Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Lipid storage diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
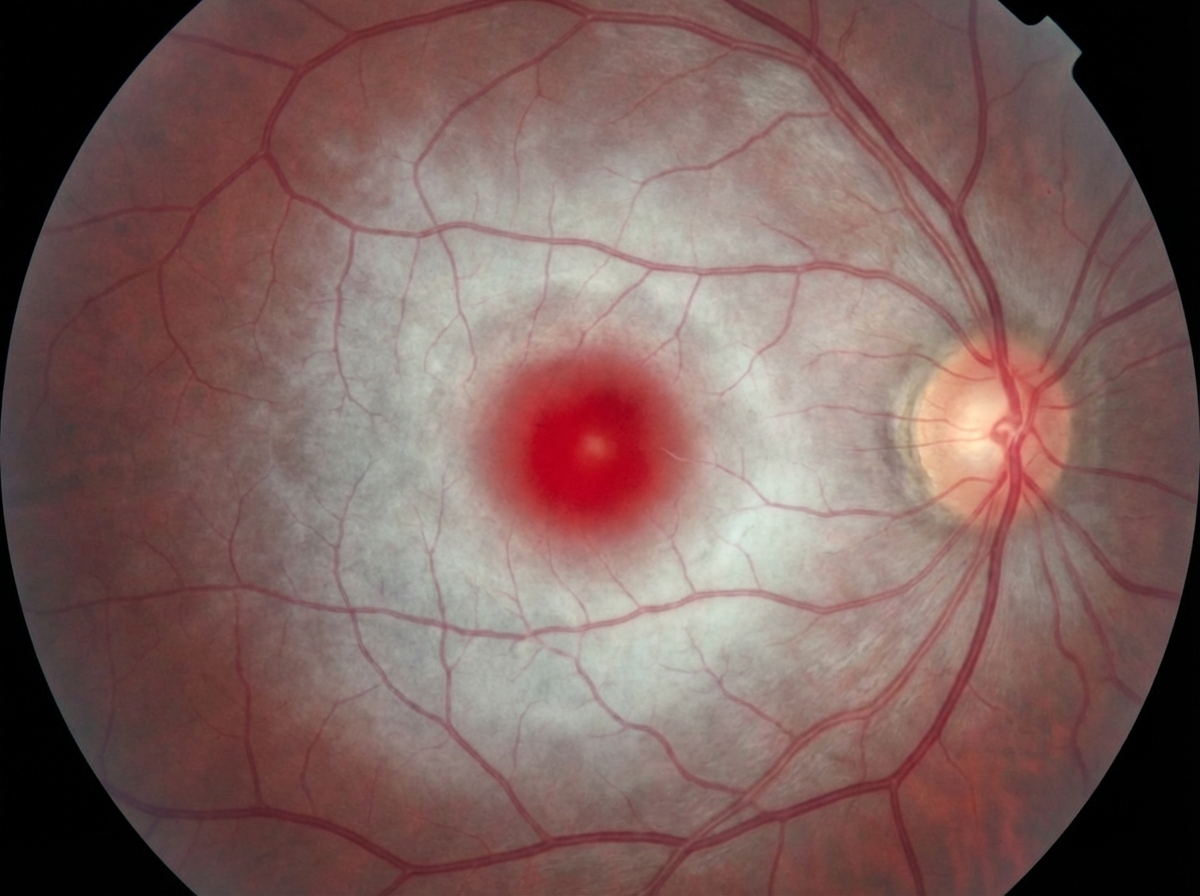
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 1: A 7-month-old boy is brought by his parents to the pediatrician’s office. His mother says the child has been weakening progressively and is not as active as he used to be when he was born. His condition seems to be getting worse, especially over the last month. He was born at 41 weeks through normal vaginal delivery. There were no complications observed during the prenatal period. He was progressing well over the 1st few months and achieving the appropriate milestones. On examination, his abdomen appears soft with no liver enlargement. The patient appears to be dehydrated and lethargic. The results of a fundoscopic examination are shown in the picture. A blood test for which of the following enzymes is the next best assay to evaluate this patient's health?
- A. Acid alpha-glucosidase
- B. Hexosaminidase (Correct Answer)
- C. Sphingomyelinase
- D. Glucocerebrosidase
- E. Arylsulfatase A
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***Hexosaminidase***
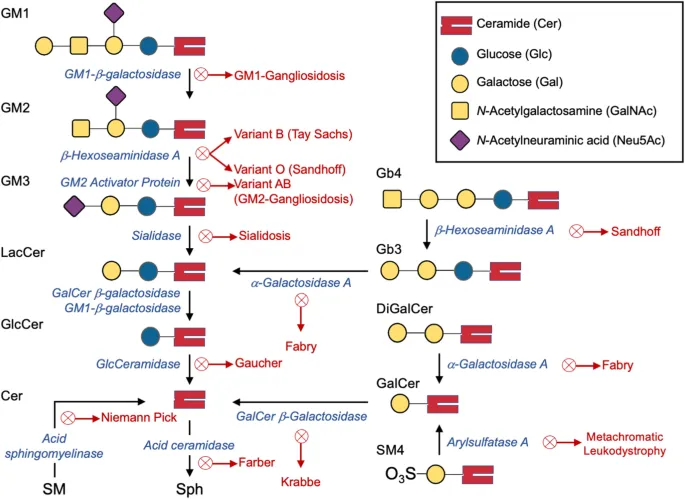
- The symptoms and history suggest **Tay-Sachs disease**, characterized by progressive weakness and developmental delay, often linked to **deficiency in hexosaminidase A**.
- A fundoscopic exam typically reveals a **cherry-red spot**, consistent with this condition, making hexosaminidase testing essential for diagnosis.
- Tay-Sachs results from accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside** in neurons due to hexosaminidase A deficiency.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- This enzyme is primarily associated with **Gaucher's disease**, which does not match the clinical features presented here.
- Symptoms of Gaucher's disease include **hepatosplenomegaly** and bone pain, not primarily weakness or lethargy in a young infant.
*Acid alpha-glucosidase*
- Generally tested for **Pompe disease**, which typically presents with **muscle weakness and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy**, not solely lethargy and failure to thrive.
- The clinical presentation in this case does not indicate glycogen storage disorder symptoms.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- This enzyme deficiency relates to **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, which often features neurological decline rather than isolated lethargy in infants.
- The specific symptoms and age do not align with the typical findings of this condition.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- Linked to **Niemann-Pick disease**, characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly** and neurological deterioration, absent in this scenario.
- The presentation of weakness does not match the classic signs expected with sphingomyelinase deficiency.
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 2: An 8-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents for gradually increasing loss of neck control and inability to roll over for the past 2 months. During this time, he has had multiple episodes of unresponsiveness with a blank stare and fluttering of the eyelids. His parents state that he sometimes does not turn when called but gets startled by loud noises. He does not maintain eye contact. He was able to roll over from front to back at 5 months of age and has not yet begun to sit or crawl. His parents are of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. Neurological examination shows generalized hypotonia. Deep tendon reflexes are 3+ bilaterally. Plantar reflex shows extensor response bilaterally. Fundoscopy shows bright red macular spots bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Sphingomyelinase deficiency
- B. β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency
- C. α-galactosidase A deficiency
- D. ATP-binding cassette transporter mutation
- E. β-hexosaminidase A deficiency (Correct Answer)
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***β-hexosaminidase A deficiency***
- The constellation of **developmental regression** (loss of neck control, inability to roll over), **hypotonia**, **exaggerated startle response**, **cherry-red macular spots**, and **Ashkenazi Jewish descent** is classic for **Tay-Sachs disease**, which is caused by a deficiency in β-hexosaminidase A.
- The patient's seizures ("unresponsiveness with a blank stare and fluttering of the eyelids") and **hyperreflexia** (3+ deep tendon reflexes, extensor plantar response) are also consistent with the progressive neurodegeneration seen in Tay-Sachs disease.
*Sphingomyelinase deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Niemann-Pick disease**, which can also present with **developmental regression**, **hypotonia**, and **cherry-red macular spots**.
- However, Niemann-Pick disease typically involves **hepatosplenomegaly** and **pulmonary involvement**, which are not mentioned in this patient's presentation.
*β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency*
- This deficiency leads to **Gaucher disease**, characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly**, **bone crises**, and cytopenias.
- While some forms can have neurological symptoms, the classic cherry-red spot and pronounced developmental regression as described are not typical of Gaucher disease.
*α-galactosidase A deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Fabry disease**, which is an **X-linked lysosomal storage disorder** presenting with **neuropathic pain**, **angiokeratomas**, **renal disease**, and **cardiac involvement** in adolescence or adulthood.
- It does not present with infantile neurodegeneration or cherry-red spots.
*ATP-binding cassette transporter mutation*
- Mutations in ABC transporters can lead to various disorders, such as **adrenoleukodystrophy** (deficiency in VLCFA transport) or **cystic fibrosis**.
- These conditions do not present with the specific combination of symptoms, especially the cherry-red macula and profound developmental regression, seen in this infant.
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 3: An 18-month-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 2-day history of cough, fever, and lethargy. He has been admitted to the hospital twice during the past year for pneumonia. He can stand without support but has not started to walk. He speaks in bisyllables. He is at the 3rd percentile for height and 4th percentile for weight. Examination shows diffuse crackles over bilateral lung fields. Abdominal examination shows hepatosplenomegaly. Fundoscopy shows bright red macular spots. Despite being given appropriate antibiotic therapy, the patient dies. A photomicrograph of a section of the spleen obtained during autopsy is shown. Accumulation of which of the following substances is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Ceramide trihexoside
- B. Cerebroside sulfate
- C. Glucocerebroside
- D. Sphingomyelin (Correct Answer)
- E. Limit dextrin
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***Sphingomyelin***
- The patient's history of **recurrent pneumonia**, **hepatosplenomegaly**, **developmental delay** (not walking, bisyllables at 18 months), **failure to thrive**, and **cherry-red macular spots** (on fundoscopy) are classic signs of **Niemann-Pick disease**.
- **Niemann-Pick disease** is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme **acid sphingomyelinase**, leading to the accumulation of **sphingomyelin** in various tissues.
*Ceramide trihexoside*
- Accumulation of **ceramide trihexoside** is characteristic of **Fabry disease**, an X-linked recessive lysosomal storage disorder.
- While Fabry disease can cause renal failure, angiokeratomas, and peripheral neuropathy, it does not typically present with **hepatosplenomegaly**, **recurrent pneumonia**, or **cherry-red macular spots** in infancy.
*Cerebroside sulfate*
- Accumulation of **cerebroside sulfate** (sulfatide) is characteristic of **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder.
- This condition primarily affects the **nervous system**, leading to demyelination and neurological deterioration, but it does not present with **hepatosplenomegaly** or **cherry-red macula**.
*Glucocerebroside*
- Accumulation of **glucocerebroside** is characteristic of **Gaucher disease**, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder.
- While Gaucher disease causes **hepatosplenomegaly** and can lead to bone crises, it does not typically present with **cherry-red macular spots**, severe early developmental delay, or recurrent pulmonary infections in the same manner as Niemann-Pick.
*Limit dextrin*
- Accumulation of **limit dextrin** is associated with **Cori disease** (Type III glycogen storage disease).
- This disorder primarily affects the **liver** and **muscles**, causing hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, and myopathy, but it does not present with **cherry-red macular spots** or specific developmental delays and recurrent infections seen in this patient.
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of fever and recurrent episodes of jerky movements of his extremities for the past 6 hours. Pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated, and development was normal until the age of 1 year. The parents report that he has had gradual loss of speech, vision, and motor skills over the past year. During this time, he has been admitted to the hospital three times because of myoclonic seizures. Physical examination shows hypertonicity of the upper and lower extremities. Fundoscopic examination shows pallor of the optic disc bilaterally. An MRI of the brain shows brain atrophy and hyperintensity of the periventricular and subcortical areas. Two days after admission, the patient dies. Histopathologic examination of the brain shows aggregation of globoid cells and loss of glial cells. The patient’s condition was most likely caused by a deficiency of which of the following enzymes?
- A. β-Galactocerebrosidase (Correct Answer)
- B. β-Glucocerebrosidase
- C. Arylsulfatase A
- D. Sphingomyelinase
- E. β-Hexosaminidase A
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***β-Galactocerebrosidase***
- The clinical presentation, including the **rapid neurodegeneration** (loss of speech, vision, motor skills), **hypertonicity**, **optic disc pallor**, brain atrophy, and periventricular/subcortical hyperintensities on MRI, is highly consistent with **Krabbe disease**.
- The classic histopathologic finding of **globoid cells** (macrophages filled with undigested galactocerebroside) and **loss of glial cells** in the brain are pathognomonic for Krabbe disease, which is caused by a deficiency of **β-galactocerebrosidase**.
*β-Glucocerebrosidase*
- Deficiency of β-glucocerebrosidase causes **Gaucher disease**, which typically involves **hepatosplenomegaly**, **bone crises**, and **pancytopenia**.
- While some forms have neurological involvement, the characteristic globoid cells and rapid neurodegeneration seen here are not typical for Gaucher disease.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- Deficiency of arylsulfatase A leads to **metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD)**, which also presents with **progressive neurological deterioration**, motor regression, and demyelination.
- However, MLD is characterized by the accumulation of **sulfatides** in white matter and detection of **metachromatic granules** in nerves and urine, not globoid cells.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- Deficiency of sphingomyelinase causes **Niemann-Pick disease**, which is characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly**, **cherry-red spots** in the macula (in type A), and foam cells in various tissues.
- The neurological symptoms and brain pathology in this child are not consistent with Niemann-Pick disease.
*β-Hexosaminidase A*
- Deficiency of β-hexosaminidase A causes **Tay-Sachs disease**, which presents with **progressive neurodegeneration**, **cherry-red spots** in the macula, and **exaggerated startle response**.
- While it causes loss of motor skills and vision, the severe demyelination with periventricular hyperintensities and globoid cells are not features of Tay-Sachs disease (which primarily involves ganglioside accumulation).
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 5: A 7-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his parents due to progressively worsening weakness for the last three months. The parents also describe the boy as having an exaggerated response when startled as well as diminishing response to visual stimuli. At birth, the boy was healthy and remained as such for the first few months of life. The mother says pregnancy was unremarkable, and the boy was born at 39 weeks with no complications during delivery. He is up to date on his vaccinations. The boy's grandparents immigrated from an eastern European country. Physical examination reveals hyperreflexia. Abdominal examination reveals no abnormalities. On fundoscopy, the following is seen. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Arylsulfatase A
- B. β-Glucosidase
- C. α-Galactosidase
- D. Hexosaminidase B
- E. Hexosaminidase A (Correct Answer)
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***Hexosaminidase A***
- Deficiency of **Hexosaminidase A** leads to **Tay-Sachs disease**, characterized by deterioration in motor and cognitive functions, aligning with the symptoms of weakness and abnormal responses.
- The condition is associated with a **cherry-red spot** on the retina, often observed in patients, further confirming the diagnosis.
- **Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry** is a key risk factor, consistent with the patient's eastern European heritage.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- Deficiency causes **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, which typically presents with **ataxia** and loss of previously attained skills, but not the exaggerated startle response noted in this case.
- The condition is not commonly associated with the specific visual and neurologic symptoms observed in the patient.
*β-Glucosidase*
- Deficiency leads to **Gaucher's disease**, which presents with splenomegaly, bone pain, and anemia, rather than the neurological symptoms seen here.
- The symptoms do not match the **progressive weakness** and startle reflex changes described.
*α-Galactosidase*
- Lack of this enzyme results in **Fabry disease**, which mainly causes pain episodes, skin lesions, and organ dysfunction, especially renal involvement.
- Neurological symptoms described here do not fit the typical presentation seen in Fabry disease.
*Hexosaminidase B*
- Deficiency causes **Sandhoff disease**, which presents similarly to Tay-Sachs with developmental regression and cherry-red spot.
- However, Sandhoff disease typically includes **hepatosplenomegaly**, which is notably absent in this patient on abdominal examination.
- The normal abdominal findings help distinguish this from Hexosaminidase A deficiency.
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A 24-year-old man comes to the physician because of chronic fatigue and generalized weakness after exertion. His legs feel stiff after walking long distances and he has leg cramps after climbing stairs. His symptoms are always relieved by rest. Urine dipstick shows 3+ blood and urinalysis is negative for RBCs. Baseline venous lactate and serum ammonia levels are collected, after which a blood pressure cuff is attached to the upper right arm. The patient is asked to continuously pump his right arm with the cuff inflated and additional venous samples are collected at 2-minute intervals. Analysis of the venous blood samples shows that, over time, serum ammonia levels increase and venous lactate levels remain stable. A biopsy of the right gastrocnemius muscle will most likely show which of the following?
- A. Intrafascicular CD8+ lymphocytic infiltration
- B. Endomysial fibrosis with absent dystrophin
- C. Intermyofibrillar proliferation of mitochondria
- D. Perivascular CD4+ lymphocytic infiltrate
- E. Subsarcolemmal periodic acid–Schiff-positive deposits (Correct Answer)
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***Subsarcolemmal acid–Schiff-positive deposits***
- The patient's symptoms (chronic fatigue, generalized weakness, leg stiffness, and cramps after exertion, relieved by rest) combined with the **ischemic forearm test** results (increased ammonia, stable lactate) are highly suggestive of **McArdle disease** (glycogen storage disease type V).
- McArdle disease is caused by a deficiency in **myophosphorylase**, leading to an inability to break down glycogen in muscles. Muscle biopsy in McArdle disease typically reveals **subsarcolemmal accumulation of glycogen**, which stains positive with periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) reagent.
*Intrafascicular CD8+ lymphocytic infiltration*
- This finding is characteristic of **polymyositis**, an inflammatory myopathy.
- Polymyositis would typically present with **progressive proximal muscle weakness** and elevated muscle enzymes, rather than activity-induced cramps and fatigue, and the ischemic forearm test would not show stable lactate.
*Endomysial fibrosis with absent dystrophin*
- This is a hallmark of **Duchenne muscular dystrophy**, a genetic disorder.
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy presents in early childhood with **progressive muscle degeneration**, Gower's sign, and significantly elevated creatine kinase, which is different from the described symptoms.
*Intermyofibrillar proliferation of mitochondria*
- This is characteristic of **mitochondrial myopathies**, such as ragged red fibers, often seen with specific stains like Gomori trichrome.
- While mitochondrial myopathies can cause exercise intolerance, the specific ischemic forearm test results (normal lactate response) do not align with a primary defect in aerobic respiration.
*Perivascular CD4+ lymphocytic infiltrate*
- This histological finding is typically associated with **dermatomyositis**, another inflammatory myopathy linked to specific skin lesions and muscle weakness.
- Dermatomyositis shares some features with polymyositis but has distinct perivascular inflammation and usually presents with pathognomonic skin rashes, which are absent in this case.
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 7: A 5-month-old boy presents with increasing weakness for the past 3 months. The patient’s mother says that the weakness is accompanied by dizziness, sweating, and vertigo early in the morning. Physical examination shows hepatomegaly. Laboratory findings show an increased amount of lactate, uric acid, and elevated triglyceride levels. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Hepatic glycogen phosphorylase
- B. Debranching enzyme
- C. Glucose-6-phosphatase (Correct Answer)
- D. Muscle glycogen phosphorylase
- E. Lysosomal α-1,4-glucosidase
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***Glucose-6-phosphatase***
- The constellation of **hypoglycemia** (weakness, dizziness, sweating, vertigo, especially early morning), **hepatomegaly**, **lactic acidosis**, **hyperuricemia**, and **hypertriglyceridemia** are classic features of **Type I glycogen storage disease (von Gierke disease)**, which is caused by a deficiency of **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- This enzyme is crucial for the final step of both **glycogenolysis** and **gluconeogenesis**, releasing free glucose into the bloodstream; its deficiency leads to an inability to maintain normal blood glucose levels during fasting and accumulation of glucose-6-phosphate, which shunts into other metabolic pathways.
*Hepatic glycogen phosphorylase*
- Deficiency in **hepatic glycogen phosphorylase** (Type VI glycogen storage disease, Hers disease) would cause **hepatomegaly** and **hypoglycemia**, but typically does not present with severe **lactic acidosis**, **hyperuricemia**, or **hypertriglyceridemia** to the same degree as von Gierke disease.
- The primary defect is in breaking down glycogen, leading to its accumulation in the liver, but the products of glycolysis can still exit the liver via gluconeogenesis.
*Debranching enzyme*
- Deficiency in **debranching enzyme** (Type III glycogen storage disease, Cori or Forbes disease) causes **hepatomegaly** and **hypoglycemia**, but usually presents with milder symptoms and less severe **lactic acidosis**, **hyperuricemia**, and **hypertriglyceridemia**.
- Patients often present with symptoms similar to Type I, but muscle involvement is also common, and **glycogen structures with short outer branches** are characteristic.
*Muscle glycogen phosphorylase*
- Deficiency in **muscle glycogen phosphorylase** (Type V glycogen storage disease, McArdle disease) primarily affects **skeletal muscle**, leading to exercise intolerance, muscle pain, and myoglobinuria.
- It does not typically cause **hypoglycemia** or **hepatomegaly**, as the liver enzyme is functional, and the symptoms described are systemic rather than muscle-specific.
*Lysosomal α-1,4-glucosidase*
- Deficiency in **lysosomal α-1,4-glucosidase** (Type II glycogen storage disease, Pompe disease) primarily affects the **heart, muscle, and liver**, causing severe **cardiomyopathy**, hypotonia, and **hepatomegaly**.
- While it involves glycogen accumulation, it typically does not present with **hypoglycemia** (as cytoplasmic glycogen metabolism is intact), **lactic acidosis**, or the specific metabolic derangements seen in this patient.
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 4-month-old boy is brought to his pediatrician for a well-child visit. His parents have noticed that he has had poor growth compared to his older siblings. The boy was delivered vaginally after a normal pregnancy. His temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 98/68 mmHg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 20/min. On exam, his abdomen appears protuberant, and the boy appears to have abnormally enlarged cheeks. A finger stick reveals that the patient’s fasting blood glucose is 50 mg/dL. On further laboratory testing, the patient is found to have elevated blood lactate levels, as well as no response to a glucagon stimulation test. What enzymatic defect is most likely present?
- A. Alpha-1,4-glucosidase
- B. Glycogen synthase
- C. Alpha-1,6-glucosidase
- D. Glucose-6-phosphatase (Correct Answer)
- E. Glycogen phosphorylase
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***Glucose-6-phosphatase***
- The patient's symptoms, including **hypoglycemia**, **hepatomegaly** (implied by protuberant abdomen), **lactic acidosis** (elevated lactate), and lack of response to **glucagon stimulation**, are classic for **Type I glycogen storage disease (von Gierke disease)**, which is caused by a deficiency in **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- This enzyme is crucial for the final step of both **glycogenolysis** and **gluconeogenesis**, and its deficiency prevents the liver from releasing glucose into the bloodstream, leading to severe hypoglycemia.
*Alpha-1,4-glucosidase*
- A deficiency in **alpha-1,4-glucosidase (acid maltase)** causes **Type II glycogen storage disease (Pompe disease)**, which primarily affects muscle (cardiac and skeletal).
- Symptoms include **cardiomyopathy**, **hypotonia**, and muscle weakness, and it does **not** typically present with hypoglycemia or lactic acidosis.
*Glycogen synthase*
- A deficiency in **glycogen synthase** would lead to an inability to synthesize glycogen, resulting in **hypoglycemia** but **low** (rather than high) glycogen levels.
- Patients typically experience fasting hypoglycemia, but **no hepatomegaly** or lactic acidosis would be expected.
*Alpha-1,6-glucosidase*
- A deficiency in **alpha-1,6-glucosidase (debranching enzyme)** causes **Type III glycogen storage disease (Cori disease)**.
- This condition presents with **hepatomegaly**, **hypoglycemia**, and sometimes muscle weakness, but patients typically **do respond to glucagon** and have less severe lactic acidosis compared to Type I.
*Glycogen phosphorylase*
- A deficiency in **glycogen phosphorylase (hepatic form, Type VI GSD or Hers disease)** primarily affects the liver's ability to break down glycogen.
- This typically causes **hepatomegaly** and **hypoglycemia**, but usually, the patients **respond to glucagon** because other pathways for glucose release (like gluconeogenesis) are intact.
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 9: A 3-month-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her parents after she appeared to have a seizure at home. On presentation, she no longer has convulsions though she is still noted to be lethargic. She was born through uncomplicated vaginal delivery and was not noted to have any abnormalities at the time of birth. Since then, she has been noted by her pediatrician to be falling behind in height and weight compared to similarly aged infants. Physical exam reveals an enlarged liver, and laboratory tests reveal a glucose of 38 mg/dL. Advanced testing shows that a storage molecule present in the cells of this patient has abnormally short outer chains. Which of the following enzymes is most likely defective in this patient?
- A. Debranching enzyme (Correct Answer)
- B. Hepatic phosphorylase
- C. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- D. Muscle phosphorylase
- E. Branching enzyme
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***Debranching enzyme***
- The presence of **abnormally short outer chains** in a storage molecule, along with **hypoglycemia** and **hepatomegaly**, strongly suggests a defect in the **debranching enzyme** (Type III Glycogen Storage Disease or Cori/Forbes disease). This enzyme is responsible for breaking down the α-1,6 glycosidic bonds at the branch points of glycogen.
- Deficiency leads to the accumulation of glycogen with **short branches**, affecting both liver and muscle.
*Hepatic phosphorylase*
- A defect in **hepatic phosphorylase** (Type VI Glycogen Storage Disease or Hers' disease) leads to similar symptoms like **hepatomegaly** and **hypoglycemia**.
- However, the glycogen structure would be normal, not characterized by abnormally short outer chains.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- A deficiency in **glucose-6-phosphatase** (Type I Glycogen Storage Disease or Von Gierke's disease) leads to severe **hypoglycemia**, **hepatomegaly**, and often **renal enlargement**.
- Glycogen structure in this condition is typically normal, with **increased hepatic glycogen stores**.
*Muscle phosphorylase*
- A deficiency in **muscle phosphorylase** (Type V Glycogen Storage Disease or McArdle's disease) primarily affects skeletal muscle function, causing **muscle cramping**, pain, and **fatigue during exercise**.
- It does not typically present with severe **hypoglycemia** or **hepatomegaly** because the liver enzyme is unaffected.
*Branching enzyme*
- A defect in the **branching enzyme** (Type IV Glycogen Storage Disease or Andersen's disease) results in glycogen with **abnormally long unbranched chains** and fewer branch points.
- This typically leads to **cirrhosis** and liver failure, and while hypoglycemia can occur, the characteristic glycogen structure is the opposite of what is described in the patient.
Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A 12-year-old girl comes to the clinic with a grossly enlarged abdomen. She has a history of frequent episodes of weakness, sweating, and pallor that are eliminated by eating. Her development has been slow. She started to walk unassisted at 2 years and was not performing well at school. Physical examination reveals a blood pressure of 100/60 mm Hg, heart rate of 80/min, and temperature of 36.9°C (98.4℉). On physical examination, the liver is enlarged, firm, and palpable up to the pelvis. The spleen and kidney are not palpable. Laboratory investigation reveals low blood glucose and pH with high lactate, triglycerides, ketones, and free fatty acids. The liver biopsy revealed high glycogen content. Hepatic glycogen structure was normal. The enzyme assay performed on the biopsy tissue revealed very low glucose-6-phosphatase levels. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pompe's disease
- B. Cori's disease
- C. Hereditary hemochromatosis
- D. Von-Gierke's disease (Correct Answer)
- E. McArdle disease
Lipid storage diseases Explanation: ***Von-Gierke's disease***
- The combination of **hepatomegaly**, **hypoglycemia** (causing weakness, sweating, pallor), **lactic acidosis**, **hyperlipidemia**, and elevated ketones points to a severe defect in glucose metabolism.
- **Very low glucose-6-phosphatase levels** on liver biopsy and normal hepatic glycogen structure are pathognomonic for Von-Gierke's disease (Glycogen Storage Disease Type I).
*Pompe's disease*
- This is a **lysosomal storage disease** affecting **alpha-1,4-glucosidase**, leading to glycogen accumulation in lysosomes.
- It primarily affects the **heart** and skeletal muscles and would not present with severe lactic acidosis and hyperlipidemia.
*Cori's disease*
- This is **Glycogen Storage Disease Type III**, caused by a deficiency in the **debranching enzyme** (amylo-alpha-1,6-glucosidase).
- While it can cause hepatomegaly and hypoglycemia, the hepatic glycogen structure would be abnormal due to incompletely debranched glycogen, and glucose-6-phosphatase levels would be normal.
*Hereditary hemochromatosis*
- This is an **iron overload disorder** leading to iron deposition in organs like the liver, heart, and pancreas.
- It would present with symptoms related to organ damage from iron accumulation, such as liver cirrhosis and diabetes, not the metabolic derangements seen here.
*McArdle disease*
- This is **Glycogen Storage Disease Type V**, due to a deficiency in **muscle glycogen phosphorylase**.
- It primarily causes exercise-induced muscle pain, cramping, and fatigue due to an inability to break down muscle glycogen for energy, not systemic metabolic disturbances or hepatomegaly.
More Lipid storage diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.