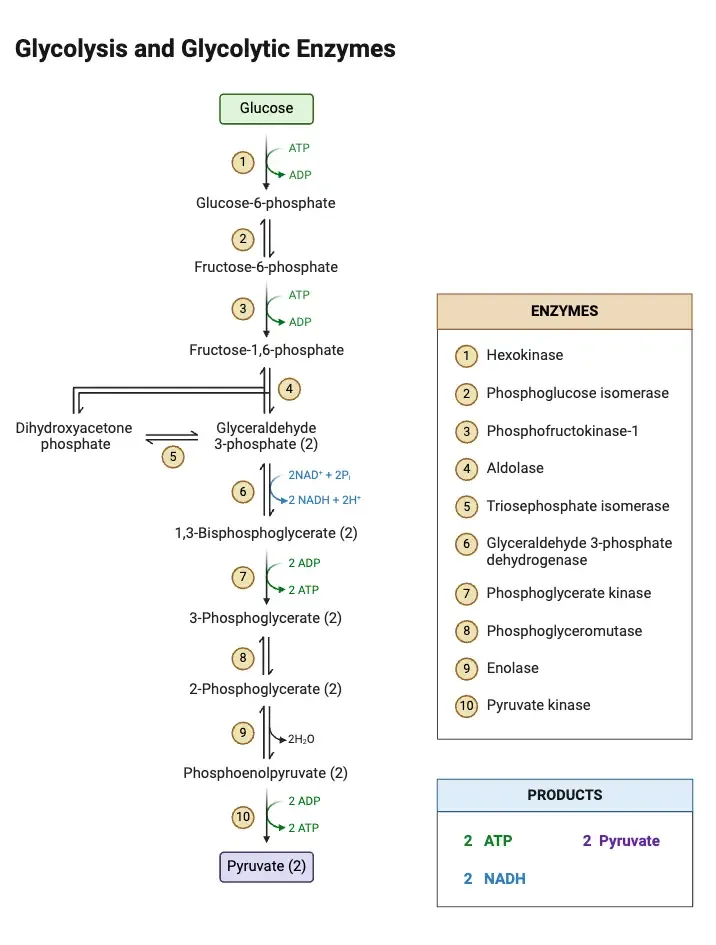
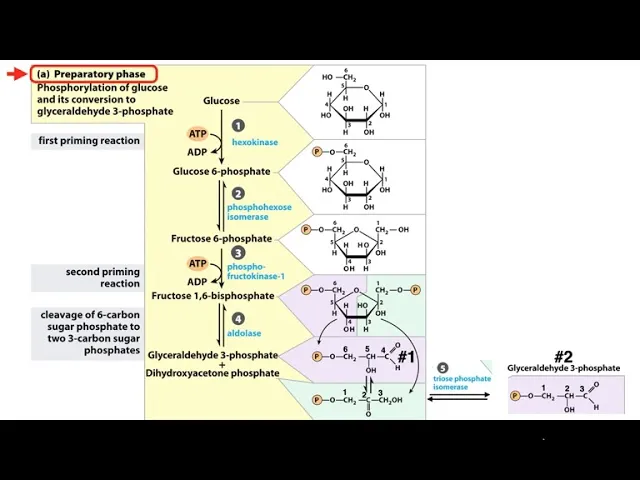
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Preparatory phase reactions. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 1: A researcher is studying the properties of an enzyme that adds phosphate groups to glucose. She discovers that the enzyme is present in most body tissues and is located in the cytoplasm of the cells expressing the enzyme. She decides to mix this enzyme under subphysiologic conditions with varying levels of glucose in order to determine the kinetic properties of the enzyme. Specifically, she adds increasing levels of glucose at a saturating concentration of phosphate and sees that the rate at which glucose becomes phosphorylated gets faster at higher levels of glucose. She observes that this rate approaches a maximum speed and calls this speed Y. She then determines the concentration of glucose that is needed to make the enzyme function at half the speed Y and calls this concentration X. Which of the following is most likely true about the properties of this enzyme?
- A. High X and high Y
- B. Low X and infinite Y
- C. Low X and high Y (Correct Answer)
- D. Low X and low Y
- E. High X and low Y
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Low X and high Y***
- The enzyme described is **hexokinase**, which has a **low Km (X)** and a **high Vmax (Y)**. It is found in **most body tissues** and is located in the **cytoplasm**, matching the description in the question.
- **Low Km (X)** means hexokinase has **high affinity for glucose** and reaches half its maximum velocity at low glucose concentrations (typically 0.1 mM), allowing it to phosphorylate glucose efficiently even at low physiologic glucose levels.
- **High Vmax (Y)** indicates hexokinase has a high maximum reaction rate when saturated with substrate, enabling efficient glucose phosphorylation for cellular energy needs.
- Hexokinase is the first enzyme in glycolysis and is inhibited by its product, glucose-6-phosphate, providing feedback regulation.
*High X and high Y*
- This describes **glucokinase**, which has **high Km (low affinity)** and **high Vmax**, but glucokinase is only found in **liver and pancreatic β-cells**, not "most body tissues" as stated in the question.
- Glucokinase acts as a glucose sensor and phosphorylates glucose proportionally to blood glucose concentration after meals.
*Low X and infinite Y*
- An **infinite Vmax (Y)** is impossible for any enzyme, as all enzymes have a finite maximum reaction rate when saturated with substrate.
- This violates basic enzyme kinetics principles.
*Low X and low Y*
- While **low Km (X)** correctly describes hexokinase's high affinity for glucose, **low Vmax (Y)** is incorrect.
- Hexokinase has a **high Vmax**, not low, allowing it to rapidly phosphorylate glucose in tissues with high metabolic demands.
*High X and low Y*
- **High Km (X)** indicates low affinity for glucose, requiring higher substrate concentrations to achieve half-maximal velocity, which does not match the enzyme described as being present in most tissues.
- **Low Vmax (Y)** would limit the enzyme's capacity to handle glucose, which is inconsistent with the role of the primary glucose-phosphorylating enzyme in most tissues.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old woman with type 1 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department by her husband because of polyuria, nausea, vomiting, and altered mental status for 4 hours. On arrival, she is unconscious. Treatment with a drug is begun that increases glucose transport to skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Which of the following cellular events is most likely to also occur in response to this drug?
- A. Dephosphorylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Correct Answer)
- B. Increased activity of acyl-CoA dehydrogenases
- C. Cleavage of UDP from UDP-glucose
- D. Upregulation of glucose transporter type 3 expression
- E. Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Dephosphorylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase***
- The patient is in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and the drug administered is insulin
- Insulin promotes glucose utilization and storage, which involves inhibiting gluconeogenesis through the dephosphorylation and inactivation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
- This is a key regulatory mechanism by which insulin suppresses hepatic glucose production
*Increased activity of acyl-CoA dehydrogenases*
- This enzyme is crucial for fatty acid oxidation, a process that is inhibited by insulin
- In DKA, fatty acid oxidation is elevated, leading to ketone body production, but insulin treatment reduces this activity
*Cleavage of UDP from UDP-glucose*
- This reaction occurs in the synthesis of glycogen from UDP-glucose by glycogen synthase, which is activated by insulin
- While insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis, the direct cleavage of UDP from UDP-glucose is part of the synthetic process, not a primary regulatory cellular event caused by insulin in the context of DKA treatment
*Upregulation of glucose transporter type 3 expression*
- Glucose transporter type 3 (GLUT3) is primarily found in neurons and has a high affinity for glucose, with its expression generally not significantly regulated by insulin
- Insulin primarily promotes GLUT4 translocation to the cell membrane in muscle and adipose tissue to increase glucose uptake
*Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase*
- Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase activates it, subsequently activating glycogen phosphorylase and promoting glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis)
- Insulin inhibits glycogenolysis and promotes glycogen synthesis, meaning insulin would deactivate glycogen phosphorylase kinase through dephosphorylation
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 3: A 52-year-old man undergoes an exercise stress test for a 1-week history of squeezing substernal chest pain that is aggravated by exercise and relieved by rest. During the test, there is a substantial increase in the breakdown of glycogen in the muscle cells. Which of the following changes best explains this intracellular finding?
- A. Activation of phosphorylase kinase (Correct Answer)
- B. Decrease in protein kinase A
- C. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase
- D. Activation of protein phosphatase
- E. Increase in glucose-6-phosphate
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Activation of phosphorylase kinase***
- Exercise, particularly in the context of **ischemic heart disease** suggested by the patient's symptoms, triggers a rapid need for energy, leading to **glycogenolysis**.
- **Phosphorylase kinase** is the key enzyme that activates **glycogen phosphorylase**, the rate-limiting step in glycogen breakdown, to release glucose-1-phosphate from glycogen stores.
*Decrease in protein kinase A*
- **Protein kinase A (PKA)** is typically activated during exercise via **epinephrine** signaling, which in turn *activates* phosphorylase kinase and *inhibits* glycogen synthase.
- A decrease in PKA activity would lead to *reduced* glycogen breakdown, which contradicts the described increase in glycogen breakdown.
*Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase*
- **Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3)** phosphorylates and inactivates **glycogen synthase**, thereby *inhibiting* glycogen synthesis.
- If GSK3 were inactivated, glycogen synthesis would be *promoted*, rather than glycogen breakdown, further contradicting the clinical scenario.
*Activation of protein phosphatase*
- **Protein phosphatases** generally remove phosphate groups, which would *deactivate* glycogen phosphorylase and *activate* glycogen synthase.
- This action would promote glycogen synthesis and inhibit glycogen breakdown, which is the opposite of the observed physiological response during exercise.
*Increase in glucose-6-phosphate*
- While **glucose-6-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycogen metabolism, an increase in its concentration would primarily signal abundant glucose and tend to *inhibit* glycogen phosphorylase and *activate* glycogen synthase.
- This effect would favor glycogen synthesis and inhibit its breakdown, making it an unlikely explanation for increased glycogen breakdown during exercise.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 4: A 22-year-old medical student decides to fast for 24 hours after reading about the possible health benefits of fasting. She read that blood glucose levels are maintained by metabolic processes such as hepatic glycogenolysis and hepatic gluconeogenesis during the initial 3 days of fasting. During the day, she did not suffer from the symptoms of hypoglycemia. Which of the following signaling molecules most likely stimulated the reaction which maintained her blood glucose after all her stored glucose was broken down and used up?
- A. Adenosine diphosphate
- B. Acetyl CoA (Correct Answer)
- C. Acetate
- D. Citrate
- E. Adenosine monophosphate
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Acetyl CoA***
- **Acetyl CoA** is the key **allosteric activator of pyruvate carboxylase**, the first committed enzyme of gluconeogenesis that converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate.
- During prolonged fasting after glycogen stores are depleted, the body shifts to **fatty acid oxidation** (β-oxidation), which produces large amounts of **Acetyl CoA**.
- High **Acetyl CoA** levels signal that fat is being oxidized for energy, and simultaneously **activate gluconeogenesis** to maintain blood glucose for glucose-dependent tissues (brain, RBCs).
- This is the primary signaling mechanism that directly stimulates the gluconeogenic pathway after glycogen is exhausted.
*Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)*
- **AMP** levels rise during energy depletion and activate **AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)**.
- However, AMPK **inhibits gluconeogenesis** (not stimulates it) because gluconeogenesis is an **ATP-consuming** anabolic process (requires 6 ATP per glucose).
- AMPK promotes ATP-generating catabolic processes like fatty acid oxidation, but suppresses ATP-consuming processes like gluconeogenesis and fatty acid synthesis.
*Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)*
- **ADP** accumulates when ATP is hydrolyzed and signals moderate energy deficit.
- ADP is primarily a substrate for ATP regeneration via oxidative phosphorylation and does not directly regulate gluconeogenesis.
- Its role in metabolic regulation is less specific than allosteric activators like Acetyl CoA.
*Acetate*
- **Acetate** can be converted to Acetyl CoA but is not a direct signaling molecule for gluconeogenesis.
- It is a minor metabolite that may be produced in specific conditions (e.g., alcohol metabolism, ketoacidosis) but does not play a primary role in fasting-induced glucose homeostasis.
*Citrate*
- **Citrate** is a Krebs cycle intermediate that inhibits **phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)** in glycolysis, thus reducing glucose breakdown.
- While citrate inhibition of glycolysis indirectly favors gluconeogenesis by preventing futile cycling, citrate does not **directly activate** gluconeogenic enzymes.
- Citrate primarily signals energy sufficiency and promotes fatty acid synthesis in the fed state, not fasting gluconeogenesis.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 5: A 24-year-old man is running a marathon. Upon reaching the finish line, his serum lactate levels were measured and were significantly increased as compared to his baseline. Which of the following pathways converts the lactate produced by muscles into glucose and transports it back to the muscles?
- A. Citric acid cycle
- B. Glycolysis
- C. Glycogenesis
- D. Pentose phosphate pathway
- E. Cori cycle (Correct Answer)
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Cori cycle***
- The **Cori cycle** is the metabolic pathway that converts **lactate** produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles (especially during intense exercise) back to **glucose in the liver** via gluconeogenesis.
- During strenuous exercise, muscles rely on anaerobic glycolysis when oxygen supply is insufficient, producing lactate and 2 ATP per glucose.
- The lactate is transported via bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted back to glucose (requiring 6 ATP), which then returns to muscles for energy or glycogen storage.
- This cycle allows muscles to continue generating ATP anaerobically while the liver handles lactate clearance.
*Citric acid cycle*
- The **citric acid cycle** (Krebs cycle) oxidizes **acetyl-CoA** to generate ATP, NADH, and FADH₂ in the mitochondrial matrix under aerobic conditions.
- It does not convert lactate to glucose; rather, pyruvate can be converted to acetyl-CoA to enter this cycle for complete oxidation.
- This is an aerobic process and does not involve the liver-muscle lactate-glucose exchange.
*Glycolysis*
- **Glycolysis** is the metabolic pathway that breaks down **glucose into pyruvate**, generating 2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose molecule.
- Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to lactate to regenerate NAD⁺ for continued glycolysis.
- This is the opposite of what the question asks—glycolysis produces lactate from glucose, not glucose from lactate.
*Glycogenesis*
- **Glycogenesis** is the process of synthesizing **glycogen from glucose** for storage, primarily in liver and muscle tissue.
- While it involves glucose storage, it does not convert lactate back to glucose or involve the metabolic exchange between muscles and liver described in the question.
*Pentose phosphate pathway*
- The **pentose phosphate pathway** (hexose monophosphate shunt) produces **NADPH** for reductive biosynthesis and **ribose-5-phosphate** for nucleotide synthesis.
- It branches from glycolysis but is not involved in lactate metabolism or the muscle-liver glucose-lactate exchange.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 6: A newborn undergoing the standard screening tests is found to have a positive test for reducing sugars. Further testing is performed and reveals that the patient does not have galactosemia, but rather is given a diagnosis of fructosuria. What levels of enzymatic activity are altered in this patient?
- A. Hexokinase decreased; fructokinase decreased
- B. Hexokinase unchanged; fructokinase unchanged
- C. Hexokinase increased; fructokinase increased
- D. Hexokinase increased; fructokinase decreased
- E. Hexokinase unchanged; fructokinase decreased (Correct Answer)
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Hexokinase unchanged; fructokinase decreased***
- **Essential fructosuria** is caused by a deficiency in **fructokinase**, the enzyme responsible for the first step of fructose metabolism (fructose → fructose-1-phosphate).
- This results in **decreased or absent fructokinase activity**, leading to fructose accumulation in blood and urine (positive reducing sugar test).
- **Hexokinase activity remains unchanged** - there is no upregulation or compensatory increase in hexokinase. The enzyme maintains its normal baseline activity.
- Essential fructosuria is a **benign, asymptomatic condition** with no metabolic stress, so no compensatory enzyme changes occur.
- The small amount of fructose that needs metabolism can be handled by normal baseline hexokinase activity (hexokinase has broad substrate specificity).
*Hexokinase decreased; fructokinase decreased*
- While **fructokinase is decreased** in essential fructosuria, hexokinase activity is not decreased.
- Hexokinase is a constitutively expressed glycolytic enzyme whose activity does not change in this benign condition.
*Hexokinase unchanged; fructokinase unchanged*
- This is incorrect because **fructokinase activity is specifically decreased** in essential fructosuria, which is the defining enzymatic defect of the condition.
- The decreased fructokinase activity causes fructose to accumulate and appear in the urine.
*Hexokinase increased; fructokinase increased*
- **Fructokinase is decreased, not increased** - an increase would prevent the fructose accumulation characteristic of this condition.
- Hexokinase activity does not increase as essential fructosuria causes no metabolic stress requiring compensation.
*Hexokinase increased; fructokinase decreased*
- While **fructokinase is decreased** in essential fructosuria, hexokinase activity does not increase.
- This is a benign condition with no compensatory enzyme upregulation - hexokinase maintains normal baseline activity levels.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 7: Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) type 2 is a consequence of a defective pancreatic enzyme, which normally acts as a glucose sensor, resulting in a mild hyperglycemia. The hyperglycemia is especially exacerbated during pregnancy. Which of the following pathways is controlled by this enzyme?
- A. Fructose-6-phosphate --> fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- B. Phosphoenolpyruvate --> pyruvate
- C. Glucose --> glucose-6-phosphate (Correct Answer)
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate --> fructose-6-phosphate
- E. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate --> 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Glucose --> glucose-6-phosphate***
- This reaction is catalyzed by **glucokinase** in the pancreatic beta cells, which serves as a **glucose sensor** by controlling the rate-limiting step of glycolysis.
- MODY type 2 is caused by mutations in the **glucokinase gene (GCK)**, leading to a higher threshold for insulin secretion and mild hyperglycemia, particularly exacerbated during pregnancy.
*Fructose-6-phosphate --> fructose-1,6-bisphosphate*
- This step is catalyzed by **phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)**, a key regulatory enzyme in glycolysis, but it is not the primary glucose sensor in pancreatic beta cells.
- While important for glycolysis, defects in PFK-1 are associated with glycolytic enzyme deficiencies (e.g., Tarui's disease), not MODY type 2.
*Phosphoenolpyruvate --> pyruvate*
- This final step of glycolysis is catalyzed by **pyruvate kinase**, an enzyme that is regulated but does not act as the primary glucose sensor.
- Pyruvate kinase deficiency leads to hemolytic anemia and is not associated with MODY type 2.
*Glucose-6-phosphate --> fructose-6-phosphate*
- This reversible isomerization step is catalyzed by **phosphoglucose isomerase**, and while part of glycolysis, it is not the rate-limiting step or the primary glucose sensing mechanism in pancreatic beta cells.
- Defects in this enzyme are rare and not linked to MODY type 2.
*Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate --> 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate*
- This step is catalyzed by **glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)**, an important enzyme in glycolysis.
- GAPDH is involved in energy production but is not considered the glucose sensor for insulin release, and its defects are not associated with MODY type 2.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 8: A 12-year-old boy and his siblings are referred to a geneticist for evaluation of a mild but chronic hemolytic anemia that has presented with fatigue, splenomegaly, and scleral icterus. Coombs test is negative and blood smear does not show any abnormal findings. An enzymatic panel is assayed, and pyruvate kinase is found to be mutated on both alleles. The geneticist explains that pyruvate kinase functions in glycolysis and is involved in a classic example of feed-forward regulation. Which of the following metabolites is able to activate pyruvate kinase?
- A. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (Correct Answer)
- B. Alanine
- C. ATP
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate
- E. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate***
- **Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate** is a potent **allosteric activator** of pyruvate kinase. This is an example of **feed-forward activation**, where a product of an early irreversible step in glycolysis (catalyzed by phosphofructokinase-1) activates a later enzyme (pyruvate kinase) in the pathway.
- This activation ensures that substrates for the later steps of glycolysis are rapidly utilized when earlier steps are highly active, matching the rate of metabolite flow and increasing the overall efficiency of glycolysis for energy production.
*Alanine*
- **Alanine** is an **inhibitor** of pyruvate kinase, not an activator. It serves as an indicator of a high cellular energy state and ample amino acid supply.
- High levels of alanine signal the cell that there is sufficient energy and building blocks, thus **shutting down** glycolysis at the pyruvate kinase step to conserve glucose for other needs like glycogen synthesis.
*ATP*
- **ATP** (adenosine triphosphate) is an **allosteric inhibitor** of pyruvate kinase. High ATP levels signal a high energy state in the cell.
- When the cell has sufficient energy, ATP binds to a regulatory site on pyruvate kinase, reducing its activity and **slowing down glycolysis** to prevent overproduction of ATP.
*Glucose-6-phosphate*
- **Glucose-6-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycolysis but does not directly activate pyruvate kinase. It can act as an allosteric inhibitor of hexokinase, the first enzyme in glycolysis, but not pyruvate kinase.
- Its accumulation typically signifies a **backup** in the glycolytic pathway (e.g., due to downstream inhibition), leading to a *reduction* in overall glucose flux rather than a direct activation of pyruvate kinase.
*Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate*
- **Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycolysis, but it does not directly activate pyruvate kinase. It is a substrate for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- While its presence indicates active glycolysis, it does not exert a specific allosteric regulatory effect on pyruvate kinase in the way fructose-1,6-bisphosphate does.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 9: A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of acute onset abdominal pain. On arrival, he also complains of nausea and shortness of breath in addition to epigastric pain. He has previously been admitted to the hospital several times for respiratory infections with Pseudomonas species and uses a nebulizer and a chest wall oscillation vest at home. The patient's acute condition is found to be due to premature activation of an enzyme that normally interacts with the brush border. Which of the following describes the activity of this enzyme?
- A. Activates pancreatic enzyme precursors (Correct Answer)
- B. Breaks down elastin molecules
- C. Hydrolyzes phospholipids
- D. Digests triglycerides
- E. Activates phospholipase A2
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Activates pancreatic enzyme precursors***
- The patient's history of **recurrent respiratory infections with Pseudomonas** and use of a **nebulizer/chest wall oscillation vest** strongly suggests **cystic fibrosis (CF)**.
- In cystic fibrosis, **thickened secretions** can obstruct the pancreatic ducts, leading to **autodigestion of the pancreas** due to obstruction preventing the release of pancreatic enzymes. The enzyme being referred to is **trypsin**, which, when prematurely activated, activates other pancreatic enzyme precursors, leading to **pancreatitis**.
*Breaks down elastin molecules*
- This activity is characteristic of **elastase**, an enzyme produced by the pancreas. While elastase is involved in the overall digestive process and can be prematurely activated, its primary role is not the one alluded to in the clinical presentation, which points to **pancreatitis** from premature activation of the cascade.
- Damage to elastin is more classically associated with conditions like **emphysema** (due to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency) rather than acute abdominal pain secondary to autodigestion.
*Hydrolyzes phospholipids*
- This is the function of **phospholipase**, another pancreatic enzyme. While also capable of contributing to pancreatic autodigestion if prematurely activated, it is typically activated by **trypsin**, making trypsin the primary enzyme responsible for initiating the cascade of activation.
- **Phospholipase A2** acts on phospholipids, but the question describes an enzyme that *normally interacts with the brush border* before activation of the precursors begins.
*Digests triglycerides*
- This is the function of **pancreatic lipase**. Premature activation of lipase can contribute to the fat necrosis seen in pancreatitis.
- However, lipase, like many other pancreatic enzymes, is activated by **trypsin**, which is the initial enzyme in the cascade of activation leading to autodigestion.
*Activates phospholipase A2*
- This describes the action of **trypsinogen turning into trypsin**, which then activates other proenzymes like **prophospholipase A2**.
- While correct that trypsin activates phospholipase A2, the question asks about the primary enzyme whose *premature activation* causes the issue, which is **trypsin** itself, as it activates *multiple* pancreatic enzyme precursors, initiating a cascade.
Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG Question 10: A 16-year-old teenager is brought to the emergency department after having slipped on ice while walking to school. She hit her head on the side of the pavement and retained consciousness. She was brought to the closest ER within an hour of the incident. The ER physician sends her immediately to get a CT scan and also orders routine blood work. The physician understands that in cases of stress, such as in this patient, the concentration of certain hormones will be increased, while others will be decreased. Considering allosteric regulation by hormones, which of the following enzymes will most likely be inhibited in this patient?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- B. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
- C. Pyruvate carboxylase
- D. Phosphofructokinase (Correct Answer)
- E. Glycogen phosphorylase
Preparatory phase reactions Explanation: ***Phosphofructokinase***
- In a stress state, **cortisol** and **epinephrine** levels are elevated, leading to increased **gluconeogenesis** and **glycogenolysis** to provide rapid energy.
- **Allosteric inhibition** of PFK-1 occurs through multiple mechanisms:
- **ATP** and **citrate** (high energy signals) act as direct **allosteric inhibitors** of PFK-1
- **Glucagon** (elevated during stress) indirectly inhibits PFK-1 by reducing levels of **fructose-2,6-bisphosphate**, a potent allosteric activator
- This inhibition of glycolysis spares glucose for critical organs like the brain and heart.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- This enzyme catalyzes the final step of **gluconeogenesis** and **glycogenolysis**, converting G6P to free glucose.
- During stress, its activity is **stimulated** to increase blood glucose levels, not inhibited.
*Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase*
- This enzyme plays a key role in **gluconeogenesis**, a process vital for maintaining glucose homeostasis during stress.
- Its activity would be **upregulated** to produce glucose, rather than inhibited.
*Pyruvate carboxylase*
- This enzyme initiates **gluconeogenesis** by converting pyruvate to oxaloacetate in the mitochondria.
- During stress, its activity is **stimulated** by elevated acetyl-CoA (an allosteric activator), not inhibited.
*Glycogen phosphorylase*
- This enzyme is responsible for **glycogenolysis**, the breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate.
- Its activity is **stimulated** by stress hormones (epinephrine and glucagon) through cAMP-mediated phosphorylation, ensuring rapid glucose availability.
More Preparatory phase reactions US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.