Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Diagnostic approaches. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
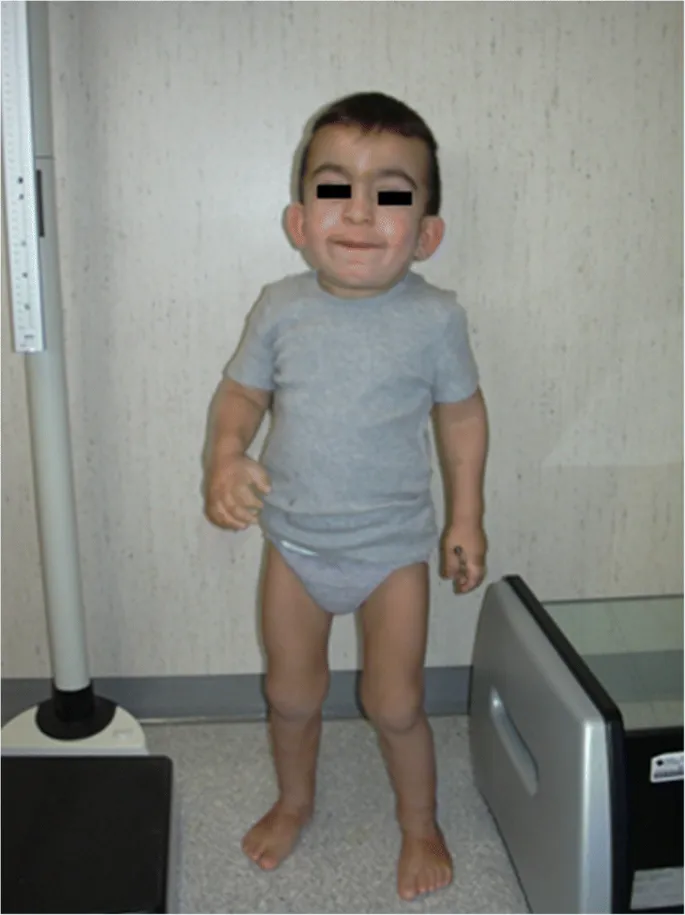
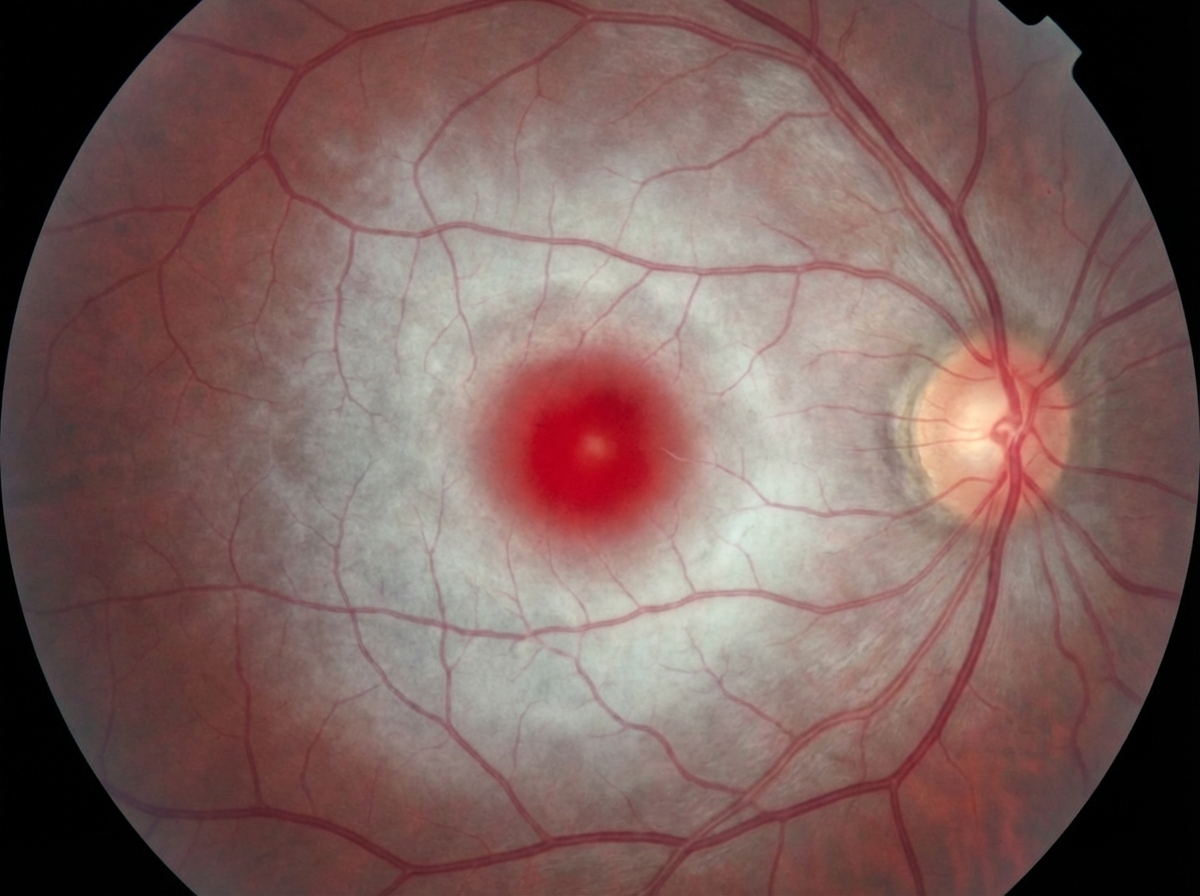
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 1: A 7-month-old boy is brought by his parents to the pediatrician’s office. His mother says the child has been weakening progressively and is not as active as he used to be when he was born. His condition seems to be getting worse, especially over the last month. He was born at 41 weeks through normal vaginal delivery. There were no complications observed during the prenatal period. He was progressing well over the 1st few months and achieving the appropriate milestones. On examination, his abdomen appears soft with no liver enlargement. The patient appears to be dehydrated and lethargic. The results of a fundoscopic examination are shown in the picture. A blood test for which of the following enzymes is the next best assay to evaluate this patient's health?
- A. Acid alpha-glucosidase
- B. Hexosaminidase (Correct Answer)
- C. Sphingomyelinase
- D. Glucocerebrosidase
- E. Arylsulfatase A
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Hexosaminidase***
- The symptoms and history suggest **Tay-Sachs disease**, characterized by progressive weakness and developmental delay, often linked to **deficiency in hexosaminidase A**.
- A fundoscopic exam typically reveals a **cherry-red spot**, consistent with this condition, making hexosaminidase testing essential for diagnosis.
- Tay-Sachs results from accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside** in neurons due to hexosaminidase A deficiency.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- This enzyme is primarily associated with **Gaucher's disease**, which does not match the clinical features presented here.
- Symptoms of Gaucher's disease include **hepatosplenomegaly** and bone pain, not primarily weakness or lethargy in a young infant.
*Acid alpha-glucosidase*
- Generally tested for **Pompe disease**, which typically presents with **muscle weakness and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy**, not solely lethargy and failure to thrive.
- The clinical presentation in this case does not indicate glycogen storage disorder symptoms.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- This enzyme deficiency relates to **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, which often features neurological decline rather than isolated lethargy in infants.
- The specific symptoms and age do not align with the typical findings of this condition.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- Linked to **Niemann-Pick disease**, characterized by **hepatosplenomegaly** and neurological deterioration, absent in this scenario.
- The presentation of weakness does not match the classic signs expected with sphingomyelinase deficiency.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 2: A deficiency in which of the following lysosomal enzymes is inherited in a pattern similar to a deficiency of iduronate sulfatase (Hunter syndrome)?
- A. Sphingomyelinase
- B. Glucocerebrosidase
- C. Galactocerebrosidase
- D. Alpha-L-iduronidase
- E. Alpha-galactosidase A (Correct Answer)
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Alpha-galactosidase A***
- A deficiency in **alpha-galactosidase A** causes **Fabry disease**, which, like Hunter syndrome (iduronate sulfatase deficiency), is inherited in an **X-linked recessive** pattern.
- Both conditions primarily affect males, with carrier females potentially exhibiting milder symptoms.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- A deficiency in sphingomyelinase leads to **Niemann-Pick disease types A and B**, which are inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- This mode of inheritance differs from the X-linked pattern of Hunter syndrome.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in glucocerebrosidase causes **Gaucher disease**, inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- This is a common lysosomal storage disorder, but its inheritance pattern is distinct from X-linked disorders.
*Galactocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in galactocerebrosidase causes **Krabbe disease (globoid cell leukodystrophy)**, which is inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- Krabbe disease is a severe neurodegenerative disorder, but its genetic transmission is not X-linked.
*Alpha-L-iduronidase*
- A deficiency in **alpha-L-iduronidase** causes **Hurler syndrome (MPS I)**, which is inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- While both Hunter and Hurler syndromes are mucopolysaccharidoses, their genetic inheritance patterns are different.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 3: A 37-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician at 13 weeks' gestation for a prenatal visit. She feels well. Her only medication is folic acid. Vital signs are within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 13-week gestation. Ultrasonography shows a nuchal translucency above the 99th percentile. Maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A is decreased and human chorionic gonadotropin concentrations are elevated to 2 times the median level. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Chorionic villus sampling (Correct Answer)
- B. Cell-free DNA testing
- C. Triple screening test
- D. Amniocentesis
- E. Quadruple marker test
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Chorionic villus sampling***
- This procedure can be performed between **10 to 13 weeks of gestation** to obtain fetal cells for genetic analysis, which is within the patient's gestational age.
- It provides a definitive diagnosis of **chromosomal abnormalities** by directly sampling placental tissue, which shares the same genetic material as the fetus.
*Cell-free DNA testing*
- While it has high sensitivity and specificity for various **aneuploidies**, it is a **screening test**, not a diagnostic one.
- An abnormal result from cell-free DNA testing still requires **confirmatory diagnostic testing** such as CVS or amniocentesis.
*Triple screening test*
- This test is typically performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation**, which is too late to confirm the findings presented at 13 weeks gestation.
- It measures **AFP, hCG, and unconjugated estriol**, and an abnormal result would indicate a need for further diagnostic testing.
*Amniocentesis*
- This procedure is generally performed later in pregnancy, typically between **15 and 20 weeks gestation**, so it would require waiting several more weeks.
- While it provides definitive genetic results, **chorionic villus sampling is preferred at 13 weeks** due to earlier diagnostic potential.
*Quadruple marker test*
- This test is also performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation** and measures **AFP, hCG, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin A**.
- It is a **screening test**, similar to the triple screen, and does not provide a definitive diagnosis, requiring further confirmatory testing if abnormal.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 4: A 4-month-old male infant is brought in because he rejects food and is losing weight. He had several upper respiratory tract infections during the last 2 months. Upon examination, hepatosplenomegaly is noted, as well as mild hypotonia. During the next few weeks, hepatosplenomegaly progresses, the boy fails to thrive, and he continues to reject food. He has a blood pressure of 100/70 mm Hg and heart rate of 84/min. Blood tests show pancytopenia and elevated levels of transaminases. Slit lamp examination shows bilateral cherry-red spots on the macula. Chest X-ray shows a reticulonodular pattern and calcified nodules. Biopsy of the liver shows foamy histiocytes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Niemann-Pick disease type A (Correct Answer)
- B. Tay-Sachs disease
- C. Gaucher disease
- D. Wolman disease
- E. GM1 gangliosidosis
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Niemann-Pick disease type A***
- This presentation of a 4-month-old with **failure to thrive**, progressive **hepatosplenomegaly**, **hypotonia**, recurrent infections, **pancytopenia**, elevated transaminases, **cherry-red spots** on the macula, and **foamy histiocytes** in the liver biopsy is characteristic of Niemann-Pick disease type A.
- Niemann-Pick disease type A is a **lysosomal storage disorder** caused by a deficiency of the enzyme **sphingomyelinase**, leading to the accumulation of **sphingomyelin** in various tissues.
- The **foamy histiocytes** (lipid-laden macrophages) are a hallmark finding, and the **reticulonodular pattern** on chest X-ray represents pulmonary infiltration.
*Incorrect: Tay-Sachs disease*
- While Tay-Sachs disease also presents with **cherry-red spots** and progressive neurological deterioration in infancy, it is caused by **hexosaminidase A deficiency**.
- Key differences: Tay-Sachs typically does **not** cause **hepatosplenomegaly** or **foamy histiocytes** in the liver; the primary pathology is neuronal accumulation of GM2 ganglioside.
- Patients usually present with developmental regression, exaggerated startle response, and hypotonia, but without the prominent organomegaly seen here.
*Incorrect: Gaucher disease*
- While Gaucher disease also presents with **hepatosplenomegaly** and can cause bone marrow involvement leading to **pancytopenia**, it typically does **not** feature **cherry-red spots** or such severe early neurological regression.
- It is caused by a deficiency of **glucocerebrosidase**, leading to accumulation of glucocerebroside in **Gaucher cells** (not foamy histiocytes).
- The infantile neuronopathic form (type 2) can present early but lacks cherry-red spots.
*Incorrect: Wolman disease*
- Wolman disease is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by **lysosomal acid lipase deficiency**, presenting with hepatosplenomegaly, failure to thrive, and foamy histiocytes.
- Key distinguishing feature: **bilateral adrenal calcifications** on imaging, which are pathognomonic for Wolman disease but not mentioned in this case.
- Does **not** typically cause cherry-red spots on fundoscopic examination.
*Incorrect: GM1 gangliosidosis*
- GM1 gangliosidosis can present with hepatosplenomegaly, developmental delay, and **cherry-red spots** (in about 50% of cases).
- However, it is characterized by distinctive **coarse facial features**, **skeletal dysplasia** (dysostosis multiplex), and **vacuolated lymphocytes** on blood smear.
- The **foamy histiocytes** and prominent pulmonary involvement are more characteristic of Niemann-Pick disease type A.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 5: A 3-month-old boy presents for routine health maintenance. The patient has coarse facial features and stiff joint movements with restricted passive and active range of motion. He also has problems following objects with his eyes and seems not to focus on anything. On physical examination, the corneas are clouded, and the patient fails to meet any 3-month developmental milestones. Genetic testing and histopathology are performed and reveal failure of a cellular structure to phosphorylate mannose residues on glycoproteins. An electron microscopy image of one of this patient’s cells is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Adrenoleukodystrophy
- B. Kartagener syndrome
- C. Tay-Sachs disease
- D. Inclusion cell disease (Correct Answer)
- E. Diamond-Blackfan anemia
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Inclusion cell disease***
- This condition is characterized by a **failure to phosphorylate mannose residues** on glycoproteins due to a defective **N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase** enzyme.
- The clinical presentation of **coarse facial features, stiff joint movements**, clouded corneas, and developmental delay is classical for **I-cell disease** (mucolipidosis II), where lysosomal enzymes are **mistargeted and secreted from cells** instead of being properly delivered to lysosomes, resulting in **lysosomes that lack hydrolytic enzymes** and accumulate undigested substrates (visible as inclusions on electron microscopy).
*Adrenoleukodystrophy*
- This is an **X-linked disorder** affecting very long chain fatty acid metabolism, leading to their accumulation in the **adrenal glands** and **white matter of the brain**.
- While it causes **neurological dysfunction** and adrenal insufficiency, it does not typically present with the coarse facial features, corneal clouding, and skeletal abnormalities seen in this patient.
*Kartagener syndrome*
- This is a form of **primary ciliary dyskinesia** characterized by impaired ciliary movement due to structural defects in **dynein arms**.
- It presents with **recurrent respiratory infections** (sinusitis, bronchitis, bronchiectasis), **situs inversus** (in about 50% of cases), and infertility, which are unrelated to the patient's symptoms.
*Tay-Sachs disease*
- This is a **lysosomal storage disorder** caused by a deficiency of **hexosaminidase A**, leading to the accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside**.
- It causes **progressive neurological deterioration**, motor weakness, and a **cherry-red spot** on the macula, but not the coarse facial features or skeletal abnormalities described.
*Diamond-Blackfan anemia*
- This is a **congenital hypoplastic anemia** characterized by a defect in **erythroid progenitor cells**, leading to severe macrocytic anemia.
- It can be associated with various congenital anomalies, but the primary presentation is **anemia** and it does not involve the lysosomal storage defects or the characteristic facial and joint features seen in this case.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 6: A 26-year-old woman presents to a physician for genetic counseling, because she is worried about trying to have a child. Specifically, she had 2 siblings that died young from a lysosomal storage disorder and is afraid that her own children will have the same disorder. Her background is Ashkenazi Jewish, but she says that her husband's background is mixed European heritage. Her physician says that since her partner is not of Jewish background, their chance of having a child with Niemann-Pick disease is dramatically decreased. Which of the following genetic principles best explains why there is an increased prevalence of this disease in some populations?
- A. Natural selection
- B. Imprinting
- C. De novo mutations
- D. Gene flow
- E. Founder effect (Correct Answer)
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Founder effect***
- The **founder effect** occurs when a new population is established by a small number of individuals, leading to a **reduced genetic diversity** and an increased frequency of certain alleles that were present in the founders. This is particularly relevant in populations like **Ashkenazi Jews**, who descended from a small, isolated group with certain allele frequencies.
- In this scenario, the high prevalence of **Niemann-Pick disease** (and other genetic disorders) in the Ashkenazi Jewish population is due to their historical isolation and intermarriage within a relatively small gene pool, trapping and concentrating certain alleles.
*Natural selection*
- **Natural selection** typically describes the process by which traits that enhance survival and reproduction become more common in a population over time, or deleterious traits become less common.
- While it can influence disease prevalence, it doesn't primarily explain the disproportionately high frequency of rare recessive disorders in specific isolated populations in the manner described.
*Imprinting*
- **Genomic imprinting** refers to the phenomenon where certain genes are expressed in a **parent-of-origin-specific manner**, meaning that only the allele inherited from either the mother or the father is expressed.
- This mechanism explains certain genetic conditions but does not account for the increased prevalence of a recessive disorder due to population history and isolation.
*De novo mutations*
- **De novo mutations** are new genetic alterations that appear for the first time in an individual and are not inherited from either parent.
- While de novo mutations are a source of genetic variation, they do not explain the high prevalence of a specific ancestral allele within an entire population.
*Gene flow*
- **Gene flow** (or migration) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another, which tends to **decrease genetic differences** between populations and introduce new alleles.
- This principle would suggest a *reduction* in the prevalence of specific rare alleles over time as populations mix, rather than an *increase* in isolated groups.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 7: A 3-month-old infant is brought to her pediatrician for a well-child visit. The infant was born to a 22-year-old mother via a spontaneous vaginal delivery at 38 weeks of gestation in her home. She moved to the United States approximately 3 weeks ago from a small village. She reports that her infant had 2 episodes of non-bloody and non-bilious vomiting. The infant's medical history includes eczema and 2 seizure episodes that resolved with benzodiazepines in the emergency department. Physical examination is notable for a musty body odor, eczema, and a fair skin complexion. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Dietary restriction (Correct Answer)
- B. Abdominal radiography
- C. Dermatology consult
- D. MRI of the brain
- E. Antiepileptic drug
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Dietary restriction***
- The infant's symptoms, including **eczema**, **seizures**, **fair skin**, and a distinctive "musty" odor, strongly suggest **phenylketonuria (PKU)**. PKU is an **autosomal recessive metabolic disorder** where the body cannot properly break down **phenylalanine**.
- The primary treatment for PKU is a **lifelong diet low in phenylalanine**. This involves restricting high-protein foods and using special medical formulas to provide adequate nutrition. Early and strict dietary management is crucial to prevent intellectual disability and other neurological complications.
*Abdominal radiography*
- While the infant experienced vomiting, the description of it being **non-bloody** and **non-bilious**, along with the absence of other gastrointestinal symptoms like distension, makes a significant abdominal pathology less likely than **metabolic derangement**.
- Abdominal radiography would be more appropriate for suspected **bowel obstruction** or perforation, for which there are no strong indications in this case.
*Dermatology consult*
- The presence of eczema is noted, but it is one of several symptoms pointing towards a **systemic metabolic disorder** rather than an isolated skin condition.
- Addressing the underlying metabolic cause (PKU) through dietary restriction will likely improve or resolve the eczema, making a consult for symptomatic treatment a secondary concern.
*MRI of the brain*
- The infant has experienced seizures, which often prompt neurological imaging. However, in the context of the other clinical findings (musty odor, fair skin, eczema), the seizures are highly suggestive of **metabolic encephalopathy** due to PKU.
- While an MRI might show changes related to chronic phenylalanine toxicity, the most urgent and effective intervention is to address the metabolic cause through **dietary restriction**.
*Antiepileptic drug*
- Starting an antiepileptic drug might control the seizures symptomatically, but it would **not address the underlying cause** of the seizures, which is the metabolic disturbance in PKU.
- **Untreated PKU** will lead to progressive neurological damage and intellectual disability even if seizures are controlled, highlighting the importance of root cause treatment.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 8: A research study evaluates three siblings with Niemann-Pick disease type C: a 6-year-old with ataxia and vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, a 10-year-old with hepatosplenomegaly and mild cognitive impairment, and a 14-year-old who is asymptomatic. Genetic testing reveals all three carry the same compound heterozygous NPC1 mutations. Fibroblast studies show similar cholesterol esterification defects and filipin staining patterns. Miglustat therapy is available. Evaluate the biological basis for phenotypic variability and optimal treatment allocation.
- A. Evaluate modifier genes, epigenetic factors, and biomarkers; treat based on individual risk stratification (Correct Answer)
- B. Treat all three immediately as genetic identity predicts identical disease course
- C. Treat only symptomatic siblings as asymptomatic carrier won't develop disease
- D. Delay all treatment until symptoms appear in the youngest to confirm diagnosis
- E. Treat the 6-year-old only as neurologic symptoms indicate blood-brain barrier dysfunction
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Evaluate modifier genes, epigenetic factors, and biomarkers; treat based on individual risk stratification***
- **Phenotypic discordance** in Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) despite identical genotypes suggests that **modifier genes**, **epigenetic factors**, and cellular environment dictate clinical onset and severity.
- Management must be personalized because **NPC1 mutations** and **filipin staining** do not perfectly correlate with clinical progression; biomarkers like **oxysterols** or **lysosphingolipids** help guide individual risk.
*Treat only symptomatic siblings as asymptomatic carrier won't develop disease*
- The asymptomatic 14-year-old is not a carrier but has already been confirmed to have **compound heterozygous NPC1 mutations** and pathognomonic **filipin staining**.
- This sibling has the disease and is at high risk for **late-onset neurological symptoms**, requiring proactive monitoring rather than being dismissed as a carrier.
*Treat all three immediately as genetic identity predicts identical disease course*
- Even with identical **NPC1 mutations**, clinical presentation varies significantly (from **supranuclear gaze palsy** to asymptomatic), meaning the disease course is not identical.
- While **Miglustat** is effective, immediate treatment in asymptomatic patients is debated; therapy is typically tailored to clinical or **biomarker evidence** of progression.
*Treat the 6-year-old only as neurologic symptoms indicate blood-brain barrier dysfunction*
- **Miglustat** crosses the **blood-brain barrier** to inhibit **glucosylceramide synthase**, but its use is not limited based on blood-brain barrier integrity.
- The 10-year-old already exhibits **hepatosplenomegaly** and **cognitive impairment**, which are clear indications for therapy to prevent further neurocognitive decline.
*Delay all treatment until symptoms appear in the youngest to confirm diagnosis*
- The diagnosis is already confirmed via **genetic testing** showing NPC1 mutations and **fibroblast studies** showing cholesterol defects.
- Delaying treatment in already symptomatic siblings (the 6 and 10-year-olds) would allow irreversible **neuronal loss** and worsening of **ataxia**.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 9: A 15-year-old boy with Hunter syndrome (MPS II) on weekly enzyme replacement therapy develops IgG antibodies with high neutralizing capacity against idursulfase. His symptoms have worsened over the past 6 months with increasing hepatosplenomegaly and joint stiffness. His brother with the same mutation shows excellent response to ERT without antibody formation. Synthesize an appropriate management plan considering immunologic and genetic factors.
- A. Switch to substrate reduction therapy as primary treatment
- B. Implement immune tolerance induction protocol with immunosuppression and continued ERT (Correct Answer)
- C. Discontinue ERT as antibodies make it ineffective; switch to supportive care only
- D. Perform HSCT to eliminate antibody production and provide endogenous enzyme
- E. Increase ERT dose to saturate antibody binding capacity
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Implement immune tolerance induction protocol with immunosuppression and continued ERT***
- The presence of **high-titer neutralizing IgG antibodies** (NABs) interferes with the efficacy of **idursulfase**, leading to the recurrence of symptoms like **hepatosplenomegaly** and joint stiffness.
- **Immune tolerance induction (ITI)** using agents like **rituximab**, **methotrexate**, and IVIG is indicated to eliminate the antibody response and restore the clinical benefit of the **enzyme replacement therapy**.
*Discontinue ERT as antibodies make it ineffective; switch to supportive care only*
- Stopping ERT allows the accumulation of **glycosaminoglycans** to continue, leading to progressive multisystemic decline and shortened **life expectancy**.
- Supportive care alone does not address the underlying **biochemical deficiency** when immune modulation could potentially rescue the primary treatment.
*Switch to substrate reduction therapy as primary treatment*
- **Substrate reduction therapy** (SRT) is not currently the standard or approved primary treatment for **Hunter syndrome** (MPS II) especially in the context of existing ERT failure.
- SRT aims to reduce the synthesis of **heparan and dermatan sulfate**, but it does not replace the missing **iduronate-2-sulfatase** enzyme activity required for clearance.
*Increase ERT dose to saturate antibody binding capacity*
- Increasing the dose of **idursulfase** often fails to overcome high-affinity **neutralizing antibodies** and may increase the risk of **infusion-related reactions** or immune complex formation.
- Antibody **saturation** is not a sustainable or effective clinical strategy for managing high-titer **anti-drug antibodies** in lysosomal storage diseases.
*Perform HSCT to eliminate antibody production and provide endogenous enzyme*
- While **hematopoietic stem cell transplantation** (HSCT) provides endogenous enzyme, it is not the preferred treatment for **MPS II** due to high procedural risks and inconsistent neurological outcomes compared to MPS I.
- HSCT is typically not used specifically as a secondary measure to treat **anti-drug antibodies** when **immune tolerance induction** is a viable and less invasive option.
Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG Question 10: A newborn screening program identifies an infant with deficient β-glucuronidase activity. The infant is currently asymptomatic at 2 weeks of age. The parents are counseled about Sly syndrome (MPS VII) and ask about prognosis. Genetic testing reveals the infant is compound heterozygous with one null allele and one missense mutation (p.P408S) that retains 8% residual enzyme activity. Evaluate the most appropriate management strategy.
- A. Begin enzyme replacement therapy immediately to prevent neurologic damage
- B. Wait and observe, as 8% residual activity will prevent disease manifestation
- C. Immediate hematopoietic stem cell transplantation before symptoms develop
- D. Gene therapy followed by enzyme replacement as bridging therapy
- E. Initiate early enzyme replacement therapy with neurodevelopmental monitoring, consider HSCT if CNS involvement develops (Correct Answer)
Diagnostic approaches Explanation: ***Initiate early enzyme replacement therapy with neurodevelopmental monitoring, consider HSCT if CNS involvement develops***
- **Sly syndrome (MPS VII)** management focuses on early intervention with **ERT (vestronidase alfa)** to reduce systemic **glycosaminoglycan (GAG)** accumulation and mitigate skeletal/organ damage.
- A **missense mutation** with **8% residual activity** often suggests an attenuated phenotype; early therapy combined with close monitoring allows for tailoring aggressive interventions like **HSCT** if CNS features emerge.
*Immediate hematopoietic stem cell transplantation before symptoms develop*
- **HSCT** is associated with significant **morbidity and mortality** and is typically reserved for severe, early-onset cases where the benefit for the CNS outweighs the procedural risks.
- Given the infant's **8% residual activity**, an immediate transplant may be premature without first assessing the efficacy of less invasive **enzyme replacement therapy**.
*Wait and observe, as 8% residual activity will prevent disease manifestation*
- While 8% activity indicates an **attenuated form**, it is insufficient to prevent the progressive accumulation of GAGs that leads to **dysostosis multiplex** and organomegaly.
- **Sly syndrome** is progressive; the
More Diagnostic approaches US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.