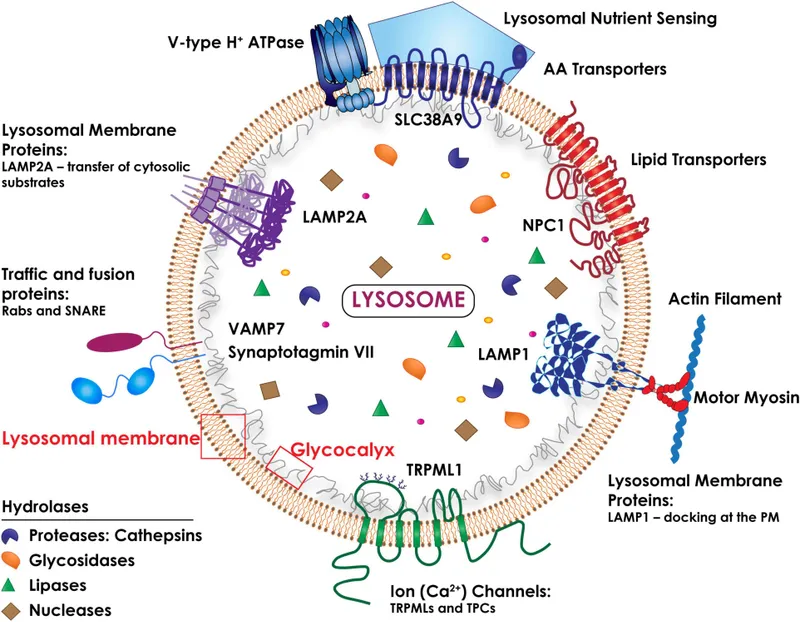
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Lysosome structure and function. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 1: A 5-month-old boy is brought to his pediatrician because his parents have noticed that he has very restricted joint movement. He was born at home without prenatal care, but they say that he appeared healthy at birth. Since then, they say that he doesn't seem to move very much and is hard to arouse. Physical exam reveals coarse facial structures and hepatosplenomegaly. Radiography reveals skeletal malformations, and serum tests show high plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes. The production of which of the following substances will most likely be disrupted in this patient?
- A. Glucocerebroside
- B. Mannose-6-phosphate (Correct Answer)
- C. Heparan sulfate
- D. Ceramide
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Mannose-6-phosphate***
- The patient's symptoms (restricted joint movement, coarse facial features, hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal malformations, and high plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes) are highly suggestive of **I-cell disease (mucolipidosis type II)**.
- I-cell disease is caused by a deficiency in the enzyme **N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase**, which is responsible for phosphorylating mannose residues to create **mannose-6-phosphate (M6P)** tags; this tag is crucial for directing lysosomal enzymes to the lysosome. Without these tags, lysosomal enzymes are secreted extracellularly (hence high plasma levels) instead of being delivered to lysosomes, leading to accumulation of undigested substrates within lysosomes.
*Glucocerebroside*
- This is a substrate that accumulates in **Gaucher disease**, a **lysosomal storage disorder** caused by a deficiency in glucocerebrosidase.
- While Gaucher disease involves hepatosplenomegaly and skeletal issues, it does not typically present with the coarse facial features, severe joint restriction, or widespread undigested lysosomal enzymes in the plasma seen in this patient.
*Heparan sulfate*
- **Heparan sulfate** is a **glycosaminoglycan** that accumulates in certain mucopolysaccharidoses (e.g., Sanfilippo syndrome, Hurler syndrome).
- While mucopolysaccharidoses also present with coarse facial features, skeletal abnormalities, and hepatosplenomegaly, they are caused by defects in the enzymes that degrade glycosaminoglycans, not a defect in the lysosomal enzyme targeting mechanism itself as suggested by the high plasma lysosomal enzymes.
*Ceramide*
- **Ceramide** is a **lipid precursor** to sphingolipids and glycosphingolipids, which accumulate in various lysosomal storage diseases (e.g., Farber disease).
- While numerous lysosomal storage disorders involve improper ceramide metabolism or its derivatives, a primary defect in ceramide production or breakdown as the root cause for the entire clinical picture with high plasma lysosomal enzymes is less likely than the targeting defect in I-cell disease.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator is studying the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in genetically modified lymphocytes. A gene is removed that facilitates the binding of ribosomes to the endoplasmic reticulum. Which of the following processes is most likely to be impaired as a result of this genetic modification?
- A. Production of secretory proteins (Correct Answer)
- B. Neutralization of toxins
- C. Ubiquitination of proteins
- D. α-Oxidation of fatty acids
- E. Synthesis of ketone bodies
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Production of secretory proteins***
- Ribosomes bound to the **rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)** are responsible for synthesizing proteins destined for secretion, insertion into membranes, or delivery to organelles like lysosomes.
- If ribosomes cannot bind to the ER, these proteins will be synthesized in the **cytosol** and lack the proper signals and processing for their intended destination and function.
*Neutralization of toxins*
- The **smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)**, not the RER, is primarily involved in **detoxification** processes, particularly drug metabolism and neutralization of toxins.
- This function relies on enzymes embedded within the SER membrane and is largely independent of ribosome binding.
*Ubiquitination of proteins*
- **Ubiquitination** is a post-translational modification that tags proteins for degradation by the **proteasome** or for trafficking to specific cellular compartments.
- This process occurs primarily in the **cytosol** and does not directly rely on ribosome binding to the ER for protein synthesis.
*α-Oxidation of fatty acids*
- **α-oxidation of fatty acids** is a metabolic pathway that occurs primarily in the **peroxisomes**.
- It is distinct from protein synthesis on the ER and would not be directly impacted by the inability of ribosomes to bind to the ER.
*Synthesis of ketone bodies*
- The **synthesis of ketone bodies** (ketogenesis) primarily occurs in the **mitochondria** of liver cells.
- This metabolic pathway is not directly dependent on ribosome binding to the endoplasmic reticulum for its function.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 3: A scientist is studying a protein that is present on the plasma membrane of cells. He therefore purifies the protein in a lipid bilayer and subjects it to a number of conditions. His investigations show that the protein has the following properties:
1) It is able to change ion concentrations across the membrane without addition of ATP to the solution.
2) Its activity increases linearly with substrate concentration without any saturation even at mildly supraphysiologic conditions.
3) In some states the protein leads to an ion concentration change; whereas, it has no effect in other states.
4) Changing the electrical charge across the membrane does not affect whether the protein has activity.
5) Adding a small amount of an additional substance to the solution reliably increases the protein's activity.
These findings are consistent with a protein with which of the following functions?
- A. Maintenance of resting sodium and potassium concentrations
- B. Transporting water in the collecting duct of the kidney
- C. Reabsorption of glucose in the proximal kidney tubule
- D. Mediating neuronal to muscle end plate communication (Correct Answer)
- E. Causing depolarization during action potentials
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: **Mediating neuronal to muscle end plate communication**
- The properties described align with **ligand-gated ion channels**, which mediate communication at the neuromuscular junction. These channels open in response to a **neurotransmitter** (the "additional substance"), allowing ion flow without direct ATP hydrolysis.
- The "some states" where it has no effect and "other states" where it leads to ion concentration change refer to its closed and open conformational states, dependent on ligand binding. The lack of saturation and independence from electrical charge are features of some channel kinetics.
*Maintenance of resting sodium and potassium concentrations*
- This function is primarily carried out by the **Na+/K+ ATPase pump**, which is an **active transporter** requiring ATP hydrolysis for its function, contradicting property (1).
- The Na+/K+ ATPase transports ions against their concentration gradients and would be affected by changes in ATP availability.
*Reabsorption of glucose in the proximal kidney tubule*
- Glucose reabsorption primarily involves **Na+-glucose cotransporters (SGLTs)**, which are secondary active transporters. While they don't directly use ATP, their activity is linked to the Na+ gradient maintained by Na+/K+ ATPase, and they can show saturation kinetics.
- SGLTs are symporters that move glucose and Na+ in the same direction and exhibit saturation at high glucose concentrations.
*Transporting water in the collecting duct of the kidney*
- Water transport in the collecting duct is mediated by **aquaporins**, which are passive water channels. Their activity is regulated by **vasopressin** (ADH), but they primarily transport water, not ions.
- Aquaporins do not typically impact ion concentrations directly and their activity is usually quite specific to water movement.
*Causing depolarization during action potentials*
- Depolarization during action potentials is caused by the opening of **voltage-gated sodium channels**. These channels are directly affected by changes in **electrical charge** across the membrane, contradicting property (4).
- Voltage-gated channels exhibit specific thresholds for activation and inactivation based on membrane potential.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator is studying the clearance of respiratory particles in healthy non-smokers. An aerosol containing radio-labeled particles that are small enough to reach the alveoli is administered to the subjects via a non-rebreather mask. A gamma scanner is then used to evaluate the rate of particle clearance from the lungs. The primary mechanism of particle clearance most likely involves which of the following cell types?
- A. Goblet cells
- B. Macrophages (Correct Answer)
- C. Club cells
- D. Type I pneumocytes
- E. Neutrophils
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Macrophages***
- **Alveolar macrophages** are the primary phagocytic cells in the alveoli responsible for clearing inhaled particles that reach this deepest part of the lung.
- They engulf and digest foreign substances, including pathogens and inert particles, protecting the delicate alveolar structures.
*Goblet cells*
- **Goblet cells** are found in the larger airways (trachea, bronchi), where they produce mucus to trap inhaled particles.
- They are not present in the alveoli, so they cannot clear particles that have reached this region.
*Club cells*
- **Club cells** (formerly Clara cells) are located in the bronchioles and secrete components of the surfactant-like material, but they do not primarily function in particle clearance.
- While they have some protective roles, they are not the main phagocytic cells for alveolar particles.
*Type I pneumocytes*
- **Type I pneumocytes** are flattened, thin cells that form the majority of the alveolar surface and are primarily involved in gas exchange.
- They are not phagocytic and do not play a direct role in clearing inhaled particles.
*Neutrophils*
- **Neutrophils** are acute inflammatory cells primarily involved in combating bacterial infections.
- While they can migrate to the lungs during inflammation, they are not the primary, routine phagocytic cells for clearing inhaled particles in healthy individuals.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 5: Antigen presentation of extracellular pathogens by antigen presenting cells requires endocytosis of the antigen, followed by the degradation in the acidic environment of the formed phagolysosome. Should the phagolysosome become unable to lower its pH, what is the most likely consequence?
- A. Deficient presentation of pathogens to CD4 T-cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Deficient cell extravasation
- C. Deficient presentation of pathogens to CD8 T-cells
- D. Deficient NK cell activation
- E. Deficient expression of B7
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Deficient presentation of pathogens to CD4 T-cells***
- The acidic environment of the **phagolysosome** is crucial for optimal **antigen degradation** and processing into peptides that can bind to **MHC class II molecules**.
- Without proper acidification, peptide loading onto **MHC class II** is impaired, leading to deficient presentation of extracellular pathogens to **CD4 T-cells**.
*Deficient cell extravasation*
- **Cell extravasation** involves events like rolling, adhesion, and transendothelial migration, which are primarily regulated by **adhesion molecules** and **chemokines**, not phagolysosomal pH.
- A defect in phagolysosomal pH would not directly impede the ability of cells to exit the vasculature.
*Deficient presentation of pathogens to CD8 T-cells*
- **CD8 T-cell** activation primarily involves the presentation of **intracellular antigens** via **MHC class I molecules**, which typically occurs through degradation in the **cytosol** via proteasomes.
- While some cross-presentation pathways exist, the primary mechanism of CD8 T-cell antigen presentation is not dependent on the acidification of phagolysosomes for extracellular pathogens.
*Deficient NK cell activation*
- **Natural Killer (NK) cells** recognize and kill target cells based on the presence or absence of **MHC class I molecules** and activating ligands, not on the processing of extracellular antigens within phagolysosomes.
- Their activation depends on cytokine environments and surface receptor interactions, not directly on phagolysosomal pH.
*Deficient expression of B7*
- **B7 molecules (CD80/CD86)** are **co-stimulatory molecules** expressed by antigen-presenting cells that are crucial for full T-cell activation. While antigen processing can influence APC activation, a specific defect in phagolysosomal pH would primarily affect the *presentation* of peptides, not the *expression* of co-stimulatory molecules.
- The expression of B7 is more broadly regulated by inflammatory signals and toll-like receptor (TLR) engagement, rather than being solely dependent on proper phagolysosomal acidification.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 6: What is the primary mechanism for maintaining acid-base balance during prolonged vomiting?
- A. Increased chloride reabsorption
- B. Increased potassium excretion
- C. Increased bicarbonate excretion (Correct Answer)
- D. Decreased hydrogen secretion
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Increased bicarbonate excretion***
- Prolonged vomiting leads to the loss of **gastric acid (HCl)**, causing **metabolic alkalosis**. The kidneys compensate by increasing the excretion of **bicarbonate (HCO3-)** to restore acid-base balance.
- This renal compensation is the primary mechanism to eliminate the excess alkali from the body.
*Increased chloride reabsorption*
- In **metabolic alkalosis** due to vomiting, the body tends to reabsorb less chloride, not more, in an attempt to excrete bicarbonate.
- **Chloride depletion** can actually hinder bicarbonate excretion by promoting sodium reabsorption with bicarbonate.
*Increased potassium excretion*
- **Hypokalemia** can occur with prolonged vomiting due to increased aldosterone activity and direct renal loss associated with metabolic alkalosis.
- However, increased potassium excretion itself is not the primary mechanism for correcting the acid-base disorder; rather, it is a consequence or a contributing factor to the imbalance.
*Decreased hydrogen secretion*
- In response to alkalosis, the kidneys would typically decrease, not increase, **hydrogen ion (H+) secretion** in an effort to retain H+ and normalize pH.
- Decreased H+ secretion is a compensatory mechanism, but the direct excretion of bicarbonate is more crucial for correcting the metabolic alkalosis.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 7: In large neurons the nucleus can be found a large distance away from the terminal end of its axon. The body has a complex system of intracellular transporters that are able to carry essential proteins from the nucleus to the distal edge of the cell and back. Which of the following proteins are essential for this function?
- A. Kinesin, Troponin
- B. Myosin, Kinesin
- C. Actin, Dynein
- D. Dynein, Kinesin (Correct Answer)
- E. Glucose, Actin
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Dynein, Kinesin***
- **Kinesin** is primarily responsible for **anterograde transport** (from the cell body to the axon terminal) along microtubules, carrying vesicles and organelles.
- **Dynein** handles **retrograde transport** (from the axon terminal back to the cell body), essential for recycling components and signaling.
*Kinesin, Troponin*
- While **Kinesin** is involved in axonal transport, **Troponin** is a protein found in muscle tissue that regulates muscle contraction, not intracellular transport in neurons.
- Troponin binds **calcium ions** and influences the interaction between actin and myosin.
*Myosin, Kinesin*
- **Kinesin** is involved in microtubule-based transport, but **Myosin** is primarily associated with **actin filaments** for muscle contraction and intracellular movement, not long-distance axonal transport.
- Myosin functions as a **motor protein** that converts chemical energy in ATP into mechanical force.
*Actin, Dynein*
- **Dynein** is crucial for retrograde axonal transport, but **Actin** is a structural protein forming microfilaments that are involved in cell shape, motility, and some short-distance transport, not the major long-distance axonal transport mechanism.
- Actin filaments serve as tracks for **myosin motors**, primarily in the cell cortex.
*Glucose, Actin*
- **Glucose** is a sugar molecule, the primary energy source for cells, and not a transport protein.
- **Actin** forms microfilaments for cell structure and short-range movement, not long-distance axonal transport as described.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 8: A 5-month-old boy presents with increasing weakness for the past 3 months. The patient’s mother says that the weakness is accompanied by dizziness, sweating, and vertigo early in the morning. Physical examination shows hepatomegaly. Laboratory findings show an increased amount of lactate, uric acid, and elevated triglyceride levels. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Hepatic glycogen phosphorylase
- B. Debranching enzyme
- C. Glucose-6-phosphatase (Correct Answer)
- D. Muscle glycogen phosphorylase
- E. Lysosomal α-1,4-glucosidase
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Glucose-6-phosphatase***
- The constellation of **hypoglycemia** (weakness, dizziness, sweating, vertigo, especially early morning), **hepatomegaly**, **lactic acidosis**, **hyperuricemia**, and **hypertriglyceridemia** are classic features of **Type I glycogen storage disease (von Gierke disease)**, which is caused by a deficiency of **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- This enzyme is crucial for the final step of both **glycogenolysis** and **gluconeogenesis**, releasing free glucose into the bloodstream; its deficiency leads to an inability to maintain normal blood glucose levels during fasting and accumulation of glucose-6-phosphate, which shunts into other metabolic pathways.
*Hepatic glycogen phosphorylase*
- Deficiency in **hepatic glycogen phosphorylase** (Type VI glycogen storage disease, Hers disease) would cause **hepatomegaly** and **hypoglycemia**, but typically does not present with severe **lactic acidosis**, **hyperuricemia**, or **hypertriglyceridemia** to the same degree as von Gierke disease.
- The primary defect is in breaking down glycogen, leading to its accumulation in the liver, but the products of glycolysis can still exit the liver via gluconeogenesis.
*Debranching enzyme*
- Deficiency in **debranching enzyme** (Type III glycogen storage disease, Cori or Forbes disease) causes **hepatomegaly** and **hypoglycemia**, but usually presents with milder symptoms and less severe **lactic acidosis**, **hyperuricemia**, and **hypertriglyceridemia**.
- Patients often present with symptoms similar to Type I, but muscle involvement is also common, and **glycogen structures with short outer branches** are characteristic.
*Muscle glycogen phosphorylase*
- Deficiency in **muscle glycogen phosphorylase** (Type V glycogen storage disease, McArdle disease) primarily affects **skeletal muscle**, leading to exercise intolerance, muscle pain, and myoglobinuria.
- It does not typically cause **hypoglycemia** or **hepatomegaly**, as the liver enzyme is functional, and the symptoms described are systemic rather than muscle-specific.
*Lysosomal α-1,4-glucosidase*
- Deficiency in **lysosomal α-1,4-glucosidase** (Type II glycogen storage disease, Pompe disease) primarily affects the **heart, muscle, and liver**, causing severe **cardiomyopathy**, hypotonia, and **hepatomegaly**.
- While it involves glycogen accumulation, it typically does not present with **hypoglycemia** (as cytoplasmic glycogen metabolism is intact), **lactic acidosis**, or the specific metabolic derangements seen in this patient.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 9: A 3-month-old boy presents for routine health maintenance. The patient has coarse facial features and stiff joint movements with restricted passive and active range of motion. He also has problems following objects with his eyes and seems not to focus on anything. On physical examination, the corneas are clouded, and the patient fails to meet any 3-month developmental milestones. Genetic testing and histopathology are performed and reveal failure of a cellular structure to phosphorylate mannose residues on glycoproteins. An electron microscopy image of one of this patient’s cells is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Adrenoleukodystrophy
- B. Kartagener syndrome
- C. Tay-Sachs disease
- D. Inclusion cell disease (Correct Answer)
- E. Diamond-Blackfan anemia
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Inclusion cell disease***
- This condition is characterized by a **failure to phosphorylate mannose residues** on glycoproteins due to a defective **N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase** enzyme.
- The clinical presentation of **coarse facial features, stiff joint movements**, clouded corneas, and developmental delay is classical for **I-cell disease** (mucolipidosis II), where lysosomal enzymes are **mistargeted and secreted from cells** instead of being properly delivered to lysosomes, resulting in **lysosomes that lack hydrolytic enzymes** and accumulate undigested substrates (visible as inclusions on electron microscopy).
*Adrenoleukodystrophy*
- This is an **X-linked disorder** affecting very long chain fatty acid metabolism, leading to their accumulation in the **adrenal glands** and **white matter of the brain**.
- While it causes **neurological dysfunction** and adrenal insufficiency, it does not typically present with the coarse facial features, corneal clouding, and skeletal abnormalities seen in this patient.
*Kartagener syndrome*
- This is a form of **primary ciliary dyskinesia** characterized by impaired ciliary movement due to structural defects in **dynein arms**.
- It presents with **recurrent respiratory infections** (sinusitis, bronchitis, bronchiectasis), **situs inversus** (in about 50% of cases), and infertility, which are unrelated to the patient's symptoms.
*Tay-Sachs disease*
- This is a **lysosomal storage disorder** caused by a deficiency of **hexosaminidase A**, leading to the accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside**.
- It causes **progressive neurological deterioration**, motor weakness, and a **cherry-red spot** on the macula, but not the coarse facial features or skeletal abnormalities described.
*Diamond-Blackfan anemia*
- This is a **congenital hypoplastic anemia** characterized by a defect in **erythroid progenitor cells**, leading to severe macrocytic anemia.
- It can be associated with various congenital anomalies, but the primary presentation is **anemia** and it does not involve the lysosomal storage defects or the characteristic facial and joint features seen in this case.
Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG Question 10: A 7-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his parents due to progressively worsening weakness for the last three months. The parents also describe the boy as having an exaggerated response when startled as well as diminishing response to visual stimuli. At birth, the boy was healthy and remained as such for the first few months of life. The mother says pregnancy was unremarkable, and the boy was born at 39 weeks with no complications during delivery. He is up to date on his vaccinations. The boy's grandparents immigrated from an eastern European country. Physical examination reveals hyperreflexia. Abdominal examination reveals no abnormalities. On fundoscopy, the following is seen. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Arylsulfatase A
- B. β-Glucosidase
- C. α-Galactosidase
- D. Hexosaminidase B
- E. Hexosaminidase A (Correct Answer)
Lysosome structure and function Explanation: ***Hexosaminidase A***
- Deficiency of **Hexosaminidase A** leads to **Tay-Sachs disease**, characterized by deterioration in motor and cognitive functions, aligning with the symptoms of weakness and abnormal responses.
- The condition is associated with a **cherry-red spot** on the retina, often observed in patients, further confirming the diagnosis.
- **Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry** is a key risk factor, consistent with the patient's eastern European heritage.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- Deficiency causes **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, which typically presents with **ataxia** and loss of previously attained skills, but not the exaggerated startle response noted in this case.
- The condition is not commonly associated with the specific visual and neurologic symptoms observed in the patient.
*β-Glucosidase*
- Deficiency leads to **Gaucher's disease**, which presents with splenomegaly, bone pain, and anemia, rather than the neurological symptoms seen here.
- The symptoms do not match the **progressive weakness** and startle reflex changes described.
*α-Galactosidase*
- Lack of this enzyme results in **Fabry disease**, which mainly causes pain episodes, skin lesions, and organ dysfunction, especially renal involvement.
- Neurological symptoms described here do not fit the typical presentation seen in Fabry disease.
*Hexosaminidase B*
- Deficiency causes **Sandhoff disease**, which presents similarly to Tay-Sachs with developmental regression and cherry-red spot.
- However, Sandhoff disease typically includes **hepatosplenomegaly**, which is notably absent in this patient on abdominal examination.
- The normal abdominal findings help distinguish this from Hexosaminidase A deficiency.
More Lysosome structure and function US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.