Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 1: A 24-year-old man presents for an annual check-up. He is a bodybuilder and tells you he is on a protein-rich diet that only allows for minimal carbohydrate intake. His friend suggests he try exogenous glucagon to help him lose some excess weight before an upcoming competition. Which of the following effects of glucagon is he attempting to exploit?
- A. Increased glucose utilization by tissues
- B. Decreased blood cholesterol level
- C. Increased hepatic gluconeogenesis
- D. Increased lipolysis in adipose tissues (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased hepatic glycogenolysis
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Increased lipolysis in adipose tissues***
- While **glucagon's primary target is the liver**, it can have **modest lipolytic effects** on adipose tissue by opposing insulin's anti-lipolytic actions.
- Glucagon stimulates cAMP production, which can activate **hormone-sensitive lipase** to break down triglycerides into **fatty acids** and **glycerol**.
- However, **catecholamines (epinephrine/norepinephrine)** are far more potent direct stimulators of adipose tissue lipolysis than glucagon.
- The friend is attempting to exploit this lipolytic effect for fat loss, though **exogenous glucagon is not an evidence-based or safe weight-loss strategy**.
*Increased glucose utilization by tissues*
- This is **opposite** to glucagon's actual effect. **Glucagon raises blood glucose** levels; it does not promote glucose uptake by peripheral tissues.
- **Insulin** is the hormone responsible for promoting glucose uptake and utilization by muscle, adipose, and other tissues.
*Decreased blood cholesterol level*
- Glucagon does not have a direct, clinically significant effect on reducing blood cholesterol levels.
- While glucagon affects overall lipid metabolism through its catabolic actions, it is not used therapeutically for hypercholesterolemia.
*Increased hepatic gluconeogenesis*
- **Glucagon strongly stimulates hepatic gluconeogenesis**, which is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors (amino acids, lactate, glycerol) in the liver.
- This action **raises blood glucose** levels and would not directly contribute to fat loss or weight reduction.
- In the context of a low-carbohydrate diet, increased gluconeogenesis would maintain blood glucose but not promote the fat loss the bodybuilder seeks.
*Increased hepatic glycogenolysis*
- **Glucagon is a potent stimulator of hepatic glycogenolysis**, the breakdown of stored liver glycogen into glucose.
- This rapidly increases blood glucose levels during fasting or hypoglycemia.
- However, this does not directly target adipose tissue for fat loss; it mobilizes glucose stores rather than fat stores, so it's not the mechanism relevant to weight loss goals.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old woman with type 1 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department by her husband because of polyuria, nausea, vomiting, and altered mental status for 4 hours. On arrival, she is unconscious. Treatment with a drug is begun that increases glucose transport to skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Which of the following cellular events is most likely to also occur in response to this drug?
- A. Dephosphorylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Correct Answer)
- B. Increased activity of acyl-CoA dehydrogenases
- C. Cleavage of UDP from UDP-glucose
- D. Upregulation of glucose transporter type 3 expression
- E. Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Dephosphorylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase***
- The patient is in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and the drug administered is insulin
- Insulin promotes glucose utilization and storage, which involves inhibiting gluconeogenesis through the dephosphorylation and inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
- This is a key regulatory mechanism by which insulin suppresses hepatic glucose production
*Increased activity of acyl-CoA dehydrogenases*
- This enzyme is crucial for fatty acid oxidation, a process that is inhibited by insulin
- In DKA, fatty acid oxidation is elevated, leading to ketone body production, but insulin treatment reduces this activity
*Cleavage of UDP from UDP-glucose*
- This reaction occurs in the synthesis of glycogen from UDP-glucose by glycogen synthase, which is activated by insulin
- While insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis, the direct cleavage of UDP from UDP-glucose is part of the synthetic process, not a primary regulatory cellular event caused by insulin in the context of DKA treatment
*Upregulation of glucose transporter type 3 expression*
- Glucose transporter type 3 (GLUT3) is primarily found in neurons and has a high affinity for glucose, with its expression generally not significantly regulated by insulin
- Insulin primarily promotes GLUT4 translocation to the cell membrane in muscle and adipose tissue to increase glucose uptake
*Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase*
- Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase activates it, subsequently activating glycogen phosphorylase and promoting glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis)
- Insulin inhibits glycogenolysis and promotes glycogen synthesis, meaning insulin would deactivate glycogen phosphorylase kinase through dephosphorylation
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 3: A 55-year-old man with alcoholic cirrhosis is admitted to the hospital for routine evaluation before liver transplantation. The physician asks the patient to stop eating 10 hours before surgery. Which of the following structures contributes directly to preventing fasting hypoglycemia by producing glucose in this patient?
- A. Adrenal cortex
- B. Skeletal muscle
- C. Red blood cells
- D. Skin
- E. Intestine (Correct Answer)
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Correct: Intestine***
- The **intestine** (particularly the small intestine) possesses the enzymatic machinery for **gluconeogenesis**, including glucose-6-phosphatase, allowing it to directly produce and release free glucose into the bloodstream.
- During prolonged fasting (>10 hours), intestinal gluconeogenesis can contribute up to **20-25% of total glucose production**, utilizing substrates like glutamine and glycerol.
- In patients with **alcoholic cirrhosis**, hepatic gluconeogenesis is impaired, making extrahepatic sites like the intestine and kidneys increasingly important for maintaining euglycemia.
- The intestine directly produces glucose and releases it into the portal circulation, making it a direct contributor to preventing fasting hypoglycemia.
*Incorrect: Skeletal muscle*
- **Skeletal muscle lacks glucose-6-phosphatase**, the enzyme required to convert glucose-6-phosphate to free glucose for release into the bloodstream.
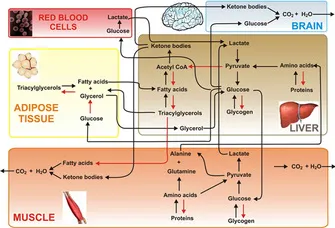
- Muscle undergoes proteolysis during fasting, releasing amino acids (particularly alanine and glutamine) that serve as gluconeogenic substrates for the liver and kidneys.
- This represents an **indirect contribution** to glucose homeostasis through substrate provision, not direct glucose production.
*Incorrect: Red blood cells*
- **Red blood cells** lack mitochondria and can only perform anaerobic glycolysis, producing lactate.
- Lactate from RBCs can be recycled to glucose in the liver via the **Cori cycle**, but RBCs themselves are net glucose consumers, not producers.
- They contribute indirectly through substrate provision, not direct glucose synthesis.
*Incorrect: Skin*
- The **skin** has no significant role in glucose production or gluconeogenesis.
- Its primary functions are protection, thermoregulation, and sensation; it does not possess the enzymatic capacity for gluconeogenesis.
- Skin does not contribute to maintaining blood glucose homeostasis during fasting.
*Incorrect: Adrenal cortex*
- The **adrenal cortex** secretes hormones (cortisol, aldosterone) that regulate glucose metabolism indirectly.
- **Cortisol** promotes hepatic and renal gluconeogenesis and decreases peripheral glucose utilization, but the adrenal gland itself does not synthesize or release glucose.
- This is a regulatory role, not direct glucose production.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 4: A 26-year-old medical student who is preparing for Step 1 exams is woken up by her friend for breakfast. She realizes that she must have fallen asleep at her desk while attempting to study through the night. While walking with her friend to breakfast, she realizes that she has not eaten since breakfast the previous day. Using this as motivation to review some biochemistry, she pauses to consider what organs are responsible for allowing her to continue thinking clearly in this physiologic state. Which of the following sets of organs are associated with the major source of energy currently facilitating her cognition?
- A. Muscle only
- B. Liver and kidney (Correct Answer)
- C. Liver and muscle
- D. Liver, muscle, and kidney
- E. Liver only
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Liver and kidney***
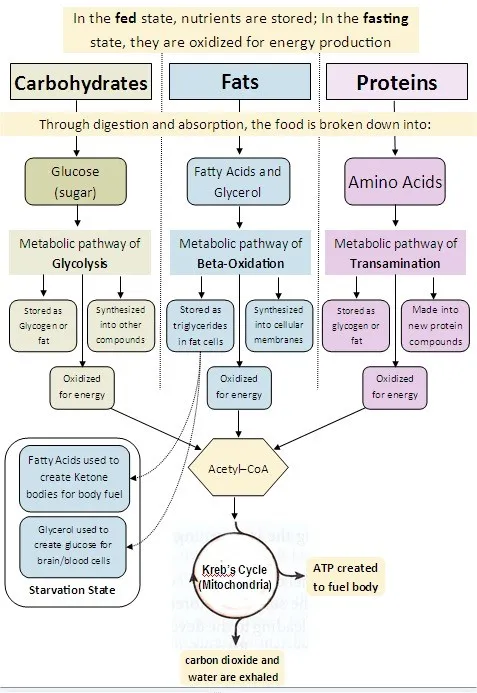
- After an overnight fast (~16-24 hours without food), the **liver** is the **primary organ** responsible for maintaining blood glucose levels through **glycogenolysis** (initially) and **gluconeogenesis** (predominantly at this stage).
- The **kidney** also contributes to **gluconeogenesis** even during an overnight fast, providing approximately **10-15% of total glucose production**. While this contribution is relatively minor compared to the liver, it becomes increasingly important during more prolonged fasting states (>48-72 hours), where it can account for up to 40% of glucose production.
- Since the brain relies almost exclusively on glucose at this stage of fasting (ketone bodies are not yet a major fuel source), both organs that produce glucose for systemic use are correctly identified here.
*Muscle only*
- Muscle glycogen can only be used by the **muscle cells themselves** due to the absence of **glucose-6-phosphatase**, so muscle cannot release free glucose into the bloodstream for use by the brain.
- While muscle does provide amino acids (particularly alanine and glutamine) for gluconeogenesis in the liver and kidney, it does not directly supply glucose to support brain function.
*Liver and muscle*
- As explained above, muscle cannot directly supply glucose to the bloodstream to support brain function due to the lack of **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- The liver is a major contributor, but muscle is not a direct source of blood glucose.
*Liver, muscle, and kidney*
- This option incorrectly includes muscle as a direct source of glucose for the brain. While liver and kidney both perform gluconeogenesis and release glucose into the bloodstream, muscle lacks this capability.
*Liver only*
- While the liver is indeed the **dominant source** of glucose during an overnight fast (contributing ~85-90% of gluconeogenesis), the **kidney also actively participates** in glucose production, contributing ~10-15% at this stage.
- Since the question asks which organs are "responsible" for maintaining cognition, and both organs contribute to systemic glucose production (even if disproportionately), "liver only" is incomplete.
- The kidney's contribution, though relatively minor during overnight fasting, becomes more substantial during prolonged fasting states.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 5: A 24-year-old man is running a marathon. Upon reaching the finish line, his serum lactate levels were measured and were significantly increased as compared to his baseline. Which of the following pathways converts the lactate produced by muscles into glucose and transports it back to the muscles?
- A. Citric acid cycle
- B. Glycolysis
- C. Glycogenesis
- D. Pentose phosphate pathway
- E. Cori cycle (Correct Answer)
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Cori cycle***
- The **Cori cycle** is the metabolic pathway that converts **lactate** produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles (especially during intense exercise) back to **glucose in the liver** via gluconeogenesis.
- During strenuous exercise, muscles rely on anaerobic glycolysis when oxygen supply is insufficient, producing lactate and 2 ATP per glucose.
- The lactate is transported via bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted back to glucose (requiring 6 ATP), which then returns to muscles for energy or glycogen storage.
- This cycle allows muscles to continue generating ATP anaerobically while the liver handles lactate clearance.
*Citric acid cycle*
- The **citric acid cycle** (Krebs cycle) oxidizes **acetyl-CoA** to generate ATP, NADH, and FADH₂ in the mitochondrial matrix under aerobic conditions.
- It does not convert lactate to glucose; rather, pyruvate can be converted to acetyl-CoA to enter this cycle for complete oxidation.
- This is an aerobic process and does not involve the liver-muscle lactate-glucose exchange.
*Glycolysis*
- **Glycolysis** is the metabolic pathway that breaks down **glucose into pyruvate**, generating 2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose molecule.
- Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to lactate to regenerate NAD⁺ for continued glycolysis.
- This is the opposite of what the question asks—glycolysis produces lactate from glucose, not glucose from lactate.
*Glycogenesis*
- **Glycogenesis** is the process of synthesizing **glycogen from glucose** for storage, primarily in liver and muscle tissue.
- While it involves glucose storage, it does not convert lactate back to glucose or involve the metabolic exchange between muscles and liver described in the question.
*Pentose phosphate pathway*
- The **pentose phosphate pathway** (hexose monophosphate shunt) produces **NADPH** for reductive biosynthesis and **ribose-5-phosphate** for nucleotide synthesis.
- It branches from glycolysis but is not involved in lactate metabolism or the muscle-liver glucose-lactate exchange.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 6: You have been asked to deliver a lecture to medical students about the effects of various body hormones and neurotransmitters on the metabolism of glucose. Which of the following statements best describes the effects of sympathetic stimulation on glucose metabolism?
- A. Norepinephrine causes increased glucose absorption within the intestines.
- B. Without epinephrine, insulin cannot act on the liver.
- C. Peripheral tissues require epinephrine to take up glucose.
- D. Epinephrine increases liver glycogenolysis. (Correct Answer)
- E. Sympathetic stimulation to alpha receptors of the pancreas increases insulin release.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Epinephrine increases liver glycogenolysis.***
- **Epinephrine**, released during sympathetic stimulation, primarily acts to increase **glucose availability** for immediate energy.
- It achieves this by stimulating **glycogenolysis** (breakdown of glycogen into glucose) in the liver via **beta-adrenergic receptors**.
*Norepinephrine causes increased glucose absorption within the intestines.*
- **Norepinephrine** primarily causes **vasoconstriction** and can *decrease* **intestinal motility** and nutrient absorption due to shunting blood away from the digestive tract during stress.
- Glucose absorption is mainly regulated by digestive enzymes and transport proteins, not directly increased by norepinephrine.
*Without epinephrine, insulin cannot act on the liver.*
- **Insulin** acts on the liver independent of epinephrine to promote **glucose uptake**, **glycogenesis**, and **lipid synthesis**.
- Epinephrine and insulin have **antagonistic effects** on liver glucose metabolism; epinephrine increases glucose output, while insulin decreases it.
*Peripheral tissues require epinephrine to take up glucose.*
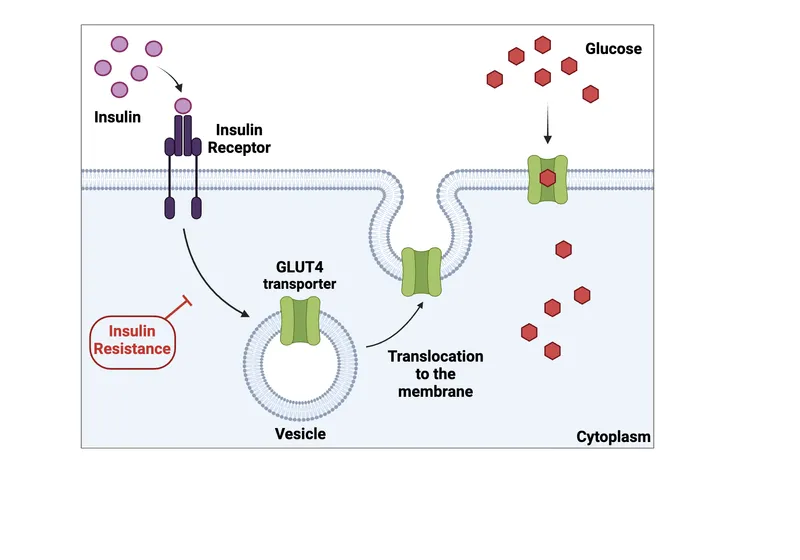
- **Insulin** is the primary hormone required for **glucose uptake** by most peripheral tissues, especially **muscle** and **adipose tissue**, via **GLUT4 transporters**.
- Epinephrine generally *reduces* glucose uptake by peripheral tissues to preserve glucose for the brain during stress.
*Sympathetic stimulation to alpha receptors of the pancreas increases insulin release.*
- Sympathetic stimulation, primarily acting through **alpha-2 adrenergic receptors** on pancreatic beta cells, actually **inhibits** **insulin secretion**.
- This inhibition helps to increase blood glucose levels by reducing insulin's glucose-lowering effects.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old African American man presents to the office for a routine examination. He has no complaints at this time. Records show that his systolic blood pressure was in the 130–138 range and diastolic blood pressure in the 88–95 range despite counseling on lifestyle modification. He admits that he was not compliant with this advice. He takes no medications and works at home as a web designer. He does not drink alcohol but smokes marijuana on a weekly basis. Temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 138/90 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, and respirations are 12/min. BMI is 29.8 kg/m2. Physical examination is normal except for truncal obesity, with a waist circumference of 44 inches. Fasting laboratory results are as follows:
Blood glucose 117 mg/dL
Total cholesterol 210 mg/dL
LDL cholesterol 120 mg/dL
HDL cholesterol 38 mg/dL
Triglycerides 240 mg/dL
Which of the following mechanisms contribute to this patient’s condition?
- A. Excessive cortisol secretion and activity
- B. Granulomatous inflammation in medium-sized vessels
- C. LDL receptor gene mutation
- D. Insulin receptor resistance (Correct Answer)
- E. Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Insulin receptor resistance***
- The patient exhibits features of **metabolic syndrome**, including **truncal obesity** (BMI 29.8 kg/m², waist circumference 44 inches), **elevated blood pressure** (138/90 mm Hg), **impaired fasting glucose** (117 mg/dL), **high triglycerides** (240 mg/dL), and **low HDL cholesterol** (38 mg/dL). These are all key manifestations of insulin resistance.
- **Insulin resistance** is central to metabolic syndrome, leading to compensatory hyperinsulinemia, which contributes to hypertension, dyslipidemia, and impaired glucose tolerance, eventually progressing to type 2 diabetes if pancreatic beta cells fail.
*Excessive cortisol secretion and activity*
- **Cushing's syndrome**, characterized by excessive cortisol, also causes truncal obesity, hypertension, and hyperglycemia, but typically presents with additional features like **moon facies**, **buffalo hump**, and **skin striae**, which are not mentioned here.
- The patient's blood pressure and glucose levels, while elevated, are not severe enough to strongly suggest Cushing's syndrome in the absence of other characteristic signs.
*Granulomatous inflammation in medium-sized vessels*
- This description is characteristic of various forms of **vasculitis**, such as **Polyarteritis Nodosa** or **Giant Cell Arteritis**.
- Vasculitis typically presents with constitutional symptoms, organ ischemia, and specific inflammatory markers, none of which are present in this patient's routine examination.
*LDL receptor gene mutation*
- An **LDL receptor gene mutation** is associated with **familial hypercholesterolemia**, primarily causing greatly elevated LDL cholesterol levels and premature cardiovascular disease.
- While this patient has elevated LDL, his overall lipid profile with high triglycerides and low HDL is more consistent with metabolic syndrome than a primary LDL receptor defect.
*Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells*
- This is the underlying mechanism of **type 1 diabetes mellitus**, which usually presents with profound hyperglycemia, polyuria, polydipsia, and weight loss, typically in younger patients.
- This patient's mild hyperglycemia and features of metabolic syndrome are more indicative of **insulin resistance (type 2 diabetes)** rather than autoimmune beta-cell destruction.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 8: A scientist is trying to design a drug to modulate cellular metabolism in the treatment of obesity. Specifically, he is interested in understanding how fats are processed in adipocytes in response to different energy states. His target is a protein within these cells that catalyzes catabolism of an energy source. The products of this reaction are subsequently used in gluconeogenesis or β-oxidation. Which of the following is true of the most likely protein that is being studied by this scientist?
- A. It is stimulated by epinephrine (Correct Answer)
- B. It is inhibited by glucagon
- C. It is inhibited by acetylcholine
- D. It is inhibited by cortisol
- E. It is stimulated by insulin
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***It is stimulated by epinephrine***
- The protein described is likely **hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL)**, which catabolizes **triglycerides** in adipocytes to **glycerol** and **fatty acids**.
- **Epinephrine** (and norepinephrine) stimulates HSL activity via a **cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)** pathway, leading to increased fatty acid release for energy.
*It is inhibited by glucagon*
- **Glucagon primarily acts on the liver** to promote gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, but it does **not directly inhibit HSL** in adipocytes.
- While glucagon has a lipolytic effect, it doesn't inhibit the enzyme that releases fatty acids.
*It is inhibited by acetylcholine*
- **Acetylcholine** is a neurotransmitter involved in the **parasympathetic nervous system**, which generally promotes energy storage.
- It does **not directly inhibit HSL**; its effects on lipid metabolism are indirect and typically involve other pathways.
*It is inhibited by cortisol*
- **Cortisol**, a glucocorticoid, generally **promotes lipolysis** (breakdown of fats) in certain contexts, particularly during stress to provide energy substrates.
- Therefore, it would **not inhibit HSL**; rather, it often enhances its activity or provides a permissive effect for other lipolytic hormones.
*It is stimulated by insulin*
- **Insulin** is an **anabolic hormone** that promotes energy storage, including **lipogenesis** (fat synthesis) and inhibits lipolysis.
- Insulin **inhibits HSL activity** by activating phosphodiesterase, which reduces cAMP levels, thus deactivating PKA and preventing HSL phosphorylation.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old woman at 36 weeks gestation presents with severe headache, epigastric pain, and visual disturbances. Her blood pressure is 160/110 mmHg. Laboratory studies show a hematocrit of 32%, leukocyte count of 9,400/mm³, and platelet count of 96,000/mm³. Serum studies reveal an aspartate aminotransferase of 94 U/L and an alanine aminotransferase of 92 U/L. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Overactivation of the coagulation pathway (Correct Answer)
- B. Thrombotic obstruction of hepatic veins
- C. Sequestration of platelets in the spleen
- D. Embolism of amniotic fluid into maternal circulation
- E. Viral reactivation and replication
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Overactivation of the coagulation pathway***
- This patient's symptoms (severe headache, epigastric pain, visual disturbances), hypertension (160/110 mmHg), **thrombocytopenia** (platelet count 96,000/mm³), and elevated liver enzymes (AST 94 U/L, ALT 92 U/L) are classic signs of **HELLP syndrome** (Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, Low Platelet count), a severe form of preeclampsia.
- HELLP syndrome is characterized by widespread **endothelial dysfunction**, leading to microvascular damage, platelet activation, and consumption, which are consequences of overactive coagulation and fibrin deposition.
*Thrombotic obstruction of hepatic veins*
- This condition, known as **Budd-Chiari syndrome**, typically presents with **ascites**, hepatomegaly, and abdominal pain, which are not primary features in this patient.
- While it can cause elevated liver enzymes, it doesn't usually explain the widespread microangiopathic changes or severe hypertension seen in HELLP syndrome.
*Sequestration of platelets in the spleen*
- **Hypersplenism** can lead to thrombocytopenia due to increased platelet destruction or sequestration in an enlarged spleen.
- However, this condition does not explain the patient's severe hypertension, elevated liver enzymes, or visual disturbances.
*Embolism of amniotic fluid into maternal circulation*
- **Amniotic fluid embolism** is a rare and catastrophic event presenting with sudden **cardiovascular collapse**, **respiratory distress**, and coagulopathy, often immediately postpartum or during labor.
- This patient's presentation with chronic symptoms like hypertension, epigastric pain, and visual disturbances is not consistent with an acute embolic event.
*Viral reactivation and replication*
- Viral infections, such as those causing **hepatitis**, can lead to elevated liver enzymes and sometimes thrombocytopenia.
- However, they typically do not cause the severe hypertension, visual disturbances, and epigastric pain characteristic of severe preeclampsia or HELLP syndrome.
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG Question 10: A 36-year-old woman is fasting prior to a religious ceremony. Her only oral intake in the last 36 hours has been small amounts of water. The metabolic enzyme that is primarily responsible for maintaining normal blood glucose in this patient is located exclusively within the mitochondria. An increase in which of the following substances is most likely to increase the activity of this enzyme?
- A. Acetyl coenzyme A (Correct Answer)
- B. Citrate
- C. Adenosine monophosphate
- D. Glucagon
- E. Oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism Explanation: ***Acetyl coenzyme A***
- The enzyme described is **pyruvate carboxylase**, which is exclusively mitochondrial and plays a crucial anaplerotic role in gluconeogenesis by converting pyruvate to **oxaloacetate**.
- **Acetyl CoA** is an allosteric activator of **pyruvate carboxylase**, signaling a high energy state and readiness for glucose synthesis from non-carbohydrate precursors.
*Citrate*
- **Citrate** is an allosteric inhibitor of **phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)** in glycolysis and can activate **acetyl-CoA carboxylase** in fatty acid synthesis.
- It does not directly activate pyruvate carboxylase.
*Adenosine monophosphate*
- **AMP** is a marker of low energy status, activating **AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)** and **phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)**, thereby stimulating glycolysis.
- Its role is to increase glucose utilization, not glucose synthesis.
*Glucagon*
- **Glucagon** is a hormone that *regulates* gluconeogenesis by signaling through GPCRs and increasing cAMP, leading to phosphorylation and activation of key gluconeogenic enzymes.
- However, glucagon itself is a signaling molecule, not a direct positive allosteric modulator of pyruvate carboxylase activity.
*Oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide*
- **NAD+** is a coenzyme primarily involved in oxidative reactions, acting as an electron acceptor and is crucial for the function of enzymes like **glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase** in glycolysis or **isocitrate dehydrogenase** in the TCA cycle.
- It is a substrate for various dehydrogenases, but not a direct allosteric activator of pyruvate carboxylase.
More Fed state vs. fasting state metabolism US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.