Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Clinical presentation patterns. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 1: A deficiency in which of the following lysosomal enzymes is inherited in a pattern similar to a deficiency of iduronate sulfatase (Hunter syndrome)?
- A. Sphingomyelinase
- B. Glucocerebrosidase
- C. Galactocerebrosidase
- D. Alpha-L-iduronidase
- E. Alpha-galactosidase A (Correct Answer)
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***Alpha-galactosidase A***
- A deficiency in **alpha-galactosidase A** causes **Fabry disease**, which, like Hunter syndrome (iduronate sulfatase deficiency), is inherited in an **X-linked recessive** pattern.
- Both conditions primarily affect males, with carrier females potentially exhibiting milder symptoms.
*Sphingomyelinase*
- A deficiency in sphingomyelinase leads to **Niemann-Pick disease types A and B**, which are inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- This mode of inheritance differs from the X-linked pattern of Hunter syndrome.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in glucocerebrosidase causes **Gaucher disease**, inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- This is a common lysosomal storage disorder, but its inheritance pattern is distinct from X-linked disorders.
*Galactocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in galactocerebrosidase causes **Krabbe disease (globoid cell leukodystrophy)**, which is inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- Krabbe disease is a severe neurodegenerative disorder, but its genetic transmission is not X-linked.
*Alpha-L-iduronidase*
- A deficiency in **alpha-L-iduronidase** causes **Hurler syndrome (MPS I)**, which is inherited in an **autosomal recessive** pattern.
- While both Hunter and Hurler syndromes are mucopolysaccharidoses, their genetic inheritance patterns are different.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 2: A 6-month-old boy is referred to a geneticist after he is found to have persistent hypotonia and failure to thrive. He has also had episodes of what appears to be respiratory distress and has an enlarged heart on physical exam. There is a family history of childhood onset hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, so a biopsy is performed showing electron dense granules within the lysosomes. Genetic testing is performed showing a defect in glycogen processing. A deficiency in which of the following enzymes is most likely to be responsible for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Lysosomal alpha 1,4-glucosidase (Correct Answer)
- B. Branching enzyme
- C. Muscle phosphorylase
- D. Debranching enzyme
- E. Glucose-6-phosphatase
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***Lysosomal alpha 1,4-glucosidase***
- The constellation of **hypotonia**, **failure to thrive**, **respiratory distress**, and **cardiomegaly** in an infant, along with **electron-dense granules in lysosomes** and a defect in **glycogen processing**, is characteristic of **Pompe disease (Type II glycogen storage disease)**.
- **Pompe disease** is caused by a deficiency of **lysosomal alpha 1,4-glucosidase** (also known as acid maltase), which is responsible for breaking down glycogen in lysosomes.
*Branching enzyme*
- A deficiency in **branching enzyme (amylo-alpha-1,4-to-alpha-1,6-transglucosidase)** causes **Andersen disease (Type IV glycogen storage disease)**, which typically presents with **hepatosplenomegaly**, **cirrhosis**, and **failure to thrive**.
- While it involves glycogenopathy, the specific features of **cardiomyopathy** and **lysosomal accumulation** are not primary to this disorder.
*Muscle phosphorylase*
- A deficiency in **muscle phosphorylase** causes **McArdle disease (Type V glycogen storage disease)**, which primarily affects **skeletal muscle**.
- Symptoms include **exercise intolerance**, **muscle cramps**, and **myoglobinuria**, typically presenting later in childhood or adolescence, and does not involve cardiomyopathy or lysosomal storage.
*Debranching enzyme*
- A deficiency in **debranching enzyme (alpha-1,6-glucosidase)** causes **Cori disease (Type III glycogen storage disease)**, which presents with **hepatomegaly**, **hypoglycemia**, and **muscle weakness**.
- While it can sometimes involve a milder form of cardiomyopathy, the significant **lysosomal involvement** and severe infantile onset with respiratory distress and profound hypotonia point away from Cori disease.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- A deficiency in **glucose-6-phosphatase** causes **Von Gierke disease (Type I glycogen storage disease)**, characterized by **severe fasting hypoglycemia**, **lactic acidosis**, **hepatomegaly**, and **hyperlipidemia**.
- This condition primarily affects the liver and kidneys, and typically does not present with primary cardiomyopathy, hypotonia, or lysosomal glycogen accumulation.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 3: A 32-year-old woman comes to the clinic for a routine evaluation. This is her first time visiting this office. Her medical history is significant for cystic medial necrosis of the aorta. Her vital signs include: heart rate 85/min, respiratory rate 15/min, temperature 36.0°C (96.8°F), and blood pressure 110/80 mm Hg. Physical examination shows she is thin and tall with abnormally long extremities and spider-like fingers. Which of the following disorders does the patient most likely have?
- A. Cystic fibrosis
- B. Marfan syndrome (Correct Answer)
- C. Tay-Sachs disease
- D. Von Hippel-Lindau disease
- E. Fabry disease
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***Marfan syndrome***
- The patient's presentation with **cystic medial necrosis of the aorta**, a **tall, thin habitus** with **abnormally long extremities**, and **arachnodactyly (spider-like fingers)** are classic features of Marfan syndrome.
- This is an **autosomal dominant disorder** caused by a defect in the **fibrillin-1 gene (FBN1)**, leading to abnormalities in connective tissue throughout the body, particularly affecting the cardiovascular, ocular, and skeletal systems.
*Cystic fibrosis*
- This is a genetic disorder primarily affecting the **lungs** and **digestive system**, leading to thick, sticky mucus.
- It does not typically present with the skeletal or cardiovascular findings described in the patient, such as tall stature, arachnodactyly, or aortic pathologies.
*Tay-Sachs disease*
- This is a rare, fatal genetic disorder that progressively destroys **nerve cells** in the brain and spinal cord, predominantly affecting infants.
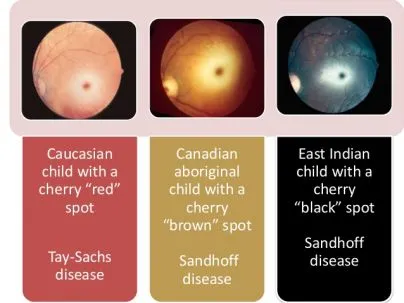
- It is characterized by neurological regression and a **cherry-red spot** on the retina, and does not involve connective tissue abnormalities or aortic disease.
*Von Hippel-Lindau disease*
- This is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of **tumors** and **cysts** in various parts of the body, including the brain, spinal cord, eyes, kidneys, and pancreas.
- It does not present with the specific skeletal or cardiovascular features observed in the patient, such as arachnodactyly or aortic cystic medial necrosis.
*Fabry disease*
- This is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder characterized by the accumulation of **globotriaosylceramide** in various tissues, leading to multi-systemic symptoms.
- While it can affect the heart and kidneys, its key features include **acroparesthesias**, **angiokeratomas**, and **corneal opacities**, none of which are mentioned here.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 4: An 8-month-old female infant from a first-degree consanguineous couple was brought to the physician because the mother noticed abnormalities in the growth of her child as well as the different lengths of her child's legs. The infant had gingival hyperplasia, restricted movement in both shoulders, a prominent, pointed forehead, and enophthalmos with a slight opacity in both corneas. A blood test revealed 10 fold higher than normal levels of the following enzymes: N-acetyl-ß-glucosaminidase, ß-glucuronidase, ß-hexosaminidase A, and alkaline phosphatase. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase
- B. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- C. N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase (Correct Answer)
- D. Glucocerebrosidase
- E. Alpha-galactosidase A
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase***
- The clinical presentation with **gingival hyperplasia**, **restricted joint movement**, **skeletal abnormalities** (growth abnormalities, leg length discrepancy, prominent forehead), and **corneal opacity** with elevated lysosomal enzymes (N-acetyl-ß-glucosaminidase, ß-glucuronidase, ß-hexosaminidase A) is highly characteristic of **I-cell disease** (mucolipidosis II).
- I-cell disease is caused by a deficiency in **N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase**, an enzyme crucial for phosphorylating mannose residues on lysosomal enzymes, tagging them for delivery to lysosomes. Without this tag, lysosomal enzymes are secreted extracellularly, leading to their accumulation in the blood and their deficiency within lysosomes, causing the clinical features.
*Lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase*
- Deficiency of **lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase** causes **Pompe disease (glycogen storage disease type II)**, which is characterized by **cardiomegaly**, hypotonia, and liver involvement, but typically does not present with the skeletal dysplasias, gingival hyperplasia, or corneal clouding seen in this patient.
- While it is a lysosomal storage disorder, the specific clinical features and panel of elevated enzymes differ significantly from this case.
*Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency of **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)** causes **G6PD deficiency**, an X-linked disorder leading to **hemolytic anemia** in response to oxidative stress (e.g., fava beans, certain drugs, infections).
- It does not present with the systemic skeletal, connective tissue, and corneal abnormalities described, nor does it involve elevated lysosomal enzyme levels.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- Deficiency of **glucocerebrosidase** causes **Gaucher disease**, which presents with **hepatosplenomegaly**, bone crises, pancytopenia, and sometimes neurological involvement.
- While it is a lysosomal storage disorder, the clinical features (e.g., absence of gingival hyperplasia, corneal opacity, or specific skeletal dysplasias like restricted joint movement) and the pattern of elevated enzymes do not match the patient's presentation.
*Alpha-galactosidase A*
- Deficiency of **alpha-galactosidase A** causes **Fabry disease**, an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder characterized by **neuropathic pain**, **angiokeratomas**, renal failure, and cardiac involvement.
- The clinical picture of Fabry disease does not include gingival hyperplasia, prominent skeletal abnormalities, or the specific pattern of elevated lysosomal enzymes observed in this patient.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 5: A 4-month-old male infant is brought in because he rejects food and is losing weight. He had several upper respiratory tract infections during the last 2 months. Upon examination, hepatosplenomegaly is noted, as well as mild hypotonia. During the next few weeks, hepatosplenomegaly progresses, the boy fails to thrive, and he continues to reject food. He has a blood pressure of 100/70 mm Hg and heart rate of 84/min. Blood tests show pancytopenia and elevated levels of transaminases. Slit lamp examination shows bilateral cherry-red spots on the macula. Chest X-ray shows a reticulonodular pattern and calcified nodules. Biopsy of the liver shows foamy histiocytes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Niemann-Pick disease type A (Correct Answer)
- B. Tay-Sachs disease
- C. Gaucher disease
- D. Wolman disease
- E. GM1 gangliosidosis
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***Niemann-Pick disease type A***
- This presentation of a 4-month-old with **failure to thrive**, progressive **hepatosplenomegaly**, **hypotonia**, recurrent infections, **pancytopenia**, elevated transaminases, **cherry-red spots** on the macula, and **foamy histiocytes** in the liver biopsy is characteristic of Niemann-Pick disease type A.
- Niemann-Pick disease type A is a **lysosomal storage disorder** caused by a deficiency of the enzyme **sphingomyelinase**, leading to the accumulation of **sphingomyelin** in various tissues.
- The **foamy histiocytes** (lipid-laden macrophages) are a hallmark finding, and the **reticulonodular pattern** on chest X-ray represents pulmonary infiltration.
*Incorrect: Tay-Sachs disease*
- While Tay-Sachs disease also presents with **cherry-red spots** and progressive neurological deterioration in infancy, it is caused by **hexosaminidase A deficiency**.
- Key differences: Tay-Sachs typically does **not** cause **hepatosplenomegaly** or **foamy histiocytes** in the liver; the primary pathology is neuronal accumulation of GM2 ganglioside.
- Patients usually present with developmental regression, exaggerated startle response, and hypotonia, but without the prominent organomegaly seen here.
*Incorrect: Gaucher disease*
- While Gaucher disease also presents with **hepatosplenomegaly** and can cause bone marrow involvement leading to **pancytopenia**, it typically does **not** feature **cherry-red spots** or such severe early neurological regression.
- It is caused by a deficiency of **glucocerebrosidase**, leading to accumulation of glucocerebroside in **Gaucher cells** (not foamy histiocytes).
- The infantile neuronopathic form (type 2) can present early but lacks cherry-red spots.
*Incorrect: Wolman disease*
- Wolman disease is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by **lysosomal acid lipase deficiency**, presenting with hepatosplenomegaly, failure to thrive, and foamy histiocytes.
- Key distinguishing feature: **bilateral adrenal calcifications** on imaging, which are pathognomonic for Wolman disease but not mentioned in this case.
- Does **not** typically cause cherry-red spots on fundoscopic examination.
*Incorrect: GM1 gangliosidosis*
- GM1 gangliosidosis can present with hepatosplenomegaly, developmental delay, and **cherry-red spots** (in about 50% of cases).
- However, it is characterized by distinctive **coarse facial features**, **skeletal dysplasia** (dysostosis multiplex), and **vacuolated lymphocytes** on blood smear.
- The **foamy histiocytes** and prominent pulmonary involvement are more characteristic of Niemann-Pick disease type A.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 6: A 3-month-old boy presents for routine health maintenance. The patient has coarse facial features and stiff joint movements with restricted passive and active range of motion. He also has problems following objects with his eyes and seems not to focus on anything. On physical examination, the corneas are clouded, and the patient fails to meet any 3-month developmental milestones. Genetic testing and histopathology are performed and reveal failure of a cellular structure to phosphorylate mannose residues on glycoproteins. An electron microscopy image of one of this patient’s cells is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Adrenoleukodystrophy
- B. Kartagener syndrome
- C. Tay-Sachs disease
- D. Inclusion cell disease (Correct Answer)
- E. Diamond-Blackfan anemia
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***Inclusion cell disease***
- This condition is characterized by a **failure to phosphorylate mannose residues** on glycoproteins due to a defective **N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase** enzyme.
- The clinical presentation of **coarse facial features, stiff joint movements**, clouded corneas, and developmental delay is classical for **I-cell disease** (mucolipidosis II), where lysosomal enzymes are **mistargeted and secreted from cells** instead of being properly delivered to lysosomes, resulting in **lysosomes that lack hydrolytic enzymes** and accumulate undigested substrates (visible as inclusions on electron microscopy).
*Adrenoleukodystrophy*
- This is an **X-linked disorder** affecting very long chain fatty acid metabolism, leading to their accumulation in the **adrenal glands** and **white matter of the brain**.
- While it causes **neurological dysfunction** and adrenal insufficiency, it does not typically present with the coarse facial features, corneal clouding, and skeletal abnormalities seen in this patient.
*Kartagener syndrome*
- This is a form of **primary ciliary dyskinesia** characterized by impaired ciliary movement due to structural defects in **dynein arms**.
- It presents with **recurrent respiratory infections** (sinusitis, bronchitis, bronchiectasis), **situs inversus** (in about 50% of cases), and infertility, which are unrelated to the patient's symptoms.
*Tay-Sachs disease*
- This is a **lysosomal storage disorder** caused by a deficiency of **hexosaminidase A**, leading to the accumulation of **GM2 ganglioside**.
- It causes **progressive neurological deterioration**, motor weakness, and a **cherry-red spot** on the macula, but not the coarse facial features or skeletal abnormalities described.
*Diamond-Blackfan anemia*
- This is a **congenital hypoplastic anemia** characterized by a defect in **erythroid progenitor cells**, leading to severe macrocytic anemia.
- It can be associated with various congenital anomalies, but the primary presentation is **anemia** and it does not involve the lysosomal storage defects or the characteristic facial and joint features seen in this case.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old man with known coronary artery disease presents to the ED with epigastric pain, worsening fatigue, and melena. He takes aspirin and rosuvastatin, but took ibuprofen over the past two weeks for lower back pain. He denies nausea, vomiting, hematemesis, chest pain, fever, and weight loss. Sitting blood pressure is 100/70 mmHg and pulse is 90/min, but standing blood pressure is 85/60 mmHg and pulse is 110/min. Airway is patent. His hands feel cold and clammy. Abdominal exam confirms epigastric pain, but no rebound tenderness or guarding. Despite 2 liters of lactated Ringer's, the blood pressure and pulse have not changed. What hemoglobin (Hb) threshold should be considered if packed red blood cell (pRBC) transfusion is ordered in this patient?
- A. < 10
- B. threshold does not matter
- C. < 9
- D. < 7
- E. < 8 (Correct Answer)
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***< 8***
- This patient presents with signs of **hemodynamic instability** (orthostasis, cold extremities, persistent hypotension despite fluid resuscitation) and active upper gastrointestinal bleeding (melena, epigastric pain, recent NSAID use).
- In patients with **hemodynamic instability** due to acute blood loss, the transfusion threshold is generally higher, at **Hb < 8 g/dL**, to ensure adequate oxygen delivery, especially in the setting of coronary artery disease.
*< 10*
- A transfusion threshold of **Hb < 10 g/dL** is typically reserved for patients with more severe conditions like **unstable angina**, active myocardial ischemia, or when severe symptoms of anemia persist despite an Hb > 8 g/dL.
- While this patient has coronary artery disease, his immediate need for transfusion is driven by acute blood loss and instability, not solely anemic angina.
*threshold does not matter*
- This statement is incorrect as transfusion decisions are based on specific **hemoglobin thresholds** and clinical context to optimize patient outcomes and avoid unnecessary transfusions.
- Ignoring thresholds could lead to either undertransfusion (risking organ damage) or overtransfusion (risking complications like TACO or TRALI).
*< 9*
- An Hb threshold of **< 9 g/dL** might be considered in some scenarios of acute bleeding, but with clear signs of **hemodynamic instability** and severe symptoms, an Hb of 8 g/dL or less is a more commonly accepted trigger.
- The combination of ongoing bleeding, significant orthostasis, and cold extremities points to a more urgent need for correction.
*< 7*
- A transfusion threshold of **Hb < 7 g/dL** is generally applied to hemodynamically stable patients without significant comorbidities, as demonstrated in the TRICC trial.
- This patient is **hemodynamically unstable** and has significant comorbidity (coronary artery disease), warranting a higher transfusion threshold.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 8: A 5-year-old girl is brought in for a routine checkup. She was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery and is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting all developmental milestones. Upon examination, she is pale with a few petechiae on her chest neck and back. Examination of the abdomen reveals painless hepatosplenomegaly. Liver enzymes are mildly elevated and complete blood cell count shows slight anemia and thrombocytopenia. Iron, B12, and folate are normal. A bone marrow biopsy shows mildly hypocellular marrows with diffuse macrophages with eosinophilic cytoplasm. The cytoplasm looks like wrinkled tissue paper on further inspection. No blasts are observed. What is the most likely diagnosis in the present case?
- A. Autoimmune disorder
- B. Gaucher disease type I (Correct Answer)
- C. Biliary obstruction
- D. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- E. Viral hepatitis
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: **Gaucher disease type I**
- The characteristic finding of **diffuse macrophages with eosinophilic cytoplasm** that resembles **"wrinkled tissue paper"** on bone marrow biopsy is pathognomonic for **Gaucher cells**, confirming **Gaucher disease type I**.
- **Painless hepatosplenomegaly**, **anemia**, **thrombocytopenia**, and **petechiae** are common clinical manifestations resulting from the accumulation of glucocerebroside in macrophages within the reticuloendothelial system.
*Autoimmune disorder*
- While autoimmune disorders can cause anemia and hepatosplenomegaly, the distinct **"wrinkled tissue paper" macrophages** found in the bone marrow biopsy are not characteristic of autoimmune conditions.
- Autoimmune disorders like lupus or autoimmune hemolytic anemia would present with different serological markers and histological findings.
*Biliary obstruction*
- **Biliary obstruction** typically presents with **jaundice**, dark urine, pale stools, and significant elevation of **liver enzymes** (especially direct bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase), which are not prominent features here.
- It would not explain the hematopoietic abnormalities (anemia, thrombocytopenia) or the presence of Gaucher cells in the bone marrow.
*Acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
- **Acute lymphoblastic leukemia** would typically show a significant presence of **blasts** (immature white blood cells) in the bone marrow, which are explicitly noted as absent in this case.
- While it can cause anemia and thrombocytopenia, the key diagnostic feature of **blasts** is missing, and the characteristic macrophages would not be present.
*Viral hepatitis*
- **Viral hepatitis** primarily causes **liver inflammation** and can lead to significant elevation of **liver enzymes** (transaminases), often much higher than "mildly elevated."
- It does not explain the **painless hepatosplenomegaly**, **anemia**, **thrombocytopenia**, or the pathognomonic **Gaucher cells** in the bone marrow.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 9: A 26-year-old woman presents to a physician for genetic counseling, because she is worried about trying to have a child. Specifically, she had 2 siblings that died young from a lysosomal storage disorder and is afraid that her own children will have the same disorder. Her background is Ashkenazi Jewish, but she says that her husband's background is mixed European heritage. Her physician says that since her partner is not of Jewish background, their chance of having a child with Niemann-Pick disease is dramatically decreased. Which of the following genetic principles best explains why there is an increased prevalence of this disease in some populations?
- A. Natural selection
- B. Imprinting
- C. De novo mutations
- D. Gene flow
- E. Founder effect (Correct Answer)
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***Founder effect***
- The **founder effect** occurs when a new population is established by a small number of individuals, leading to a **reduced genetic diversity** and an increased frequency of certain alleles that were present in the founders. This is particularly relevant in populations like **Ashkenazi Jews**, who descended from a small, isolated group with certain allele frequencies.
- In this scenario, the high prevalence of **Niemann-Pick disease** (and other genetic disorders) in the Ashkenazi Jewish population is due to their historical isolation and intermarriage within a relatively small gene pool, trapping and concentrating certain alleles.
*Natural selection*
- **Natural selection** typically describes the process by which traits that enhance survival and reproduction become more common in a population over time, or deleterious traits become less common.
- While it can influence disease prevalence, it doesn't primarily explain the disproportionately high frequency of rare recessive disorders in specific isolated populations in the manner described.
*Imprinting*
- **Genomic imprinting** refers to the phenomenon where certain genes are expressed in a **parent-of-origin-specific manner**, meaning that only the allele inherited from either the mother or the father is expressed.
- This mechanism explains certain genetic conditions but does not account for the increased prevalence of a recessive disorder due to population history and isolation.
*De novo mutations*
- **De novo mutations** are new genetic alterations that appear for the first time in an individual and are not inherited from either parent.
- While de novo mutations are a source of genetic variation, they do not explain the high prevalence of a specific ancestral allele within an entire population.
*Gene flow*
- **Gene flow** (or migration) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another, which tends to **decrease genetic differences** between populations and introduce new alleles.
- This principle would suggest a *reduction* in the prevalence of specific rare alleles over time as populations mix, rather than an *increase* in isolated groups.
Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG Question 10: A 6-month-old boy is brought to a pediatrician by his parents for his first visit after they adopt him from a European country. His parents are concerned about the boy’s short episodes of shaking of his arms and legs; they believe it might be epilepsy. They also note that the child is less responsive than other children of his age. The family is unable to provide any vaccination, birth, or family history. His pulse is 130/min, respiratory rate is 28/min, and blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg. The boy has a light skin tone and emits a noticeable musty body odor. Which of the following should be supplemented in this patient’s diet?
- A. Isoleucine
- B. Leucine
- C. Tyrosine (Correct Answer)
- D. Phenylalanine
- E. Histidine
Clinical presentation patterns Explanation: ***Tyrosine***
- The patient's presentation with **seizures**, **developmental delay** (less responsive), **light skin tone**, and a **musty body odor** is highly suggestive of **phenylketonuria (PKU)**.
- In PKU, there is a deficiency in the enzyme **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, which converts **phenylalanine** to **tyrosine**. Therefore, **tyrosine** becomes an **essential amino acid** and must be supplemented in the diet.
*Isoleucine*
- **Isoleucine** is a **branched-chain amino acid** that is typically restricted, along with leucine and valine, in conditions like **maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)**, not PKU.
- Supplementation of isoleucine would be detrimental in MSUD and is not indicated for PKU.
*Leucine*
- Similar to isoleucine, **leucine** is a **branched-chain amino acid** whose metabolism is impaired in **MSUD**, not PKU.
- Supplementing leucine is not beneficial for PKU and would be harmful in MSUD.
*Phenylalanine*
- **Phenylalanine** is the amino acid that accumulates to toxic levels in **PKU** due to the enzyme deficiency.
- Therefore, phenylalanine must be **strictly restricted** in the patient's diet, not supplemented.
*Histidine*
- **Histidine** is an essential amino acid but is not directly involved in the metabolic pathway affected by PKU.
- There is no indication for histidine supplementation in the management of PKU.
More Clinical presentation patterns US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.