Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Alternative glycolytic pathways. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 1: A 20-year-old male with no significant medical history comes to you with a urine positive for fructose. He does not have diabetes mellitus. Which enzyme is most likely to be deficient in this patient?
- A. Pyruvate kinase
- B. Lactase
- C. Fructokinase (Correct Answer)
- D. Aldolase B
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***Fructokinase***
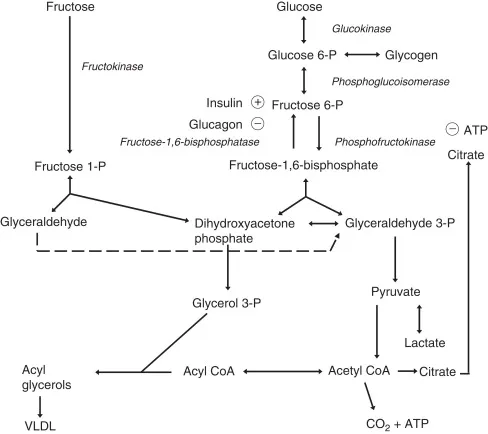
- A urine positive for **fructose** without symptoms of diabetes mellitus (i.e., **benign fructosuria**) is characteristic of a **fructokinase deficiency**.
- **Fructokinase** is the enzyme responsible for the first step in fructose metabolism, converting **fructose to fructose-1-phosphate**.
*Pyruvate kinase*
- Deficiency of **pyruvate kinase** primarily affects **glycolysis** in red blood cells and leads to **hemolytic anemia**, not fructosuria.
- This enzyme converts **phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate**.
*Lactase*
- **Lactase** is an enzyme that digests **lactose** (milk sugar) into glucose and galactose.
- A deficiency in lactase causes **lactose intolerance**, presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms like bloating and diarrhea after consuming dairy products, not fructose in the urine.
*Aldolase B*
- A deficiency in **aldolase B** leads to **hereditary fructose intolerance**, a severe condition where **fructose-1-phosphate accumulates** after fructose ingestion.
- This typically presents with symptoms such as **hypoglycemia**, vomiting, jaundice, and liver damage, which are not described in this benign case of fructosuria.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 2: A 2-day-old boy is examined on day of discharge from the newborn nursery. He was born at 39 weeks by vaginal delivery to a primigravid mother. The pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated, and the baby has been stooling, urinating, and feeding normally. Both the patient’s mother and father have no known past medical history and are found to have normal hemoglobin electrophoresis results. Compared to adult hemoglobin, the infant’s predominant hemoglobin is most likely to exhibit which of the following properties?
- A. Decreased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (Correct Answer)
- B. More likely to form hexagonal crystals
- C. More likely to cause red blood cell sickling
- D. Lower affinity for binding oxygen
- E. Increased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***Decreased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate***
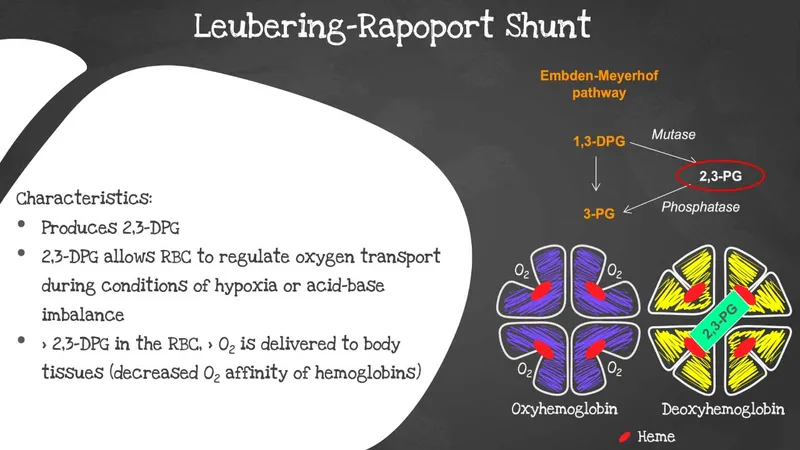
- The baby's predominant hemoglobin is **hemoglobin F (HbF)**, which has a **gamma globin subunit** instead of the beta globin subunit found in adult hemoglobin (HbA).
- The gamma subunit of HbF results in a **reduced binding affinity to 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG)**, which in turn leads to a **higher affinity for oxygen** and more efficient oxygen transfer from the mother to the fetus.
*More likely to form hexagonal crystals*
- The formation of **hexagonal crystals** is characteristic of **hemoglobin C (HbC)** disease, a variant of adult hemoglobin, which is not predominant in a newborn.
- The parents have normal hemoglobin electrophoresis, ruling out the inheritance of significant hemoglobinopathies like HbC in a homozygous or compound heterozygous state.
*More likely to cause red blood cell sickling*
- **Red blood cell sickling** is a hallmark of **sickle cell anemia**, caused by hemoglobin S (HbS) which is an abnormal adult hemoglobin, not fetal hemoglobin.
- The parents have normal hemoglobin electrophoresis, meaning they are unlikely to carry the sickle cell trait, and the newborn's predominant HbF actually protects against sickling.
*Lower affinity for binding oxygen*
- HbF in newborns has a **higher affinity for oxygen** than adult hemoglobin (HbA) to facilitate efficient oxygen extraction from maternal blood across the placenta.
- A lower affinity for oxygen would be detrimental for a newborn as it would impair proper tissue oxygenation.
*Increased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate*
- HbF has a **decreased affinity for 2,3-BPG**. An increased affinity for 2,3-BPG would lead to a reduction in oxygen binding affinity, which is the opposite of the physiological need in a newborn.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 3: A 6-month-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of recurrent vomiting and yellowing of his eyes. The mother says that he has been eating poorly since she started weaning him off of breast milk 5 days ago. At this time, mashed vegetables and fruits were added to his diet. Examination shows scleral jaundice and dry mucous membranes. The tip of the liver is palpable 4 cm below the right costal margin. His serum glucose concentration is 47 mg/dL, serum alanine aminotransferase is 55 U/L, and serum aspartate aminotransferase is 66 U/L. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient?
- A. Fructokinase
- B. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- C. Galactokinase
- D. Galactose-1 phosphate uridyltransferase
- E. Aldolase B (Correct Answer)
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***Aldolase B***
- The symptoms, including **jaundice**, vomiting, **hepatomegaly**, and **hypoglycemia** following the introduction of solid foods (specifically fruits and vegetables containing **fructose**), are classic for **hereditary fructose intolerance**.
- **Aldolase B** is crucial for metabolizing fructose in the liver; its deficiency leads to the buildup of **fructose-1-phosphate**, which is toxic to hepatocytes and inhibits glucose production.
*Fructokinase*
- Fructokinase deficiency causes **essential fructosuria**, a benign condition characterized by fructose in the urine, but without the severe metabolic disturbances like hypoglycemia and liver damage seen in this patient.
- This condition does not typically present with the **jaundice**, vomiting, and liver enlargement found in the given case.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- A deficiency in **glucose-6-phosphatase** causes **Type I glycogen storage disease (Von Gierke disease)**, which presents with severe hypoglycemia and hepatomegaly.
- However, it does not typically cause the **jaundice** or acute symptoms triggered by the introduction of solid foods containing fructose as described in this case.
*Galactokinase*
- Deficiency of galactokinase leads to **Type II galactosemia**, characterized primarily by **cataracts** and galactosemia, but typically without the profound liver damage, jaundice, or acute hypoglycemia seen here.
- The symptoms in this case are related to **fructose** intake, not galactose.
*Galactose-1 phosphate uridyltransferase*
- Deficiency in **galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase** causes **classic galactosemia**, which presents with **jaundice**, hepatosplenomegaly, vomiting, and cataracts, often triggered by lactose (galactose) intake.
- While it shares some symptoms with the patient's presentation, the trigger of symptoms upon introducing fruits and vegetables (high in fructose) points specifically to an issue with **fructose metabolism**, not galactose.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator is studying the changes that occur in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve of different types of hemoglobin under various conditions. The blood obtained from a male infant shows decreased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid. Which of the following is the most likely composition of the hemoglobin molecule in this sample?
- A. α2βS2
- B. α2β2
- C. α2δ2
- D. α2γ2 (Correct Answer)
- E. β4
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***α2γ2***
- This formula represents **fetal hemoglobin (HbF)**, which is the predominant hemoglobin in infants.
- HbF has **decreased affinity for 2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (2,3-BPG)** compared to adult hemoglobin (HbA) because 2,3-BPG binds less avidly to the gamma chains.
- This decreased 2,3-BPG binding results in HbF having **higher oxygen affinity** than HbA (left-shifted oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve).
- The higher oxygen affinity allows fetal blood to efficiently extract oxygen from maternal blood across the placenta.
*α2βS2*
- This represents **hemoglobin S (HbS)**, found in **sickle cell disease**.
- HbS has similar 2,3-BPG binding to HbA, not decreased affinity.
- Its primary characteristic is polymerization and red blood cell sickling under deoxygenated conditions.
*α2β2*
- This represents **adult hemoglobin (HbA)**, the most common type of hemoglobin in adults.
- HbA has **higher affinity for 2,3-BPG** compared to HbF because 2,3-BPG binds strongly to the beta chains.
- The binding of 2,3-BPG to HbA decreases oxygen affinity, facilitating oxygen release to tissues.
*α2δ2*
- This represents **hemoglobin A2 (HbA2)**, a minor component of adult hemoglobin (typically <3.5%).
- HbA2 has normal 2,3-BPG binding similar to HbA, not decreased affinity.
- This doesn't fit the clinical description of an infant with decreased 2,3-BPG affinity.
*β4*
- This represents **hemoglobin H (HbH)**, which occurs in **alpha-thalassemia** where there is an excess of beta chains that form tetramers.
- HbH has **extremely high oxygen affinity** and does not release oxygen well to tissues.
- While HbH also has decreased 2,3-BPG binding, it is not found in healthy infants and represents a pathological condition.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 5: A 59-year-old man comes to the physician because of bilateral blurry vision and difficulty driving at night that has been worsening progressively over the past 5 months. He has hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia. His hemoglobin A1c concentration is 8.9 mg/dL. A slit-lamp shows cloudy opacities of the lenses bilaterally. The patient's eye condition is most likely due to increased activity of which of the following enzymes?
- A. Galactokinase
- B. Aldolase B
- C. Sorbitol dehydrogenase
- D. Aldose reductase (Correct Answer)
- E. Glucokinase
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: **Aldose reductase**
- The patient's presentation of **bilateral blurry vision**, **difficulty driving at night**, and **cloudy lens opacities** in the context of poorly controlled diabetes (HbA1c 8.9%) is classic for **diabetic cataracts**.
- **Aldose reductase** is the key enzyme in the polyol pathway that converts **glucose to sorbitol**. In hyperglycemia, increased activity of this enzyme leads to **sorbitol accumulation** in lens cells, causing osmotic damage and cataract formation.
*Galactokinase*
- **Galactokinase** is involved in galactose metabolism, converting galactose to galactose-1-phosphate.
- Deficiencies in this enzyme can lead to **galactosemia** and early-onset cataracts, but this typically presents in infancy or early childhood, not in a 59-year-old with diabetes.
*Aldolase B*
- **Aldolase B** is an enzyme critical for the metabolism of fructose in the liver.
- Its deficiency causes **hereditary fructose intolerance**, leading to symptoms like hypoglycemia, jaundice, and vomiting upon fructose ingestion, which are not relevant to this patient's eye condition.
*Sorbitol dehydrogenase*
- **Sorbitol dehydrogenase** converts **sorbitol to fructose** in the polyol pathway.
- While part of the same pathway, its activity prevents sorbitol accumulation, so an *increase* in its activity would likely be protective against diabetic complications, not causative of cataracts.
*Glucokinase*
- **Glucokinase** (also known as hexokinase IV) is an enzyme that phosphorylates glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, mainly in the liver and pancreatic beta cells.
- Mutations in glucokinase can cause various forms of diabetes, but its activity is primarily involved in glucose sensing and metabolism, not directly in the pathogenesis of diabetic cataracts through increased polyol pathway flux.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 6: An 11-year-old boy is brought to the emergency room with acute abdominal pain and hematuria. Past medical history is significant for malaria. On physical examination, he has jaundice and a generalized pallor. His hemoglobin is 5 g/dL, and his peripheral blood smear reveals fragmented RBC, microspherocytes, and eccentrocytes (bite cells). Which of the following reactions catalyzed by the enzyme is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Glucose-1-phosphate + UTP → UDP-glucose + pyrophosphate
- B. Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP + H+
- C. D-glucose 6-phosphate → D-fructose-6-phosphate
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate + H2O → glucose + Pi
- E. D-glucose-6-phosphate + NADP+ → 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + NADPH + H+ (Correct Answer)
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***D-glucose-6-phosphate + NADP+ → 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone + NADPH + H+***
- This reaction is catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)**, an enzyme critical for the production of **NADPH** in the **pentose phosphate pathway**.
- **NADPH** is essential for reducing **oxidative stress** in red blood cells. A deficiency in G6PD leads to increased susceptibility to hemolysis, especially under oxidative triggers like malaria, resulting in symptoms such as **acute hemolytic anemia**, jaundice, and specific morphological changes (e.g., **fragmented RBCs**, **microspherocytes**, and **eccentrocytes**, also known as **bite cells**).
*Glucose-1-phosphate + UTP → UDP-glucose + pyrophosphate*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase** and is important for **glycogen synthesis**.
- A deficiency in this enzyme would primarily affect glycogen metabolism and would not explain the **hemolytic anemia** or the characteristic red blood cell morphology seen in the patient.
*Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP + H+*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **hexokinase**, the first committed step in **glycolysis**.
- While hexokinase deficiency can cause **hemolytic anemia**, it generally presents with chronic, moderate anemia and does not typically involve the specific red blood cell morphology (eccentrocytes/bite cells) associated with oxidative damage found in G6PD deficiency.
*D-glucose 6-phosphate → D-fructose-6-phosphate*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **phosphoglucose isomerase** (also known as phosphohexose isomerase) and is part of **glycolysis**.
- A deficiency in this enzyme would impair glycolysis and lead to **hemolytic anemia**, but its clinical presentation and RBC morphology differ from what is typically seen in G6PD deficiency, particularly the absence of oxidative stress markers like bite cells.
*Glucose-6-phosphate + H2O → glucose + Pi*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **glucose-6-phosphatase**, an enzyme found primarily in the liver and kidney, responsible for the final step in **gluconeogenesis** and glycogenolysis to release free glucose into the bloodstream.
- A deficiency in glucose-6-phosphatase leads to **glycogen storage disease type I (Von Gierke's disease)**, characterized by **hypoglycemia**, **lactic acidosis**, and hepatomegaly, not hemolytic anemia.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 7: A 3-week-old newborn is brought to the pediatrician by his mother. His mother is concerned about her son’s irritability and vomiting, particularly after breastfeeding him. The infant was born at 39 weeks via spontaneous vaginal delivery. His initial physical was benign. Today the newborn appears mildly jaundiced with palpable hepatomegaly, and his eyes appear cloudy, consistent with the development of cataracts. The newborn is also in the lower weight-age percentile. The physician considers a hereditary enzyme deficiency and orders blood work and a urinalysis to confirm his diagnosis. He recommends that milk and foods high in galactose and/or lactose be eliminated from the diet. Which of the following is the most likely deficient enzyme in this metabolic disorder?
- A. Aldose reductase
- B. Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (Correct Answer)
- C. UDP-galactose-4-epimerase
- D. Galactokinase
- E. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
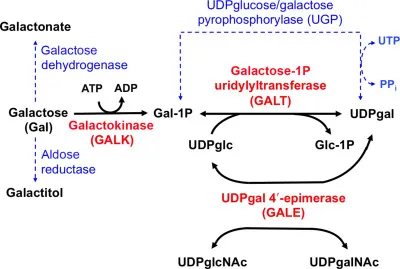
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase***
- The constellation of symptoms including **vomiting**, **irritability**, **jaundice**, **hepatomegaly**, **cataracts**, and **failure to thrive** in a neonate, with improvement upon eliminating galactose/lactose from the diet, is highly characteristic of **classic galactosemia**.
- **Classic galactosemia** is caused by a deficiency in **galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT)**, leading to the accumulation of galactose-1-phosphate, which is toxic to various tissues.
*Aldose reductase*
- This enzyme converts galactose to **galactitol**, which can accumulate in the lens and cause **cataracts** in all forms of galactosemia if left untreated.
- However, isolated aldose reductase deficiency does not explain the full spectrum of severe systemic symptoms like hepatomegaly, jaundice, and failure to thrive observed in this neonate, which are indicative of classic galactosemia.
*UDP-galactose-4-epimerase*
- Deficiency in **UDP-galactose-4-epimerase (GALE)**, also known as epimerase deficiency galactosemia, has a wide range of severity.
- While it can present with similar symptoms to GALT deficiency, its severe form is rarer, and the classic, pronounced presentation described here is more commonly associated with GALT deficiency.
*Galactokinase*
- Deficiency in **galactokinase (GALK)** causes **Type II galactosemia**, which primarily manifests as **cataracts** due to galactitol accumulation.
- It typically does not present with the severe hepatic (jaundice, hepatomegaly) or systemic symptoms (vomiting, failure to thrive) seen in classic galactosemia.
*Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- **Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency** primarily causes **hemolytic anemia** triggered by certain drugs, infections, or fava beans.
- It does not present with the specific constellation of symptoms related to galactose metabolism, such as cataracts, hepatomegaly, and vomiting upon milk ingestion, as described in this case.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 8: A 12-year-old boy and his siblings are referred to a geneticist for evaluation of a mild but chronic hemolytic anemia that has presented with fatigue, splenomegaly, and scleral icterus. Coombs test is negative and blood smear does not show any abnormal findings. An enzymatic panel is assayed, and pyruvate kinase is found to be mutated on both alleles. The geneticist explains that pyruvate kinase functions in glycolysis and is involved in a classic example of feed-forward regulation. Which of the following metabolites is able to activate pyruvate kinase?
- A. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (Correct Answer)
- B. Alanine
- C. ATP
- D. Glucose-6-phosphate
- E. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate***
- **Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate** is a potent **allosteric activator** of pyruvate kinase. This is an example of **feed-forward activation**, where a product of an early irreversible step in glycolysis (catalyzed by phosphofructokinase-1) activates a later enzyme (pyruvate kinase) in the pathway.
- This activation ensures that substrates for the later steps of glycolysis are rapidly utilized when earlier steps are highly active, matching the rate of metabolite flow and increasing the overall efficiency of glycolysis for energy production.
*Alanine*
- **Alanine** is an **inhibitor** of pyruvate kinase, not an activator. It serves as an indicator of a high cellular energy state and ample amino acid supply.
- High levels of alanine signal the cell that there is sufficient energy and building blocks, thus **shutting down** glycolysis at the pyruvate kinase step to conserve glucose for other needs like glycogen synthesis.
*ATP*
- **ATP** (adenosine triphosphate) is an **allosteric inhibitor** of pyruvate kinase. High ATP levels signal a high energy state in the cell.
- When the cell has sufficient energy, ATP binds to a regulatory site on pyruvate kinase, reducing its activity and **slowing down glycolysis** to prevent overproduction of ATP.
*Glucose-6-phosphate*
- **Glucose-6-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycolysis but does not directly activate pyruvate kinase. It can act as an allosteric inhibitor of hexokinase, the first enzyme in glycolysis, but not pyruvate kinase.
- Its accumulation typically signifies a **backup** in the glycolytic pathway (e.g., due to downstream inhibition), leading to a *reduction* in overall glucose flux rather than a direct activation of pyruvate kinase.
*Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate*
- **Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate** is an intermediate in glycolysis, but it does not directly activate pyruvate kinase. It is a substrate for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- While its presence indicates active glycolysis, it does not exert a specific allosteric regulatory effect on pyruvate kinase in the way fructose-1,6-bisphosphate does.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 9: A 7-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician for a change in his behavior. The patient has been exclusively breastfeeding up until this point and has been meeting his developmental milestones. He is in the 90th percentile for weight and 89th percentile for height. Two weeks ago, his parents began introducing weaning foods including fruit purees and baby formula. This past week, the patient has been increasingly lethargic, vomiting, and has been refusing to eat. The patient's parents state that he had an episode this morning where he was not responsive and was moving his extremities abnormally followed by a period of somnolence. The patient's past medical history is notable for shoulder dystocia and poorly managed maternal diabetes during the pregnancy. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 60/30 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. On physical exam, you note a lethargic infant with a distinctive sweet, fruity smell to his breath. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase (Correct Answer)
- B. Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase
- C. Aldolase B
- D. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- E. Ornithine transcarbamolase
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***Branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase***
- This patient's presentation is classic for **maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)**, caused by deficiency of branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex.
- The **distinctive sweet, fruity smell to the breath** (and urine) is pathognomonic for MSUD, resulting from accumulation of branched chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, valine) and their ketoacid metabolites.
- Symptoms typically manifest upon introduction of **increased protein load** (baby formula), presenting with **lethargy, vomiting, poor feeding, seizures, and encephalopathy** due to neurotoxicity from elevated leucine and other metabolites.
- The timing (introduced weaning foods including formula) and clinical picture of acute metabolic crisis with characteristic odor make this the most likely diagnosis.
*Ornithine transcarbamylase*
- OTC deficiency causes **hyperammonemic crisis** with similar neurological symptoms (lethargy, vomiting, seizures) triggered by protein intake.
- However, hyperammonemia typically produces a **musty or ammonia-like odor**, NOT the sweet, fruity smell described in this case.
- While the clinical timing fits, the **characteristic breath odor is inconsistent** with urea cycle disorders.
*Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase*
- Deficiency causes **classic galactosemia**, presenting with **vomiting, lethargy, jaundice, hepatomegaly, and cataracts** after lactose exposure (milk/formula).
- The **sweet, fruity breath odor is NOT characteristic** of galactosemia.
- While formula introduction could trigger symptoms, the specific odor and predominant neurological presentation point away from this diagnosis.
*Aldolase B*
- **Hereditary fructose intolerance** manifests upon fructose exposure (fruit purees) with **vomiting, hypoglycemia, jaundice, hepatomegaly, and renal dysfunction**.
- The patient did consume fruit purees, but the **sweet, fruity breath odor is NOT a feature** of fructose intolerance.
- The severe acute encephalopathy and characteristic odor make MSUD more likely.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- **Von Gierke disease (Type I GSD)** presents with **severe fasting hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, hepatomegaly, and hyperlipidemia**.
- The **sweet, fruity odor is NOT characteristic**, and symptoms are primarily related to fasting/glucose homeostasis rather than acute protein-induced metabolic crisis.
- The clinical picture does not fit a glycogen storage disorder.
Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG Question 10: A 6-month-old infant male is brought to the emergency department with a 1-hour history of vomiting and convulsions. He was born at home and had sporadic prenatal care though his parents say that he appeared healthy at birth. He initially fed well; however, his parents have noticed that he has been feeding poorly and is very irritable since they moved on to baby foods. They have also noticed mild yellowing of his skin but assumed it would go away over time. On presentation, he is found to be very sleepy, and physical exam reveals an enlarged liver and spleen. The rest of the physical exam is normal. Which of the following enzymes is most likely functioning abnormally in this patient?
- A. Aldolase B (Correct Answer)
- B. Galactokinase
- C. Lactase
- D. Fructokinase
- E. Gal-1-phosphate uridyl transferase
Alternative glycolytic pathways Explanation: ***Aldolase B***
- The symptoms of vomiting, irritability, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, and poor feeding in an infant after starting baby foods strongly suggest **hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI)**.
- HFI is caused by a deficiency in **Aldolase B**, which is responsible for cleaving **fructose-1-phosphate** into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde in the liver, kidney, and small intestine.
*Galactokinase*
- A deficiency in **galactokinase** causes **galactosemia type II**, characterized primarily by **cataracts** from birth, with milder symptoms compared to classic galactosemia.
- It does not typically present with the severe liver failure, vomiting, and convulsions seen in this patient.
*Lactase*
- **Lactase deficiency** causes **lactose intolerance**, presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms like bloating, gas, and diarrhea, particularly after consuming milk products.
- It does not typically cause the systemic symptoms of liver dysfunction, vomiting, convulsions, or jaundice experienced by this infant.
*Fructokinase*
- A deficiency in **fructokinase** causes **essential fructosuria**, which is a **benign, asymptomatic** metabolic disorder.
- Fructose accumulates in the urine but does not lead to the severe clinical manifestations such as vomiting, convulsions, or liver enlargement.
*Gal-1-phosphate uridyl transferase*
- A deficiency in **Gal-1-phosphate uridyl transferase** causes **classic galactosemia**, which would also present with vomiting, feeding difficulties, jaundice, and hepatosplenomegaly.
- However, classic galactosemia symptoms appear upon ingestion of **lactose** (from breast milk or formula), typically much earlier than the introduction of baby foods containing fructose.
More Alternative glycolytic pathways US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.