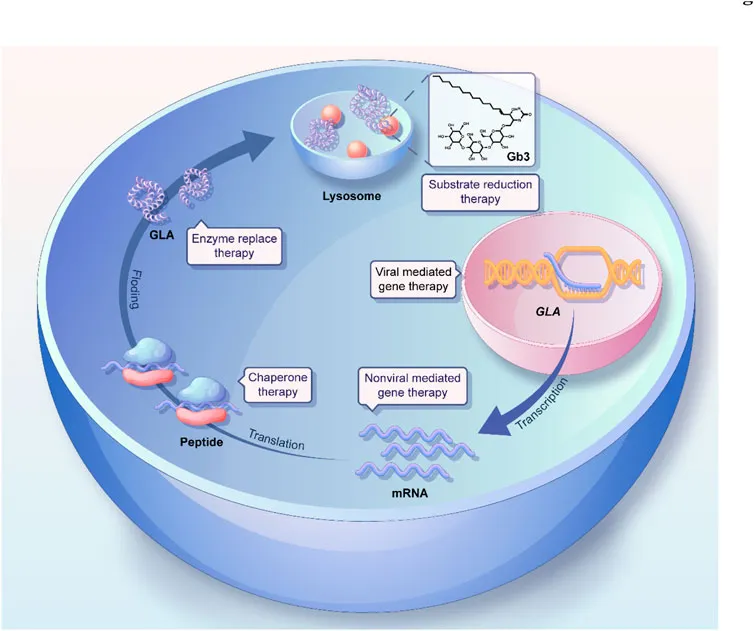
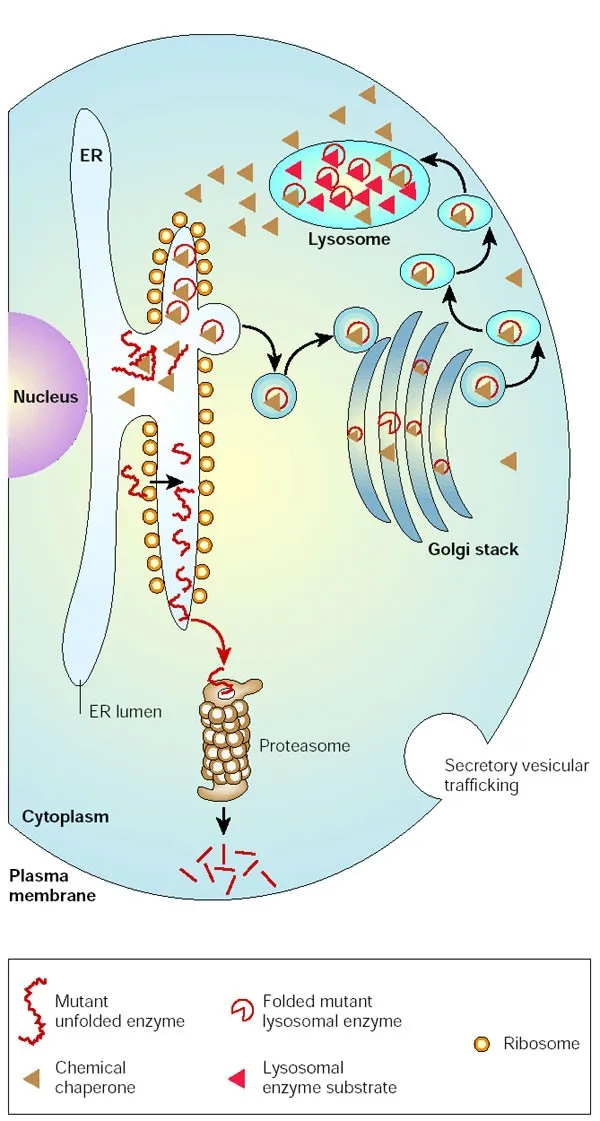
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 1: You are taking care of a patient with renal failure secondary to anti-fungal therapy. The patient is a 66-year-old male being treated for cryptococcal meningitis. This drug has a variety of known side effects including acute febrile reactions to infusions, anemia, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase
- B. Binding of the 50S subunit
- C. Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding (Correct Answer)
- D. Disruption of microtubule formation
- E. Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding***
- This describes the mechanism of action of **amphotericin B**, the antifungal agent used for cryptococcal meningitis.
- Amphotericin B binds to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, leading to the formation of pores, disruption of membrane integrity, and ultimately cell death.
- The side effects described—**nephrotoxicity with renal failure, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia**—are classic adverse effects of amphotericin B due to its effect on renal tubular cells and electrolyte wasting.
*Inhibition of squalene epoxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **terbinafine**, an antifungal primarily used for dermatophyte infections (e.g., onychomycosis), not systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
- Terbinafine inhibits ergosterol synthesis at an earlier step but does not cause the severe nephrotoxicity and electrolyte disturbances described.
*Binding of the 50S subunit*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **macrolide antibiotics** like azithromycin or clarithromycin, which are antibacterial agents, not antifungals.
- These drugs inhibit bacterial protein synthesis and are ineffective against fungal infections.
*Disruption of microtubule formation*
- This is the mechanism of action for **griseofulvin**, an antifungal drug used for dermatophyte infections of the skin, hair, and nails.
- Griseofulvin interferes with fungal cell division and is not used for life-threatening systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
*Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase*
- This mechanism is associated with **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin), which inhibit fungal cell wall synthesis.
- While echinocandins are used for some systemic fungal infections (particularly Candida and Aspergillus), they do not typically cause the severe renal failure and electrolyte disturbances characteristic of amphotericin B.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 2: A drug discovery team is conducting research to observe the characteristics of a novel drug under different experimental conditions. The drug is converted into the inactive metabolites by an action of an enzyme E. After multiple experiments, the team concludes that as compared to physiologic pH, the affinity of the enzyme E for the drug decreases markedly in acidic pH. Co-administration of an antioxidant A increases the value of Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) for the enzyme reaction, while co-administration of a drug B decreases the value of Km. Assume the metabolism of the novel drug follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics at the therapeutic dose, and that the effects of different factors on the metabolism of the drug are first-order linear. For which of the following conditions will the metabolism of the drug be the slowest?
- A. Acidic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A and of drug B
- B. Acidic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A, no administration of drug B (Correct Answer)
- C. Physiologic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A, no administration of drug B
- D. Acidic pH, co-administration of drug B, no administration of antioxidant A
- E. Acidic pH, without administration of antioxidant A or drug B
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***Acidic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A, no administration of drug B***
- **Decreased affinity** at acidic pH reduces the enzyme's ability to bind the drug, slowing metabolism.
- Co-administration of **antioxidant A increases Km**, indicating a further reduction in enzyme affinity and thus slower metabolism.
*Acidic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A and of drug B*
- While acidic pH and antioxidant A slow metabolism, co-administration of **drug B decreases Km**, which would increase enzyme affinity and counteract the slowing effect to some extent.
- The combination would result in a slower metabolism than baseline, but likely not the slowest possible due to the partially opposing effects of A and B.
*Physiologic pH, co-administration of antioxidant A, no administration of drug B*
- At **physiologic pH**, the enzyme's affinity for the drug is higher than at acidic pH, promoting faster metabolism.
- Although antioxidant A increases Km, the favorable pH for enzyme activity means metabolism will not be as slow as under acidic conditions.
*Acidic pH, co-administration of drug B, no administration of antioxidant A*
- **Acidic pH** reduces enzyme affinity, slowing metabolism.
- However, the co-administration of **drug B decreases Km**, which increases enzyme affinity and would partially offset the reduced affinity caused by the acidic pH, leading to a faster metabolism compared to when antioxidant A is present.
*Acidic pH, without administration of antioxidant A or drug B*
- At **acidic pH**, the enzyme's affinity for the drug decreases, which slows metabolism.
- However, in this condition, there are no additional factors (like antioxidant A) further increasing Km, nor factors (like drug B) decreasing Km, so the metabolic rate would be slower than physiologic pH but not as slow as when antioxidant A is also present.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 3: A steel welder presents to his family physician with a one-week history of intense abdominal cramping with nausea, vomiting, constipation, headaches, myalgias, and arthralgias. He claims that the symptoms started about two months after he began work on replacing the pipes in an early 20th century house. Blood was taken and he was found to have a microcytic, hypochromic anemia with basophilic stippling. Which of the following is the best treatment for his symptoms?
- A. Prussian blue
- B. Deferasirox
- C. EDTA (Correct Answer)
- D. N-acetylcysteine
- E. Deferoxamine
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***EDTA***
- The patient's symptoms (abdominal cramping, nausea, vomiting, constipation, headaches, myalgias, arthralgias), occupation (steel welder working on old pipes), and lab findings (**microcytic, hypochromic anemia** with **basophilic stippling**) are highly suggestive of **lead poisoning**.
- **EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)** is a chelating agent that binds to lead and promotes its excretion, making it the most appropriate treatment for severe lead poisoning.
*Prussian blue*
- This is an antidote for **thallium** and **radioactive cesium poisoning**, not lead.
- It works by trapping these ions in the gut, preventing their absorption and increasing their fecal excretion.
*Deferasirox*
- This is an **oral iron chelator** used for treating **iron overload**, particularly in patients with thalassemia who receive frequent blood transfusions.
- It is not indicated for lead poisoning.
*N-acetylcysteine*
- This agent is primarily used as an antidote for **acetaminophen overdose** by replenishing glutathione stores.
- It also has applications in certain respiratory conditions as a mucolytic, but not in lead poisoning.
*Deferoxamine*
- This is another **iron chelator**, administered intravenously or subcutaneously, primarily used for acute iron intoxication or chronic iron overload (e.g., hemochromatosis).
- Like deferasirox, it is specific for iron and not used for lead poisoning.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 4: A 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of headaches and back pain. Examination shows mild sensorineural hearing loss. Serum concentration of alkaline phosphatase is increased. An x-ray of the skull is shown. The most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient is a drug that has which of the following mechanisms of action?
- A. Inhibition of proteasomes
- B. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization
- C. Apoptosis of osteoclasts (Correct Answer)
- D. Formation of DNA strand breaks
- E. Inhibition of nuclear factor-κB
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***Apoptosis of osteoclasts***
- The patient's symptoms (headaches, back pain, sensorineural hearing loss, elevated alkaline phosphatase) and the skull X-ray showing diffuse sclerosis (\"cotton wool\" appearance) are classic for **Paget's disease of bone**.
- **Bisphosphonates** (which induce osteoclast apoptosis) are the first-line treatment for Paget's disease by reducing abnormal bone turnover.
*Inhibition of proteasomes*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of drugs like **bortezomib**, which are primarily used in the treatment of **multiple myeloma**.
- Multiple myeloma causes osteolytic lesions and hypercalcemia, but the X-ray findings and overall clinical picture are not consistent with this diagnosis.
*Inhibition of tubulin polymerization*
- Drugs that inhibit tubulin polymerization, such as **colchicine** (for gout) or **vincristine/vinblastine** (for various cancers), prevent cell division and migration.
- This mechanism is not relevant to the pathophysiology or treatment of Paget's disease.
*Formation of DNA strand breaks*
- This is the mechanism of action for certain **chemotherapeutic agents** (e.g., alkylating agents, platinum compounds) that damage DNA to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells.
- Paget's disease is a disorder of bone remodeling, not a primary malignancy requiring such aggressive therapy.
*Inhibition of nuclear factor-κB*
- **NF-κB** is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA and is involved in immune responses and inflammation.
- While NF-κB inhibitors are being investigated for various inflammatory conditions and cancers, they are not the primary pharmacotherapy for Paget's disease of bone.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 5: What is the primary mechanism for glucose uptake in neurons?
- A. GLUT1
- B. GLUT2
- C. GLUT3 (Correct Answer)
- D. GLUT4
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***GLUT3***
- **GLUT3** is the primary glucose transporter in **neurons** and has a **high affinity** for glucose.
- This high affinity ensures that neurons can continuously take up glucose, even when blood glucose levels are relatively low, to meet their significant energy demands.
*GLUT1*
- **GLUT1** is abundant in **red blood cells** and at the **blood-brain barrier**, where it provides basal glucose transport to many cell types.
- While present in the brain, it is primarily responsible for glucose transport across the **blood-brain barrier** into the interstitial fluid, not directly into neurons as the main mechanism.
*GLUT2*
- **GLUT2** has a **low affinity** and **high capacity** for glucose, primarily found in the **liver, pancreatic beta cells, kidney, and intestine**.
- Its role is to sense high glucose levels and transport large amounts of glucose accordingly, which is not characteristic of neuronal glucose uptake.
*GLUT4*
- **GLUT4** is the **insulin-sensitive** glucose transporter, predominantly found in **adipose tissue** and **skeletal muscle**.
- Its translocation to the cell membrane is stimulated by insulin, a mechanism not central to neuronal glucose uptake.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 6: A 5-year-old girl is brought in for a routine checkup. She was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery and is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting all developmental milestones. Upon examination, she is pale with a few petechiae on her chest neck and back. Examination of the abdomen reveals painless hepatosplenomegaly. Liver enzymes are mildly elevated and complete blood cell count shows slight anemia and thrombocytopenia. Iron, B12, and folate are normal. A bone marrow biopsy shows mildly hypocellular marrows with diffuse macrophages with eosinophilic cytoplasm. The cytoplasm looks like wrinkled tissue paper on further inspection. No blasts are observed. What is the most likely diagnosis in the present case?
- A. Autoimmune disorder
- B. Gaucher disease type I (Correct Answer)
- C. Biliary obstruction
- D. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- E. Viral hepatitis
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: **Gaucher disease type I**
- The characteristic finding of **diffuse macrophages with eosinophilic cytoplasm** that resembles **"wrinkled tissue paper"** on bone marrow biopsy is pathognomonic for **Gaucher cells**, confirming **Gaucher disease type I**.
- **Painless hepatosplenomegaly**, **anemia**, **thrombocytopenia**, and **petechiae** are common clinical manifestations resulting from the accumulation of glucocerebroside in macrophages within the reticuloendothelial system.
*Autoimmune disorder*
- While autoimmune disorders can cause anemia and hepatosplenomegaly, the distinct **"wrinkled tissue paper" macrophages** found in the bone marrow biopsy are not characteristic of autoimmune conditions.
- Autoimmune disorders like lupus or autoimmune hemolytic anemia would present with different serological markers and histological findings.
*Biliary obstruction*
- **Biliary obstruction** typically presents with **jaundice**, dark urine, pale stools, and significant elevation of **liver enzymes** (especially direct bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase), which are not prominent features here.
- It would not explain the hematopoietic abnormalities (anemia, thrombocytopenia) or the presence of Gaucher cells in the bone marrow.
*Acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
- **Acute lymphoblastic leukemia** would typically show a significant presence of **blasts** (immature white blood cells) in the bone marrow, which are explicitly noted as absent in this case.
- While it can cause anemia and thrombocytopenia, the key diagnostic feature of **blasts** is missing, and the characteristic macrophages would not be present.
*Viral hepatitis*
- **Viral hepatitis** primarily causes **liver inflammation** and can lead to significant elevation of **liver enzymes** (transaminases), often much higher than "mildly elevated."
- It does not explain the **painless hepatosplenomegaly**, **anemia**, **thrombocytopenia**, or the pathognomonic **Gaucher cells** in the bone marrow.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old woman presents to a physician for genetic counseling, because she is worried about trying to have a child. Specifically, she had 2 siblings that died young from a lysosomal storage disorder and is afraid that her own children will have the same disorder. Her background is Ashkenazi Jewish, but she says that her husband's background is mixed European heritage. Her physician says that since her partner is not of Jewish background, their chance of having a child with Niemann-Pick disease is dramatically decreased. Which of the following genetic principles best explains why there is an increased prevalence of this disease in some populations?
- A. Natural selection
- B. Imprinting
- C. De novo mutations
- D. Gene flow
- E. Founder effect (Correct Answer)
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***Founder effect***
- The **founder effect** occurs when a new population is established by a small number of individuals, leading to a **reduced genetic diversity** and an increased frequency of certain alleles that were present in the founders. This is particularly relevant in populations like **Ashkenazi Jews**, who descended from a small, isolated group with certain allele frequencies.
- In this scenario, the high prevalence of **Niemann-Pick disease** (and other genetic disorders) in the Ashkenazi Jewish population is due to their historical isolation and intermarriage within a relatively small gene pool, trapping and concentrating certain alleles.
*Natural selection*
- **Natural selection** typically describes the process by which traits that enhance survival and reproduction become more common in a population over time, or deleterious traits become less common.
- While it can influence disease prevalence, it doesn't primarily explain the disproportionately high frequency of rare recessive disorders in specific isolated populations in the manner described.
*Imprinting*
- **Genomic imprinting** refers to the phenomenon where certain genes are expressed in a **parent-of-origin-specific manner**, meaning that only the allele inherited from either the mother or the father is expressed.
- This mechanism explains certain genetic conditions but does not account for the increased prevalence of a recessive disorder due to population history and isolation.
*De novo mutations*
- **De novo mutations** are new genetic alterations that appear for the first time in an individual and are not inherited from either parent.
- While de novo mutations are a source of genetic variation, they do not explain the high prevalence of a specific ancestral allele within an entire population.
*Gene flow*
- **Gene flow** (or migration) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another, which tends to **decrease genetic differences** between populations and introduce new alleles.
- This principle would suggest a *reduction* in the prevalence of specific rare alleles over time as populations mix, rather than an *increase* in isolated groups.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 8: A 1-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician for a follow-up appointment. He was recently diagnosed with failure to thrive and developmental delay. His weight is 7 kg (15.4 lb), height is 61 cm (24 in), and head circumference is 42 cm (16.5 in). The patient’s father had a younger sister who suffered from mental and physical delay and died at a very young age. The patient was able to raise his head at the age of 7 months and began to sit alone only recently. He babbles, coos, and smiles to other people. On presentation, his blood pressure is 75/40 mm Hg, heart rate is 147/min, respiratory rate is 28/min, and temperature is 36.4°C (97.5°F). He has a coarse face with small deep orbits, proptotic eyes, big lips, and gingival hyperplasia. His skin is pale with decreased elasticity. His lung and heart sounds are normal. Abdominal examination reveals diminished anterior abdominal wall muscle tone and hepatomegaly. Muscle tone is increased in all groups of muscles on both upper and lower extremities. The physician becomes concerned and performs testing for the suspected hereditary disease. A blood test shows increased lysosomal enzyme concentration in the serum and decreased N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase (GlcNAc phosphotransferase) activity within the leukocytes. Which of the statements listed below describes the mechanism of the patient’s condition?
- A. The lysosomal enzymes are secreted from the cells instead of being targeted to lysosomes because of lack of mannose phosphorylation on N-linked glycoproteins. (Correct Answer)
- B. There is impaired hydrolysis of GM2-ganglioside, which accumulates in the cytoplasm.
- C. Due to enzyme deficiency, glycogen is extensively accumulated within the hepatocytes.
- D. The patient’s symptoms are due to dysfunctional metabolism of sphingomyelin, which accumulates within the lysosomes.
- E. The symptoms result from defective glycolysis, which results in a total energy deficiency.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***The lysosomal enzymes are secreted from the cells instead of being targeted to lysosomes because of lack of mannose phosphorylation on N-linked glycoproteins.***
- This describes **I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II)**, a lysosomal storage disorder characterized by a deficiency of **N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase**.
- Without this enzyme, mannose residues on lysosomal enzymes cannot be phosphorylated, preventing their proper targeting to lysosomes and leading to their secretion into the bloodstream.
*There is impaired hydrolysis of GM2-ganglioside, which accumulates in the cytoplasm.*
- This mechanism describes **Tay-Sachs disease**, which is caused by a deficiency in B-hexosaminidase A.
- While Tay-Sachs also causes developmental delay, the clinical features and biochemical findings (specifically the lysosomal enzyme activity levels in serum and leukocytes) do not match those of the described patient.
*Due to enzyme deficiency, glycogen is extensively accumulated within the hepatocytes.*
- This mechanism describes **glycogen storage diseases**, such as Von Gierke disease (type I) or Pompe disease (type II).
- While Pompe disease is a lysosomal storage disorder, the enzymatic defect involves **acid alpha-glucosidase** and leads to glycogen accumulation primarily in muscles and heart, not related to N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase deficiency.
*The patient’s symptoms are due to dysfunctional metabolism of sphingomyelin, which accumulates within the lysosomes.*
- This mechanism describes **Niemann-Pick disease**, caused by a deficiency in **sphingomyelinase**.
- While it is a lysosomal storage disease with hepatosplenomegaly and developmental delay, the specific enzymatic defect and the coarse facial features do not align with the patient's presentation and lab results.
*The symptoms result from defective glycolysis, which results in a total energy deficiency.*
- Defective glycolysis would lead to issues with cellular energy production, causing symptoms such as muscle weakness and fatigue.
- However, this mechanism does not explain the specific clinical features like coarse facies, gingival hyperplasia, hepatomegaly, or the characteristic enzymatic defect seen in I-cell disease.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 9: A research study evaluates three siblings with Niemann-Pick disease type C: a 6-year-old with ataxia and vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, a 10-year-old with hepatosplenomegaly and mild cognitive impairment, and a 14-year-old who is asymptomatic. Genetic testing reveals all three carry the same compound heterozygous NPC1 mutations. Fibroblast studies show similar cholesterol esterification defects and filipin staining patterns. Miglustat therapy is available. Evaluate the biological basis for phenotypic variability and optimal treatment allocation.
- A. Evaluate modifier genes, epigenetic factors, and biomarkers; treat based on individual risk stratification (Correct Answer)
- B. Treat all three immediately as genetic identity predicts identical disease course
- C. Treat only symptomatic siblings as asymptomatic carrier won't develop disease
- D. Delay all treatment until symptoms appear in the youngest to confirm diagnosis
- E. Treat the 6-year-old only as neurologic symptoms indicate blood-brain barrier dysfunction
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***Evaluate modifier genes, epigenetic factors, and biomarkers; treat based on individual risk stratification***
- **Phenotypic discordance** in Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) despite identical genotypes suggests that **modifier genes**, **epigenetic factors**, and cellular environment dictate clinical onset and severity.
- Management must be personalized because **NPC1 mutations** and **filipin staining** do not perfectly correlate with clinical progression; biomarkers like **oxysterols** or **lysosphingolipids** help guide individual risk.
*Treat only symptomatic siblings as asymptomatic carrier won't develop disease*
- The asymptomatic 14-year-old is not a carrier but has already been confirmed to have **compound heterozygous NPC1 mutations** and pathognomonic **filipin staining**.
- This sibling has the disease and is at high risk for **late-onset neurological symptoms**, requiring proactive monitoring rather than being dismissed as a carrier.
*Treat all three immediately as genetic identity predicts identical disease course*
- Even with identical **NPC1 mutations**, clinical presentation varies significantly (from **supranuclear gaze palsy** to asymptomatic), meaning the disease course is not identical.
- While **Miglustat** is effective, immediate treatment in asymptomatic patients is debated; therapy is typically tailored to clinical or **biomarker evidence** of progression.
*Treat the 6-year-old only as neurologic symptoms indicate blood-brain barrier dysfunction*
- **Miglustat** crosses the **blood-brain barrier** to inhibit **glucosylceramide synthase**, but its use is not limited based on blood-brain barrier integrity.
- The 10-year-old already exhibits **hepatosplenomegaly** and **cognitive impairment**, which are clear indications for therapy to prevent further neurocognitive decline.
*Delay all treatment until symptoms appear in the youngest to confirm diagnosis*
- The diagnosis is already confirmed via **genetic testing** showing NPC1 mutations and **fibroblast studies** showing cholesterol defects.
- Delaying treatment in already symptomatic siblings (the 6 and 10-year-olds) would allow irreversible **neuronal loss** and worsening of **ataxia**.
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG Question 10: A 15-year-old boy with Hunter syndrome (MPS II) on weekly enzyme replacement therapy develops IgG antibodies with high neutralizing capacity against idursulfase. His symptoms have worsened over the past 6 months with increasing hepatosplenomegaly and joint stiffness. His brother with the same mutation shows excellent response to ERT without antibody formation. Synthesize an appropriate management plan considering immunologic and genetic factors.
- A. Switch to substrate reduction therapy as primary treatment
- B. Implement immune tolerance induction protocol with immunosuppression and continued ERT (Correct Answer)
- C. Discontinue ERT as antibodies make it ineffective; switch to supportive care only
- D. Perform HSCT to eliminate antibody production and provide endogenous enzyme
- E. Increase ERT dose to saturate antibody binding capacity
Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) Explanation: ***Implement immune tolerance induction protocol with immunosuppression and continued ERT***
- The presence of **high-titer neutralizing IgG antibodies** (NABs) interferes with the efficacy of **idursulfase**, leading to the recurrence of symptoms like **hepatosplenomegaly** and joint stiffness.
- **Immune tolerance induction (ITI)** using agents like **rituximab**, **methotrexate**, and IVIG is indicated to eliminate the antibody response and restore the clinical benefit of the **enzyme replacement therapy**.
*Discontinue ERT as antibodies make it ineffective; switch to supportive care only*
- Stopping ERT allows the accumulation of **glycosaminoglycans** to continue, leading to progressive multisystemic decline and shortened **life expectancy**.
- Supportive care alone does not address the underlying **biochemical deficiency** when immune modulation could potentially rescue the primary treatment.
*Switch to substrate reduction therapy as primary treatment*
- **Substrate reduction therapy** (SRT) is not currently the standard or approved primary treatment for **Hunter syndrome** (MPS II) especially in the context of existing ERT failure.
- SRT aims to reduce the synthesis of **heparan and dermatan sulfate**, but it does not replace the missing **iduronate-2-sulfatase** enzyme activity required for clearance.
*Increase ERT dose to saturate antibody binding capacity*
- Increasing the dose of **idursulfase** often fails to overcome high-affinity **neutralizing antibodies** and may increase the risk of **infusion-related reactions** or immune complex formation.
- Antibody **saturation** is not a sustainable or effective clinical strategy for managing high-titer **anti-drug antibodies** in lysosomal storage diseases.
*Perform HSCT to eliminate antibody production and provide endogenous enzyme*
- While **hematopoietic stem cell transplantation** (HSCT) provides endogenous enzyme, it is not the preferred treatment for **MPS II** due to high procedural risks and inconsistent neurological outcomes compared to MPS I.
- HSCT is typically not used specifically as a secondary measure to treat **anti-drug antibodies** when **immune tolerance induction** is a viable and less invasive option.
More Treatment options (ERT, substrate reduction, chaperones) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.