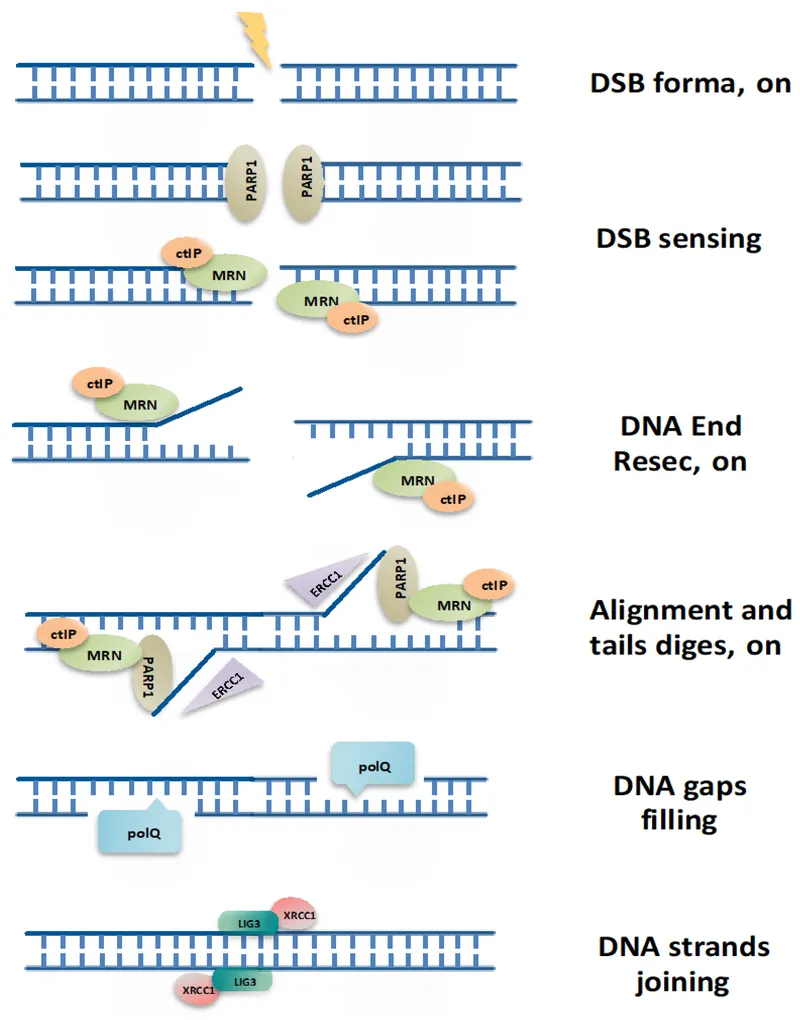
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Non-homologous end joining. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old woman presents with heavy menstrual bleeding between her periods. The patient also complains of experiencing an irregular menstrual cycle, weight loss, bloating, and constipation. She has had 3 uncomplicated pregnancies, all of which ended with normal vaginal deliveries at term. She has never taken oral contraception, and she does not take any medication at the time of presentation. She has no family history of any gynecological malignancy; however, her grandfather and mother had colon cancer that was diagnosed before they turned 50. On physical examination, the patient appears pale. Gynecological examination reveals a bloody cervical discharge and slight uterine enlargement. Endometrial biopsy reveals endometrial adenocarcinoma. Colonoscopy reveals several polyps located in the ascending colon, which are shown to be adenocarcinomas on histological evaluation. Which of the following mechanisms of DNA repair is likely to be disrupted in this patient?
- A. Mismatch repair (Correct Answer)
- B. Homologous recombination
- C. Nucleotide-excision repair
- D. Non-homologous end joining
- E. Base-excision repair
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: ***Mismatch repair***
- The patient's presentation with **endometrial adenocarcinoma** and **synchronous colon adenocarcinomas** (diagnosed before age 50 in multiple family members) is highly suggestive of **Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer or HNPCC)**.
- Lynch syndrome is caused by a germline mutation in one of the **DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes** (e.g., MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2), leading to an inability to correct replication errors and resulting in microsatellite instability and cancer development.
*Homologous recombination*
- This pathway is crucial for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks** and is often deficient in cancers associated with **BRCA1/2 mutations**, leading to syndromes like hereditary breast and ovarian cancer.
- While homologous recombination defects can cause cancer, they are not typically linked to the specific constellation of endometrial and colon cancers seen in Lynch syndrome.
*Nucleotide-excision repair*
- This pathway is primarily responsible for repairing bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by **UV radiation** or certain **chemotherapeutic agents**.
- Defects in nucleotide-excision repair are associated with conditions like **xeroderma pigmentosum**, characterized by extreme sensitivity to sunlight and skin cancers, which is not relevant to this patient's presentation.
*Non-homologous end joining*
- This is another major pathway for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**, but it is generally considered more error-prone than homologous recombination.
- While defects in this pathway can lead to genomic instability and cancer, it is not the primary mechanism disrupted in Lynch syndrome.
*Base-excision repair*
- This pathway is responsible for removing damaged or modified bases from DNA, often initiated by **oxidative damage or alkylation**.
- While essential for maintaining genomic integrity, defects in base-excision repair are not the characteristic mechanism underlying the cancer predisposition seen in Lynch syndrome.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 2: A 29-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of progressively worsening fatigue and shortness of breath for the past 2 weeks. His only medication is insulin. Examination shows elevated jugular venous distention and coarse crackles in both lungs. Despite appropriate life-saving measures, he dies. Gross examination of the heart at autopsy shows concentrically thickened myocardium and microscopic examination shows large cardiomyocytes with intracellular iron granules. Examination of the spinal cord shows atrophy of the lateral corticospinal tracts, spinocerebellar tracts, and dorsal columns. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's condition?
- A. CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion on chromosome 19
- B. SOD1 gene mutation on chromosome 21
- C. SMN1 gene mutation on chromosome 5
- D. GAA trinucleotide repeat expansion on chromosome 9 (Correct Answer)
- E. Dystrophin gene mutation on the X chromosome
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: ***GAA trinucleotide repeat expansion on chromosome 9***
- The patient's presentation with **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy** (concentrically thickened myocardium, large cardiomyocytes) and **neurological degeneration** affecting the **lateral corticospinal tracts, spinocerebellar tracts, and dorsal columns** is characteristic of **Friedreich ataxia**.
- **Friedreich ataxia** is caused by a **GAA trinucleotide repeat expansion** in the **FXN gene on chromosome 9**, leading to reduced frataxin protein and mitochondrial dysfunction.
*CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion on chromosome 19*
- This mutation is associated with **myotonic dystrophy type 1**, which presents with **myotonia**, muscle weakness, and often cardiac conduction abnormalities or dilated cardiomyopathy, but typically not hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or the specific spinal cord degeneration described.
- While cardiac involvement can occur, the neurological pattern of **spinal cord tract degeneration** and **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy** is not typical for myotonic dystrophy type 1.
*SOD1 gene mutation on chromosome 21*
- Mutations in the **SOD1 gene** are a common cause of **familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)**, characterized by progressive degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons.
- ALS primarily presents with muscle weakness, atrophy, and fasciculations, but does not typically involve **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy** or the specific pattern of **sensory tract degeneration** seen in this patient.
*SMN1 gene mutation on chromosome 5*
- This mutation causes **spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)**, a genetic disorder characterized by the loss of motor neurons in the spinal cord, leading to progressive muscle weakness and atrophy.
- SMA does not typically involve **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy** or the specific combination of motor and sensory tract degeneration described in the patient.
*Dystrophin gene mutation on the X chromosome*
- Mutations in the **dystrophin gene** cause **Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies**, which are characterized by progressive muscle weakness and **dilated cardiomyopathy**, not hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- While these disorders affect muscles, the specific pattern of **spinal cord tract atrophy** described is not a feature of dystrophinopathies.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 3: A 3-year-old male child is found to have a disease involving DNA repair. Specifically, he is found to have a defect in the endonucleases involved in the nucleotide excision repair of pyrimidine dimers. Which of the following is a unique late-stage complication of this child's disease?
- A. Telangiectasia
- B. Colorectal cancer
- C. Malignant melanoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Lymphomas
- E. Endometrial cancer
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: **Malignant melanoma**
- The described condition is **xeroderma pigmentosum**, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a defect in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, specifically the inability to remove **pyrimidine dimers** caused by **UV radiation**.
- This severely impaired DNA repair leads to an extreme predisposition to **UV-induced skin cancers**, including basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, and, most aggressively, **malignant melanoma**, which is a unique and life-threatening late-stage complication.
*Telangiectasia*
- **Telangiectasias** are dilated small blood vessels that appear on the skin or mucous membranes and can be associated with various conditions.
- While skin abnormalities are prevalent in xeroderma pigmentosum due to sun damage, **melanoma** is a more specific and severe late-stage complication directly resulting from the DNA repair defect.
*Colorectal cancer*
- **Colorectal cancer** is typically associated with other DNA repair defects, such as those in the **mismatch repair system**, as seen in conditions like **Lynch syndrome**.
- It is not a primary or most significant late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum, which is primarily characterized by skin cancers.
*Lymphomas*
- **Lymphomas** are cancers of the lymphatic system, often linked to immune deficiencies or specific genetic translocations.
- While individuals with genetic syndromes can have increased cancer risks, **lymphoma** is not the hallmark late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum; skin cancers are the predominant concern.
*Endometrial cancer*
- **Endometrial cancer** is a gynecological cancer often associated with hormonal factors or genetic predispositions like Lynch syndrome, which involves mismatch repair defects.
- This type of cancer is not a characteristic or unique late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum, whose pathology is centered on **UV-induced DNA damage** and subsequent skin malignancies.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old man comes to the physician because his vision has worsened rapidly over the last 2 months. His maternal uncle lost his vision suddenly over a period of 3 months at 26 years of age. The patient's wife and 1-year-old son have normal vision. Funduscopic examination of the patient shows bilateral circumpapillary telangiectasia. Genetic testing shows a missense mutation in one of the genes of the electron transport chain complexes. The probability that this patient's son will be affected by the same disease is closest to which of the following?
- A. 33%
- B. 100%
- C. 0% (Correct Answer)
- D. 25%
- E. 50%
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: ***0%***
- This condition, **Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)**, is caused by a mutation in **mitochondrial DNA**.
- **Mitochondrial DNA** is exclusively inherited from the mother, meaning the father cannot pass it on to his children.
*33%*
- This percentage does not align with any known pattern of Mendelian inheritance or mitochondrial inheritance.
- It would be too low for a dominant mitochondrial disorder and too high for a recessive one if the mother were a carrier.
*100%*
- While all children of an affected mother would inherit the disease, the patient is a male, and mitochondria are inherited maternally.
- Therefore, the father cannot pass on his **mitochondrial DNA** to his son.
*25%*
- This percentage is typically associated with **autosomal recessive inheritance**, where both parents are carriers.
- LHON follows a **mitochondrial inheritance pattern**, which is distinct from autosomal inheritance.
*50%*
- This percentage is characteristic of **autosomal dominant inheritance** or X-linked recessive inheritance where the mother is a carrier.
- Since this is a **mitochondrial disorder**, the father's genes are not involved in transmission to his son.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 5: A 24-year-old woman comes to the clinic complaining of headache and sinus drainage for the past 13 days. She reports cold-like symptoms 2 weeks ago that progressively got worse. The patient endorses subjective fever, congestion, sinus headache, cough, and chills. She claims that this is her 5th episode within the past year and is concerned if “there’s something else going on.” Her medical history is significant for asthma that is adequately controlled with her albuterol inhaler. Her laboratory findings are shown below:
Serum:
Hemoglobin: 16.2 g/dL
Hematocrit: 39 %
Leukocyte count: 7,890/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 200,000/mm^3
IgA: 54 mg/dL (Normal: 76-390 mg/dL)
IgE: 0 IU/mL (Normal: 0-380 IU/mL)
IgG: 470 mg/dL (Normal: 650-1500 mg/dL)
IgM: 29 mg/dL (Normal: 40-345 mg/dL)
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- B. Selective IgA deficiency
- C. Common variable immunodeficiency (Correct Answer)
- D. Ataxia-telangiectasia
- E. X-linked agammaglobinemia
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: ***Common variable immunodeficiency***
- This patient presents with recurrent sinopulmonary infections (5 episodes in the past year) and significantly **low levels of IgA, IgG, and IgM**, which is characteristic of **common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)**.
- CVID often manifests in adulthood (patient is 24) with infections, and laboratory findings typically show **decreased levels of at least two immunoglobulin classes**, most commonly IgG and IgA, with or without low IgM.
*Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by the triad of **thrombocytopenia**, **eczema**, and **recurrent infections**, often presenting in early childhood.
- While recurrent infections are present, this patient does not have thrombocytopenia or eczema, and the immunoglobulin profile for Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome typically shows **low IgM** with **normal to elevated IgA and IgE**.
*Selective IgA deficiency*
- This condition is defined by **isolated low IgA levels** (<7 mg/dL), with normal levels of IgG and IgM.
- This patient has low IgA, but also significantly low IgG and IgM, ruling out a selective IgA deficiency.
*Ataxia-telangiectasia*
- This is a rare, autosomal recessive disorder characterized by **ataxia**, **telangiectasias**, and **immunodeficiency** (often involving IgA and IgE, but can also affect IgG subclasses).
- The patient does not present with ataxia or telangiectasias, which are hallmark features of this syndrome.
*X-linked agammaglobinemia*
- This condition is almost exclusively found in **males** and typically presents with recurrent infections in **infancy** after maternal antibodies wane.
- It is characterized by **profoundly low or absent levels of all immunoglobulin classes** (IgG, IgA, IgM) and the **absence of B cells**, which is not entirely consistent with this female patient's presentation and immunoglobulin levels.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 6: While performing a Western blot, a graduate student spilled a small amount of the radiolabeled antibody on her left forearm. Although very little harm was done to the skin, the radiation did cause minor damage to the DNA of the exposed skin by severing covalent bonds between the nitrogenous bases and the deoxyribose sugar, leaving several apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Damaged cells would most likely repair these sites by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Nucleotide excision repair
- B. Nonhomologous end joining repair
- C. Homologous recombination
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Base excision repair (Correct Answer)
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: **Base excision repair**
- This mechanism is specifically involved in correcting **single-base DNA damage** or **modified bases**, such as **apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites**.
- It involves removing the damaged base by a **DNA glycosylase**, creating an AP site, which is then processed by an **AP endonuclease** to cleave the phosphodiester backbone, followed by DNA polymerase and ligase.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- Primarily repairs **bulky DNA lesions**, such as **thymine dimers** caused by UV radiation, or damage from chemical adducts that distort the DNA helix.
- It involves excising a larger oligonucleotide containing the damage, not just a single base.
*Nonhomologous end joining repair*
- This pathway is used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks**, where both strands of the DNA molecule are broken.
- It is a "quick-and-dirty" repair mechanism that ligates the broken ends together, often leading to small insertions or deletions.
*Homologous recombination*
- A repair mechanism for **double-strand DNA breaks** that uses a homologous DNA template (e.g., sister chromatid) to accurately repair the break.
- This process is highly accurate but occurs only when a homologous template is available, typically during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
*Mismatch repair*
- Corrects **base-pair mismatches** and **small insertions/deletions** that occur during DNA replication, which were not corrected by DNA polymerase proofreading.
- It targets newly synthesized DNA strands based on methylation patterns in the parental strand.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 7: An investigator is studying DNA repair processes in an experimental animal. The investigator inactivates a gene encoding a protein that physiologically excises nucleotides from damaged, bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands. A patient with a similar defect in this gene is most likely to present with which of the following findings?
- A. Ataxic gait and facial telangiectasias
- B. Malignant breast and ovarian growths
- C. Leukocoria and a painful bone mass
- D. Colorectal and endometrial cancers
- E. Dry skin and increased photosensitivity (Correct Answer)
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: ***Dry skin and increased photosensitivity***
- The description of excising **nucleotides from damaged, bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands** points to a defect in **Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)**.
- Patients with defects in NER, such as those with **xeroderma pigmentosum**, are highly susceptible to UV-induced DNA damage, leading to **dry skin, increased photosensitivity**, and a high risk of skin cancers.
*Ataxic gait and facial telangiectasias*
- This constellation of symptoms is characteristic of **ataxia-telangiectasia**, a disorder caused by mutations in the **ATM gene**, which is involved in **DNA double-strand break repair**.
- While a DNA repair defect, it's not primarily linked to the excision of bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands.
*Malignant breast and ovarian growths*
- These cancers are commonly associated with mutations in the **BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes**, which play crucial roles in **homologous recombination repair of DNA double-strand breaks**.
- This type of repair is distinct from the excision of bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands described in the question.
*Leukocoria and a painful bone mass*
- **Leukocoria** can indicate **retinoblastoma**, linked to mutations in the **RB1 tumor suppressor gene**, which regulates the cell cycle but isn't primarily a DNA repair gene.
- A painful bone mass could suggest **osteosarcoma**, which is sometimes seen in retinoblastoma patients but not directly related to the specific DNA repair defect described.
*Colorectal and endometrial cancers*
- These cancers are hallmarks of **Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer - HNPCC)**, which is caused by defects in **Mismatch Repair (MMR)** genes (e.g., MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2).
- Mismatch repair corrects errors that arise during DNA replication, which is different from excising bulky, helix-distorting DNA damage.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 8: A 47-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for fatigue. Over the past 3 months, his tiredness has impacted his ability to work as a corporate lawyer. He denies any changes to his diet, exercise regimen, bowel movements, or urinary frequency. His past medical history is notable for obesity, type II diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. He takes metformin and enalapril. His family history is notable for colorectal cancer in his father and paternal grandfather and endometrial cancer in his paternal aunt. He has a 20-pack-year smoking history and drinks one 6-pack of beer a week. His temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 129/71 mmHg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 17/min. On exam, he has conjunctival pallor. A stool sample is positive for occult blood. A colonoscopy reveals a small hemorrhagic mass at the junction of the ascending and transverse colon. Which of the following processes is likely impaired in this patient?
- A. Mismatch repair (Correct Answer)
- B. Homologous recombination
- C. Non-homologous end joining
- D. Nucleotide excision repair
- E. Base excision repair
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: ***Mismatch repair***
- The patient's presentation with **colorectal cancer** at a relatively young age and a strong family history of various cancers (colorectal, endometrial) in **first-degree and second-degree relatives** suggests Lynch syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer).
- **Lynch syndrome** is caused by inherited mutations in genes responsible for **DNA mismatch repair**, leading to an accumulation of errors and increased cancer risk.
*Homologous recombination*
- This repair mechanism is crucial for fixing **double-strand DNA breaks** using a homologous DNA template, important for genetic stability and primarily associated with genes like BRCA1/2.
- While defects in homologous recombination can lead to cancer (e.g., **breast and ovarian cancers**), it is not the primary mechanism implicated in Lynch syndrome or the patient's specific presentation of colorectal and endometrial cancer families.
*Non-homologous end joining*
- This is another major pathway for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**, but it does so by directly ligating the broken ends, often with some loss of genetic information, and does not rely on a homologous template.
- Defects in non-homologous end joining are not typically linked to the specific spectrum of cancers seen in **Lynch syndrome**.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- This pathway is responsible for removing bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by **UV light (e.g., pyrimidine dimers)** or certain chemical mutagens, and its defects are associated with conditions like xeroderma pigmentosum.
- The clinical picture and family history are not characteristic of disorders related to impaired **nucleotide excision repair**.
*Base excision repair*
- This repair pathway primarily corrects small, non-bulky DNA lesions, such as **oxidized, alkylated, or deaminated bases**, that do not distort the DNA helix.
- While important for maintaining genomic integrity, defects in base excision repair are typically associated with different cancer susceptibilities and not the specific features of **Lynch syndrome**.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 9: A 54-year-old woman with breast cancer comes to the physician because of redness and pain in the right breast. She has been undergoing ionizing radiation therapy daily for the past 2 weeks as adjuvant treatment for her breast cancer. Physical examination shows erythema, edema, and superficial desquamation of the skin along the right breast at the site of radiation. Sensation to light touch is intact. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of DNA repair responsible for preventing radiation-induced damage to neighboring neurons?
- A. Homology-directed repair
- B. Base excision repair
- C. Nonhomologous end joining repair (Correct Answer)
- D. DNA mismatch repair
- E. Nucleotide excision repair
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: ***Nonhomologous end joining repair***
- This pathway is crucial for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**, which are a major form of damage caused by **ionizing radiation**.
- It directly ligates the broken DNA ends without requiring a homologous template, making it an efficient but potentially error-prone repair mechanism.
*Homology-directed repair*
- This pathway is also used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks** but requires a **homologous DNA template** (usually a sister chromatid) for accurate repair.
- While highly accurate, it is typically active during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and is generally slower and less dominant than NHEJ for immediate radiation-induced damage in non-dividing cells like neurons.
*Base excision repair*
- This mechanism primarily corrects damage to individual DNA bases, such as **oxidative damage**, alkylation, or deamination.
- It is not the primary mechanism for repairing the **double-strand breaks** induced by ionizing radiation.
*DNA mismatch repair*
- This pathway corrects errors that arise during **DNA replication**, specifically mismatched base pairs or small insertions/deletions.
- It is not involved in repairing radiation-induced DNA damage like **double-strand breaks**.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- This pathway repairs bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by **UV radiation** (e.g., pyrimidine dimers) or chemical mutagens.
- It removes a segment of DNA containing the damage but is not the primary repair mechanism for **double-strand breaks** caused by ionizing radiation.
Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG Question 10: An investigator is studying the incidence of sickle cell trait in African American infants. To identify the trait, polymerase chain reaction testing is performed on venous blood samples obtained from the infants. Which of the following is required for this laboratory technique?
- A. Single-stranded binding proteins
- B. Ligation of Okazaki fragments
- C. Primers complementary to target DNA sequences (Correct Answer)
- D. Complete genome DNA sequence
- E. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
Non-homologous end joining Explanation: ***Primers complementary to target DNA sequences***
- **Primers** are short, synthetic single-stranded DNA sequences that **bind specifically** to the flanking regions of the target DNA sequence to be amplified.
- In PCR, these primers define the **start and end points** of the DNA segment that will be copied, allowing for the exponential amplification of a specific region of interest.
*Single-stranded binding proteins*
- **Single-stranded binding proteins (SSBs)** are crucial in **DNA replication** to stabilize unwound single-stranded DNA and prevent re-annealing or degradation.
- They are generally **not required** in standard PCR as the DNA strands are separated by heat denaturation, and the rapid cooling in primer annealing prevents re-annealing of the entire template.
*Ligation of Okazaki fragments*
- **Okazaki fragments** are short DNA segments synthesized on the **lagging strand** during **DNA replication**.
- Their ligation by **DNA ligase** is a key step in DNA replication, but it is **not part of the PCR process**, which synthesizes DNA continuously from primers.
*Complete genome DNA sequence*
- While knowing the **complete genome sequence** of an organism would be helpful for understanding the entire genetic makeup, it is **not a prerequisite** for performing PCR.
- PCR only requires knowledge of the **short flanking sequences** where the primers will bind to amplify a specific gene or region.
*RNA-dependent DNA polymerase*
- **RNA-dependent DNA polymerase**, also known as **reverse transcriptase**, is used to synthesize DNA from an RNA template in **reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR)**.
- While RT-PCR is a variant of PCR, standard PCR, as described for identifying a genetic trait in DNA, **does not require this enzyme**; instead, it uses a **DNA-dependent DNA polymerase** (e.g., Taq polymerase).
More Non-homologous end joining US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.