Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pentose phosphate pathway. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 1: To prepare for an endoscopy, a 27-year-old male was asked by the gastroenterologist to fast overnight for his 12 p.m. appointment the next day. Therefore, his last meal was dinner at 5 p.m. the day before the appointment. By 12 p.m. the day of the appointment, his primary source of glucose was being generated from gluconeogenesis, which occurs via the reversal of glycolysis with extra enzymes to bypass the irreversible steps in glycolysis. Which of the following irreversible steps of gluconeogenesis occurs in the mitochondria?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose
- B. Pyruvate to oxaloacetate (Correct Answer)
- C. Phosphoenolypyruvate to pyruvate
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone
- E. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Pyruvate to oxaloacetate***
- This step, catalyzed by **pyruvate carboxylase**, is the initial and irreversible step of **gluconeogenesis** that occurs within the **mitochondrial matrix**.
- **Pyruvate** is converted to **oxaloacetate**, which then either is converted to malate to exit the mitochondria or remains in the mitochondria for subsequent steps of gluconeogenesis depending on the tissue.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose*
- This final dephosphorylation step of gluconeogenesis, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphatase**, occurs in the **endoplasmic reticulum** lumen, not the mitochondria.
- It is crucial for releasing free glucose into the bloodstream.
*Phosphoenolypyruvate to pyruvate*
- This is an irreversible step in **glycolysis**, catalyzed by **pyruvate kinase**, and it is going in the *opposite direction* to what happens in gluconeogenesis.
- In gluconeogenesis, **pyruvate** is converted back to **phosphoenolpyruvate** via oxaloacetate, involving enzymes in both the mitochondria and cytoplasm.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone*
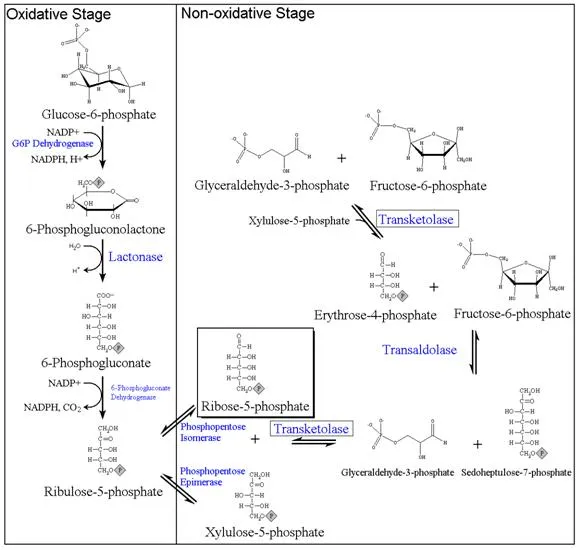
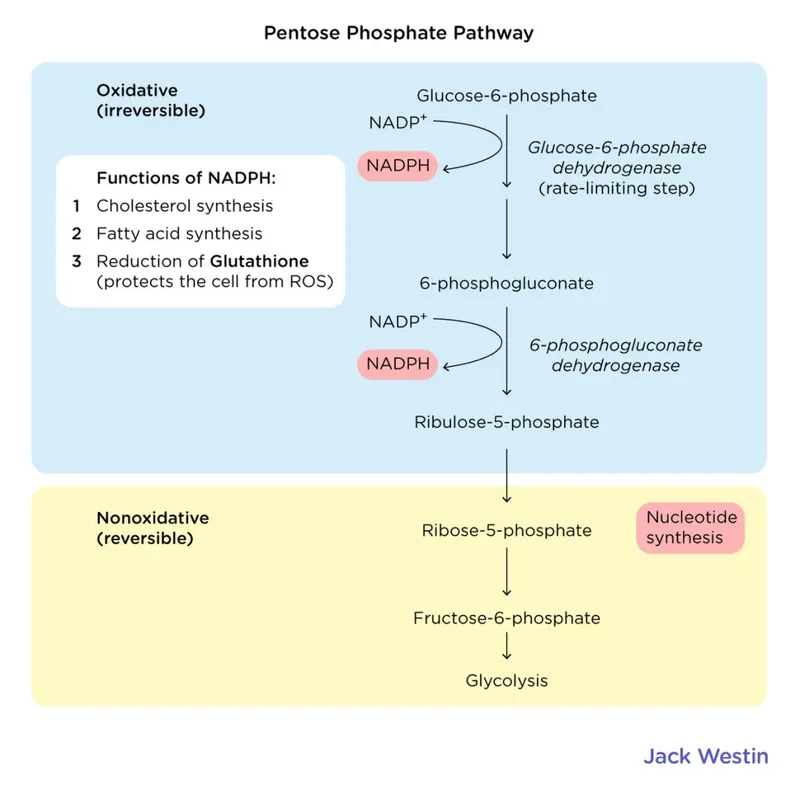
- This reaction is the first committed step of the **pentose phosphate pathway**, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase** and it occurs in the cytoplasm, not mitochondria.
- It is involved in producing NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate, not directly in gluconeogenesis.
*Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate*
- This irreversible dephosphorylation step in gluconeogenesis, catalyzed by **fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase**, occurs in the **cytoplasm**.
- It bypasses the phosphofructokinase-1 step of glycolysis.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old African American man presents with fever, abdominal pain, and severe weakness since yesterday. On physical examination, the patient is jaundiced and shows a generalized pallor. Past medical history is significant for recently receiving anti-malaria prophylaxis before visiting Nigeria. Laboratory tests show decreased glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) levels. Peripheral smear shows the presence of bite cells and Heinz bodies. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- B. Sickle cell disease
- C. Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency (Correct Answer)
- D. Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
- E. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, abdominal pain, jaundice, and pallor** following **anti-malarial prophylaxis** (known triggers for G6PD deficiency) is highly suggestive of an acute hemolytic crisis.
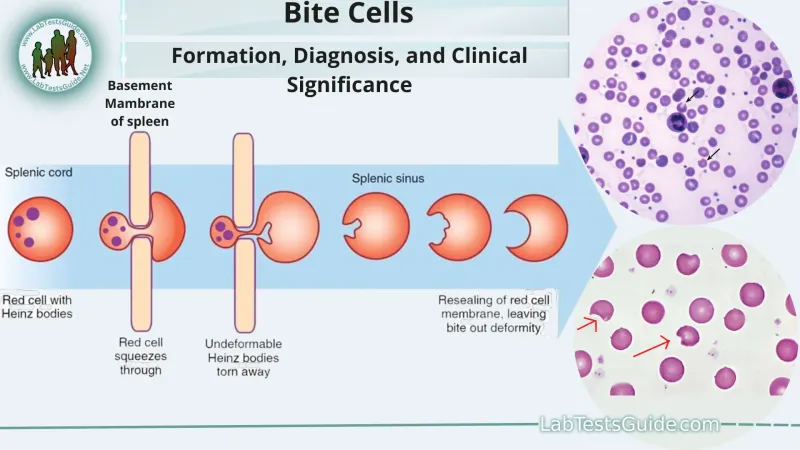
- The laboratory findings of **decreased G6PD levels, bite cells, and Heinz bodies** on peripheral smear are pathognomonic for G6PD deficiency causing hemolytic anemia.
*Autoimmune hemolytic anemia*
- This condition is typically characterized by a **positive Coombs test**, which is not mentioned here and would not explain the presence of bite cells or Heinz bodies.
- It results from the body's immune system attacking its own red blood cells, rather than oxidative stress from drug exposure.
*Sickle cell disease*
- Patients with sickle cell disease have **abnormally shaped red blood cells** (sickle cells) and experience vaso-occlusive crises, often presenting with severe pain, but the key findings of bite cells and Heinz bodies are not characteristic.
- While it can manifest with anemia and jaundice, the specific trigger and peripheral smear findings point away from sickle cell disease.
*Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia*
- This involves red blood cell fragmentation due to passage through fibrin strands in small vessels, leading to **schistocytes** on peripheral smear, not bite cells or Heinz bodies.
- Conditions like **DIC, TTP, or HUS** are common causes, none of which are suggested by the clinical picture or lab findings.
*Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)*
- PNH is characterized by **dark urine in the morning (hemoglobinuria)**, thrombosis, and bone marrow failure, and it is a clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorder.
- The diagnosis is confirmed by flow cytometry showing absence of **CD55 and CD59** on red blood cells, and the peripheral smear findings are not consistent with PNH.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 3: An 11-year-old boy is brought to the emergency room with acute abdominal pain and hematuria. Past medical history is significant for malaria. On physical examination, he has jaundice and a generalized pallor. His hemoglobin is 5 g/dL, and his peripheral blood smear reveals fragmented RBC, microspherocytes, and eccentrocytes (bite cells). Which of the following reactions catalyzed by the enzyme is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Glucose-1-phosphate + UTP → UDP-glucose + pyrophosphate
- B. Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP + H+
- C. D-glucose 6-phosphate → D-fructose-6-phosphate
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate + H2O → glucose + Pi
- E. D-glucose-6-phosphate + NADP+ → 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + NADPH + H+ (Correct Answer)
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***D-glucose-6-phosphate + NADP+ → 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + NADPH + H+***
- This reaction is catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)**, an enzyme critical for the production of **NADPH** in the **pentose phosphate pathway**.
- **NADPH** is essential for reducing **oxidative stress** in red blood cells. A deficiency in G6PD leads to increased susceptibility to hemolysis, especially under oxidative triggers like malaria, resulting in symptoms such as **acute hemolytic anemia**, jaundice, and specific morphological changes (e.g., **fragmented RBCs**, **microspherocytes**, and **eccentrocytes**, also known as **bite cells**).
*Glucose-1-phosphate + UTP → UDP-glucose + pyrophosphate*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase** and is important for **glycogen synthesis**.
- A deficiency in this enzyme would primarily affect glycogen metabolism and would not explain the **hemolytic anemia** or the characteristic red blood cell morphology seen in the patient.
*Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP + H+*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **hexokinase**, the first committed step in **glycolysis**.
- While hexokinase deficiency can cause **hemolytic anemia**, it generally presents with chronic, moderate anemia and does not typically involve the specific red blood cell morphology (eccentrocytes/bite cells) associated with oxidative damage found in G6PD deficiency.
*D-glucose 6-phosphate → D-fructose-6-phosphate*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **phosphoglucose isomerase** (also known as phosphohexose isomerase) and is part of **glycolysis**.
- A deficiency in this enzyme would impair glycolysis and lead to **hemolytic anemia**, but its clinical presentation and RBC morphology differ from what is typically seen in G6PD deficiency, particularly the absence of oxidative stress markers like bite cells.
*Glucose-6-phosphate + H2O → glucose + Pi*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphatase**, an enzyme found primarily in the liver and kidney, responsible for the final step in **gluconeogenesis** and glycogenolysis to release free glucose into the bloodstream.
- A deficiency in glucose-6-phosphatase leads to **glycogen storage disease type I (Von Gierke's disease)**, characterized by **hypoglycemia**, **lactic acidosis**, and hepatomegaly, not hemolytic anemia.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 4: A 26-year-old African American man comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fatigue, back pain, and dark urine. One week ago, he developed a headache and was treated with aspirin. He does not smoke or use illicit drugs. Physical examination shows conjunctival pallor. A peripheral blood smear shows erythrocytes with inclusions of denatured hemoglobin. Which of the following enzymes is involved in providing precursors for nucleotide synthesis in this patient?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
- C. Pyruvate carboxylase
- D. Transaldolase (Correct Answer)
- E. Enolase
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Transaldolase***
- This patient likely has **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**, indicated by fatigue, dark urine (hemolysis), and **Heinz bodies** (erythrocytes with inclusions of denatured hemoglobin) after aspirin exposure, which is an **oxidative stressor**.
- **Transaldolase** is an enzyme in the **non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)**, which produces **ribose-5-phosphate**, a precursor for nucleotide synthesis.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- **Glucose-6-phosphatase** is involved in **gluconeogenesis** and glycogenolysis, primarily in the liver and kidneys, to release free glucose into the bloodstream.
- Deficiency leads to **Von Gierke disease**, characterized by hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, lactic acidosis, and hyperlipidemia, which are not described here.
*Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I*
- **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)** is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in the **urea cycle**, converting ammonia and bicarbonate into carbamoyl phosphate.
- Its deficiency causes **hyperammonemia**, not hemolytic anemia or issues with nucleotide synthesis.
*Pyruvate carboxylase*
- **Pyruvate carboxylase** is a mitochondrial enzyme that converts **pyruvate to oxaloacetate**, a crucial step in **gluconeogenesis** and replenishing intermediates of the citric acid cycle.
- Deficiency can lead to lactic acidosis and hypoglycemia, which are not the primary symptoms here.
*Enolase*
- **Enolase** is an enzyme in **glycolysis** that catalyzes the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
- It is not directly involved in providing precursors for nucleotide synthesis.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 5: A 3-week-old newborn is brought to the pediatrician by his mother. His mother is concerned about her son’s irritability and vomiting, particularly after breastfeeding him. The infant was born at 39 weeks via spontaneous vaginal delivery. His initial physical was benign. Today the newborn appears mildly jaundiced with palpable hepatomegaly, and his eyes appear cloudy, consistent with the development of cataracts. The newborn is also in the lower weight-age percentile. The physician considers a hereditary enzyme deficiency and orders blood work and a urinalysis to confirm his diagnosis. He recommends that milk and foods high in galactose and/or lactose be eliminated from the diet. Which of the following is the most likely deficient enzyme in this metabolic disorder?
- A. Aldose reductase
- B. Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (Correct Answer)
- C. UDP-galactose-4-epimerase
- D. Galactokinase
- E. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase***
- The constellation of symptoms including **vomiting**, **irritability**, **jaundice**, **hepatomegaly**, **cataracts**, and **failure to thrive** in a neonate, with improvement upon eliminating galactose/lactose from the diet, is highly characteristic of **classic galactosemia**.
- **Classic galactosemia** is caused by a deficiency in **galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT)**, leading to the accumulation of galactose-1-phosphate, which is toxic to various tissues.
*Aldose reductase*
- This enzyme converts galactose to **galactitol**, which can accumulate in the lens and cause **cataracts** in all forms of galactosemia if left untreated.
- However, isolated aldose reductase deficiency does not explain the full spectrum of severe systemic symptoms like hepatomegaly, jaundice, and failure to thrive observed in this neonate, which are indicative of classic galactosemia.
*UDP-galactose-4-epimerase*
- Deficiency in **UDP-galactose-4-epimerase (GALE)**, also known as epimerase deficiency galactosemia, has a wide range of severity.
- While it can present with similar symptoms to GALT deficiency, its severe form is rarer, and the classic, pronounced presentation described here is more commonly associated with GALT deficiency.
*Galactokinase*
- Deficiency in **galactokinase (GALK)** causes **Type II galactosemia**, which primarily manifests as **cataracts** due to galactitol accumulation.
- It typically does not present with the severe hepatic (jaundice, hepatomegaly) or systemic symptoms (vomiting, failure to thrive) seen in classic galactosemia.
*Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- **Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency** primarily causes **hemolytic anemia** triggered by certain drugs, infections, or fava beans.
- It does not present with the specific constellation of symptoms related to galactose metabolism, such as cataracts, hepatomegaly, and vomiting upon milk ingestion, as described in this case.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 6: An investigator is studying biomolecular mechanisms in human cells. A radioactive isotope that is unable to cross into organelles is introduced into a sample of cells. The cells are then fragmented via centrifugation and the isotope-containing components are isolated. Which of the following reactions is most likely to be present in this cell component?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose
- B. Isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate
- C. Carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline
- D. Fatty acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA
- E. Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone (Correct Answer)
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone***
- This reaction is the first step of the **pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)**, which occurs in the **cytosol**.
- Since the isotope cannot cross into organelles and is found in the cytosolic fraction, this pathway is a likely candidate.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose*
- This reaction describes the dephosphorylation of **glucose-6-phosphate** to **glucose**, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- While important for glucose release, this enzyme is primarily located in the **endoplasmic reticulum** of the liver and kidneys, an organelle.
*Isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate*
- This is a step in the **Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)**, which takes place in the **mitochondrial matrix**.
- The isotope would not be found in this compartmentalized reaction because it cannot enter organelles.
*Carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline*
- This reaction is part of the **urea cycle**, which has steps occurring in both the **mitochondrial matrix** and the cytosol. The initial step, forming carbamoyl phosphate, is mitochondrial.
- The isotope, being unable to cross into organelles, would not readily participate in the mitochondrial portion of this pathway.
*Fatty acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA*
- This reaction represents **beta-oxidation of fatty acids**, a process that primarily occurs in the **mitochondria** and peroxisomes.
- As the isotope is excluded from organelles, it would not be involved in these reactions.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 8: A 26-year-old man comes to the physician for evaluation of fatigue, facial rash, hair loss, and tingling of his hands and feet. He has followed a vegetarian diet for the past 3 years and has eaten 8 raw egg whites daily for the past year in preparation for a bodybuilding competition. Physical examination shows conjunctival injections and a scaly, erythematous rash around the eyes and mouth. Laboratory studies show decreased activity of propionyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Which of the following substances is most likely to be decreased in this patient?
- A. Methylmalonyl-CoA (Correct Answer)
- B. Cystathionine
- C. Lactate
- D. Adenine
- E. Ribulose-5-phosphate
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Methylmalonyl-CoA***
- This patient has classic **biotin deficiency** due to consumption of raw egg whites. **Avidin** in raw egg whites binds biotin and prevents its absorption, leading to symptoms of dermatitis, alopecia, conjunctivitis, and neurological manifestations.
- Biotin is an essential cofactor for several carboxylase enzymes, including **propionyl-CoA carboxylase**, which catalyzes the conversion of **propionyl-CoA → methylmalonyl-CoA**.
- With **decreased propionyl-CoA carboxylase activity** (as stated in the question), the enzyme cannot efficiently convert its substrate to product. This results in **decreased formation of the product, methylmalonyl-CoA**.
- While propionyl-CoA (the substrate) would accumulate, methylmalonyl-CoA (the product) would be **decreased** due to impaired enzymatic conversion.
*Cystathionine*
- Cystathionine is an intermediate in the **transsulfuration pathway** (homocysteine → cysteine), which requires **vitamin B6** as a cofactor, not biotin.
- Its levels would not be directly affected by biotin deficiency or decreased propionyl-CoA carboxylase activity.
*Lactate*
- Lactate levels are elevated in conditions involving **anaerobic metabolism** or impaired mitochondrial function.
- Biotin deficiency can affect pyruvate carboxylase (another biotin-dependent enzyme), but this would not specifically decrease lactate levels. If anything, impaired pyruvate carboxylase might increase lactate by limiting pyruvate's entry into gluconeogenesis.
*Adenine*
- Adenine is a purine nucleobase involved in nucleotide synthesis and salvage pathways.
- Its metabolism is unrelated to biotin-dependent carboxylases and would not be affected in this patient.
*Ribulose-5-phosphate*
- Ribulose-5-phosphate is an intermediate in the **pentose phosphate pathway**, which generates NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate for nucleotide synthesis.
- This pathway is independent of biotin-dependent enzymes and would not be directly affected by propionyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 9: A 14-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of a 12-hour history of abdominal pain and dark urine. Three days ago, he developed a cough, sore throat, and rhinorrhea. Examination shows conjunctival pallor, scleral icterus, and mild splenomegaly. A peripheral blood smear shows small round inclusions within erythrocytes and several erythrocytes with semicircular indentations. The underlying cause of this patient's condition is most likely to also affect which of the following processes?
- A. Anchoring proteins to cell surface
- B. Function of myeloperoxidase
- C. Biosynthesis of glutathione
- D. Generation of superoxide (Correct Answer)
- E. Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Generation of superoxide***
- This patient presents with signs of **hemolytic anemia** (abdominal pain, dark urine, conjunctival pallor, scleral icterus), likely triggered by an infection (cough, sore throat, rhinorrhea), and a peripheral blood smear showing **Heinz bodies** (small round inclusions) and **bite cells** (semicircular indentations). These findings are classic for **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**.
- **G6PD deficiency** impairs the **pentose phosphate pathway**, which is essential for producing **NADPH**. NADPH is required by **NADPH oxidase** for the **generation of superoxide** in phagocytes through the **respiratory burst** to kill bacteria.
*Anchoring proteins to cell surface*
- This process is primarily affected in diseases like **paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria** (PNH), where there is a defect in the **PIG-A gene** leading to deficient synthesis of **GPI anchors**.
- PNH presents with hemolytic anemia but lacks the characteristic Heinz bodies and bite cells seen in G6PD deficiency and is not typically triggered by infection in this acute manner.
*Function of myeloperoxidase*
- **Myeloperoxidase deficiency** leads to impaired killing of bacteria and fungi within phagocytes, increasing susceptibility to recurrent infections.
- While patients with myeloperoxidase deficiency have a normal respiratory burst, they do not present with hemolytic anemia or the specific red blood cell findings of G6PD deficiency.
*Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate*
- **Pyruvate kinase deficiency** affects the final step in **glycolysis**, causing a buildup of **2,3-BPG** and impaired ATP production in red blood cells.
- This leads to chronic hemolytic anemia but does not present with Heinz bodies or bite cells, nor is it acutely triggered by infection in the same way as G6PD deficiency.
*Biosynthesis of glutathione*
- While G6PD deficiency impacts the **reduction of oxidized glutathione** (GSSG) back to **reduced glutathione** (GSH), it does not directly affect the *biosynthesis* of glutathione.
- The problem in G6PD deficiency is G6PD's inability to produce sufficient NADPH, which is a cofactor for **glutathione reductase**, thereby impairing the regeneration of GSH necessary to protect red blood cells from oxidative stress.
Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG Question 10: A 30-year-old man presents with dark urine and fatigue. The patient states that the symptoms started 2 days ago. Since yesterday, he also noticed that his eyes look yellow. The past medical history is significant for recent right ear pain diagnosed 3 days ago as acute otitis media, which he was prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. He currently does not take any other medications on a daily basis. The patient was adopted and has no knowledge of his family history. The vital signs include: temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 100/75 mm Hg, pulse 105/min, respiratory rate 15/min, and oxygen saturation 100% on room air. On physical exam, the patient is alert and cooperative. The cardiac exam is significant for an early systolic murmur that is best heard at the 2nd intercostal space, midclavicular line. There is scleral icterus present. The peripheral blood smear shows the presence of bite cells and Heinz bodies. Which of the following laboratory findings would most likely be present in this patient?
- A. Decreased indirect bilirubin levels
- B. Decreased reticulocyte count
- C. Increased serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased serum haptoglobin
- E. Decreased mean corpuscular volume
Pentose phosphate pathway Explanation: ***Increased serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)***
- The patient's symptoms (dark urine, fatigue, jaundice), recent trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole use, and peripheral blood smear findings (bite cells, Heinz bodies) are classic for **G6PD deficiency** with acute **hemolytic anemia**.
- **LDH** is an intracellular enzyme found in red blood cells, and its release into the bloodstream is a marker of **cell lysis**, which is elevated in hemolytic anemia due to the breakdown of red blood cells.
*Decreased indirect bilirubin levels*
- In **hemolytic anemia**, there is an increased breakdown of red blood cells, leading to a surplus of **unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin** that overwhelms the liver's capacity for conjugation.
- Therefore, **indirect bilirubin levels** would be **increased**, not decreased, contributing to the observed jaundice.
*Decreased reticulocyte count*
- The body compensates for acute hemolytic anemia by increasing red blood cell production in the bone marrow, which is reflected by an **increased reticulocyte count**.
- A **decreased reticulocyte count** would suggest bone marrow suppression or aplastic anemia, which is not indicated here.
*Increased serum haptoglobin*
- **Haptoglobin** is a protein that binds to free hemoglobin released during red blood cell destruction. In hemolytic anemia, haptoglobin is rapidly consumed and cleared from the blood.
- Thus, **serum haptoglobin levels** would be **decreased**, not increased, as it is used used up in an attempt to clear the free hemoglobin.
*Decreased mean corpuscular volume*
- **Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)** measures the average size of red blood cells. G6PD deficiency with hemolytic anemia is typically a **normocytic anemia**, meaning the red blood cells are of normal size.
- A **decreased MCV** would suggest microcytic anemia, such as iron deficiency or thalassemias, which is not consistent with the clinical picture or blood smear findings.
More Pentose phosphate pathway US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.