Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Metabolic adaptations in starvation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after vomiting blood. The patient reports that he only ate a small snack the morning before and had not eaten anything for over 24 hours. At the hospital, the patient is stabilized. He is admitted to a surgical floor and placed on NPO with a nasogastric tube set to intermittent suction. He has been previously diagnosed with liver cirrhosis. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) has been planned for the next afternoon. At the time of endoscopy, some pathways were generating glucose to maintain serum glucose levels. Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the irreversible biochemical reaction of this process?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- B. Glycogen phosphorylase
- C. Enolase
- D. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- E. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Correct Answer)
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase***
- The scenario describes a patient in a fasting state for over 24 hours, during which **gluconeogenesis** is crucial for maintaining blood glucose levels.
- **Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase** is one of the key regulatory enzymes in gluconeogenesis, catalyzing an **irreversible reaction** that bypasses the phosphofructokinase-1 step of glycolysis.
*Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- This enzyme is involved in the **pentose phosphate pathway**, which generates NADPH and precursors for nucleotide synthesis.
- It does not directly participate in gluconeogenesis to produce glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
*Glycogen phosphorylase*
- This enzyme is involved in **glycogenolysis**, the breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate.
- While it releases glucose, the body's glycogen stores would likely be depleted after over 24 hours of fasting, making gluconeogenesis the primary pathway for glucose production.
*Enolase*
- Enolase is an enzyme in the glycolytic pathway, catalyzing the reversible conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
- It is not an enzyme of gluconeogenesis, nor does it catalyze an irreversible step in the glucose production process during fasting.
*Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- This enzyme is also part of glycolysis, catalyzing the reversible oxidation and phosphorylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
- Like enolase, it is not an irreversible enzyme in gluconeogenesis that would be generating glucose under fasting conditions.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator is studying severely ill patients who experience hypoglycemia and ketonuria during times of fasting. The investigator determines that during these episodes, amino acids liberated from muscle proteins are metabolized to serve as substrates for gluconeogenesis. Nitrogen from this process is transported to the liver primarily in the form of which of the following molecules?
- A. Glutamate
- B. α-ketoglutarate
- C. Alanine (Correct Answer)
- D. Arginine
- E. Pyruvate
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Alanine***
- During prolonged fasting, **muscle proteins are catabolized** to provide amino acids for gluconeogenesis in the liver.
- **Alanine** is the primary amino acid released from muscle into the bloodstream to transport nitrogen to the liver through the **glucose-alanine cycle (Cahill cycle)**.
- In this cycle, pyruvate in muscle accepts an amino group from glutamate to form alanine, which is then transported to the liver, where it is deaminated back to pyruvate (for gluconeogenesis) and ammonia (for the urea cycle).
- **Glutamine** also serves as an important nitrogen transporter, particularly to the kidneys and intestines.
*Glutamate*
- **Glutamate** is an important amino acid in nitrogen metabolism within tissues, but it is not the primary form in which nitrogen is transported from muscle to the liver in significant quantities.
- While glutamate participates in transamination reactions within muscle, its efflux from muscle into the blood is less prominent than alanine for inter-organ nitrogen transport.
*α-ketoglutarate*
- **α-ketoglutarate** is a key intermediate in the **Krebs cycle** and accepts an amino group to form glutamate.
- It is an alpha-keto acid, not an amino acid, and therefore does not directly transport nitrogen in the form of an amino group to the liver via the bloodstream.
*Arginine*
- **Arginine** is primarily involved in the **urea cycle** within the liver, where it helps in the detoxification of ammonia, but it is not a major transporter of nitrogen from peripheral tissues to the liver for gluconeogenesis.
- Its role is mainly within the liver for urea synthesis, not for inter-organ nitrogen transport in this context.
*Pyruvate*
- **Pyruvate** is a keto acid that can be converted to alanine via transamination.
- While pyruvate is a precursor to alanine and a substrate for gluconeogenesis, it transports carbon skeletons and not nitrogen itself; **alanine is the actual nitrogen carrier** in this cycle.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old man presents for an annual check-up. He is a bodybuilder and tells you he is on a protein-rich diet that only allows for minimal carbohydrate intake. His friend suggests he try exogenous glucagon to help him lose some excess weight before an upcoming competition. Which of the following effects of glucagon is he attempting to exploit?
- A. Increased glucose utilization by tissues
- B. Decreased blood cholesterol level
- C. Increased hepatic gluconeogenesis
- D. Increased lipolysis in adipose tissues (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased hepatic glycogenolysis
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Increased lipolysis in adipose tissues***
- While **glucagon's primary target is the liver**, it can have **modest lipolytic effects** on adipose tissue by opposing insulin's anti-lipolytic actions.
- Glucagon stimulates cAMP production, which can activate **hormone-sensitive lipase** to break down triglycerides into **fatty acids** and **glycerol**.
- However, **catecholamines (epinephrine/norepinephrine)** are far more potent direct stimulators of adipose tissue lipolysis than glucagon.
- The friend is attempting to exploit this lipolytic effect for fat loss, though **exogenous glucagon is not an evidence-based or safe weight-loss strategy**.
*Increased glucose utilization by tissues*
- This is **opposite** to glucagon's actual effect. **Glucagon raises blood glucose** levels; it does not promote glucose uptake by peripheral tissues.
- **Insulin** is the hormone responsible for promoting glucose uptake and utilization by muscle, adipose, and other tissues.
*Decreased blood cholesterol level*
- Glucagon does not have a direct, clinically significant effect on reducing blood cholesterol levels.
- While glucagon affects overall lipid metabolism through its catabolic actions, it is not used therapeutically for hypercholesterolemia.
*Increased hepatic gluconeogenesis*
- **Glucagon strongly stimulates hepatic gluconeogenesis**, which is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors (amino acids, lactate, glycerol) in the liver.
- This action **raises blood glucose** levels and would not directly contribute to fat loss or weight reduction.
- In the context of a low-carbohydrate diet, increased gluconeogenesis would maintain blood glucose but not promote the fat loss the bodybuilder seeks.
*Increased hepatic glycogenolysis*
- **Glucagon is a potent stimulator of hepatic glycogenolysis**, the breakdown of stored liver glycogen into glucose.
- This rapidly increases blood glucose levels during fasting or hypoglycemia.
- However, this does not directly target adipose tissue for fat loss; it mobilizes glucose stores rather than fat stores, so it's not the mechanism relevant to weight loss goals.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old male prisoner goes on a hunger strike to protest the conditions of his detainment. After 5 days without food, he suffers a seizure for which he is taken into a medical facility. On physical examination, he looks pale and diaphoretic. His blood glucose level is 50 mg/dL. In order to keep a constant supply of energy to his brain, which of the following molecules is his liver releasing into the bloodstream?
- A. Glycogen
- B. Glucose-6-phosphate
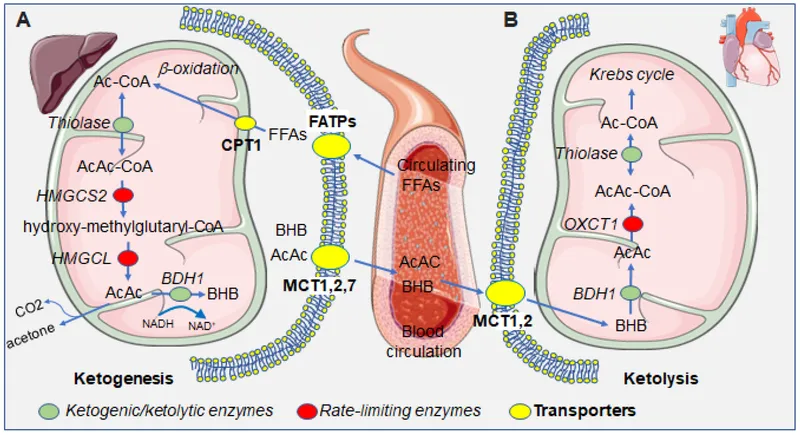
- C. ß-hydroxybutyric acid (Correct Answer)
- D. Fatty acids
- E. Glucose-1-phosphate
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***ß-hydroxybutyric acid***
- After 5 days of a hunger strike, **glycogen stores** are depleted, forcing the body to rely on **fatty acid oxidation** and **ketone body production** in the liver as an alternative fuel source for the brain.
- **ß-hydroxybutyrate** is one of the primary ketone bodies released by the liver into the bloodstream to provide energy, especially for the brain, during prolonged fasting.
*Glycogen*
- **Glycogenolysis** (breakdown of glycogen) is a short-term response to low blood glucose and supplies glucose for only about 24-36 hours of fasting. After 5 days, **hepatic glycogen stores** would be largely depleted.
- The liver releases **free glucose** into the bloodstream, not intact glycogen, from glycogen breakdown.
*Glucose-6-phosphate*
- **Glucose-6-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, but it is not directly released into the bloodstream by the liver.
- It must be converted to **free glucose** by glucose-6-phosphatase before it can exit the hepatocyte and enter circulation.
*Fatty acids*
- The liver takes up **fatty acids** from adipose tissue breakdown during prolonged fasting to convert them into **ketone bodies**.
- While fatty acids are a major energy source for other tissues, the **brain cannot directly utilize fatty acids** for energy due to the inability of long-chain fatty acids to cross the blood-brain barrier.
*Glucose-1-phosphate*
- **Glucose-1-phosphate** is an intermediate formed during the breakdown of glycogen (glycogenolysis).
- Like glucose-6-phosphate, it is not directly released into the bloodstream but is further metabolized within the hepatocyte, eventually leading to the release of **free glucose**.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 5: A 55-year-old man with alcoholic cirrhosis is admitted to the hospital for routine evaluation before liver transplantation. The physician asks the patient to stop eating 10 hours before surgery. Which of the following structures contributes directly to preventing fasting hypoglycemia by producing glucose in this patient?
- A. Adrenal cortex
- B. Skeletal muscle
- C. Red blood cells
- D. Skin
- E. Intestine (Correct Answer)
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Correct: Intestine***
- The **intestine** (particularly the small intestine) possesses the enzymatic machinery for **gluconeogenesis**, including glucose-6-phosphatase, allowing it to directly produce and release free glucose into the bloodstream.
- During prolonged fasting (>10 hours), intestinal gluconeogenesis can contribute up to **20-25% of total glucose production**, utilizing substrates like glutamine and glycerol.
- In patients with **alcoholic cirrhosis**, hepatic gluconeogenesis is impaired, making extrahepatic sites like the intestine and kidneys increasingly important for maintaining euglycemia.
- The intestine directly produces glucose and releases it into the portal circulation, making it a direct contributor to preventing fasting hypoglycemia.
*Incorrect: Skeletal muscle*
- **Skeletal muscle lacks glucose-6-phosphatase**, the enzyme required to convert glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose for release into the bloodstream.
- Muscle undergoes proteolysis during fasting, releasing amino acids (particularly alanine and glutamine) that serve as gluconeogenic substrates for the liver and kidneys.
- This represents an **indirect contribution** to glucose homeostasis through substrate provision, not direct glucose production.
*Incorrect: Red blood cells*
- **Red blood cells** lack mitochondria and can only perform anaerobic glycolysis, producing lactate.
- Lactate from RBCs can be recycled to glucose in the liver via the **Cori cycle**, but RBCs themselves are net glucose consumers, not producers.
- They contribute indirectly through substrate provision, not direct glucose synthesis.
*Incorrect: Skin*
- The **skin** has no significant role in glucose production or gluconeogenesis.
- Its primary functions are protection, thermoregulation, and sensation; it does not possess the enzymatic capacity for gluconeogenesis.
- Skin does not contribute to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis during fasting.
*Incorrect: Adrenal cortex*
- The **adrenal cortex** secretes hormones (cortisol, aldosterone) that regulate glucose metabolism indirectly.
- **Cortisol** promotes hepatic and renal gluconeogenesis and decreases peripheral glucose utilization, but the adrenal gland itself does not synthesize or release glucose.
- This is a regulatory role, not direct glucose production.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 6: A 26-year-old medical student who is preparing for Step 1 exams is woken up by her friend for breakfast. She realizes that she must have fallen asleep at her desk while attempting to study through the night. While walking with her friend to breakfast, she realizes that she has not eaten since breakfast the previous day. Using this as motivation to review some biochemistry, she pauses to consider what organs are responsible for allowing her to continue thinking clearly in this physiologic state. Which of the following sets of organs are associated with the major source of energy currently facilitating her cognition?
- A. Muscle only
- B. Liver and kidney (Correct Answer)
- C. Liver and muscle
- D. Liver, muscle, and kidney
- E. Liver only
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Liver and kidney***
- After an overnight fast (~16-24 hours without food), the **liver** is the **primary organ** responsible for maintaining blood glucose levels through **glycogenolysis** (initially) and **gluconeogenesis** (predominantly at this stage).
- The **kidney** also contributes to **gluconeogenesis** even during an overnight fast, providing approximately **10-15% of total glucose production**. While this contribution is relatively minor compared to the liver, it becomes increasingly important during more prolonged fasting states (>48-72 hours), where it can account for up to 40% of glucose production.
- Since the brain relies almost exclusively on glucose at this stage of fasting (ketone bodies are not yet a major fuel source), both organs that produce glucose for systemic use are correctly identified here.
*Muscle only*
- Muscle glycogen can only be used by the **muscle cells themselves** due to the absence of **glucose-6-phosphatase**, so muscle cannot release free glucose into the bloodstream for use by the brain.
- While muscle does provide amino acids (particularly alanine and glutamine) for gluconeogenesis in the liver and kidney, it does not directly supply glucose to support brain function.
*Liver and muscle*
- As explained above, muscle cannot directly supply glucose to the bloodstream to support brain function due to the lack of **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- The liver is a major contributor, but muscle is not a direct source of blood glucose.
*Liver, muscle, and kidney*
- This option incorrectly includes muscle as a direct source of glucose for the brain. While liver and kidney both perform gluconeogenesis and release glucose into the bloodstream, muscle lacks this capability.
*Liver only*
- While the liver is indeed the **dominant source** of glucose during an overnight fast (contributing ~85-90% of gluconeogenesis), the **kidney also actively participates** in glucose production, contributing ~10-15% at this stage.
- Since the question asks which organs are "responsible" for maintaining cognition, and both organs contribute to systemic glucose production (even if disproportionately), "liver only" is incomplete.
- The kidney's contribution, though relatively minor during overnight fasting, becomes more substantial during prolonged fasting states.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 7: A 10-month-old boy with a seizure disorder is brought to the physician by his mother because of a 2-day history of vomiting and lethargy. Laboratory studies show a decreased serum glucose concentration with low ketones. Further testing confirms a deficiency in an enzyme involved in fatty acid oxidation. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (Correct Answer)
- B. HMG-CoA reductase
- C. Glycerol kinase
- D. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- E. Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase***
- The combination of **hypoglycemia** with **low ketones** in a setting of prolonged vomiting (stress) strongly suggests a **disorder of fatty acid oxidation**. These disorders impair the body's ability to produce ketones when glucose stores are low.
- **Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase** is a key enzyme in the mitochondrial β-oxidation of fatty acids. A deficiency prevents the breakdown of fatty acids into acetyl-CoA, which is necessary for ketogenesis and to fuel gluconeogenesis indirectly.
*HMG-CoA reductase*
- This enzyme is involved in **cholesterol synthesis**, not directly in fatty acid oxidation or ketone body formation from fatty acids.
- Deficiency would primarily affect cholesterol levels and not typically present with the described metabolic crisis of hypoglycemia and low ketones.
*Glycerol kinase*
- **Glycerol kinase** phosphorylates glycerol, a product of triglyceride hydrolysis, allowing it to enter glycolysis or gluconeogenesis.
- A deficiency would impair glycerol utilization but would not directly impact fatty acid oxidation pathways that are critical for ketone production during hypoglycemia.
*Acetyl-CoA carboxylase*
- **Acetyl-CoA carboxylase** is the rate-limiting enzyme in **fatty acid synthesis**, not degradation.
- A deficiency would lead to impaired fatty acid synthesis, which is the opposite of the metabolic problem described (impaired breakdown of fatty acids).
*Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- This enzyme is involved in the conversion of **dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)** to **glycerol-3-phosphate** in both triglyceride synthesis and the glycerol phosphate shuttle.
- While related to lipid metabolism, a deficiency would not directly cause the severe hypoglycemia and hypoketosis seen with a fatty acid oxidation defect.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 8: A 22-year-old medical student decides to fast for 24 hours after reading about the possible health benefits of fasting. She read that blood glucose levels are maintained by metabolic processes such as hepatic glycogenolysis and hepatic gluconeogenesis during the initial 3 days of fasting. During the day, she did not suffer from the symptoms of hypoglycemia. Which of the following signaling molecules most likely stimulated the reaction which maintained her blood glucose after all her stored glucose was broken down and used up?
- A. Adenosine diphosphate
- B. Acetyl CoA (Correct Answer)
- C. Acetate
- D. Citrate
- E. Adenosine monophosphate
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Acetyl CoA***
- **Acetyl CoA** is the key **allosteric activator of pyruvate carboxylase**, the first committed enzyme of gluconeogenesis that converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate.
- During prolonged fasting after glycogen stores are depleted, the body shifts to **fatty acid oxidation** (β-oxidation), which produces large amounts of **Acetyl CoA**.
- High **Acetyl CoA** levels signal that fat is being oxidized for energy, and simultaneously **activate gluconeogenesis** to maintain blood glucose for glucose-dependent tissues (brain, RBCs).
- This is the primary signaling mechanism that directly stimulates the gluconeogenic pathway after glycogen is exhausted.
*Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)*
- **AMP** levels rise during energy depletion and activate **AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)**.
- However, AMPK **inhibits gluconeogenesis** (not stimulates it) because gluconeogenesis is an **ATP-consuming** anabolic process (requires 6 ATP per glucose).
- AMPK promotes ATP-generating catabolic processes like fatty acid oxidation, but suppresses ATP-consuming processes like gluconeogenesis and fatty acid synthesis.
*Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)*
- **ADP** accumulates when ATP is hydrolyzed and signals moderate energy deficit.
- ADP is primarily a substrate for ATP regeneration via oxidative phosphorylation and does not directly regulate gluconeogenesis.
- Its role in metabolic regulation is less specific than allosteric activators like Acetyl CoA.
*Acetate*
- **Acetate** can be converted to Acetyl CoA but is not a direct signaling molecule for gluconeogenesis.
- It is a minor metabolite that may be produced in specific conditions (e.g., alcohol metabolism, ketoacidosis) but does not play a primary role in fasting-induced glucose homeostasis.
*Citrate*
- **Citrate** is a Krebs cycle intermediate that inhibits **phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)** in glycolysis, thus reducing glucose breakdown.
- While citrate inhibition of glycolysis indirectly favors gluconeogenesis by preventing futile cycling, citrate does not **directly activate** gluconeogenic enzymes.
- Citrate primarily signals energy sufficiency and promotes fatty acid synthesis in the fed state, not fasting gluconeogenesis.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 9: A 24-year-old man is running a marathon. Upon reaching the finish line, his serum lactate levels were measured and were significantly increased as compared to his baseline. Which of the following pathways converts the lactate produced by muscles into glucose and transports it back to the muscles?
- A. Citric acid cycle
- B. Glycolysis
- C. Glycogenesis
- D. Pentose phosphate pathway
- E. Cori cycle (Correct Answer)
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Cori cycle***
- The **Cori cycle** is the metabolic pathway that converts **lactate** produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles (especially during intense exercise) back to **glucose in the liver** via gluconeogenesis.
- During strenuous exercise, muscles rely on anaerobic glycolysis when oxygen supply is insufficient, producing lactate and 2 ATP per glucose.
- The lactate is transported via bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted back to glucose (requiring 6 ATP), which then returns to muscles for energy or glycogen storage.
- This cycle allows muscles to continue generating ATP anaerobically while the liver handles lactate clearance.
*Citric acid cycle*
- The **citric acid cycle** (Krebs cycle) oxidizes **acetyl-CoA** to generate ATP, NADH, and FADH₂ in the mitochondrial matrix under aerobic conditions.
- It does not convert lactate to glucose; rather, pyruvate can be converted to acetyl-CoA to enter this cycle for complete oxidation.
- This is an aerobic process and does not involve the liver-muscle lactate-glucose exchange.
*Glycolysis*
- **Glycolysis** is the metabolic pathway that breaks down **glucose into pyruvate**, generating 2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose molecule.
- Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to lactate to regenerate NAD⁺ for continued glycolysis.
- This is the opposite of what the question asks—glycolysis produces lactate from glucose, not glucose from lactate.
*Glycogenesis*
- **Glycogenesis** is the process of synthesizing **glycogen from glucose** for storage, primarily in liver and muscle tissue.
- While it involves glucose storage, it does not convert lactate back to glucose or involve the metabolic exchange between muscles and liver described in the question.
*Pentose phosphate pathway*
- The **pentose phosphate pathway** (hexose monophosphate shunt) produces **NADPH** for reductive biosynthesis and **ribose-5-phosphate** for nucleotide synthesis.
- It branches from glycolysis but is not involved in lactate metabolism or the muscle-liver glucose-lactate exchange.
Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG Question 10: A 33-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 26 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a routine prenatal examination. Her pregnancy has been uneventful. Physical examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 26-week gestation. She is given an oral 50-g glucose load; 1 hour later, her serum glucose concentration is 116 mg/dL. Which of the following most likely occurred immediately after the entrance of glucose into the patient's pancreatic beta-cells?
- A. Closure of membranous potassium channels
- B. Generation of adenosine triphosphate (Correct Answer)
- C. Increased expression of hexokinase I mRNA
- D. Exocytosis of insulin granules
- E. Depolarization of beta-cell membrane
Metabolic adaptations in starvation Explanation: ***Generation of adenosine triphosphate***
- Immediately after glucose enters pancreatic beta-cells via **GLUT2 transporters**, it is phosphorylated by **glucokinase (hexokinase IV)** to glucose-6-phosphate.
- This glucose is then metabolized through **glycolysis** and the **Krebs cycle**, leading to the generation of **ATP**.
- This increase in intracellular **ATP/ADP ratio** is the **primary signal** that links glucose metabolism to insulin secretion.
- Among the listed options, ATP generation is the **earliest event** that occurs.
*Closure of membranous potassium channels*
- The elevated **ATP** levels from glucose metabolism lead to the closure of **ATP-sensitive potassium (K-ATP) channels**.
- This closure is a subsequent event that depends on the increased ATP/ADP ratio, not an immediate consequence of glucose entry.
*Increased expression of hexokinase I mRNA*
- While **glucokinase (hexokinase IV)** activity is crucial for glucose phosphorylation in beta-cells, increased mRNA expression is a **long-term adaptive response** requiring transcription and translation.
- The immediate response involves the existing enzyme converting glucose to **glucose-6-phosphate**, followed by ATP generation.
*Exocytosis of insulin granules*
- **Insulin granule exocytosis** is the final step in insulin release, occurring after a cascade of events: ATP generation → K-ATP channel closure → membrane depolarization → calcium influx.
- This event is a *downstream consequence*, not an immediate result of glucose entering the cell.
*Depolarization of beta-cell membrane*
- **Membrane depolarization** follows the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels, which then leads to the opening of **voltage-gated calcium channels**.
- This is a subsequent event that depends on the initial ATP generation and K-ATP channel closure.
More Metabolic adaptations in starvation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.