Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Fatty acid synthesis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 1: A scientist is trying to design a drug to modulate cellular metabolism in the treatment of obesity. Specifically, he is interested in understanding how fats are processed in adipocytes in response to different energy states. His target is a protein within these cells that catalyzes catabolism of an energy source. The products of this reaction are subsequently used in gluconeogenesis or β-oxidation. Which of the following is true of the most likely protein that is being studied by this scientist?
- A. It is stimulated by epinephrine (Correct Answer)
- B. It is inhibited by glucagon
- C. It is inhibited by acetylcholine
- D. It is inhibited by cortisol
- E. It is stimulated by insulin
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***It is stimulated by epinephrine***
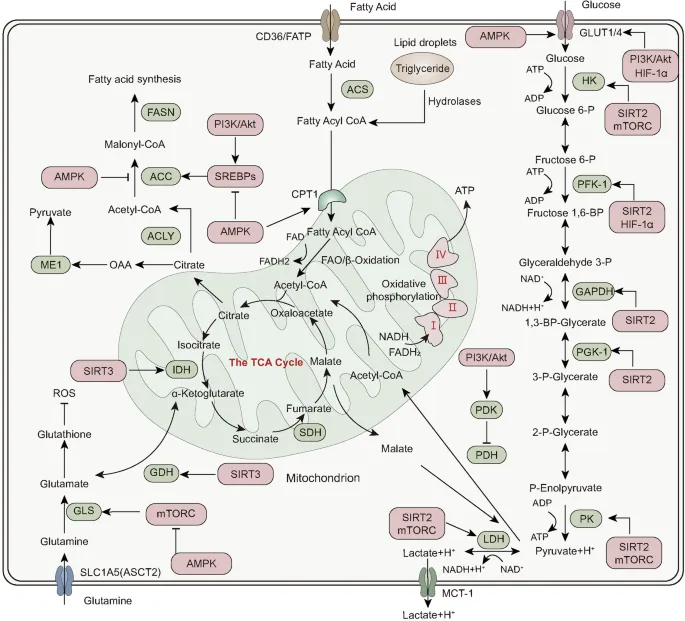
- The protein described is likely **hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL)**, which catabolizes **triglycerides** in adipocytes to **glycerol** and **fatty acids**.
- **Epinephrine** (and norepinephrine) stimulates HSL activity via a **cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)** pathway, leading to increased fatty acid release for energy.
*It is inhibited by glucagon*
- **Glucagon primarily acts on the liver** to promote gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, but it does **not directly inhibit HSL** in adipocytes.
- While glucagon has a lipolytic effect, it doesn't inhibit the enzyme that releases fatty acids.
*It is inhibited by acetylcholine*
- **Acetylcholine** is a neurotransmitter involved in the **parasympathetic nervous system**, which generally promotes energy storage.
- It does **not directly inhibit HSL**; its effects on lipid metabolism are indirect and typically involve other pathways.
*It is inhibited by cortisol*
- **Cortisol**, a glucocorticoid, generally **promotes lipolysis** (breakdown of fats) in certain contexts, particularly during stress to provide energy substrates.
- Therefore, it would **not inhibit HSL**; rather, it often enhances its activity or provides a permissive effect for other lipolytic hormones.
*It is stimulated by insulin*
- **Insulin** is an **anabolic hormone** that promotes energy storage, including **lipogenesis** (fat synthesis) and inhibits lipolysis.
- Insulin **inhibits HSL activity** by activating phosphodiesterase, which reduces cAMP levels, thus deactivating PKA and preventing HSL phosphorylation.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 2: Researchers are experimenting with hormone levels in mice in fasting and fed states. To test hormone levels in the fed state, the mice are given an oral glucose load and various hormones are measured in a blood sample. Researchers are most interested in the hormone whose blood levels track evenly with C-peptide levels. The hormone the researchers are most interested in is responsible for which of the following actions in the body?
- A. Protein catabolism
- B. Fatty acid breakdown
- C. Fatty acid synthesis (Correct Answer)
- D. Ketogenesis
- E. Lipolysis
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Fatty acid synthesis***
- The hormone whose blood levels track evenly with **C-peptide** levels after a glucose load is **insulin**.
- Insulin is a key anabolic hormone that promotes **fatty acid synthesis** from excess glucose in the fed state, particularly in the liver and adipose tissue.
*Protein catabolism*
- **Insulin** is an anabolic hormone that generally **inhibits protein catabolism** and promotes protein synthesis.
- Conditions like **glucagon excess** or **cortisol excess** promote protein catabolism, not insulin.
*Fatty acid breakdown*
- **Insulin inhibits fatty acid breakdown** (beta-oxidation) by suppressing hormone-sensitive lipase.
- **Glucagon** and **epinephrine** promote fatty acid breakdown, especially during fasting.
*Ketogenesis*
- **Insulin inhibits ketogenesis** by reducing the supply of fatty acids to the liver and inhibiting the enzymes involved in ketone body formation.
- **Glucagon** and **low insulin levels** (as in uncontrolled diabetes or prolonged fasting) promote ketogenesis.
*Lipolysis*
- **Insulin is a potent inhibitor of lipolysis** (breakdown of triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol) in adipose tissue.
- **Glucagon**, **catecholamines**, and **growth hormone** stimulate lipolysis.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is studying a hereditary defect in the mitochondrial enzyme succinyl-CoA synthetase. In addition to succinate, the reaction catalyzed by this enzyme produces a molecule that is utilized as an energy source for protein translation. This molecule is also required for which of the following conversion reactions?
- A. Oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate (Correct Answer)
- B. Pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
- C. Acetaldehyde to acetate
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone
- E. Fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate***
- The reaction catalyzed by **succinyl-CoA synthetase** (also known as succinate thiokinase) produces **GTP** (guanosine triphosphate) from GDP and Pi, in addition to succinate.
- **GTP** is required for the conversion of **oxaloacetate** to **phosphoenolpyruvate** in gluconeogenesis, catalyzed by **PEP carboxykinase**.
*Pyruvate to acetyl-CoA*
- This reaction is catalyzed by the **pyruvate dehydrogenase complex** and produces NADH, not GTP.
- It is an irreversible step linking glycolysis to the citric acid cycle.
*Acetaldehyde to acetate*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **aldehyde dehydrogenase** and uses **NAD+** as a cofactor, producing NADH.
- It is involved in alcohol metabolism.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone*
- This is the first committed step of the **pentose phosphate pathway**, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase**.
- It uses **NADP+** as a cofactor, producing NADPH.
*Fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate*
- This reaction is a key regulatory step in **glycolysis**, catalyzed by **phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)**.
- It consumes **ATP**, rather than producing GTP or utilizing it as a cofactor in the context of this question.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 4: A 22-year-old medical student decides to fast for 24 hours after reading about the possible health benefits of fasting. She read that blood glucose levels are maintained by metabolic processes such as hepatic glycogenolysis and hepatic gluconeogenesis during the initial 3 days of fasting. During the day, she did not suffer from the symptoms of hypoglycemia. Which of the following signaling molecules most likely stimulated the reaction which maintained her blood glucose after all her stored glucose was broken down and used up?
- A. Adenosine diphosphate
- B. Acetyl CoA (Correct Answer)
- C. Acetate
- D. Citrate
- E. Adenosine monophosphate
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Acetyl CoA***
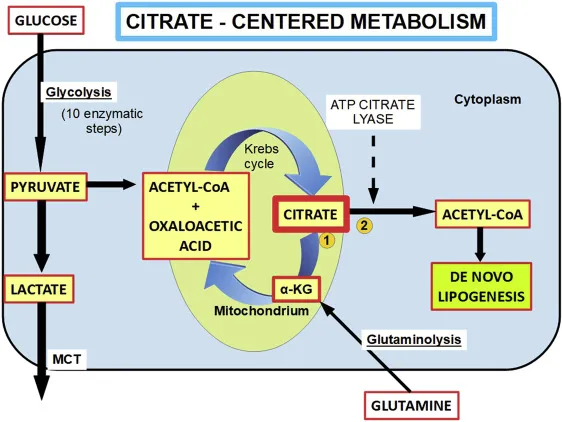
- **Acetyl CoA** is the key **allosteric activator of pyruvate carboxylase**, the first committed enzyme of gluconeogenesis that converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate.
- During prolonged fasting after glycogen stores are depleted, the body shifts to **fatty acid oxidation** (β-oxidation), which produces large amounts of **Acetyl CoA**.
- High **Acetyl CoA** levels signal that fat is being oxidized for energy, and simultaneously **activate gluconeogenesis** to maintain blood glucose for glucose-dependent tissues (brain, RBCs).
- This is the primary signaling mechanism that directly stimulates the gluconeogenic pathway after glycogen is exhausted.
*Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)*
- **AMP** levels rise during energy depletion and activate **AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)**.
- However, AMPK **inhibits gluconeogenesis** (not stimulates it) because gluconeogenesis is an **ATP-consuming** anabolic process (requires 6 ATP per glucose).
- AMPK promotes ATP-generating catabolic processes like fatty acid oxidation, but suppresses ATP-consuming processes like gluconeogenesis and fatty acid synthesis.
*Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)*
- **ADP** accumulates when ATP is hydrolyzed and signals moderate energy deficit.
- ADP is primarily a substrate for ATP regeneration via oxidative phosphorylation and does not directly regulate gluconeogenesis.
- Its role in metabolic regulation is less specific than allosteric activators like Acetyl CoA.
*Acetate*
- **Acetate** can be converted to Acetyl CoA but is not a direct signaling molecule for gluconeogenesis.
- It is a minor metabolite that may be produced in specific conditions (e.g., alcohol metabolism, ketoacidosis) but does not play a primary role in fasting-induced glucose homeostasis.
*Citrate*
- **Citrate** is a Krebs cycle intermediate that inhibits **phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)** in glycolysis, thus reducing glucose breakdown.
- While citrate inhibition of glycolysis indirectly favors gluconeogenesis by preventing futile cycling, citrate does not **directly activate** gluconeogenic enzymes.
- Citrate primarily signals energy sufficiency and promotes fatty acid synthesis in the fed state, not fasting gluconeogenesis.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 5: Steroid hormone synthesis, lipid synthesis, and chemical detoxification are activities of which of the following?
- A. Peroxisomes
- B. Nucleolus
- C. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- D. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Correct Answer)
- E. Golgi bodies
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum***
- The **smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)** is rich in enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of **lipids**, including steroid hormones, and is crucial for the detoxification of drugs and poisons, particularly in liver cells.
- Its tubular structure, devoid of ribosomes, differentiates its functions from the rough ER, focusing on metabolic processes like **calcium ion storage** and carbohydrate metabolism.
*Peroxisomes*
- Peroxisomes are primarily involved in the breakdown of **fatty acids** and amino acids, producing hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct.
- They also play a role in detoxification but are not the primary site for steroid hormone or general lipid synthesis.
*Nucleolus*
- The **nucleolus** is a dense structure within the nucleus responsible for synthesizing **ribosomal RNA (rRNA)** and assembling ribosomes.
- It has no direct role in steroid hormone synthesis, lipid metabolism, or chemical detoxification.
*Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum*
- The **rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)** is studded with **ribosomes** and is primarily involved in the synthesis and modification of **proteins** destined for secretion or insertion into membranes.
- While it's part of the endomembrane system, it does not directly perform lipid synthesis or chemical detoxification as its main functions.
*Golgi bodies*
- **Golgi bodies (or Golgi apparatus)** are responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging **proteins and lipids** synthesized in the ER into vesicles for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
- They do not perform the initial synthesis of steroid hormones or lipids, nor are they the primary site for chemical detoxification.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 6: The balance between glycolysis and gluconeogenesis is regulated at several steps, and accumulation of one or more products/chemicals can either promote or inhibit one or more enzymes in either pathway. Which of the following molecules if increased in concentration can promote gluconeogenesis?
- A. ADP
- B. Acetyl-CoA (Correct Answer)
- C. AMP
- D. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
- E. Insulin
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Acetyl-CoA***
- **Acetyl-CoA** promotes gluconeogenesis by activating **pyruvate carboxylase**, the enzyme that converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate, effectively pushing the pathway forward.
- High levels of **Acetyl-CoA** generally signal a state of abundant energy from fatty acid oxidation, indicating that glucose is not immediately needed for energy and can be synthesized for storage or use elsewhere.
*ADP*
- **ADP** is a key indicator of low cellular energy and **stimulates** glycolysis while **inhibiting** gluconeogenesis to produce ATP.
- Its presence signals a need for energy synthesis rather than glucose production.
*AMP*
- **AMP** also signals low energy status and is a powerful **allosteric activator** of **phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)**, the rate-limiting enzyme in glycolysis.
- Activates **AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)**, which promotes catabolic processes like glycolysis and inhibits anabolic processes like gluconeogenesis.
*Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate*
- **Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate** is a potent **allosteric activator** of **PFK-1** in glycolysis and a strong **inhibitor** of **fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase** in gluconeogenesis.
- Its levels increase in response to insulin, promoting glucose utilization and inhibiting glucose production.
*Insulin*
- **Insulin** is a hormone that **promotes glucose uptake** and utilization by tissues and **inhibits gluconeogenesis**.
- It achieves this by activating enzymes involved in glycolysis and glycogen synthesis while inhibiting key enzymes in gluconeogenesis, such as **fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase**.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 7: The human body obtains vitamin D either from diet or from sun exposure. Darker-skinned individuals require more sunlight to create adequate vitamin D stores as the increased melanin in their skin acts like sunscreen; thus, it blocks the necessary UV required for vitamin D synthesis. Therefore, if these individuals spend inadequate time in the light, dietary sources of vitamin D are necessary. Which of the following requires sunlight for its formation?
- A. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
- B. 25-hydroxyvitamin D
- C. 7-dehydrocholesterol
- D. Cholecalciferol (D3) (Correct Answer)
- E. Ergocalciferol (D2)
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Cholecalciferol (D3)***
- **Cholecalciferol** (vitamin D3) is synthesized in the skin when **7-dehydrocholesterol** is exposed to **ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation** from sunlight.
- This is the initial step in the body's natural production of vitamin D, which then undergoes further hydroxylation in the liver and kidneys to become its active form.
*1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D*
- This is the **active form of vitamin D**, also known as **calcitriol**, produced in the **kidneys** from 25-hydroxyvitamin D via 1-alpha-hydroxylase.
- Its formation requires prior synthesis of cholecalciferol and subsequent hydroxylation, but it does not directly require sunlight.
*25-hydroxyvitamin D*
- This compound, also known as **calcidiol**, is formed in the **liver** from cholecalciferol (or ergocalciferol) through **25-hydroxylation**.
- While its precursor, cholecalciferol, is sunlight-dependent, 25-hydroxyvitamin D itself is not directly formed by sunlight.
*7-dehydrocholesterol*
- **7-dehydrocholesterol** is a **precursor molecule** found in the skin that is converted to cholecalciferol upon exposure to sunlight.
- It is not "formed" by sunlight; rather, it's the substrate upon which sunlight acts.
*Ergocalciferol (D2)*
- **Ergocalciferol** (vitamin D2) is primarily obtained from **plant-based sources** and fortified foods.
- It is not synthesized in the human skin through exposure to sunlight.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of dark urine, increasing abdominal pain, and a tingling sensation in her arms and legs. She has a history of epilepsy. Her current medication is phenytoin. She is nauseated and confused. Following the administration of hemin and glucose, her symptoms improve. The beneficial effect of this treatment is most likely due to inhibition of which of the following enzymes?
- A. Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
- B. Porphobilinogen deaminase
- C. Aminolevulinic acid synthase (Correct Answer)
- D. Ferrochelatase
- E. Aminolevulinate dehydratase
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Aminolevulinic acid synthase***
- The patient's symptoms (dark urine, abdominal pain, neurological symptoms like tingling and confusion) and improvement with **hemin** and **glucose** strongly suggest an acute porphyria, most likely **acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)**.
- **Hemin** and **glucose** work by downregulating **aminolevulinic acid synthase (ALAS)**, the rate-limiting enzyme in heme synthesis, thereby reducing the production of neurotoxic porphyrin precursors (ALA and PBG).
*Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase*
- Deficiency in **uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase** is associated with **porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)**, which primarily causes cutaneous photosensitivity, not acute neurovisceral symptoms.
- PCT does not typically present with acute life-threatening attacks or respond acutely to hemin and glucose.
*Porphobilinogen deaminase*
- Deficiency of **porphobilinogen deaminase (PBG deaminase)** is the underlying genetic defect in **acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)**.
- While this is the enzyme deficient in AIP, hemin and glucose don't directly inhibit this enzyme; their action is upstream on ALAS to prevent the accumulation of toxic precursors.
*Ferrochelatase*
- Deficiency of **ferrochelatase** causes **erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP)**, leading to painful photosensitivity and sometimes liver disease, but generally not acute neurovisceral attacks.
- The symptoms presented and the treatment response are not consistent with EPP.
*Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase*
- Deficiency in **aminolevulinic acid dehydratase** causes **ALA dehydratase deficiency porphyria**, a very rare form of porphyria with symptoms similar to lead poisoning.
- While it involves elevated ALA, it's less common than AIP, and the broad clinical picture with the dramatic response to hemin points more directly to the regulation of ALAS.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is studying biomolecular mechanisms in human cells. A radioactive isotope that is unable to cross into organelles is introduced into a sample of cells. The cells are then fragmented via centrifugation and the isotope-containing components are isolated. Which of the following reactions is most likely to be present in this cell component?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose
- B. Isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate
- C. Carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline
- D. Fatty acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA
- E. Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone (Correct Answer)
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone***
- This reaction is the first step of the **pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)**, which occurs in the **cytosol**.
- Since the isotope cannot cross into organelles and is found in the cytosolic fraction, this pathway is a likely candidate.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose*
- This reaction describes the dephosphorylation of **glucose-6-phosphate** to **glucose**, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- While important for glucose release, this enzyme is primarily located in the **endoplasmic reticulum** of the liver and kidneys, an organelle.
*Isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate*
- This is a step in the **Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)**, which takes place in the **mitochondrial matrix**.
- The isotope would not be found in this compartmentalized reaction because it cannot enter organelles.
*Carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline*
- This reaction is part of the **urea cycle**, which has steps occurring in both the **mitochondrial matrix** and the cytosol. The initial step, forming carbamoyl phosphate, is mitochondrial.
- The isotope, being unable to cross into organelles, would not readily participate in the mitochondrial portion of this pathway.
*Fatty acyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA*
- This reaction represents **beta-oxidation of fatty acids**, a process that primarily occurs in the **mitochondria** and peroxisomes.
- As the isotope is excluded from organelles, it would not be involved in these reactions.
Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG Question 10: A 24-year-old man is running a marathon. Upon reaching the finish line, his serum lactate levels were measured and were significantly increased as compared to his baseline. Which of the following pathways converts the lactate produced by muscles into glucose and transports it back to the muscles?
- A. Citric acid cycle
- B. Glycolysis
- C. Glycogenesis
- D. Pentose phosphate pathway
- E. Cori cycle (Correct Answer)
Fatty acid synthesis Explanation: ***Cori cycle***
- The **Cori cycle** is the metabolic pathway that converts **lactate** produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles (especially during intense exercise) back to **glucose in the liver** via gluconeogenesis.
- During strenuous exercise, muscles rely on anaerobic glycolysis when oxygen supply is insufficient, producing lactate and 2 ATP per glucose.
- The lactate is transported via bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted back to glucose (requiring 6 ATP), which then returns to muscles for energy or glycogen storage.
- This cycle allows muscles to continue generating ATP anaerobically while the liver handles lactate clearance.
*Citric acid cycle*
- The **citric acid cycle** (Krebs cycle) oxidizes **acetyl-CoA** to generate ATP, NADH, and FADH₂ in the mitochondrial matrix under aerobic conditions.
- It does not convert lactate to glucose; rather, pyruvate can be converted to acetyl-CoA to enter this cycle for complete oxidation.
- This is an aerobic process and does not involve the liver-muscle lactate-glucose exchange.
*Glycolysis*
- **Glycolysis** is the metabolic pathway that breaks down **glucose into pyruvate**, generating 2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose molecule.
- Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to lactate to regenerate NAD⁺ for continued glycolysis.
- This is the opposite of what the question asks—glycolysis produces lactate from glucose, not glucose from lactate.
*Glycogenesis*
- **Glycogenesis** is the process of synthesizing **glycogen from glucose** for storage, primarily in liver and muscle tissue.
- While it involves glucose storage, it does not convert lactate back to glucose or involve the metabolic exchange between muscles and liver described in the question.
*Pentose phosphate pathway*
- The **pentose phosphate pathway** (hexose monophosphate shunt) produces **NADPH** for reductive biosynthesis and **ribose-5-phosphate** for nucleotide synthesis.
- It branches from glycolysis but is not involved in lactate metabolism or the muscle-liver glucose-lactate exchange.
More Fatty acid synthesis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.