formation** is a survival mechanism used by certain bacteria (e.g., *Clostridium*, *Bacillus*) to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
- It is not a mechanism for **horizontal gene transfer** or the transmission of toxin-encoding genetic material between bacteria.
*Transformation*
- **Transformation** is the uptake of **naked DNA** from the environment by a bacterial cell.
- While *Vibrio cholerae* can be naturally competent for transformation, the cholera toxin genes are primarily acquired through **phage-mediated transduction**, not free DNA uptake.
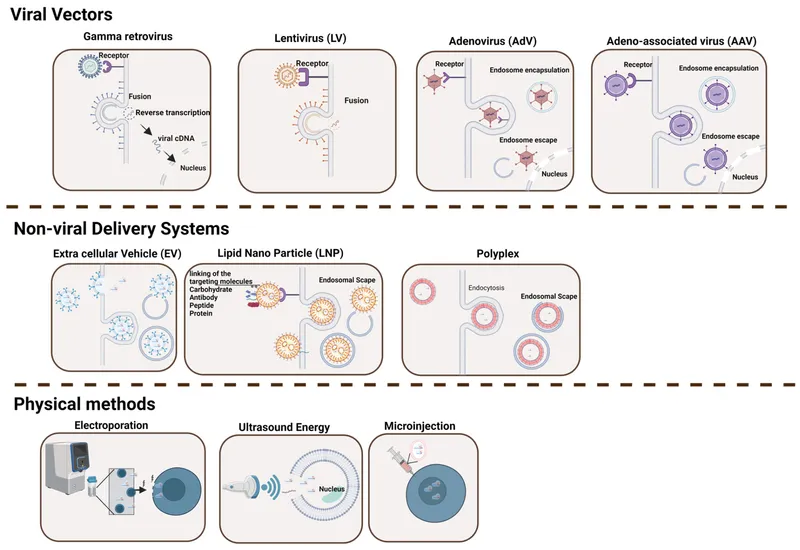
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 6: A 9-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents after a 2-day history of fever, productive cough, and severe dyspnea. The parents report that the boy had no health problems at birth but developed respiratory problems as an infant that have continued throughout his life, including recurrent pulmonary infections. Vital signs include: temperature of 37.5ºC (99.5ºF), pulse of 105/min, respiratory rate of 34/min, and SpO2 of 87%. Physical examination shows digital clubbing and cyanosis. Chest X-rays show hyperinflation of the lungs and chronic interstitial changes. The boy’s FEV1/FVC ratio is decreased, and his FRC is increased. The resident reviewing his case is studying new gene therapies for this boy’s condition that will reintroduce the gene for which this boy is defective. An important component of this therapy is identifying a vector for the selective introduction of the replacement gene into the human body. Which of the following would be the best vector to provide gene therapy for this boy’s respiratory symptoms?
- A. Human immunodeficiency virus-1
- B. Adenovirus (Correct Answer)
- C. Rabies virus
- D. Rhinovirus
- E. Coxsackie A virus
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***Adenovirus***
- Adenoviruses are the **most suitable vector for respiratory gene therapy** due to their high efficiency in gene delivery to respiratory epithelial cells and their ability to infect both dividing and non-dividing cells.
- The clinical presentation (recurrent pulmonary infections, dyspnea, hyperinflation, digital clubbing, and cyanosis) is characteristic of **cystic fibrosis**, which results from a defect in the *CFTR* gene—a prime target for gene therapy via respiratory delivery.
- Adenoviral vectors were extensively studied in CF gene therapy trials due to their **excellent tropism for airway epithelium**.
*Incorrect: Human immunodeficiency virus-1*
- While HIV-1-derived lentiviruses can transduce non-dividing cells and integrate into the host genome, they are **less efficient in delivering genes to respiratory epithelial cells** compared to adenoviruses.
- Concerns regarding **potential insertional mutagenesis** and immune responses make them less ideal for respiratory gene therapy.
*Incorrect: Rabies virus*
- Rabies virus has strong **neurotropism**, meaning it primarily targets the nervous system, making it unsuitable for direct delivery to lung epithelial cells.
- Its use would likely lead to **severe neurological side effects** without effectively treating the underlying lung pathology.
*Incorrect: Rhinovirus*
- Rhinoviruses typically cause **mild, self-limiting infections of the upper respiratory tract** and are not optimized for stable gene transfer to the lower respiratory tract.
- They lack the capacity for **long-term gene expression** required for conditions like cystic fibrosis.
*Incorrect: Coxsackie A virus*
- Coxsackie A viruses are associated with diseases such as **hand, foot, and mouth disease** and cause acute, transient infections.
- They are **not efficient gene delivery vectors** for the respiratory system and could cause unwanted inflammatory responses in the lungs.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 7: An investigator is studying the mechanism of HIV infection in cells obtained from a human donor. The effect of a drug that impairs viral fusion and entry is being evaluated. This drug acts on a protein that is cleaved off of a larger glycosylated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum of the host cell. The protein that is affected by the drug is most likely encoded by which of the following genes?
- A. gag
- B. env (Correct Answer)
- C. tat
- D. pol
- E. rev
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***env***
- The **env (envelope) gene** of HIV encodes for the precursor protein **gp160**, which is then cleaved by host cellular proteases into **gp120** and **gp41** within the endoplasmic reticulum.
- **gp120** and **gp41** together form the viral envelope glycoproteins responsible for viral binding to host cells and **fusion/entry**, making them the target of drugs that impair these processes.
*gag*
- The **gag (group-specific antigen) gene** encodes for structural proteins of the viral core, such as **p24 (capsid protein)**, p17 (matrix protein), and p7 (nucleocapsid protein).
- These proteins are primarily involved in the assembly of new virions and do not directly mediate viral fusion and entry.
*tat*
- The **tat (trans-activator of transcription) gene** encodes a regulatory protein that significantly enhances the transcription of viral genes.
- It plays a crucial role in the viral life cycle by increasing the efficiency of HIV gene expression, but it is not directly involved in viral fusion or entry.
*pol*
- The **pol (polymerase) gene** encodes for essential viral enzymes, including **reverse transcriptase**, integrase, and protease.
- These enzymes are critical for converting viral RNA into DNA, integrating viral DNA into the host genome, and cleaving viral polyproteins, respectively, but they are not involved in mediating viral entry.
*rev*
- The **rev (regulator of virion expression) gene** encodes a regulatory protein that facilitates the transport of unspliced and partially spliced viral RNAs from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
- This transport is crucial for the synthesis of structural and enzymatic proteins and for packaging viral RNA into new virions, but it does not directly participate in viral fusion and entry.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 8: A healthy 30-year-old woman comes to the physician with her husband for preconception counseling. Her husband is healthy but she is concerned because her brother was recently diagnosed with a genetic liver condition for which he takes penicillamine. Her father-in-law has liver cirrhosis and a tremor. The results of genetic testing show that both the patient and her husband are carriers of a mutation in the ATP7B gene. Which of the following is the chance that this patient’s offspring will eventually develop the hereditary condition?
- A. 0%
- B. 25% (Correct Answer)
- C. 100%
- D. 50%
- E. 75%
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***25%***
- The familial history (brother with a genetic liver condition, father-in-law with cirrhosis and tremor) and the **ATP7B gene mutation** indicate **Wilson's disease**, which is typically inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- If both parents are carriers (heterozygous for the mutation), the probability that their offspring will inherit two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) and, therefore, develop the condition is **25%** as per Mendelian inheritance.
*0%*
- This is incorrect because both parents are identified as carriers, meaning there is a definite risk of passing on the mutated genes to their offspring.
- For the risk to be 0%, at least one parent would need to be completely free of the mutation or the inheritance pattern would need to be dominant with no penetrance.
*100%*
- This would only be the case if both parents had the disease (were homozygous for the mutation) or if the condition were dominant and at least one parent had the disease and passed on the dominant allele.
- Since both are carriers, the chance of inheriting two mutated alleles is not 100%.
*50%*
- A 50% chance would apply if one parent had the disease (homozygous recessive) and the other was a carrier, or if it were an autosomal dominant condition with one affected heterozygous parent.
- This does not reflect the inheritance pattern for two carrier parents in an autosomal recessive condition.
*75%*
- A 75% chance is not typical for a single genetic outcome in standard Mendelian inheritance patterns from carrier parents.
- In the context of two carriers for an autosomal recessive trait, 75% represents the chance of the offspring either being a carrier (50%) or being completely unaffected (25%), but not the chance of developing the condition.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 9: Although nucleotide addition during DNA replication in prokaryotes proceeds approximately 20-times faster than in eukaryotes, why can much larger amounts of DNA be replicated in eukaryotes in a time-effective manner?
- A. Eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication (Correct Answer)
- B. Eukaryotes have helicase which can more easily unwind DNA strands
- C. Eukaryotes have fewer polymerase types
- D. Eukaryotes have less genetic material to replicate
- E. Eukaryotes have a single, circular chromosome
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***Eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication***
- Eukaryotic chromosomes are much larger than prokaryotic chromosomes and require multiple origins of replication to complete DNA synthesis within a reasonable timeframe.
- Each origin of replication initiates simultaneously, allowing DNA synthesis to occur at many sites along the chromosome, effectively increasing the overall speed of replication.
- This compensates for the slower rate of nucleotide addition by DNA polymerase in eukaryotes compared to prokaryotes.
*Eukaryotes have helicase which can more easily unwind DNA strands*
- While helicase activity is crucial for unwinding DNA, there is no evidence to suggest that eukaryotic helicases are significantly more efficient or faster at unwinding DNA compared to prokaryotic helicases in a way that would account for the large difference in overall replication time.
- The rate of DNA unwinding by helicase is a factor in replication speed, but it does not overcome the fundamental limitation of a single origin of replication in prokaryotes.
*Eukaryotes have fewer polymerase types*
- Eukaryotic cells actually have **more** types of DNA polymerases than prokaryotic cells, each specialized for different functions like replication, repair, and mitochondrial DNA synthesis.
- The number of polymerase types does not directly relate to the speed or efficiency of overall DNA replication in terms of replicating large amounts of DNA.
*Eukaryotes have less genetic material to replicate*
- Eukaryotic organisms typically have significantly **more** genetic material (a larger genome size) than prokaryotic organisms, not less.
- If eukaryotes had less genetic material, the question itself about effective replication of "much larger amounts of DNA" would be contradictory.
*Eukaryotes have a single, circular chromosome*
- Eukaryotic cells have **multiple, linear chromosomes** within a membrane-bound nucleus, not a single circular chromosome.
- Prokaryotic cells typically have a single, circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region.
- The linear structure of eukaryotic chromosomes with multiple origins is actually what enables efficient replication of large genomes, making this statement both factually incorrect and contradictory to the mechanism in question.
Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG Question 10: An investigator is studying the effect of chromatin structure on gene regulation. The investigator isolates a class of proteins that compact DNA by serving as spools upon which DNA winds around. These proteins are most likely rich in which of the following compounds?
- A. Phosphate
- B. Disulfide-bonded cysteine
- C. Lysine and arginine (Correct Answer)
- D. Heparan sulfate
- E. Proline and alanine
Gene therapy approaches Explanation: ***Lysine and arginine***
- DNA is **negatively charged** due to its phosphate backbone. Proteins that compact DNA (like **histones**) must be **positively charged** to electrostatically interact with and bind to DNA.
- **Lysine** and **arginine** are positively charged amino acids that are abundant in histones, facilitating this interaction.
*Phosphate*
- **Phosphate** groups are negatively charged and are a major component of the **DNA backbone** itself, not the proteins that compact DNA.
- Proteins rich in phosphate would be negatively charged, which would inhibit DNA binding due to **electrostatic repulsion**.
*Disulfide-bonded cysteine*
- **Cysteine residues** can form disulfide bonds, which are important for maintaining the **tertiary and quaternary structure** of many proteins.
- However, disulfide bonds do not primarily contribute to the basicity or positive charge required for DNA binding; rather, they play a crucial role in protein **folding and stability**.
*Heparan sulfate*
- **Heparan sulfate** is a **glycosaminoglycan** that is negatively charged and found on cell surfaces and in the extracellular matrix.
- It plays roles in cell signaling and adhesion but is not a component of the core histone proteins that compact DNA.
*Proline and alanine*
- **Proline** and **alanine** are common amino acids, but they are **nonpolar** or **neutral** at physiological pH.
- They do not contribute a significant **positive charge** to proteins, which is essential for binding to the negatively charged DNA.
More Gene therapy approaches US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.