Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 1: A 5-month-old boy is brought to his pediatrician because his parents have noticed that he has very restricted joint movement. He was born at home without prenatal care, but they say that he appeared healthy at birth. Since then, they say that he doesn't seem to move very much and is hard to arouse. Physical exam reveals coarse facial structures and hepatosplenomegaly. Radiography reveals skeletal malformations, and serum tests show high plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes. The production of which of the following substances will most likely be disrupted in this patient?
- A. Glucocerebroside
- B. Mannose-6-phosphate (Correct Answer)
- C. Heparan sulfate
- D. Ceramide
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***Mannose-6-phosphate***
- The patient's symptoms (restricted joint movement, coarse facial features, hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal malformations, and high plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes) are highly suggestive of **I-cell disease (mucolipidosis type II)**.
- I-cell disease is caused by a deficiency in the enzyme **N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase**, which is responsible for phosphorylating mannose residues to create **mannose-6-phosphate (M6P)** tags; this tag is crucial for directing lysosomal enzymes to the lysosome. Without these tags, lysosomal enzymes are secreted extracellularly (hence high plasma levels) instead of being delivered to lysosomes, leading to accumulation of undigested substrates within lysosomes.
*Glucocerebroside*
- This is a substrate that accumulates in **Gaucher disease**, a **lysosomal storage disorder** caused by a deficiency in glucocerebrosidase.
- While Gaucher disease involves hepatosplenomegaly and skeletal issues, it does not typically present with the coarse facial features, severe joint restriction, or widespread undigested lysosomal enzymes in the plasma seen in this patient.
*Heparan sulfate*
- **Heparan sulfate** is a **glycosaminoglycan** that accumulates in certain mucopolysaccharidoses (e.g., Sanfilippo syndrome, Hurler syndrome).
- While mucopolysaccharidoses also present with coarse facial features, skeletal abnormalities, and hepatosplenomegaly, they are caused by defects in the enzymes that degrade glycosaminoglycans, not a defect in the lysosomal enzyme targeting mechanism itself as suggested by the high plasma lysosomal enzymes.
*Ceramide*
- **Ceramide** is a **lipid precursor** to sphingolipids and glycosphingolipids, which accumulate in various lysosomal storage diseases (e.g., Farber disease).
- While numerous lysosomal storage disorders involve improper ceramide metabolism or its derivatives, a primary defect in ceramide production or breakdown as the root cause for the entire clinical picture with high plasma lysosomal enzymes is less likely than the targeting defect in I-cell disease.
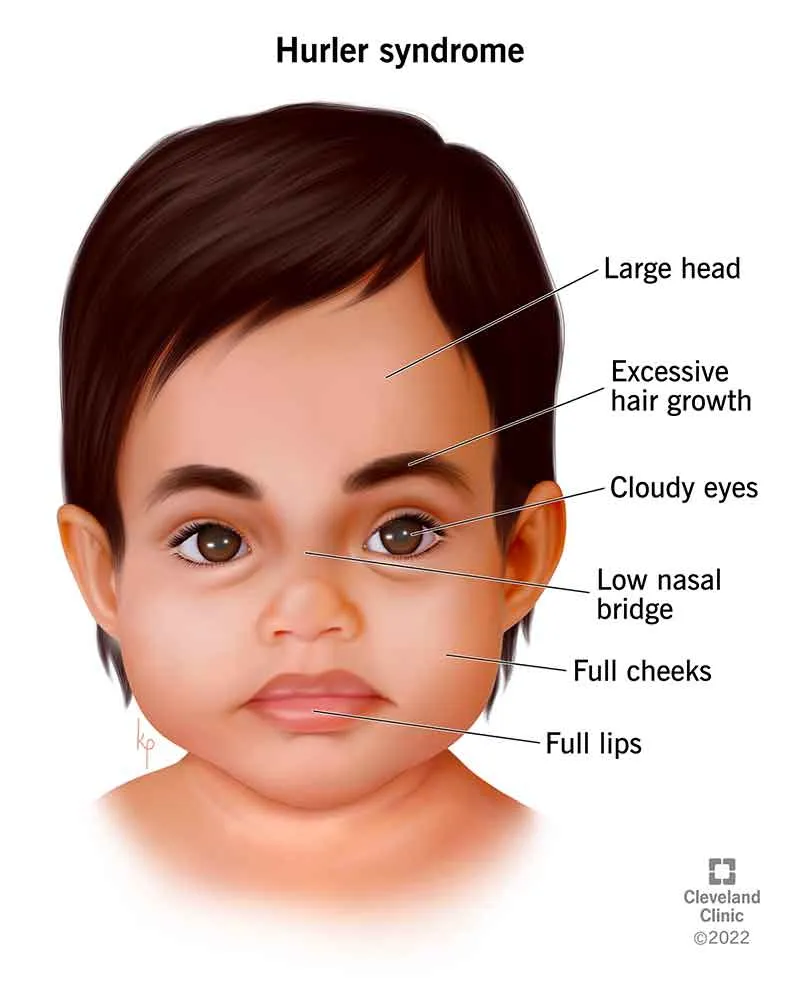
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 2: An 18-month-old boy is brought in by his parents for a routine check-up. The parents state that the patient still has not had any language development, and they are concerned about developmental delay. Of note, they have also noticed that the patient’s facial features have changed significantly in the last year. The patient also seems to have trouble visually focusing on objects or on the television. On exam, the patient's temperature is 98.2°F (36.8°C), blood pressure is 108/72 mmHg, pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 14/min. Of interest, the patient has not increased much in length or weight in the past 3 months. He is now in the 25th percentile for weight but is in the 90th percentile for head circumference. The patient does not appear to have any gross or fine motor deficiencies. Of note, he has coarse facial features that were not previously noted, including a long face, prominent forehead, and protruding eyes. The patient has corneal clouding bilaterally. At rest, the patient keeps his mouth hanging open. After extensive workup, the patient is found to have 2 mutated copies of the IDUA gene, with no production of the protein iduronidase. Which of the following is the likely mutation found in this disease?
- A. Interstitial deletion
- B. Silent mutation
- C. Missense mutation
- D. Chromosomal translocation
- E. Nonsense mutation (Correct Answer)
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***Nonsense mutation***
- A **nonsense mutation** leads to the formation of a **premature stop codon**, resulting in a truncated, non-functional protein, which aligns with the total absence of iduronidase.
- This type of mutation can severely impair protein function, leading to the severe phenotype described with **Hurler syndrome**, which is caused by a complete lack of **alpha-L-iduronidase** activity due to mutations in the *IDUA* gene.
*Interstitial deletion*
- An **interstitial deletion** involves the loss of a segment of a chromosome; while it can cause genetic disorders, it typically results in the **complete absence of a gene** or multiple genes, not specific protein truncation from a gene sequence.
- Though a deletion in the *IDUA* gene could cause Hurler syndrome, the specific finding of **no production of the protein iduronidase** suggests a point mutation affecting protein synthesis rather than a large chromosomal deletion.
*Silent mutation*
- A **silent mutation** is a change in a single nucleotide that does not alter the **amino acid sequence** of the protein due to the redundancy of the genetic code.
- This type of mutation would **not cause any change** in protein function or expression, as seen in this patient with complete absence of iduronidase.
*Missense mutation*
- A **missense mutation** involves a change in a single nucleotide that results in a **different amino acid** being incorporated into the protein.
- While a missense mutation can impair protein function, it typically results in a **partially functional** or altered protein, not the complete absence of protein product as described.
*Chromosomal translocation*
- A **chromosomal translocation** involves the rearrangement of parts between non-homologous chromosomes.
- While translocations can lead to genetic disorders by disrupting gene function or dosage, they are less likely to cause a **complete absence of a specific enzyme** unless the translocation directly disrupts the gene's coding region or regulatory elements in a way that prevents any transcription or translation.
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 3: A 7-month-old boy is brought by his parents to the pediatrician’s office. His mother says the child has been weakening progressively and is not as active as he used to be when he was born. His condition seems to be getting worse, especially over the last month. He was born at 41 weeks through normal vaginal delivery. There were no complications observed during the prenatal period. He was progressing well over the 1st few months and achieving the appropriate milestones. On examination, his abdomen appears soft with no liver enlargement. The patient appears to be dehydrated and lethargic. The results of a fundoscopic examination are shown in the picture. A blood test for which of the following enzymes is the next best assay to evaluate this patient's health?
- A. Acid alpha-glucosidase
- B. Hexosaminidase (Correct Answer)
- C. Sphingomyelinase
- D. Glucocerebrosidase
- E. Arylsulfatase A
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***Hexosaminidase***
- The symptoms and history suggest **Tay-Sachs disease**, characterized by progressive weakness and developmental delay, often linked to **deficiency in hexosaminidase A**.
- A fundoscopic exam typically reveals a **cherry-red spot**, consistent with this condition, making hexosaminidase testing essential for diagnosis.
- Tay-Sachs results from accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside** in neurons due to hexosaminidase A deficiency.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- This enzyme is primarily associated with **Gaucher's disease**, which does not match the clinical features presented here.
- Symptoms of Gaucher's disease include **hepatosplenomegaly** and bone pain, not primarily weakness or lethargy in a young infant.
*Acid alpha-glucosidase*
- Generally tested for **Pompe disease**, which typically presents with **muscle weakness and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy**, not solely lethargy and failure to thrive.
- The clinical presentation in this case does not indicate glycogen storage disorder symptoms.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- This enzyme deficiency relates to **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, which often features neurological decline rather than isolated lethargy in infants.
- The specific symptoms and age do not align with the typical findings of this condition.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- Linked to **Niemann-Pick disease**, characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly** and neurological deterioration, absent in this scenario.
- The presentation of weakness does not match the classic signs expected with sphingomyelinase deficiency.
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 4: An 8-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents for gradually increasing loss of neck control and inability to roll over for the past 2 months. During this time, he has had multiple episodes of unresponsiveness with a blank stare and fluttering of the eyelids. His parents state that he sometimes does not turn when called but gets startled by loud noises. He does not maintain eye contact. He was able to roll over from front to back at 5 months of age and has not yet begun to sit or crawl. His parents are of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. Neurological examination shows generalized hypotonia. Deep tendon reflexes are 3+ bilaterally. Plantar reflex shows extensor response bilaterally. Fundoscopy shows bright red macular spots bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Sphingomyelinase deficiency
- B. β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency
- C. α-galactosidase A deficiency
- D. ATP-binding cassette transporter mutation
- E. β-hexosaminidase A deficiency (Correct Answer)
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***β-hexosaminidase A deficiency***
- The constellation of **developmental regression** (loss of neck control, inability to roll over), **hypotonia**, **exaggerated startle response**, **cherry-red macular spots**, and **Ashkenazi Jewish descent** is classic for **Tay-Sachs disease**, which is caused by a deficiency in β-hexosaminidase A.
- The patient's seizures ("unresponsiveness with a blank stare and fluttering of the eyelids") and **hyperreflexia** (3+ deep tendon reflexes, extensor plantar response) are also consistent with the progressive neurodegeneration seen in Tay-Sachs disease.
*Sphingomyelinase deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Niemann-Pick disease**, which can also present with **developmental regression**, **hypotonia**, and **cherry-red macular spots**.
- However, Niemann-Pick disease typically involves **hepatosplenomegaly** and **pulmonary involvement**, which are not mentioned in this patient's presentation.
*β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency*
- This deficiency leads to **Gaucher disease**, characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly**, **bone crises**, and cytopenias.
- While some forms can have neurological symptoms, the classic cherry-red spot and pronounced developmental regression as described are not typical of Gaucher disease.
*α-galactosidase A deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Fabry disease**, which is an **X-linked lysosomal storage disorder** presenting with **neuropathic pain**, **angiokeratomas**, **renal disease**, and **cardiac involvement** in adolescence or adulthood.
- It does not present with infantile neurodegeneration or cherry-red spots.
*ATP-binding cassette transporter mutation*
- Mutations in ABC transporters can lead to various disorders, such as **adrenoleukodystrophy** (deficiency in VLCFA transport) or **cystic fibrosis**.
- These conditions do not present with the specific combination of symptoms, especially the cherry-red macula and profound developmental regression, seen in this infant.
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 5: An 18-month-old boy of Ashkenazi-Jewish descent presents with loss of developmental milestones. On ocular exam, a cherry-red macular spot is observed. No hepatomegaly is observed on physical exam. Microscopic exam shows lysosomes with onion-skin appearance.
What is the most likely underlying biochemical abnormality?
- A. Accumulation of ceramide trihexoside
- B. Accumulation of glucocerebroside
- C. Accumulation of galactocerebroside
- D. Accumulation of sphingomyelin
- E. Accumulation of GM2 ganglioside (Correct Answer)
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***Accumulation of GM2 ganglioside***
- This constellation of symptoms—**loss of developmental milestones**, **cherry-red macular spot**, absence of hepatomegaly, and **lysosomes with onion-skin appearance** in an individual of **Ashkenazi-Jewish descent**—is classic for **Tay-Sachs disease**.
- **Tay-Sachs disease** is caused by a deficiency of **hexosaminidase A**, leading to the accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside** in neuronal lysosomes.
*Accumulation of ceramide trihexoside*
- This refers to **Fabry disease**, which is an **X-linked disorder** presenting in adolescence or adulthood with acroparesthesias, angiokeratomas, and renal/cardiac complications.
- While it involves a lysosomal storage, its clinical presentation and the absence of a cherry-red spot differentiate it from the case described.
*Accumulation of glucocerebroside*
- This is characteristic of **Gaucher disease**, which is caused by a deficiency in **glucocerebrosidase**.
- Key features include **hepatosplenomegaly**, bone pain, and pancytopenia, which are not consistent with the patient's presentation.
*Accumulation of galactocerebroside*
- This describes **Krabbe disease**, a **globoid cell leukodystrophy** caused by a deficiency in galactocerebrosidase.
- Krabbe disease primarily affects the **myelin sheath** in the nervous system, leading to neurological degeneration but typically does not present with a cherry-red macular spot.
*Accumulation of sphingomyelin*
- This is the hallmark of **Niemann-Pick disease**, caused by **sphingomyelinase deficiency**.
- While Niemann-Pick disease also presents with a **cherry-red macular spot** and neurodegeneration, it is classically associated with **hepatosplenomegaly**, which is explicitly stated to be absent in this patient.
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 6: A deficiency in which of the following lysosomal enzymes is inherited in a pattern similar to a deficiency of iduronate sulfatase (Hunter syndrome)?
- A. Sphingomyelinase
- B. Glucocerebrosidase
- C. Galactocerebrosidase
- D. Alpha-L-iduronidase
- E. Alpha-galactosidase A (Correct Answer)
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***Alpha-galactosidase A***
- A deficiency in **alpha-galactosidase A** causes **Fabry disease**, which, like Hunter syndrome (iduronate sulfatase deficiency), is inherited in an **X-linked recessive** pattern.
- Both conditions primarily affect males, with carrier females potentially exhibiting milder symptoms.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- A deficiency in sphingomyelinase leads to **Niemann-Pick disease types A and B**, which are inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- This mode of inheritance differs from the X-linked pattern of Hunter syndrome.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in glucocerebrosidase causes **Gaucher disease**, inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- This is a common lysosomal storage disorder, but its inheritance pattern is distinct from X-linked disorders.
*Galactocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in galactocerebrosidase causes **Krabbe disease (globoid cell leukodystrophy)**, which is inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- Krabbe disease is a severe neurodegenerative disorder, but its genetic transmission is not X-linked.
*Alpha-L-iduronidase*
- A deficiency in **alpha-L-iduronidase** causes **Hurler syndrome (MPS I)**, which is inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- While both Hunter and Hurler syndromes are mucopolysaccharidoses, their genetic inheritance patterns are different.
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of a left-sided headache and right-sided blurry vision. She states that 2 weeks ago she developed dark urine and abdominal pain. She thought it was a urinary tract infection so she took trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole that she had left over. She planned on going to her primary care physician today but then she developed headache and blurry vision so she came to the emergency department. The patient states she is otherwise healthy. Her family history is significant for a brother with sickle cell trait. On physical examination, there is mild abdominal tenderness, and the liver edge is felt 4 cm below the right costal margin. Labs are drawn as below:
Hemoglobin: 7.0 g/dL
Platelets: 149,000/mm^3
Reticulocyte count: 5.4%
Lactate dehydrogenase: 3128 U/L
Total bilirubin: 2.1 mg/dL
Indirect bilirubin: 1.4 mg/dL
Aspartate aminotransferase: 78 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase: 64 U/L
A peripheral smear shows polychromasia. A Doppler ultrasound of the liver shows decreased flow in the right hepatic vein. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is pending. Which of the following tests, if performed, would most likely identify the patient’s diagnosis?
- A. Flow cytometry (Correct Answer)
- B. Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase levels
- C. Anti-histone antibodies
- D. Bone marrow biopsy
- E. Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***Flow cytometry***
- The patient's symptoms (headache, blurry vision, dark urine, abdominal pain, hepatomegaly) along with laboratory findings of **hemolytic anemia** (low hemoglobin, elevated reticulocyte count, high LDH, elevated indirect bilirubin) and signs of **thrombosis** (decreased hepatic vein flow, neurological symptoms) are highly suggestive of **paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)**.
- **Flow cytometry** is the gold standard for diagnosing PNH by detecting the absence of **CD55** and **CD59** on red blood cells, granulocytes, and monocytes, indicating a deficiency in the **GPI anchor protein**.
*Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase levels*
- **G6PD deficiency** typically presents with hemolytic anemia triggered by **oxidant stressors** (like trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) but does not typically cause **thrombosis** or widespread organ involvement (e.g., hepatic vein thrombosis, neurological symptoms) as seen in this patient.
- Measuring G6PD levels would be appropriate if G6PD deficiency was suspected, but the clinical picture points more strongly to PNH due to the thrombotic events.
*Anti-histone antibodies*
- **Anti-histone antibodies** are primarily associated with drug-induced **lupus erythematosus**, which can manifest with various systemic symptoms, but not typically with severe hemolytic anemia and thrombotic microangiopathy in this specific pattern.
- While drug exposure is present (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole), the overall clinical and lab findings (especially the severe hemolytic picture and thrombosis) are not characteristic of drug-induced lupus in this context.
*Bone marrow biopsy*
- A **bone marrow biopsy** might show findings consistent with increased erythropoiesis due to hemolysis but is not a primary diagnostic test for PNH or its associated thrombotic complications.
- While it could be part of an evaluation for underlying bone marrow disorders, it would not directly confirm a diagnosis of PNH, which requires specific surface marker detection.
*Hemoglobin electrophoresis*
- **Hemoglobin electrophoresis** is used to diagnose **hemoglobinopathies** such as **sickle cell disease** or **thalassemia**. The patient's brother has sickle cell trait, but the patient's symptoms, particularly the prominent hemolytic anemia and thrombotic events, are not typical of a hemoglobinopathy in this acute presentation.
- While it could rule out a hemoglobinopathy, it wouldn't explain the full spectrum of symptoms, especially the thrombosis and the specific pattern of hemolysis (e.g., elevated LDH, indirect bilirubin).
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 8: A 22-year-old man presents to the physician due to a progressively worsening weakness and an increasingly large abdomen. He notes that he eats well and is fairly active; however, his abdomen has become increasingly protuberant. He also complains of easy bruisability. His medical history is not significant and he takes no medications. Physical examination reveals hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. Several bruises can be seen on the inside of his arms and legs. His skin has a yellowish tinge to it. Laboratory testing shows the following:
Hematocrit 25%
Erythrocyte count 2.5 x 106/mm3
Thrombocyte count 25,000/mm3
A bone marrow biopsy shows a crinkled-paper appearance to the macrophages. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Arylsulfatase A
- B. Sphingomyelinase
- C. α-galactosidase
- D. Hexosaminidase
- E. β-glucosidase (Correct Answer)
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***β-glucosidase***
- The patient's symptoms (hepatosplenomegaly, easy bruisability, anemia, thrombocytopenia) and the characteristic **crinkled-paper appearance of macrophages** on bone marrow biopsy are pathognomonic for **Gaucher disease**.
- **Gaucher disease** is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme **β-glucosidase** (also known as glucocerebrosidase), leading to the accumulation of glucocerebroside.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- Deficiency of **arylsulfatase A** causes **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, characterized by progressive demyelination and neurological symptoms, not the hematological and visceral findings seen here.
- While it is also a lysosomal storage disorder, the clinical presentation and specific cell morphology are distinct.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- Deficiency of **sphingomyelinase** leads to **Niemann-Pick disease**, which shares some features with Gaucher disease, such as hepatosplenomegaly.
- However, the characteristic cell found in Niemann-Pick disease is a lipid-laden macrophage with a **foamy appearance**, not a "crinkled-paper" appearance.
*α-galactosidase*
- Deficiency of **α-galactosidase A** causes **Fabry disease**, an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder.
- Symptoms include episodic pain, acroparesthesias, angiokeratomas, and renal/cardiac involvement, which are not described in this patient.
*Hexosaminidase*
- Deficiency of **hexosaminidase A** causes **Tay-Sachs disease**, a lysosomal storage disorder primarily affecting the central nervous system.
- It is characterized by progressive neurodegeneration, developmental delay, and a **cherry-red spot** on the retina, without the hepatosplenomegaly or characteristic macrophages seen in this case.
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 9: An 18-month-old girl is brought to the pediatrician’s office for failure to thrive and developmental delay. The patient’s mother says she has not started speaking and is just now starting to pull herself up to standing position. Furthermore, her movement appears to be restricted. Physical examination reveals coarse facial features and restricted joint mobility. Laboratory studies show increased plasma levels of several enzymes. Which of the following is the underlying biochemical defect in this patient?
- A. Congenital lack of lysosomal formation
- B. Inappropriate protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum
- C. Failure of mannose phosphorylation (Correct Answer)
- D. Inappropriate degradation of lysosomal enzymes
- E. Misfolding of nuclear proteins
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***Failure of mannose phosphorylation***
- The constellation of **failure to thrive**, **developmental delay**, **coarse facial features**, restricted joint mobility, and elevated plasma enzymes in an 18-month-old girl is highly suggestive of **I-cell disease** (mucolipidosis type II).
- **I-cell disease** is caused by the deficiency of **N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase**, an enzyme responsible for phosphorylating mannose residues on lysosomal enzymes, which is crucial for proper targeting to the lysosome.
*Congenital lack of lysosomal formation*
- **Lysosomes** are present in this condition, but their enzymes are misdirected.
- A congenital lack of lysosomal formation would present with even more severe and widespread cellular dysfunction, possibly incompatible with life beyond early embryonic stages.
*Inappropriate protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum*
- Proteins destined for the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are typically targeted by an N-terminal signal peptide and then processed within the ER.
- While ER dysfunction can cause various disorders, the specific symptoms and enzyme elevations point away from a primary ER targeting defect related to lysosomal enzymes.
*Inappropriate degradation of lysosomal enzymes*
- In I-cell disease, lysosomal enzymes are synthesized but are **not properly targeted to the lysosomes**; instead, they are secreted into the bloodstream, leading to their elevated plasma levels.
- While some degradation might occur, the primary issue is mis-packaging and secretion, not increased degradation within the cell.
*Misfolding of nuclear proteins*
- Misfolding of nuclear proteins can lead to a variety of genetic disorders and cellular stress responses, but the clinical presentation, particularly the accumulation of undegraded material and elevated plasma lysosomal enzymes, is not characteristic of primary nuclear protein misfolding.
- The pathology in I-cell disease centers on lysosomal dysfunction rather than nuclear protein abnormalities.
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG Question 10: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother for evaluation of recurrent infections and easy bruising. He has been hospitalized 3 times for severe skin and respiratory infections, which responded to treatment with antibiotics. Examination shows sparse silvery hair. The skin is hypopigmented and there are diffuse petechiae. Laboratory studies show a hemoglobin concentration of 8 g/dL, leukocyte count of 3000/mm3, and platelet count of 45,000/mm3. A peripheral blood smear shows giant cytoplasmic granules in granulocytes and platelets. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Defective tyrosine kinase gene
- B. WAS gene mutation
- C. Defective NADPH oxidase
- D. Defective lysosomal trafficking regulator gene (Correct Answer)
- E. Defective CD40 ligand
Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies Explanation: ***Defective lysosomal trafficking regulator gene***
- This clinical presentation including **recurrent infections**, **easy bruising (thrombocytopenia)**, **sparse silvery hair**, **hypopigmented skin**, and **giant cytoplasmic granules in granulocytes and platelets** is characteristic of **Chediak-Higashi syndrome**.
- **Chediak-Higashi syndrome** is an **autosomal recessive disorder** caused by a mutation in the **LYST (lysosomal trafficking regulator)** gene, leading to defective lysosomal function and formation of giant granules.
*Defective tyrosine kinase gene*
- A defective tyrosine kinase gene (such as **BTK**) is associated with **X-linked agammaglobulinemia (Bruton's agammaglobulinemia)**, which features recurrent bacterial infections due to absent B cells and immunoglobulins.
- It does not typically present with **oculocutaneous albinism**, **bleeding diathesis**, or **giant granules** in white blood cells.
*WAS gene mutation*
- A **WAS gene mutation** causes **Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome**, an **X-linked recessive disorder** characterized by the triad of **thrombocytopenia with small platelets**, **eczema**, and **recurrent infections**.
- While it involves recurrent infections and easy bruising, it does not include **silvery hair**, **hypopigmentation**, or **giant cytoplasmic granules**.
*Defective NADPH oxidase*
- A defective **NADPH oxidase** causes **Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD)**, characterized by **recurrent severe bacterial and fungal infections** due to impaired phagocyte oxidative burst.
- CGD is not associated with **silvery hair**, **hypopigmentation**, **thrombocytopenia**, or the presence of **giant cytoplasmic granules**.
*Defective CD40 ligand*
- A defective **CD40 ligand** on T cells causes **Hyper-IgM syndrome**, an **X-linked immunodeficiency** characterized by normal or elevated IgM levels but low levels of IgG, IgA, and IgE, leading to recurrent infections.
- It does not present with **silvery hair**, **hypopigmentation**, or the characteristic **hematologic abnormalities** seen in this patient.
More Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.