Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Energy yield and ATP production. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after vomiting blood. The patient reports that he only ate a small snack the morning before and had not eaten anything for over 24 hours. At the hospital, the patient is stabilized. He is admitted to a surgical floor and placed on NPO with a nasogastric tube set to intermittent suction. He has been previously diagnosed with liver cirrhosis. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) has been planned for the next afternoon. At the time of endoscopy, some pathways were generating glucose to maintain serum glucose levels. Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the irreversible biochemical reaction of this process?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- B. Glycogen phosphorylase
- C. Enolase
- D. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- E. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Correct Answer)
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase***
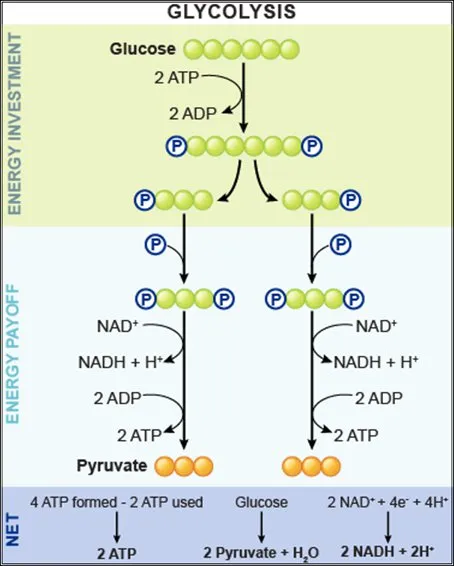
- The scenario describes a patient in a fasting state for over 24 hours, during which **gluconeogenesis** is crucial for maintaining blood glucose levels.
- **Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase** is one of the key regulatory enzymes in gluconeogenesis, catalyzing an **irreversible reaction** that bypasses the phosphofructokinase-1 step of glycolysis.
*Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- This enzyme is involved in the **pentose phosphate pathway**, which generates NADPH and precursors for nucleotide synthesis.
- It does not directly participate in gluconeogenesis to produce glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
*Glycogen phosphorylase*
- This enzyme is involved in **glycogenolysis**, the breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate.
- While it releases glucose, the body's glycogen stores would likely be depleted after over 24 hours of fasting, making gluconeogenesis the primary pathway for glucose production.
*Enolase*
- Enolase is an enzyme in the glycolytic pathway, catalyzing the reversible conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
- It is not an enzyme of gluconeogenesis, nor does it catalyze an irreversible step in the glucose production process during fasting.
*Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- This enzyme is also part of glycolysis, catalyzing the reversible oxidation and phosphorylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
- Like enolase, it is not an irreversible enzyme in gluconeogenesis that would be generating glucose under fasting conditions.
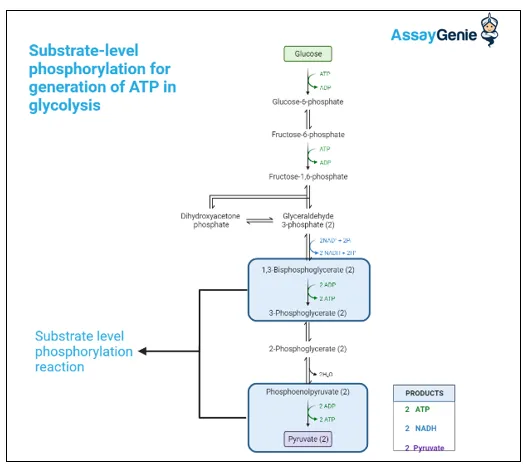
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 2: To prepare for an endoscopy, a 27-year-old male was asked by the gastroenterologist to fast overnight for his 12 p.m. appointment the next day. Therefore, his last meal was dinner at 5 p.m. the day before the appointment. By 12 p.m. the day of the appointment, his primary source of glucose was being generated from gluconeogenesis, which occurs via the reversal of glycolysis with extra enzymes to bypass the irreversible steps in glycolysis. Which of the following irreversible steps of gluconeogenesis occurs in the mitochondria?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose
- B. Pyruvate to oxaloacetate (Correct Answer)
- C. Phosphoenolypyruvate to pyruvate
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone
- E. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Pyruvate to oxaloacetate***
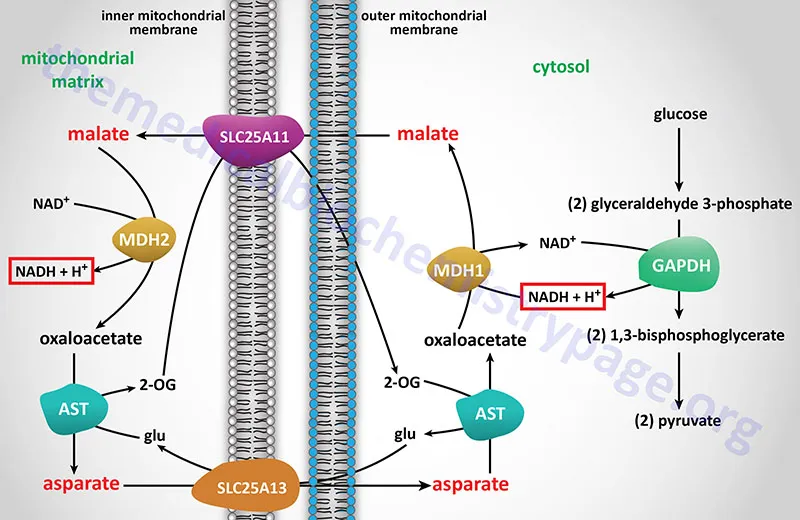
- This step, catalyzed by **pyruvate carboxylase**, is the initial and irreversible step of **gluconeogenesis** that occurs within the **mitochondrial matrix**.
- **Pyruvate** is converted to **oxaloacetate**, which then either is converted to malate to exit the mitochondria or remains in the mitochondria for subsequent steps of gluconeogenesis depending on the tissue.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to glucose*
- This final dephosphorylation step of gluconeogenesis, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphatase**, occurs in the **endoplasmic reticulum** lumen, not the mitochondria.
- It is crucial for releasing free glucose into the bloodstream.
*Phosphoenolypyruvate to pyruvate*
- This is an irreversible step in **glycolysis**, catalyzed by **pyruvate kinase**, and it is going in the *opposite direction* to what happens in gluconeogenesis.
- In gluconeogenesis, **pyruvate** is converted back to **phosphoenolpyruvate** via oxaloacetate, involving enzymes in both the mitochondria and cytoplasm.
*Glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone*
- This reaction is the first committed step of the **pentose phosphate pathway**, catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase** and it occurs in the cytoplasm, not mitochondria.
- It is involved in producing NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate, not directly in gluconeogenesis.
*Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate*
- This irreversible dephosphorylation step in gluconeogenesis, catalyzed by **fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase**, occurs in the **cytoplasm**.
- It bypasses the phosphofructokinase-1 step of glycolysis.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 3: A 26-year-old African American man comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fatigue, back pain, and dark urine. One week ago, he developed a headache and was treated with aspirin. He does not smoke or use illicit drugs. Physical examination shows conjunctival pallor. A peripheral blood smear shows erythrocytes with inclusions of denatured hemoglobin. Which of the following enzymes is involved in providing precursors for nucleotide synthesis in this patient?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
- C. Pyruvate carboxylase
- D. Transaldolase (Correct Answer)
- E. Enolase
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Transaldolase***
- This patient likely has **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**, indicated by fatigue, dark urine (hemolysis), and **Heinz bodies** (erythrocytes with inclusions of denatured hemoglobin) after aspirin exposure, which is an **oxidative stressor**.
- **Transaldolase** is an enzyme in the **non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)**, which produces **ribose-5-phosphate**, a precursor for nucleotide synthesis.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- **Glucose-6-phosphatase** is involved in **gluconeogenesis** and glycogenolysis, primarily in the liver and kidneys, to release free glucose into the bloodstream.
- Deficiency leads to **Von Gierke disease**, characterized by hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, lactic acidosis, and hyperlipidemia, which are not described here.
*Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I*
- **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)** is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in the **urea cycle**, converting ammonia and bicarbonate into carbamoyl phosphate.
- Its deficiency causes **hyperammonemia**, not hemolytic anemia or issues with nucleotide synthesis.
*Pyruvate carboxylase*
- **Pyruvate carboxylase** is a mitochondrial enzyme that converts **pyruvate to oxaloacetate**, a crucial step in **gluconeogenesis** and replenishing intermediates of the citric acid cycle.
- Deficiency can lead to lactic acidosis and hypoglycemia, which are not the primary symptoms here.
*Enolase*
- **Enolase** is an enzyme in **glycolysis** that catalyzes the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
- It is not directly involved in providing precursors for nucleotide synthesis.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 4: A 52-year-old man undergoes an exercise stress test for a 1-week history of squeezing substernal chest pain that is aggravated by exercise and relieved by rest. During the test, there is a substantial increase in the breakdown of glycogen in the muscle cells. Which of the following changes best explains this intracellular finding?
- A. Activation of phosphorylase kinase (Correct Answer)
- B. Decrease in protein kinase A
- C. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase
- D. Activation of protein phosphatase
- E. Increase in glucose-6-phosphate
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Activation of phosphorylase kinase***
- Exercise, particularly in the context of **ischemic heart disease** suggested by the patient's symptoms, triggers a rapid need for energy, leading to **glycogenolysis**.
- **Phosphorylase kinase** is the key enzyme that activates **glycogen phosphorylase**, the rate-limiting step in glycogen breakdown, to release glucose-1-phosphate from glycogen stores.
*Decrease in protein kinase A*
- **Protein kinase A (PKA)** is typically activated during exercise via **epinephrine** signaling, which in turn *activates* phosphorylase kinase and *inhibits* glycogen synthase.
- A decrease in PKA activity would lead to *reduced* glycogen breakdown, which contradicts the described increase in glycogen breakdown.
*Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase*
- **Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3)** phosphorylates and inactivates **glycogen synthase**, thereby *inhibiting* glycogen synthesis.
- If GSK3 were inactivated, glycogen synthesis would be *promoted*, rather than glycogen breakdown, further contradicting the clinical scenario.
*Activation of protein phosphatase*
- **Protein phosphatases** generally remove phosphate groups, which would *deactivate* glycogen phosphorylase and *activate* glycogen synthase.
- This action would promote glycogen synthesis and inhibit glycogen breakdown, which is the opposite of the observed physiological response during exercise.
*Increase in glucose-6-phosphate*
- While **glucose-6-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycogen metabolism, an increase in its concentration would primarily signal abundant glucose and tend to *inhibit* glycogen phosphorylase and *activate* glycogen synthase.
- This effect would favor glycogen synthesis and inhibit its breakdown, making it an unlikely explanation for increased glycogen breakdown during exercise.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 5: After being warned by the locals not to consume the freshwater, a group of American backpackers set off on a week-long hike into a region of the Ecuadorean Amazon forest known for large gold mines. The group of hikers stopped near a small stream and used the water they filtered from the stream to make dinner. Within the next half hour, the hikers began to experience headaches, vertigo, visual disturbances, confusion, tachycardia, and altered levels of consciousness. Which of the following enzymes was most likely inhibited in this group of hikers?
- A. NADH dehydrogenase
- B. ATP synthase
- C. Cytochrome c oxidase (Correct Answer)
- D. Cytochrome bc1 complex
- E. Succinate dehydrogenase
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Cytochrome c oxidase***
- The symptoms described (headaches, vertigo, visual disturbances, confusion, tachycardia, altered consciousness occurring within 30 minutes) are characteristic of **acute cyanide poisoning**.
- **Cyanide** is commonly found in water near **gold mining operations**, where it is used in the gold extraction process and can contaminate local water sources.
- **Cyanide** is a potent inhibitor of **cytochrome c oxidase** (Complex IV) in the electron transport chain, binding to the heme iron (Fe³⁺) and preventing oxygen utilization, leading to **histotoxic hypoxia**.
- This results in cellular energy failure, particularly affecting high-energy-demand organs like the brain and heart, explaining the acute neurological and cardiovascular symptoms.
*NADH dehydrogenase*
- While NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) is a component of the electron transport chain, it is not the primary target of **cyanide poisoning**.
- Inhibitors of Complex I include rotenone and barbiturates, which cause different clinical presentations and do not produce the rapid onset of symptoms seen with cyanide.
*ATP synthase*
- **ATP synthase** (Complex V) synthesizes ATP using the proton gradient, but it is not directly inhibited by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of ATP synthase, such as oligomycin, prevent ATP synthesis by blocking the enzyme directly, whereas cyanide acts upstream at Complex IV.
*Cytochrome bc1 complex*
- The **cytochrome bc1 complex** (Complex III) is involved in electron transfer and proton pumping, but it is not the primary enzyme inhibited by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of Complex III include antimycin A, which would disrupt the electron transport chain but do not cause the characteristic rapid-onset symptoms of cyanide poisoning.
*Succinate dehydrogenase*
- **Succinate dehydrogenase** (Complex II) participates in both the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain, but it is not targeted by **cyanide**.
- Inhibitors of Complex II, such as malonate, competitively block succinate oxidation but do not produce the acute systemic toxicity characteristic of cyanide poisoning.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 6: An investigator is studying muscle tissue in high-performance athletes. He obtains blood samples from athletes before and after a workout session consisting of short, fast sprints. Which of the following findings is most likely upon evaluation of blood obtained after the workout session?
- A. Decreased concentration of NADH
- B. Increased concentration of H+ (Correct Answer)
- C. Decreased concentration of lactate
- D. Increased concentration of insulin
- E. Increased concentration of ATP
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Increased concentration of H+***
- During **anaerobic metabolism** in high-intensity exercise like sprints, pyruvate is converted to **lactate** by **lactate dehydrogenase** to regenerate NAD+. This process produces H+, leading to a decrease in pH and an increase in H+ concentration in the blood.
- The accumulation of **hydrogen ions (H+)** contributes to metabolic acidosis, muscle fatigue, and the burning sensation experienced during intense exertion.
- Blood gas analysis would show **decreased pH** and **increased H+ concentration**.
*Decreased concentration of NADH*
- NADH is primarily an **intracellular metabolite** and is not typically measured in blood samples as it does not circulate freely in significant concentrations.
- Within muscle cells during anaerobic glycolysis, NADH is consumed by lactate dehydrogenase to convert pyruvate to lactate, regenerating NAD+ for continued glycolysis.
- This option is not a realistic blood finding from a clinical laboratory perspective.
*Decreased concentration of lactate*
- **High-intensity sprints** primarily rely on **anaerobic metabolism**, which rapidly produces **lactate** from pyruvate.
- Therefore, the concentration of lactate in the blood would significantly **increase** after such a workout, not decrease.
- Elevated blood lactate is a hallmark finding after intense anaerobic exercise.
*Increased concentration of insulin*
- **Insulin** levels typically **decrease** during exercise, especially high-intensity exercise, due to **sympathetic nervous system activation** and the body's need to mobilize glucose from liver glycogen and fatty acids.
- Exercise promotes glucose uptake through **insulin-independent mechanisms** (GLUT4 translocation via AMP-activated protein kinase).
- Increased insulin would be counterproductive during intense exercise when glucose mobilization is needed.
*Increased concentration of ATP*
- ATP does not circulate in blood in measurable concentrations as a typical laboratory finding.
- Within muscle cells, ATP is rapidly **consumed** during intense exercise to fuel muscle contraction.
- While cells work to maintain ATP levels through anaerobic glycolysis and the creatine phosphate system, net ATP does not accumulate in the blood.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 7: A research group is investigating an allosteric modulator to improve exercise resistance and tolerance at low-oxygen conditions. The group has created cultures of myocytes derived from high-performance college athletes. The application of this compound to these cultures in a low-oxygen environment and during vigorous contraction leads to longer utilization of glucose before reaching a plateau and cell death; however, the culture medium is significantly acidified in this experiment. An activating effect on which of the following enzymes would explain these results?
- A. Bisphosphoglycerate mutase
- B. Lactate dehydrogenase (Correct Answer)
- C. Enolase
- D. Malate dehydrogenase
- E. Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Lactate dehydrogenase***
- Enhanced **lactate dehydrogenase** activity would lead to increased conversion of **pyruvate to lactate**, regenerating **NAD+** for glycolysis to continue under **anaerobic conditions**.
- This process explains the **longer glucose utilization** and the significant **acidification of the medium** due to lactate production.
*Bisphosphoglycerate mutase*
- This enzyme is involved in the synthesis of **2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG)** in red blood cells, which affects **hemoglobin's oxygen affinity**, not direct glucose utilization in myocytes under anaerobic conditions.
- While important for oxygen delivery, its activation would not primarily explain the observed **increased glucose utilization** and **lactic acid accumulation** in myocyte cultures.
*Enolase*
- **Enolase** catalyzes the conversion of **2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate** in glycolysis.
- While crucial for glycolysis, its activation alone without an efficient disposal pathway for **pyruvate** (like lactate formation) would not sustain glucose metabolism and lead to such pronounced acidification under anaerobic stress.
*Malate dehydrogenase*
- **Malate dehydrogenase** is primarily involved in the **citric acid cycle** and the **malate-aspartate shuttle**, operating under **aerobic conditions** to convert malate to oxaloacetate.
- Its activation would not sustain glycolysis or lead to the observed **acidification** in a low-oxygen environment, where the citric acid cycle is inhibited.
*Pyruvate dehydrogenase*
- **Pyruvate dehydrogenase** converts **pyruvate to acetyl-CoA**, shunting carbons into the **citric acid cycle** for **aerobic respiration**.
- In a **low-oxygen environment**, this enzyme's activity would be limited due to reduced oxygen, and its activation would not explain the sustained glucose utilization or the significant **lactic acid accumulation** from anaerobic metabolism.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 8: A startup is working on a novel project in which they claim they can replicate the organelle that is defective in MELAS syndrome. Which of the following metabolic processes must they be able to replicate if their project is to mimic the metabolic processes of this organelle?
- A. Hexose monophosphate shunt
- B. Cholesterol synthesis
- C. Glycolysis
- D. Fatty acid (beta) oxidation (Correct Answer)
- E. Fatty acid synthesis
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Fatty acid (beta) oxidation***
- **MELAS syndrome** (Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like episodes) is caused by defects in **mitochondrial function**.
- **Beta-oxidation of fatty acids** is a crucial metabolic process that occurs within the mitochondria, generating ATP.
*Hexose monophosphate shunt*
- The **hexose monophosphate shunt** (pentose phosphate pathway) occurs in the **cytosol** and is primarily involved in producing NADPH and synthesizing nucleotides, not a primary mitochondrial function.
- Its dysfunction is not directly linked to the core metabolic defects seen in MELAS syndrome.
*Cholesterol synthesis*
- **Cholesterol synthesis** primarily occurs in the **cytosol** and the **endoplasmic reticulum**, not within the mitochondria.
- While cholesterol metabolism can be indirectly affected by mitochondrial health, it is not a direct mitochondrial metabolic pathway.
*Glycolysis*
- **Glycolysis** is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, occurring in the **cytosol**.
- Although it precedes mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis itself does not occur within the mitochondria.
*Fatty acid synthesis*
- **Fatty acid synthesis** primarily takes place in the **cytosol** and endoplasmic reticulum, utilizing NADPH from the hexose monophosphate shunt.
- It is an anabolic process, while MELAS typically involves defects in catabolic/energy-producing mitochondrial pathways.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 9: A 16-year-old teenager is brought to the emergency department after having slipped on ice while walking to school. She hit her head on the side of the pavement and retained consciousness. She was brought to the closest ER within an hour of the incident. The ER physician sends her immediately to get a CT scan and also orders routine blood work. The physician understands that in cases of stress, such as in this patient, the concentration of certain hormones will be increased, while others will be decreased. Considering allosteric regulation by hormones, which of the following enzymes will most likely be inhibited in this patient?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- B. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
- C. Pyruvate carboxylase
- D. Phosphofructokinase (Correct Answer)
- E. Glycogen phosphorylase
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Phosphofructokinase***
- In a stress state, **cortisol** and **epinephrine** levels are elevated, leading to increased **gluconeogenesis** and **glycogenolysis** to provide rapid energy.
- **Allosteric inhibition** of PFK-1 occurs through multiple mechanisms:
- **ATP** and **citrate** (high energy signals) act as direct **allosteric inhibitors** of PFK-1
- **Glucagon** (elevated during stress) indirectly inhibits PFK-1 by reducing levels of **fructose-2,6-bisphosphate**, a potent allosteric activator
- This inhibition of glycolysis spares glucose for critical organs like the brain and heart.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- This enzyme catalyzes the final step of **gluconeogenesis** and **glycogenolysis**, converting G6P to free glucose.
- During stress, its activity is **stimulated** to increase blood glucose levels, not inhibited.
*Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase*
- This enzyme plays a key role in **gluconeogenesis**, a process vital for maintaining glucose homeostasis during stress.
- Its activity would be **upregulated** to produce glucose, rather than inhibited.
*Pyruvate carboxylase*
- This enzyme initiates **gluconeogenesis** by converting pyruvate to oxaloacetate in the mitochondria.
- During stress, its activity is **stimulated** by elevated acetyl-CoA (an allosteric activator), not inhibited.
*Glycogen phosphorylase*
- This enzyme is responsible for **glycogenolysis**, the breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate.
- Its activity is **stimulated** by stress hormones (epinephrine and glucagon) through cAMP-mediated phosphorylation, ensuring rapid glucose availability.
Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG Question 10: A 12-year-old boy and his siblings are referred to a geneticist for evaluation of a mild but chronic hemolytic anemia that has presented with fatigue, splenomegaly, and scleral icterus. Coombs test is negative and blood smear does not show any abnormal findings. An enzymatic panel is assayed, and pyruvate kinase is found to be mutated on both alleles. The geneticist explains that pyruvate kinase functions in glycolysis and is involved in a classic example of feed-forward regulation. Which of the following metabolites is able to activate pyruvate kinase?
- A. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (Correct Answer)
- B. Alanine
- C. ATP
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate
- E. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Energy yield and ATP production Explanation: ***Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate***
- **Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate** is a potent **allosteric activator** of pyruvate kinase. This is an example of **feed-forward activation**, where a product of an early irreversible step in glycolysis (catalyzed by phosphofructokinase-1) activates a later enzyme (pyruvate kinase) in the pathway.
- This activation ensures that substrates for the later steps of glycolysis are rapidly utilized when earlier steps are highly active, matching the rate of metabolite flow and increasing the overall efficiency of glycolysis for energy production.
*Alanine*
- **Alanine** is an **inhibitor** of pyruvate kinase, not an activator. It serves as an indicator of a high cellular energy state and ample amino acid supply.
- High levels of alanine signal the cell that there is sufficient energy and building blocks, thus **shutting down** glycolysis at the pyruvate kinase step to conserve glucose for other needs like glycogen synthesis.
*ATP*
- **ATP** (adenosine triphosphate) is an **allosteric inhibitor** of pyruvate kinase. High ATP levels signal a high energy state in the cell.
- When the cell has sufficient energy, ATP binds to a regulatory site on pyruvate kinase, reducing its activity and **slowing down glycolysis** to prevent overproduction of ATP.
*Glucose-6-phosphate*
- **Glucose-6-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycolysis but does not directly activate pyruvate kinase. It can act as an allosteric inhibitor of hexokinase, the first enzyme in glycolysis, but not pyruvate kinase.
- Its accumulation typically signifies a **backup** in the glycolytic pathway (e.g., due to downstream inhibition), leading to a *reduction* in overall glucose flux rather than a direct activation of pyruvate kinase.
*Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate*
- **Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycolysis, but it does not directly activate pyruvate kinase. It is a substrate for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- While its presence indicates active glycolysis, it does not exert a specific allosteric regulatory effect on pyruvate kinase in the way fructose-1,6-bisphosphate does.
More Energy yield and ATP production US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.