Overview - The Sugar Factory
- Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is the metabolic pathway that synthesizes new glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors, crucial for maintaining glucose homeostasis during fasting.
- Primary Sites: Liver (major, ~90%) and kidney cortex (minor, ~10%).
- Cellular Locations: Occurs in both the mitochondria and cytosol, requiring transport of intermediates between compartments.
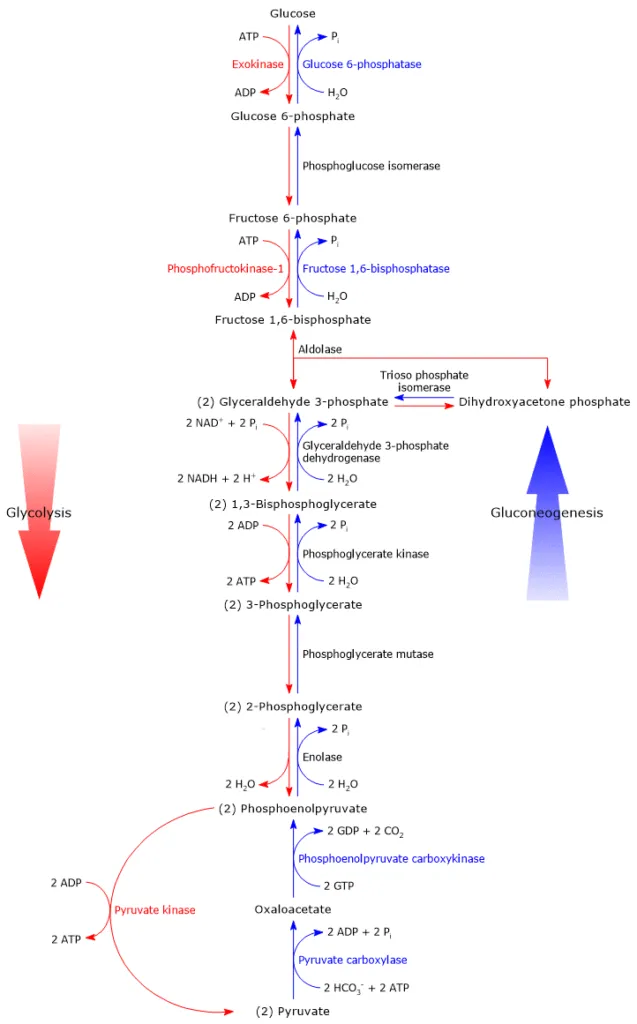
⭐ Gluconeogenesis is NOT the simple reversal of glycolysis; it bypasses three irreversible glycolytic steps with four unique enzymes.
Substrates - The Starting Lineup
Key molecules that can be converted to pyruvate or TCA cycle intermediates:
- Lactate: From anaerobic glycolysis in RBCs & muscle (Cori cycle).
- Alanine: From muscle protein breakdown (Alanine-Cahill cycle).
- Glycerol-3-Phosphate: From triacylglycerol (TAG) breakdown in adipose tissue.
- Propionyl-CoA: From odd-chain fatty acids & certain amino acids (Val, Ile, Met, Thr).
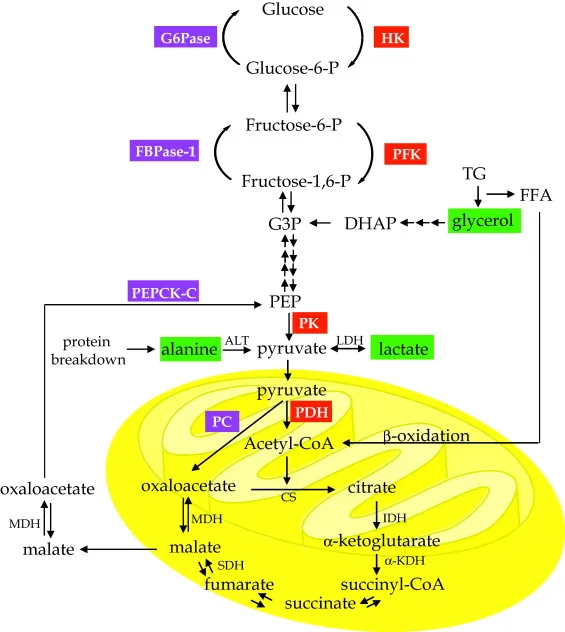
⭐ Even-chain fatty acids CANNOT yield net glucose because they are metabolized to acetyl-CoA, and the PDH complex reaction is irreversible.
Key Enzymes - The Bypass Crew
Gluconeogenesis circumvents the irreversible steps of glycolysis using four unique enzymes. These enzymes effectively "bypass" the roadblocks set by glucokinase/hexokinase, PFK-1, and pyruvate kinase.
📌 Pathway Produces Fresh Glucose
- Pyruvate Carboxylase
- Location: Mitochondria
- Action: Converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate.
- $Pyruvate + CO_2 + ATP \rightarrow Oxaloacetate + ADP + P_i$
- Requires: Biotin (Vitamin B7).
- PEPCK (Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase)
- Location: Cytosol / Mitochondria
- Action: Converts oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyrate (PEP).
- Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
- Location: Cytosol
- Action: Dephosphorylates fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate.
- Glucose-6-phosphatase
- Location: Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Action: Dephosphorylates glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose.
⭐ Glucose-6-phosphatase is only found in the endoplasmic reticulum of the liver and kidneys, allowing them to release free glucose into the blood.
Regulation - Traffic Control
Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated. Key control points prevent wasteful futile cycles.
| Regulator Type | Activators (↑ Gluconeogenesis) | Inhibitors (↓ Gluconeogenesis) |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal | Glucagon, Epinephrine, Cortisol | Insulin |
| Allosteric | Acetyl-CoA (activates Pyruvate Carboxylase) | AMP, Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (inhibit F-1,6-bisphosphatase) |
| flowchart TD |
Glucagon["<b>🍕 Glucagon</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Fasting state</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• ⬆️ cAMP levels</span>"]
Insulin["<b>💉 Insulin</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Fed state</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• ⬆️ Tyrosine kinase</span>"]
PKA["<b>⚡ PKA</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Protein Kinase A</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Phosphorylation</span>"]
Phosphatase["<b>💧 Phosphatase</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Dephosphorylation</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Protein PP-1</span>"]
FBPase2["<b>🧬 FBPase-2</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Active if phospho</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• ⬇️ F-2,6-BP</span>"]
PFK2["<b>🧬 PFK-2</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Active if dephospho</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• ⬆️ F-2,6-BP</span>"]
F26BP["<b>🧪 F-2,6-BP</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Potent regulator</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Controls flux</span>"]
F16BPase["<b>✂️ F-1,6-BPase</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Gluconeogenesis</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Rate-limiting step</span>"]
GlucoNeo["<b>🍞 Gluconeogenesis</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Glucose synthesis</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Occurs in liver</span>"]
Glucagon -->|+ | PKA
PKA -->|+ | FBPase2
FBPase2 -->|⬇️| F26BP
Insulin -->|+ | Phosphatase
Phosphatase -->|+ | PFK2
PFK2 -->|⬆️| F26BP
F26BP -->|- | F16BPase
F16BPase -->|+ | GlucoNeo
style Glucagon fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
style Insulin fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
style PKA fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8
style Phosphatase fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8
style FBPase2 fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8
style PFK2 fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8
style F26BP fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
style F16BPase fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8
style GlucoNeo fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252
> ⭐ Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate is the most important allosteric regulator. It is a powerful inhibitor of gluconeogenesis (by inhibiting F-1,6-BPase) and a potent activator of glycolysis.
## Clinical Tie-ins - When GNG Fails
* Impaired GNG manifests as severe **fasting hypoglycemia** and **lactic acidosis**, as pyruvate cannot be converted back to glucose.
* **Inherited Enzyme Deficiencies**:
- **Von Gierke disease** (G6Pase def.): Presents with hepatomegaly, steatosis, and hyperuricemia.
- **PEPCK deficiency**: Affects a key rate-limiting step.
- **Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency**: Impairs the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate.
> ⭐ Chronic alcohol consumption increases the NADH/NAD+ ratio, shunting gluconeogenic precursors (pyruvate to lactate, OAA to malate), thereby inhibiting gluconeogenesis and causing hypoglycemia.
📌 Mnemonic for key enzymes: **V**ery **P**oor **F**armer (Von Gierke, PEPCK, F-1,6-bisphosphatase).
> * Gluconeogenesis synthesizes **new glucose** from **non-carbohydrate precursors**, mainly in the **liver**.
> * Key substrates are **lactate** (Cori cycle), **alanine** (Cahill cycle), and **glycerol-3-phosphate**.
> * Bypasses glycolysis's irreversible steps via **Pyruvate carboxylase**, **PEPCK**, **Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase**, and **Glucose-6-phosphatase**.
> * **Even-chain fatty acids cannot** yield new glucose because they produce only **acetyl-CoA**.
> * Stimulated by **glucagon** and **cortisol**; inhibited by **insulin** and high **AMP**.
> * **Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate** is a key allosteric **inhibitor**.

