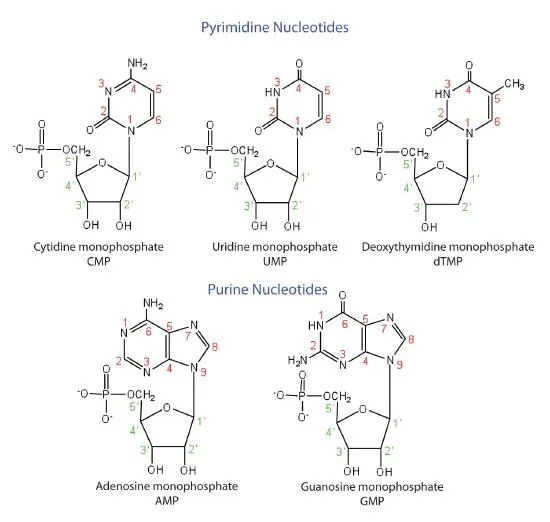
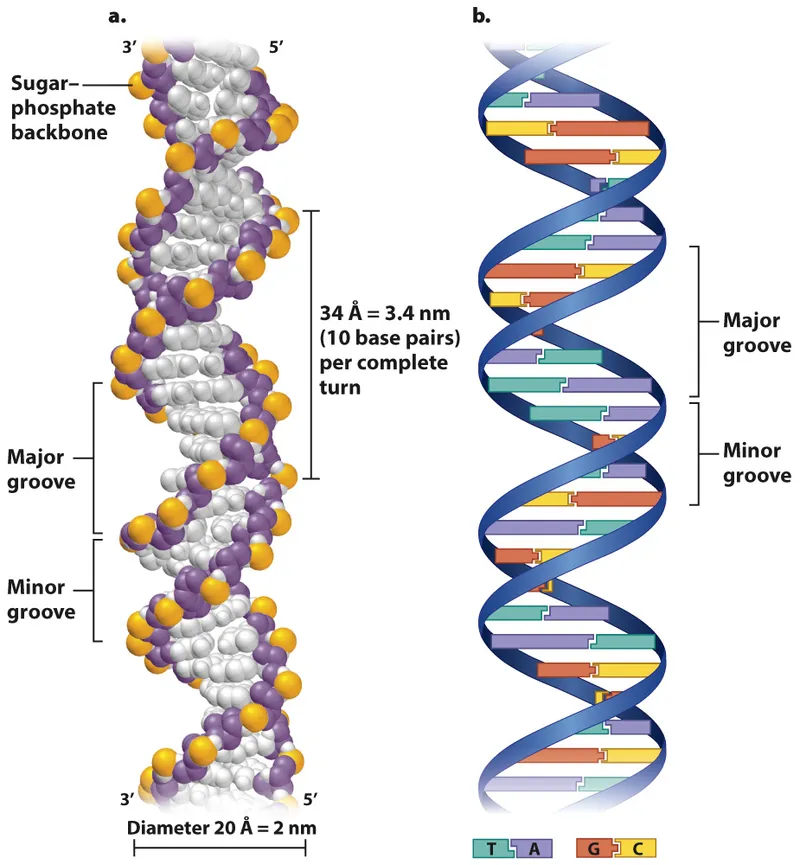
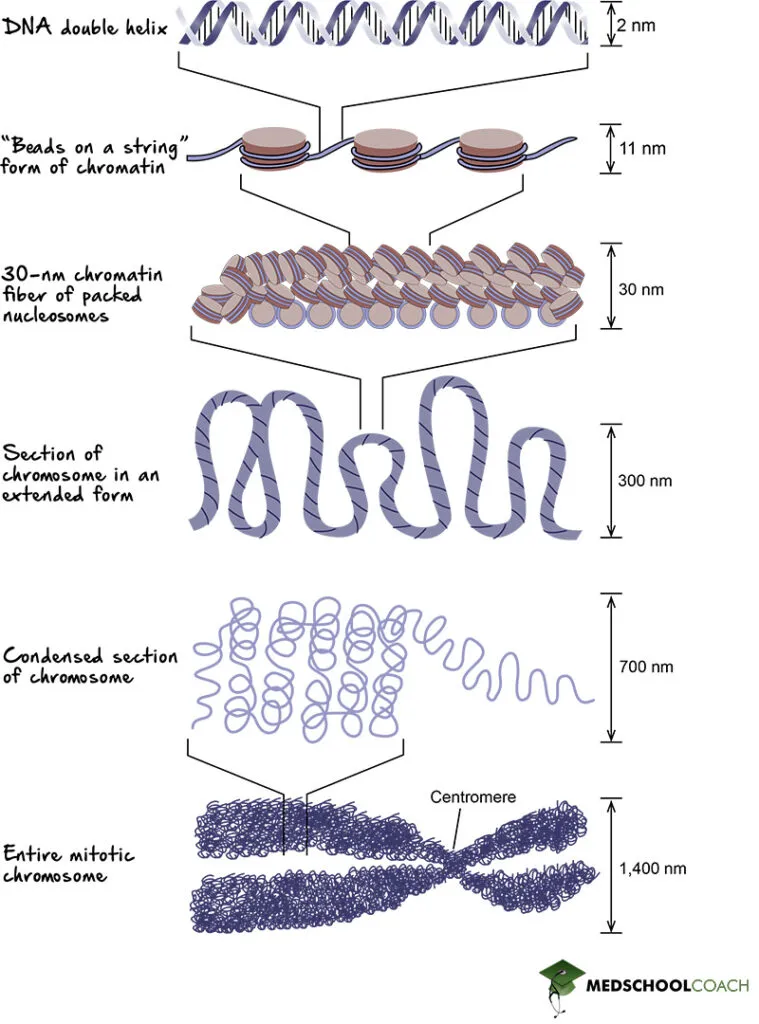
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for DNA structure and organization. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 1: A researcher is investigating compounds that modulate the cell cycle as possible chemotherapeutic agents against peripheral T-cell lymphoma. The researcher discovers a group of natural compounds with inhibitory activity against histone deacetylases, a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups from the lysine residues of histones. A histone deacetylase inhibitor most likely causes which of the following?
- A. Prevention of DNA strand reannealing
- B. Increased heterochromatin formation
- C. Suppression of gene transcription
- D. Relaxation of DNA coiling (Correct Answer)
- E. Tighter coiling of DNA
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***Relaxation of DNA coiling***
- Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors block the removal of **acetyl groups** from **histones**, leading to increased histone acetylation.
- Increased acetylation **reduces the positive charge** of histones, loosening their grip on the negatively charged DNA and causing **relaxation of DNA coiling**.
*Prevention of DNA strand reannealing*
- This process is primarily influenced by factors affecting **hydrogen bonding** between DNA strands, such as **temperature** or **DNA denaturing agents**, not directly by histone acetylation.
- DNA reannealing is the reformation of a **double helix** from single strands, a different mechanism than chromatin structure.
*Increased heterochromatin formation*
- **Heterochromatin** is characterized by **tightly coiled DNA** and is associated with **deacetylated histones** and gene silencing.
- Increased acetylation, as caused by HDAC inhibitors, would lead to less heterochromatin and more **euchromatin**.
*Suppression of gene transcription*
- **Relaxation of DNA coiling** makes the DNA more accessible to transcription factors and RNA polymerase, thereby generally **promoting gene transcription**, not suppressing it.
- **HDAC inhibitors** primarily promote gene expression by increasing the accessibility of DNA to the transcriptional machinery.
*Tighter coiling of DNA*
- **Deacetylation of histones** leads to stronger interaction between histones and DNA, resulting in **tighter coiling** and chromatin condensation.
- HDAC inhibitors, by preventing deacetylation, promote the opposite effect: **DNA uncoiling** and relaxation.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 2: A 17-year-old patient presents to the emergency department with left wrist pain after falling off of his bike and landing on his left hand. On physical exam the thenar eminence is red, swollen, and tender to palpation, so a radiograph is ordered. The patient is worried because he learned in biology class that radiography can cause cancer through damaging DNA but the physician reassures him that radiographs give a very minor dose of radiation. What is the most common mechanism by which ionizing radiation damages DNA?
- A. Strand breakage (Correct Answer)
- B. Thymidine dimer formation
- C. Microsatellite instability
- D. Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer formation
- E. Cytosine deamination
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***Strand breakage***
- Ionizing radiation, such as X-rays, directly or indirectly causes **breaks in the phosphodiester backbone** of DNA, resulting in single or double-strand breaks.
- **Double-strand breaks** are particularly dangerous as they are difficult to repair and can lead to chromosomal rearrangements and cell death or malignant transformation.
*Thymidine dimer formation*
- This is primarily caused by **ultraviolet (UV) radiation**, not ionizing radiation like X-rays.
- **UV radiation** causes covalent bonds between adjacent pyrimidine bases, particularly thymine, leading to the formation of thymine dimers.
*Microsatellite instability*
- This is a hallmark of defects in **DNA mismatch repair pathways**, often associated with hereditary disorders like Lynch syndrome or certain sporadic cancers.
- It involves changes in the length of **microsatellites** (short, repetitive DNA sequences) due to insertion or deletion errors, not direct radiation damage.
*Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer formation*
- Similar to thymidine dimers, **cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs)** are the most common photoproducts formed in DNA after exposure to **UV radiation**.
- These dimers distort the DNA helix and interfere with replication and transcription, but are not characteristic of ionizing radiation damage.
*Cytosine deamination*
- This is a spontaneous chemical reaction where a **cytosine base (C)** loses its amino group and is converted to **uracil (U)**.
- It is a common endogenous DNA lesion that can lead to C-to-T transition mutations if not repaired, but it is not directly induced by ionizing radiation.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is comparing DNA replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. He finds that the entire genome of E. coli (4 × 106 base pairs) is replicated in approximately 30 minutes. A mammalian genome (3 × 109 base pairs) is usually replicated within 3 hours. Which of the following characteristics of eukaryotic DNA replication is the most accurate explanation for this finding?
- A. Replication inhibition at checkpoint
- B. Absence of telomerase enzyme activity
- C. DNA compaction in chromatin
- D. Simultaneous replication at multiple origins (Correct Answer)
- E. More efficient DNA polymerase activity
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***Simultaneous replication at multiple origins***
- Eukaryotic DNA replication initializes at **multiple origins of replication** along each chromosome, allowing synthesis to occur concurrently in many places.
- This strategy compensates for the much larger eukaryotic genome size, enabling its complete replication within a reasonable timeframe despite slower polymerase speed compared to prokaryotes.
*Replication inhibition at checkpoint*
- **Cell cycle checkpoints**, such as those in G1, S, and G2 phases, ensure the integrity of DNA replication and repair.
- While these checkpoints can *pause* or *inhibit* replication if errors occur, they do not fundamentally explain the *speed* or **efficiency** of replication across the entire genome.
*Absence of telomerase enzyme activity*
- **Telomerase** is an enzyme that maintains the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes (telomeres) by adding repetitive DNA sequences.
- Its presence or absence is related to telomere length regulation and cellular aging, not the overall speed of genome replication.
*DNA compaction in chromatin*
- Eukaryotic DNA is compact and organized into **chromatin** within the nucleus, which presents a challenge to replication by limiting access to the DNA.
- While enzymes must overcome this compaction, it is a *hindrance* rather than an enabler of replication speed. If anything, it would slow down replication.
*More efficient DNA polymerase activity*
- In actuality, **prokaryotic DNA polymerases** (e.g., DNA Pol III in *E. coli*) are generally more processive and faster than eukaryotic DNA polymerases.
- Therefore, more efficient polymerase activity is not a characteristic that would explain the relatively fast replication of a larger eukaryotic genome.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator studying protein synthesis in human stem cells isolates tRNA molecules bound to mRNA molecules. The isolated tRNA molecules have inosine in the 5' position of the anticodon; of these, some are bound to adenine, some to cytosine, and some to uracil at the 3' position of the mRNA codon. Which of the following properties of the genetic code is best illustrated by this finding?
- A. Unambiguity
- B. Non-overlapping
- C. Degeneracy (Correct Answer)
- D. Specificity of the start codon
- E. Specificity of stop codons
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***Degeneracy***
- The finding that a single tRNA anticodon (with **inosine** at the 5' position) can bind to multiple different mRNA codons (ending in **adenine, cytosine, or uracil**) illustrates the concept of **degeneracy** in the genetic code.
- This **wobble hypothesis** allows fewer tRNAs to recognize more than one codon for a given amino acid, meaning multiple codons can code for the same amino acid.
*Unambiguity*
- The genetic code is unambiguous, meaning that each codon specifies **only one specific amino acid** (or a stop signal) and never two different amino acids.
- This finding, however, shows one tRNA recognizing multiple codons, not one codon coding for multiple amino acids.
*Non-overlapping*
- The **non-overlapping** nature of the genetic code means that each nucleotide in an mRNA sequence is read only once as part of a single codon, without sharing nucleotides between adjacent codons.
- This concept describes how codons are read sequentially, not the flexibility of codon-anticodon pairing.
*Specificity of the start codon*
- The **start codon (AUG)** specifically initiates translation, coding for methionine, and signals the beginning of a polypeptide chain.
- This finding relates to the wobble pairing at the 3' end of the codon, not the initiation of translation.
*Specificity of stop codons*
- **Stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA)** specifically signal the termination of translation without coding for any amino acid.
- This finding describes the flexibility of codon-anticodon pairing, not the distinct function of termination codons.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 5: Replication in eukaryotic cells is a highly organized and accurate process. The process involves a number of enzymes such as primase, DNA polymerase, topoisomerase II, and DNA ligase. In which of the following directions is DNA newly synthesized?
- A. 3' --> 5'
- B. N terminus --> C terminus
- C. C terminus --> N terminus
- D. 3' --> 5' & 5' --> 3'
- E. 5' --> 3' (Correct Answer)
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***5' --> 3'***
- DNA polymerase can only add **nucleotides** to the 3' end of a growing strand, meaning synthesis always proceeds in a **5' to 3' direction**.
- This is true for both the **leading strand** (synthesized continuously) and the **lagging strand** (synthesized discontinuously via Okazaki fragments).
*3' --> 5'*
- While the parental template strand is read in the 3' to 5' direction, the *newly synthesized* DNA strand is always built in the **opposite, antiparallel 5' to 3' direction**.
- DNA polymerase lacks the ability to add new nucleotides to the **5' phosphate group** of the growing strand.
*N terminus --> C terminus*
- This directional notation refers to the synthesis of **proteins**, where amino acids are added to the C (carboxyl) terminus of the growing polypeptide chain.
- It does not apply to the synthesis direction of **nucleic acids (DNA or RNA)**.
*C terminus --> N terminus*
- This directional notation is incorrectly applied; protein synthesis always proceeds from the **N (amino) terminus to the C (carboxyl) terminus**.
- This has no relevance to the synthesis direction of **DNA**.
*3' --> 5' & 5' --> 3'*
- Although DNA replication involves two strands, one is synthesized continuously in the **5' → 3' direction (leading strand)** and the other discontinuously, but still *each fragment* is synthesized in the **5' → 3' direction (lagging strand)**.
- No new DNA strand is synthesized in the **3' → 5' direction**.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 6: A group of microbiological investigators is studying bacterial DNA replication in E. coli colonies. While the cells are actively proliferating, the investigators stop the bacterial cell cycle during S phase and isolate an enzyme involved in DNA replication. An assay of the enzyme's exonuclease activity determines that it is active on both intact and demethylated thymine nucleotides. Which of the following enzymes have the investigators most likely isolated?
- A. DNA ligase
- B. Telomerase
- C. Primase
- D. DNA topoisomerase
- E. DNA polymerase I (Correct Answer)
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***DNA polymerase I***
- **DNA polymerase I** possesses **5' to 3' exonuclease activity**, which is crucial for removing **RNA primers** (intact nucleotides) laid down by primase during DNA replication.
- This 5' to 3' exonuclease activity also allows it to excise damaged DNA, including DNA containing **demethylated thymine nucleotides**.
- It also has 3' to 5' exonuclease activity for proofreading.
- **Key distinction:** While DNA polymerase III (the main replicative enzyme) only has 3' to 5' exonuclease activity, DNA polymerase I has **both** 3' to 5' and 5' to 3' exonuclease activities, making it essential for primer removal and DNA repair.
*DNA ligase*
- **DNA ligase** functions to form a **phosphodiester bond** between adjacent nucleotides to seal nicks in the DNA backbone, but it does not have exonuclease activity.
- Its primary role is in joining Okazaki fragments and repairing single-strand breaks.
*Telomerase*
- **Telomerase** is a specialized reverse transcriptase that extends the telomeres at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, but is not present in prokaryotes like *E. coli*.
- It uses an RNA template to synthesize DNA, and it lacks exonuclease activity.
*Primase*
- **Primase** is an RNA polymerase that synthesizes short **RNA primers** on the DNA template, providing a starting point for DNA synthesis.
- It is involved in synthesizing primers, not in removing or excising nucleotides, and has no exonuclease activity.
*DNA topoisomerase*
- **DNA topoisomerases** relieve supercoiling in DNA during replication and transcription by cutting and rejoining DNA strands.
- While they act on DNA, their function is to manage topological stress, and they do not exhibit exonuclease activity on nucleotides.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 7: A 62-year-old man with small cell lung cancer undergoes radiation therapy. His oncologist explains that radiation causes DNA damage and double strand breaks and this damage stops the cancer cells from growing because they can no longer replicate their DNA. One key mediator of this process is a cell cycle regulator called P53, which is upregulated after DNA damage and helps to trigger cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. One mechanism by which P53 activity is increased is a certain chromatin modification that loosens DNA coiling allowing for greater transcription of the proteins within that region of DNA. Which of the following enzymes most likely causes the chromatin modification described in this case?
- A. Histone deacetylase
- B. Histone acetyltransferase (Correct Answer)
- C. Histone methyltransferase
- D. DNA methyltransferase
- E. Xist
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***Histone acetyltransferase***
- This enzyme **acetylates histone proteins**, neutralizing their positive charge and thereby weakening their interaction with negatively charged DNA.
- This modification leads to a more **relaxed chromatin structure (euchromatin)**, making DNA more accessible for **transcription**, which is consistent with the upregulation of P53.
*Histone deacetylase*
- This enzyme **removes acetyl groups from histones**, making them more positively charged and increasing their affinity for DNA.
- This results in **condensed chromatin (heterochromatin)**, which generally **represses gene transcription**.
*Histone methyltransferase*
- This enzyme **adds methyl groups to histones**, which can either activate or repress gene transcription depending on the specific **lysine or arginine residue** methylated and the number of methyl groups added.
- While methylation is a chromatin modification, the question specifically describes a process of **loosening DNA coiling for greater transcription**, which is more characteristic of acetylation.
*DNA methyltransferase*
- This enzyme **adds methyl groups directly to DNA**, typically at **CpG sites**, leading to **gene silencing** by hindering transcription factor binding or recruiting repressor complexes.
- This modification primarily affects DNA directly, not histone proteins, and generally **inhibits gene expression**.
*Xist*
- **Xist (X-inactive specific transcript)** is a **long non-coding RNA** that plays a crucial role in **X-chromosome inactivation** in females.
- It functions by coating one of the X chromosomes, leading to its transcriptional silencing, rather than directly modifying chromatin for general gene upregulation.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 8: Although nucleotide addition during DNA replication in prokaryotes proceeds approximately 20-times faster than in eukaryotes, why can much larger amounts of DNA be replicated in eukaryotes in a time-effective manner?
- A. Eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication (Correct Answer)
- B. Eukaryotes have helicase which can more easily unwind DNA strands
- C. Eukaryotes have fewer polymerase types
- D. Eukaryotes have less genetic material to replicate
- E. Eukaryotes have a single, circular chromosome
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***Eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication***
- Eukaryotic chromosomes are much larger than prokaryotic chromosomes and require multiple origins of replication to complete DNA synthesis within a reasonable timeframe.
- Each origin of replication initiates simultaneously, allowing DNA synthesis to occur at many sites along the chromosome, effectively increasing the overall speed of replication.
- This compensates for the slower rate of nucleotide addition by DNA polymerase in eukaryotes compared to prokaryotes.
*Eukaryotes have helicase which can more easily unwind DNA strands*
- While helicase activity is crucial for unwinding DNA, there is no evidence to suggest that eukaryotic helicases are significantly more efficient or faster at unwinding DNA compared to prokaryotic helicases in a way that would account for the large difference in overall replication time.
- The rate of DNA unwinding by helicase is a factor in replication speed, but it does not overcome the fundamental limitation of a single origin of replication in prokaryotes.
*Eukaryotes have fewer polymerase types*
- Eukaryotic cells actually have **more** types of DNA polymerases than prokaryotic cells, each specialized for different functions like replication, repair, and mitochondrial DNA synthesis.
- The number of polymerase types does not directly relate to the speed or efficiency of overall DNA replication in terms of replicating large amounts of DNA.
*Eukaryotes have less genetic material to replicate*
- Eukaryotic organisms typically have significantly **more** genetic material (a larger genome size) than prokaryotic organisms, not less.
- If eukaryotes had less genetic material, the question itself about effective replication of "much larger amounts of DNA" would be contradictory.
*Eukaryotes have a single, circular chromosome*
- Eukaryotic cells have **multiple, linear chromosomes** within a membrane-bound nucleus, not a single circular chromosome.
- Prokaryotic cells typically have a single, circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region.
- The linear structure of eukaryotic chromosomes with multiple origins is actually what enables efficient replication of large genomes, making this statement both factually incorrect and contradictory to the mechanism in question.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is studying the biology of human sperm cells. She isolates spermatogonia obtained on a testicular biopsy from a group of healthy male volunteers. She finds that the DNA of spermatogonia obtained from these men show a large number of TTAGGG sequence repeats. This finding can best be explained by increased activity of an enzyme with which of the following functions?
- A. Ligation of Okazaki fragments
- B. Proofreading of synthesized daughter strands
- C. RNA-dependent synthesis of DNA (Correct Answer)
- D. Production of short RNA sequences
- E. Hemimethylation of DNA strand
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***RNA-dependent synthesis of DNA***
- The TTAGGG sequence repeats are **telomeric sequences**, which are maintained by **telomerase**, an enzyme that synthesizes DNA from an RNA template.
- **Spermatogonia** are germline stem cells that express high levels of telomerase to maintain telomere length across generations.
*Ligation of Okazaki fragments*
- This function is carried out by **DNA ligase**, which joins discontinuous DNA fragments during replication on the lagging strand.
- This process is essential for general DNA replication but is not specific to the formation or maintenance of telomeric repeats.
*Proofreading of synthesized daughter strands*
- This is a function of **DNA polymerase exonuclease activity**, which corrects errors during DNA replication.
- While important for genetic fidelity, it does not explain the presence or increase of specific TTAGGG repeat sequences at telomeres.
*Production of short RNA sequences*
- This function is performed by **primase**, which synthesizes RNA primers necessary to initiate DNA synthesis during replication.
- These RNA primers are later removed and replaced with DNA, and this process is not directly responsible for generating or extending telomeric repeats.
*Hemimethylation of DNA strand*
- Hemimethylation occurs during **DNA replication** when new DNA strands are unmethylated while parental strands are methylated.
- This phenomenon is involved in DNA repair and gene regulation but is unrelated to the synthesis or regulation of telomeric sequences.
DNA structure and organization US Medical PG Question 10: An investigator is studying the effect of chromatin structure on gene regulation. The investigator isolates a class of proteins that compact DNA by serving as spools upon which DNA winds around. These proteins are most likely rich in which of the following compounds?
- A. Phosphate
- B. Disulfide-bonded cysteine
- C. Lysine and arginine (Correct Answer)
- D. Heparan sulfate
- E. Proline and alanine
DNA structure and organization Explanation: ***Lysine and arginine***
- DNA is **negatively charged** due to its phosphate backbone. Proteins that compact DNA (like **histones**) must be **positively charged** to electrostatically interact with and bind to DNA.
- **Lysine** and **arginine** are positively charged amino acids that are abundant in histones, facilitating this interaction.
*Phosphate*
- **Phosphate** groups are negatively charged and are a major component of the **DNA backbone** itself, not the proteins that compact DNA.
- Proteins rich in phosphate would be negatively charged, which would inhibit DNA binding due to **electrostatic repulsion**.
*Disulfide-bonded cysteine*
- **Cysteine residues** can form disulfide bonds, which are important for maintaining the **tertiary and quaternary structure** of many proteins.
- However, disulfide bonds do not primarily contribute to the basicity or positive charge required for DNA binding; rather, they play a crucial role in protein **folding and stability**.
*Heparan sulfate*
- **Heparan sulfate** is a **glycosaminoglycan** that is negatively charged and found on cell surfaces and in the extracellular matrix.
- It plays roles in cell signaling and adhesion but is not a component of the core histone proteins that compact DNA.
*Proline and alanine*
- **Proline** and **alanine** are common amino acids, but they are **nonpolar** or **neutral** at physiological pH.
- They do not contribute a significant **positive charge** to proteins, which is essential for binding to the negatively charged DNA.
More DNA structure and organization US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.