Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 1: An 8-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents for gradually increasing loss of neck control and inability to roll over for the past 2 months. During this time, he has had multiple episodes of unresponsiveness with a blank stare and fluttering of the eyelids. His parents state that he sometimes does not turn when called but gets startled by loud noises. He does not maintain eye contact. He was able to roll over from front to back at 5 months of age and has not yet begun to sit or crawl. His parents are of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. Neurological examination shows generalized hypotonia. Deep tendon reflexes are 3+ bilaterally. Plantar reflex shows extensor response bilaterally. Fundoscopy shows bright red macular spots bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Sphingomyelinase deficiency
- B. β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency
- C. α-galactosidase A deficiency
- D. ATP-binding cassette transporter mutation
- E. β-hexosaminidase A deficiency (Correct Answer)
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***β-hexosaminidase A deficiency***
- The constellation of **developmental regression** (loss of neck control, inability to roll over), **hypotonia**, **exaggerated startle response**, **cherry-red macular spots**, and **Ashkenazi Jewish descent** is classic for **Tay-Sachs disease**, which is caused by a deficiency in β-hexosaminidase A.
- The patient's seizures ("unresponsiveness with a blank stare and fluttering of the eyelids") and **hyperreflexia** (3+ deep tendon reflexes, extensor plantar response) are also consistent with the progressive neurodegeneration seen in Tay-Sachs disease.
*Sphingomyelinase deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Niemann-Pick disease**, which can also present with **developmental regression**, **hypotonia**, and **cherry-red macular spots**.
- However, Niemann-Pick disease typically involves **hepatosplenomegaly** and **pulmonary involvement**, which are not mentioned in this patient's presentation.
*β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency*
- This deficiency leads to **Gaucher disease**, characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly**, **bone crises**, and cytopenias.
- While some forms can have neurological symptoms, the classic cherry-red spot and pronounced developmental regression as described are not typical of Gaucher disease.
*α-galactosidase A deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Fabry disease**, which is an **X-linked lysosomal storage disorder** presenting with **neuropathic pain**, **angiokeratomas**, **renal disease**, and **cardiac involvement** in adolescence or adulthood.
- It does not present with infantile neurodegeneration or cherry-red spots.
*ATP-binding cassette transporter mutation*
- Mutations in ABC transporters can lead to various disorders, such as **adrenoleukodystrophy** (deficiency in VLCFA transport) or **cystic fibrosis**.
- These conditions do not present with the specific combination of symptoms, especially the cherry-red macula and profound developmental regression, seen in this infant.
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 2: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of fever and recurrent episodes of jerky movements of his extremities for the past 6 hours. Pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated, and development was normal until the age of 1 year. The parents report that he has had gradual loss of speech, vision, and motor skills over the past year. During this time, he has been admitted to the hospital three times because of myoclonic seizures. Physical examination shows hypertonicity of the upper and lower extremities. Fundoscopic examination shows pallor of the optic disc bilaterally. An MRI of the brain shows brain atrophy and hyperintensity of the periventricular and subcortical areas. Two days after admission, the patient dies. Histopathologic examination of the brain shows aggregation of globoid cells and loss of glial cells. The patient’s condition was most likely caused by a deficiency of which of the following enzymes?
- A. β-Galactocerebrosidase (Correct Answer)
- B. β-Glucocerebrosidase
- C. Arylsulfatase A
- D. Sphingomyelinase
- E. β-Hexosaminidase A
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***β-Galactocerebrosidase***
- The clinical presentation, including the **rapid neurodegeneration** (loss of speech, vision, motor skills), **hypertonicity**, **optic disc pallor**, brain atrophy, and periventricular/subcortical hyperintensities on MRI, is highly consistent with **Krabbe disease**.
- The classic histopathologic finding of **globoid cells** (macrophages filled with undigested galactocerebroside) and **loss of glial cells** in the brain are pathognomonic for Krabbe disease, which is caused by a deficiency of **β-galactocerebrosidase**.
*β-Glucocerebrosidase*
- Deficiency of β-glucocerebrosidase causes **Gaucher disease**, which typically involves **hepatosplenomegaly**, **bone crises**, and **pancytopenia**.
- While some forms have neurological involvement, the characteristic globoid cells and rapid neurodegeneration seen here are not typical for Gaucher disease.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- Deficiency of arylsulfatase A leads to **metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD)**, which also presents with **progressive neurological deterioration**, motor regression, and demyelination.
- However, MLD is characterized by the accumulation of **sulfatides** in white matter and detection of **metachromatic granules** in nerves and urine, not globoid cells.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- Deficiency of sphingomyelinase causes **Niemann-Pick disease**, which is characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly**, **cherry-red spots** in the macula (in type A), and foam cells in various tissues.
- The neurological symptoms and brain pathology in this child are not consistent with Niemann-Pick disease.
*β-Hexosaminidase A*
- Deficiency of β-hexosaminidase A causes **Tay-Sachs disease**, which presents with **progressive neurodegeneration**, **cherry-red spots** in the macula, and **exaggerated startle response**.
- While it causes loss of motor skills and vision, the severe demyelination with periventricular hyperintensities and globoid cells are not features of Tay-Sachs disease (which primarily involves ganglioside accumulation).
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 3: An 18-month-old boy of Ashkenazi-Jewish descent presents with loss of developmental milestones. On ocular exam, a cherry-red macular spot is observed. No hepatomegaly is observed on physical exam. Microscopic exam shows lysosomes with onion-skin appearance.
What is the most likely underlying biochemical abnormality?
- A. Accumulation of ceramide trihexoside
- B. Accumulation of glucocerebroside
- C. Accumulation of galactocerebroside
- D. Accumulation of sphingomyelin
- E. Accumulation of GM2 ganglioside (Correct Answer)
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***Accumulation of GM2 ganglioside***
- This constellation of symptoms—**loss of developmental milestones**, **cherry-red macular spot**, absence of hepatomegaly, and **lysosomes with onion-skin appearance** in an individual of **Ashkenazi-Jewish descent**—is classic for **Tay-Sachs disease**.
- **Tay-Sachs disease** is caused by a deficiency of **hexosaminidase A**, leading to the accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside** in neuronal lysosomes.
*Accumulation of ceramide trihexoside*
- This refers to **Fabry disease**, which is an **X-linked disorder** presenting in adolescence or adulthood with acroparesthesias, angiokeratomas, and renal/cardiac complications.
- While it involves a lysosomal storage, its clinical presentation and the absence of a cherry-red spot differentiate it from the case described.
*Accumulation of glucocerebroside*
- This is characteristic of **Gaucher disease**, which is caused by a deficiency in **glucocerebrosidase**.
- Key features include **hepatosplenomegaly**, bone pain, and pancytopenia, which are not consistent with the patient's presentation.
*Accumulation of galactocerebroside*
- This describes **Krabbe disease**, a **globoid cell leukodystrophy** caused by a deficiency in galactocerebrosidase.
- Krabbe disease primarily affects the **myelin sheath** in the nervous system, leading to neurological degeneration but typically does not present with a cherry-red macular spot.
*Accumulation of sphingomyelin*
- This is the hallmark of **Niemann-Pick disease**, caused by **sphingomyelinase deficiency**.
- While Niemann-Pick disease also presents with a **cherry-red macular spot** and neurodegeneration, it is classically associated with **hepatosplenomegaly**, which is explicitly stated to be absent in this patient.
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 4: An 8-month-old female infant from a first-degree consanguineous couple was brought to the physician because the mother noticed abnormalities in the growth of her child as well as the different lengths of her child's legs. The infant had gingival hyperplasia, restricted movement in both shoulders, a prominent, pointed forehead, and enophthalmos with a slight opacity in both corneas. A blood test revealed 10 fold higher than normal levels of the following enzymes: N-acetyl-ß-glucosaminidase, ß-glucuronidase, ß-hexosaminidase A, and alkaline phosphatase. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase
- B. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- C. N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase (Correct Answer)
- D. Glucocerebrosidase
- E. Alpha-galactosidase A
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase***
- The clinical presentation with **gingival hyperplasia**, **restricted joint movement**, **skeletal abnormalities** (growth abnormalities, leg length discrepancy, prominent forehead), and **corneal opacity** with elevated lysosomal enzymes (N-acetyl-ß-glucosaminidase, ß-glucuronidase, ß-hexosaminidase A) is highly characteristic of **I-cell disease** (mucolipidosis II).
- I-cell disease is caused by a deficiency in **N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase**, an enzyme crucial for phosphorylating mannose residues on lysosomal enzymes, tagging them for delivery to lysosomes. Without this tag, lysosomal enzymes are secreted extracellularly, leading to their accumulation in the blood and their deficiency within lysosomes, causing the clinical features.
*Lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase*
- Deficiency of **lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase** causes **Pompe disease (glycogen storage disease type II)**, which is characterized by **cardiomegaly**, hypotonia, and liver involvement, but typically does not present with the skeletal dysplasias, gingival hyperplasia, or corneal clouding seen in this patient.
- While it is a lysosomal storage disorder, the specific clinical features and panel of elevated enzymes differ significantly from this case.
*Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency of **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)** causes **G6PD deficiency**, an X-linked disorder leading to **hemolytic anemia** in response to oxidative stress (e.g., fava beans, certain drugs, infections).
- It does not present with the systemic skeletal, connective tissue, and corneal abnormalities described, nor does it involve elevated lysosomal enzyme levels.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- Deficiency of **glucocerebrosidase** causes **Gaucher disease**, which presents with **hepatosplenomegaly**, bone crises, pancytopenia, and sometimes neurological involvement.
- While it is a lysosomal storage disorder, the clinical features (e.g., absence of gingival hyperplasia, corneal opacity, or specific skeletal dysplasias like restricted joint movement) and the pattern of elevated enzymes do not match the patient's presentation.
*Alpha-galactosidase A*
- Deficiency of **alpha-galactosidase A** causes **Fabry disease**, an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder characterized by **neuropathic pain**, **angiokeratomas**, renal failure, and cardiac involvement.
- The clinical picture of Fabry disease does not include gingival hyperplasia, prominent skeletal abnormalities, or the specific pattern of elevated lysosomal enzymes observed in this patient.
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 5: A 4-month-old male infant is brought in because he rejects food and is losing weight. He had several upper respiratory tract infections during the last 2 months. Upon examination, hepatosplenomegaly is noted, as well as mild hypotonia. During the next few weeks, hepatosplenomegaly progresses, the boy fails to thrive, and he continues to reject food. He has a blood pressure of 100/70 mm Hg and heart rate of 84/min. Blood tests show pancytopenia and elevated levels of transaminases. Slit lamp examination shows bilateral cherry-red spots on the macula. Chest X-ray shows a reticulonodular pattern and calcified nodules. Biopsy of the liver shows foamy histiocytes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Niemann-Pick disease type A (Correct Answer)
- B. Tay-Sachs disease
- C. Gaucher disease
- D. Wolman disease
- E. GM1 gangliosidosis
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***Niemann-Pick disease type A***
- This presentation of a 4-month-old with **failure to thrive**, progressive **hepatosplenomegaly**, **hypotonia**, recurrent infections, **pancytopenia**, elevated transaminases, **cherry-red spots** on the macula, and **foamy histiocytes** in the liver biopsy is characteristic of Niemann-Pick disease type A.
- Niemann-Pick disease type A is a **lysosomal storage disorder** caused by a deficiency of the enzyme **sphingomyelinase**, leading to the accumulation of **sphingomyelin** in various tissues.
- The **foamy histiocytes** (lipid-laden macrophages) are a hallmark finding, and the **reticulonodular pattern** on chest X-ray represents pulmonary infiltration.
*Incorrect: Tay-Sachs disease*
- While Tay-Sachs disease also presents with **cherry-red spots** and progressive neurological deterioration in infancy, it is caused by **hexosaminidase A deficiency**.
- Key differences: Tay-Sachs typically does **not** cause **hepatosplenomegaly** or **foamy histiocytes** in the liver; the primary pathology is neuronal accumulation of GM2 ganglioside.
- Patients usually present with developmental regression, exaggerated startle response, and hypotonia, but without the prominent organomegaly seen here.
*Incorrect: Gaucher disease*
- While Gaucher disease also presents with **hepatosplenomegaly** and can cause bone marrow involvement leading to **pancytopenia**, it typically does **not** feature **cherry-red spots** or such severe early neurological regression.
- It is caused by a deficiency of **glucocerebrosidase**, leading to accumulation of glucocerebroside in **Gaucher cells** (not foamy histiocytes).
- The infantile neuronopathic form (type 2) can present early but lacks cherry-red spots.
*Incorrect: Wolman disease*
- Wolman disease is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by **lysosomal acid lipase deficiency**, presenting with hepatosplenomegaly, failure to thrive, and foamy histiocytes.
- Key distinguishing feature: **bilateral adrenal calcifications** on imaging, which are pathognomonic for Wolman disease but not mentioned in this case.
- Does **not** typically cause cherry-red spots on fundoscopic examination.
*Incorrect: GM1 gangliosidosis*
- GM1 gangliosidosis can present with hepatosplenomegaly, developmental delay, and **cherry-red spots** (in about 50% of cases).
- However, it is characterized by distinctive **coarse facial features**, **skeletal dysplasia** (dysostosis multiplex), and **vacuolated lymphocytes** on blood smear.
- The **foamy histiocytes** and prominent pulmonary involvement are more characteristic of Niemann-Pick disease type A.
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 6: A 6-month-old infant male is brought to the emergency department with a 1-hour history of vomiting and convulsions. He was born at home and had sporadic prenatal care though his parents say that he appeared healthy at birth. He initially fed well; however, his parents have noticed that he has been feeding poorly and is very irritable since they moved on to baby foods. They have also noticed mild yellowing of his skin but assumed it would go away over time. On presentation, he is found to be very sleepy, and physical exam reveals an enlarged liver and spleen. The rest of the physical exam is normal. Which of the following enzymes is most likely functioning abnormally in this patient?
- A. Aldolase B (Correct Answer)
- B. Galactokinase
- C. Lactase
- D. Fructokinase
- E. Gal-1-phosphate uridyl transferase
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***Aldolase B***
- The symptoms of vomiting, irritability, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, and poor feeding in an infant after starting baby foods strongly suggest **hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI)**.
- HFI is caused by a deficiency in **Aldolase B**, which is responsible for cleaving **fructose-1-phosphate** into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde in the liver, kidney, and small intestine.
*Galactokinase*
- A deficiency in **galactokinase** causes **galactosemia type II**, characterized primarily by **cataracts** from birth, with milder symptoms compared to classic galactosemia.
- It does not typically present with the severe liver failure, vomiting, and convulsions seen in this patient.
*Lactase*
- **Lactase deficiency** causes **lactose intolerance**, presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms like bloating, gas, and diarrhea, particularly after consuming milk products.
- It does not typically cause the systemic symptoms of liver dysfunction, vomiting, convulsions, or jaundice experienced by this infant.
*Fructokinase*
- A deficiency in **fructokinase** causes **essential fructosuria**, which is a **benign, asymptomatic** metabolic disorder.
- Fructose accumulates in the urine but does not lead to the severe clinical manifestations such as vomiting, convulsions, or liver enlargement.
*Gal-1-phosphate uridyl transferase*
- A deficiency in **Gal-1-phosphate uridyl transferase** causes **classic galactosemia**, which would also present with vomiting, feeding difficulties, jaundice, and hepatosplenomegaly.
- However, classic galactosemia symptoms appear upon ingestion of **lactose** (from breast milk or formula), typically much earlier than the introduction of baby foods containing fructose.
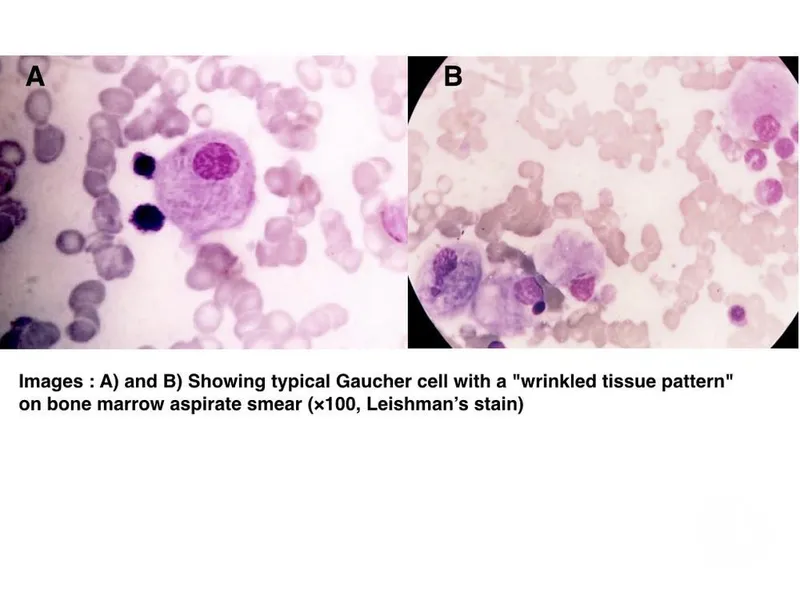
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 7: A 5-year-old girl is brought in for a routine checkup. She was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery and is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting all developmental milestones. Upon examination, she is pale with a few petechiae on her chest neck and back. Examination of the abdomen reveals painless hepatosplenomegaly. Liver enzymes are mildly elevated and complete blood cell count shows slight anemia and thrombocytopenia. Iron, B12, and folate are normal. A bone marrow biopsy shows mildly hypocellular marrows with diffuse macrophages with eosinophilic cytoplasm. The cytoplasm looks like wrinkled tissue paper on further inspection. No blasts are observed. What is the most likely diagnosis in the present case?
- A. Autoimmune disorder
- B. Gaucher disease type I (Correct Answer)
- C. Biliary obstruction
- D. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- E. Viral hepatitis
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: **Gaucher disease type I**
- The characteristic finding of **diffuse macrophages with eosinophilic cytoplasm** that resembles **"wrinkled tissue paper"** on bone marrow biopsy is pathognomonic for **Gaucher cells**, confirming **Gaucher disease type I**.
- **Painless hepatosplenomegaly**, **anemia**, **thrombocytopenia**, and **petechiae** are common clinical manifestations resulting from the accumulation of glucocerebroside in macrophages within the reticuloendothelial system.
*Autoimmune disorder*
- While autoimmune disorders can cause anemia and hepatosplenomegaly, the distinct **"wrinkled tissue paper" macrophages** found in the bone marrow biopsy are not characteristic of autoimmune conditions.
- Autoimmune disorders like lupus or autoimmune hemolytic anemia would present with different serological markers and histological findings.
*Biliary obstruction*
- **Biliary obstruction** typically presents with **jaundice**, dark urine, pale stools, and significant elevation of **liver enzymes** (especially direct bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase), which are not prominent features here.
- It would not explain the hematopoietic abnormalities (anemia, thrombocytopenia) or the presence of Gaucher cells in the bone marrow.
*Acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
- **Acute lymphoblastic leukemia** would typically show a significant presence of **blasts** (immature white blood cells) in the bone marrow, which are explicitly noted as absent in this case.
- While it can cause anemia and thrombocytopenia, the key diagnostic feature of **blasts** is missing, and the characteristic macrophages would not be present.
*Viral hepatitis*
- **Viral hepatitis** primarily causes **liver inflammation** and can lead to significant elevation of **liver enzymes** (transaminases), often much higher than "mildly elevated."
- It does not explain the **painless hepatosplenomegaly**, **anemia**, **thrombocytopenia**, or the pathognomonic **Gaucher cells** in the bone marrow.
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 8: A 26-year-old woman presents to a physician for genetic counseling, because she is worried about trying to have a child. Specifically, she had 2 siblings that died young from a lysosomal storage disorder and is afraid that her own children will have the same disorder. Her background is Ashkenazi Jewish, but she says that her husband's background is mixed European heritage. Her physician says that since her partner is not of Jewish background, their chance of having a child with Niemann-Pick disease is dramatically decreased. Which of the following genetic principles best explains why there is an increased prevalence of this disease in some populations?
- A. Natural selection
- B. Imprinting
- C. De novo mutations
- D. Gene flow
- E. Founder effect (Correct Answer)
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***Founder effect***
- The **founder effect** occurs when a new population is established by a small number of individuals, leading to a **reduced genetic diversity** and an increased frequency of certain alleles that were present in the founders. This is particularly relevant in populations like **Ashkenazi Jews**, who descended from a small, isolated group with certain allele frequencies.
- In this scenario, the high prevalence of **Niemann-Pick disease** (and other genetic disorders) in the Ashkenazi Jewish population is due to their historical isolation and intermarriage within a relatively small gene pool, trapping and concentrating certain alleles.
*Natural selection*
- **Natural selection** typically describes the process by which traits that enhance survival and reproduction become more common in a population over time, or deleterious traits become less common.
- While it can influence disease prevalence, it doesn't primarily explain the disproportionately high frequency of rare recessive disorders in specific isolated populations in the manner described.
*Imprinting*
- **Genomic imprinting** refers to the phenomenon where certain genes are expressed in a **parent-of-origin-specific manner**, meaning that only the allele inherited from either the mother or the father is expressed.
- This mechanism explains certain genetic conditions but does not account for the increased prevalence of a recessive disorder due to population history and isolation.
*De novo mutations*
- **De novo mutations** are new genetic alterations that appear for the first time in an individual and are not inherited from either parent.
- While de novo mutations are a source of genetic variation, they do not explain the high prevalence of a specific ancestral allele within an entire population.
*Gene flow*
- **Gene flow** (or migration) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another, which tends to **decrease genetic differences** between populations and introduce new alleles.
- This principle would suggest a *reduction* in the prevalence of specific rare alleles over time as populations mix, rather than an *increase* in isolated groups.
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 9: A research study evaluates three siblings with Niemann-Pick disease type C: a 6-year-old with ataxia and vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, a 10-year-old with hepatosplenomegaly and mild cognitive impairment, and a 14-year-old who is asymptomatic. Genetic testing reveals all three carry the same compound heterozygous NPC1 mutations. Fibroblast studies show similar cholesterol esterification defects and filipin staining patterns. Miglustat therapy is available. Evaluate the biological basis for phenotypic variability and optimal treatment allocation.
- A. Evaluate modifier genes, epigenetic factors, and biomarkers; treat based on individual risk stratification (Correct Answer)
- B. Treat all three immediately as genetic identity predicts identical disease course
- C. Treat only symptomatic siblings as asymptomatic carrier won't develop disease
- D. Delay all treatment until symptoms appear in the youngest to confirm diagnosis
- E. Treat the 6-year-old only as neurologic symptoms indicate blood-brain barrier dysfunction
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***Evaluate modifier genes, epigenetic factors, and biomarkers; treat based on individual risk stratification***
- **Phenotypic discordance** in Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) despite identical genotypes suggests that **modifier genes**, **epigenetic factors**, and cellular environment dictate clinical onset and severity.
- Management must be personalized because **NPC1 mutations** and **filipin staining** do not perfectly correlate with clinical progression; biomarkers like **oxysterols** or **lysosphingolipids** help guide individual risk.
*Treat only symptomatic siblings as asymptomatic carrier won't develop disease*
- The asymptomatic 14-year-old is not a carrier but has already been confirmed to have **compound heterozygous NPC1 mutations** and pathognomonic **filipin staining**.
- This sibling has the disease and is at high risk for **late-onset neurological symptoms**, requiring proactive monitoring rather than being dismissed as a carrier.
*Treat all three immediately as genetic identity predicts identical disease course*
- Even with identical **NPC1 mutations**, clinical presentation varies significantly (from **supranuclear gaze palsy** to asymptomatic), meaning the disease course is not identical.
- While **Miglustat** is effective, immediate treatment in asymptomatic patients is debated; therapy is typically tailored to clinical or **biomarker evidence** of progression.
*Treat the 6-year-old only as neurologic symptoms indicate blood-brain barrier dysfunction*
- **Miglustat** crosses the **blood-brain barrier** to inhibit **glucosylceramide synthase**, but its use is not limited based on blood-brain barrier integrity.
- The 10-year-old already exhibits **hepatosplenomegaly** and **cognitive impairment**, which are clear indications for therapy to prevent further neurocognitive decline.
*Delay all treatment until symptoms appear in the youngest to confirm diagnosis*
- The diagnosis is already confirmed via **genetic testing** showing NPC1 mutations and **fibroblast studies** showing cholesterol defects.
- Delaying treatment in already symptomatic siblings (the 6 and 10-year-olds) would allow irreversible **neuronal loss** and worsening of **ataxia**.
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG Question 10: A 15-year-old boy with Hunter syndrome (MPS II) on weekly enzyme replacement therapy develops IgG antibodies with high neutralizing capacity against idursulfase. His symptoms have worsened over the past 6 months with increasing hepatosplenomegaly and joint stiffness. His brother with the same mutation shows excellent response to ERT without antibody formation. Synthesize an appropriate management plan considering immunologic and genetic factors.
- A. Switch to substrate reduction therapy as primary treatment
- B. Implement immune tolerance induction protocol with immunosuppression and continued ERT (Correct Answer)
- C. Discontinue ERT as antibodies make it ineffective; switch to supportive care only
- D. Perform HSCT to eliminate antibody production and provide endogenous enzyme
- E. Increase ERT dose to saturate antibody binding capacity
Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) Explanation: ***Implement immune tolerance induction protocol with immunosuppression and continued ERT***
- The presence of **high-titer neutralizing IgG antibodies** (NABs) interferes with the efficacy of **idursulfase**, leading to the recurrence of symptoms like **hepatosplenomegaly** and joint stiffness.
- **Immune tolerance induction (ITI)** using agents like **rituximab**, **methotrexate**, and IVIG is indicated to eliminate the antibody response and restore the clinical benefit of the **enzyme replacement therapy**.
*Discontinue ERT as antibodies make it ineffective; switch to supportive care only*
- Stopping ERT allows the accumulation of **glycosaminoglycans** to continue, leading to progressive multisystemic decline and shortened **life expectancy**.
- Supportive care alone does not address the underlying **biochemical deficiency** when immune modulation could potentially rescue the primary treatment.
*Switch to substrate reduction therapy as primary treatment*
- **Substrate reduction therapy** (SRT) is not currently the standard or approved primary treatment for **Hunter syndrome** (MPS II) especially in the context of existing ERT failure.
- SRT aims to reduce the synthesis of **heparan and dermatan sulfate**, but it does not replace the missing **iduronate-2-sulfatase** enzyme activity required for clearance.
*Increase ERT dose to saturate antibody binding capacity*
- Increasing the dose of **idursulfase** often fails to overcome high-affinity **neutralizing antibodies** and may increase the risk of **infusion-related reactions** or immune complex formation.
- Antibody **saturation** is not a sustainable or effective clinical strategy for managing high-titer **anti-drug antibodies** in lysosomal storage diseases.
*Perform HSCT to eliminate antibody production and provide endogenous enzyme*
- While **hematopoietic stem cell transplantation** (HSCT) provides endogenous enzyme, it is not the preferred treatment for **MPS II** due to high procedural risks and inconsistent neurological outcomes compared to MPS I.
- HSCT is typically not used specifically as a secondary measure to treat **anti-drug antibodies** when **immune tolerance induction** is a viable and less invasive option.
More Sphingolipidoses (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher, Niemann-Pick) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.