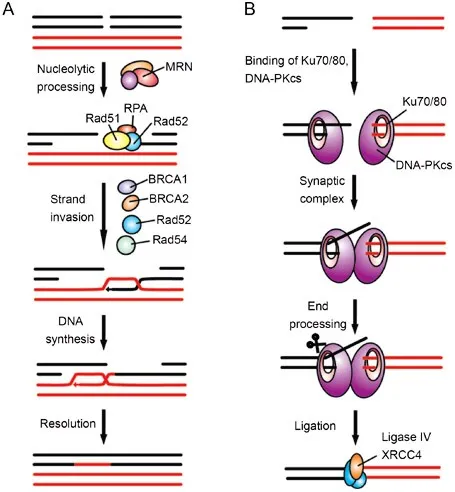
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Double-strand break repair. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 1: A 5-month-old male infant from a consanguineous marriage presents with severe sunburns and freckling in sun exposed areas. The mother explains that the infant experiences these sunburns every time the infant goes outside despite applying copious amounts of sunscreen. Which of the following DNA repair mechanisms is defective in this child?
- A. Non-homologous end joining
- B. Homologous recombination
- C. Base excision repair
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Nucleotide excision repair (Correct Answer)
Double-strand break repair Explanation: ***Nucleotide excision repair***
- The symptoms of **severe sunburns** and **freckling in sun-exposed areas** are classic manifestations of **Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP)**.
- XP is caused by a defect in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, which is crucial for removing **UV-induced DNA damage**, such as **pyrimidine dimers**.
*Non-homologous end joining*
- This mechanism repairs **double-strand DNA breaks** by directly ligating the broken ends, often with some loss of genetic information.
- Defects in non-homologous end joining are associated with conditions like **immunodeficiency** and increased cancer risk, but not with UV sensitivity like XP.
*Homologous recombination*
- This high-fidelity repair pathway uses a **homologous DNA template** to accurately repair **double-strand breaks** and interstrand crosslinks.
- Impaired homologous recombination is linked to conditions like **Fanconi anemia** and increased risk of certain cancers, but not primarily to UV hypersensitivity.
*Base excision repair*
- **Base excision repair (BER)** is responsible for removing **damaged or modified bases** from DNA, such as oxidized or alkylated bases.
- Defects in BER can lead to increased spontaneous mutagenesis and cancer, but do not explain the specific sensitivity to UV light seen in this infant.
*Mismatch repair*
- **Mismatch repair (MMR)** corrects errors that occur during DNA replication, such as **base mismatches** or small insertions/deletions.
- Defective MMR is strongly associated with **hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome)**, but not with severe reactions to sun exposure.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 2: A 42-year-old woman is seen by her primary care physician for her annual checkup. She has no current concerns and says that she has been healthy over the last year except for a bout of the flu in December. She has no significant past medical history and is not currently taking any medications. She has smoked 1 pack per day since she was 21 and drinks socially with her friends. Her family history is significant for prostate cancer in her dad when he was 51 years of age and ovarian cancer in her paternal aunt when she was 41 years of age. Physical exam reveals a firm, immobile, painless lump in the upper outer quadrant of her left breast as well as 2 smaller nodules in the lower quadrants of her right breast. Biopsy of these lesions shows small, atypical, glandular, duct-like cells with stellate morphology. Which of the following pathways is most likely abnormal in this patient?
- A. Nucleotide excision repair
- B. Base excision repair
- C. Non-homologous end joining
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Homologous recombination (Correct Answer)
Double-strand break repair Explanation: ***Homologous recombination***
- The patient's presentation with **multiple, bilateral breast lumps** and a strong family history of **early-onset breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers** suggests a hereditary cancer syndrome, most notably related to **BRCA1/2 mutations**.
- **BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes** are crucial for **homologous recombination**, a major pathway for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**. Defects in this pathway lead to genomic instability and increased cancer risk.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- This pathway primarily repairs bulky DNA adducts, such as **pyrimidine dimers** caused by UV radiation, and maintains DNA integrity by excising the damaged segment.
- Deficiencies in nucleotide excision repair are associated with diseases like **xeroderma pigmentosum**, which is characterized by extreme sensitivity to sunlight and skin cancers, not the pattern seen in this patient.
*Base excision repair*
- **Base excision repair** is responsible for repairing small, non-bulky DNA lesions, such as **oxidized or deaminated bases**, by removing the damaged base and replacing it.
- While essential for DNA integrity, its malfunction is not typically linked to the **hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome** suggested by the patient's family history and clinical presentation.
*Non-homologous end joining*
- **Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)** is an error-prone pathway for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks** by directly ligating the broken ends without a homologous template.
- While critical for DNA repair, defects in NHEJ are not the primary cause of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer, which is more specifically linked to the **BRCA1/2 genes** and the homologous recombination pathway.
*Mismatch repair*
- **Mismatch repair (MMR)** corrects errors that occur during DNA replication, such as mismatched bases or small insertions/deletions.
- Deficiencies in MMR lead to **microsatellite instability** and are characteristic of **Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer)**, which primarily increases the risk of colorectal, endometrial, and other specific cancers, but not the pattern of breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers seen here.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 3: While performing a Western blot, a graduate student spilled a small amount of the radiolabeled antibody on her left forearm. Although very little harm was done to the skin, the radiation did cause minor damage to the DNA of the exposed skin by severing covalent bonds between the nitrogenous bases and the deoxyribose sugar, leaving several apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Damaged cells would most likely repair these sites by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Nucleotide excision repair
- B. Nonhomologous end joining repair
- C. Homologous recombination
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Base excision repair (Correct Answer)
Double-strand break repair Explanation: **Base excision repair**
- This mechanism is specifically involved in correcting **single-base DNA damage** or **modified bases**, such as **apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites**.
- It involves removing the damaged base by a **DNA glycosylase**, creating an AP site, which is then processed by an **AP endonuclease** to cleave the phosphodiester backbone, followed by DNA polymerase and ligase.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- Primarily repairs **bulky DNA lesions**, such as **thymine dimers** caused by UV radiation, or damage from chemical adducts that distort the DNA helix.
- It involves excising a larger oligonucleotide containing the damage, not just a single base.
*Nonhomologous end joining repair*
- This pathway is used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks**, where both strands of the DNA molecule are broken.
- It is a "quick-and-dirty" repair mechanism that ligates the broken ends together, often leading to small insertions or deletions.
*Homologous recombination*
- A repair mechanism for **double-strand DNA breaks** that uses a homologous DNA template (e.g., sister chromatid) to accurately repair the break.
- This process is highly accurate but occurs only when a homologous template is available, typically during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
*Mismatch repair*
- Corrects **base-pair mismatches** and **small insertions/deletions** that occur during DNA replication, which were not corrected by DNA polymerase proofreading.
- It targets newly synthesized DNA strands based on methylation patterns in the parental strand.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 4: DNA replication is a highly complex process where replication occurs on both strands of DNA. On the leading strand of DNA, replication occurs uninterrupted, but on the lagging strand, replication is interrupted and occurs in fragments called Okazaki fragments. These fragments need to be joined, which of the following enzymes is involved in the penultimate step before ligation can occur?
- A. DNA gyrase
- B. DNA ligase
- C. DNA helicase
- D. DNA polymerase I (Correct Answer)
- E. DNA polymerase III
Double-strand break repair Explanation: **DNA polymerase I**
- **DNA polymerase I** plays a crucial role in removing the **RNA primers** from the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
- After primer removal, it fills the resulting gaps with **deoxyribonucleotides** before DNA ligase seals the nicks.
*DNA gyrase*
- **DNA gyrase** (a type of **topoisomerase**) is involved in relieving **supercoiling** ahead of the replication fork.
- It does not directly participate in the joining of Okazaki fragments, but rather in maintaining DNA topology during replication.
*DNA ligase*
- **DNA ligase** is responsible for the **final sealing** of the nicks between adjacent Okazaki fragments.
- It forms a **phosphodiester bond** between the 3'-hydroxyl end of one fragment and the 5'-phosphate end of the next, following primer removal and gap filling.
*DNA helicase*
- **DNA helicase** unwinds the double-stranded DNA helix, separating the two strands at the **replication fork**.
- This enzyme is essential for initiating replication but does not participate in processing Okazaki fragments.
*DNA polymerase III*
- **DNA polymerase III** is the primary enzyme responsible for the **elongation of new DNA strands** in both leading and lagging strand synthesis.
- It synthesizes the actual Okazaki fragments but does not directly remove primers or fill the gaps.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 5: A 34-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of a breast lump she noticed 2 days ago while showering. She has no history of major illness. Her mother died of ovarian cancer at age 38, and her sister was diagnosed with breast cancer at age 33. Examination shows a 1.5-cm, nontender, mobile mass in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. Mammography shows pleomorphic calcifications. Biopsy of the mass shows invasive ductal carcinoma. The underlying cause of this patient's condition is most likely a mutation of a gene involved in which of the following cellular events?
- A. Repair of double-stranded DNA breaks (Correct Answer)
- B. Inhibition of programmed cell death
- C. Regulation of intercellular adhesion
- D. Activity of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase
- E. Arrest of cell cycle in G1 phase
Double-strand break repair Explanation: ***Repair of double-stranded DNA breaks***
- The patient's **family history** (mother with ovarian cancer at 38, sister with breast cancer at 33) and early onset of **invasive ductal carcinoma** strongly suggest an inherited cancer syndrome.
- **BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes** are tumor suppressor genes responsible for repairing **double-stranded DNA breaks**, and mutations in these genes significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
*Inhibition of programmed cell death*
- Mutations leading to the **inhibition of programmed cell death (apoptosis)**, such as those affecting the **Bcl-2 gene**, can contribute to cancer by allowing damaged cells to survive and proliferate.
- While relevant to cancer pathogenesis, it is not the primary mechanism associated with the specific familial breast/ovarian cancer pattern seen here, which points more directly to DNA repair defects.
*Regulation of intercellular adhesion*
- Defects in **intercellular adhesion**, often involving **E-cadherin** (CDH1 gene) mutations, are associated with cancers like **lobular breast carcinoma** and **hereditary diffuse gastric cancer**.
- This patient has **invasive ductal carcinoma**, and the specific familial pattern is less characteristic of intercellular adhesion defects.
*Activity of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase*
- Abnormal **cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase activity** is implicated in various cancers (e.g., **HER2/neu** amplification in breast cancer, **BCR-ABL** fusion in CML).
- While HER2/neu overexpression is common in breast cancer, it is typically a somatic mutation or amplification, and not the underlying germline defect explaining the strong family history of early-onset breast and ovarian cancer.
*Arrest of cell cycle in G1 phase*
- The **arrest of the cell cycle at the G1 phase** is mainly regulated by **p53** and **Rb tumor suppressor genes**, which prevent uncontrolled cell division.
- While mutations in these genes are crucial in many cancers, the specific familial pattern (breast and ovarian cancer) points more strongly to defects in homologous recombination via BRCA1/2, a different DNA repair pathway.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 6: A 54-year-old woman with breast cancer comes to the physician because of redness and pain in the right breast. She has been undergoing ionizing radiation therapy daily for the past 2 weeks as adjuvant treatment for her breast cancer. Physical examination shows erythema, edema, and superficial desquamation of the skin along the right breast at the site of radiation. Sensation to light touch is intact. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of DNA repair responsible for preventing radiation-induced damage to neighboring neurons?
- A. Homology-directed repair
- B. Base excision repair
- C. Nonhomologous end joining repair (Correct Answer)
- D. DNA mismatch repair
- E. Nucleotide excision repair
Double-strand break repair Explanation: ***Nonhomologous end joining repair***
- This pathway is crucial for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**, which are a major form of damage caused by **ionizing radiation**.
- It directly ligates the broken DNA ends without requiring a homologous template, making it an efficient but potentially error-prone repair mechanism.
*Homology-directed repair*
- This pathway is also used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks** but requires a **homologous DNA template** (usually a sister chromatid) for accurate repair.
- While highly accurate, it is typically active during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and is generally slower and less dominant than NHEJ for immediate radiation-induced damage in non-dividing cells like neurons.
*Base excision repair*
- This mechanism primarily corrects damage to individual DNA bases, such as **oxidative damage**, alkylation, or deamination.
- It is not the primary mechanism for repairing the **double-strand breaks** induced by ionizing radiation.
*DNA mismatch repair*
- This pathway corrects errors that arise during **DNA replication**, specifically mismatched base pairs or small insertions/deletions.
- It is not involved in repairing radiation-induced DNA damage like **double-strand breaks**.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- This pathway repairs bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by **UV radiation** (e.g., pyrimidine dimers) or chemical mutagens.
- It removes a segment of DNA containing the damage but is not the primary repair mechanism for **double-strand breaks** caused by ionizing radiation.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 7: A 47-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for fatigue. Over the past 3 months, his tiredness has impacted his ability to work as a corporate lawyer. He denies any changes to his diet, exercise regimen, bowel movements, or urinary frequency. His past medical history is notable for obesity, type II diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. He takes metformin and enalapril. His family history is notable for colorectal cancer in his father and paternal grandfather and endometrial cancer in his paternal aunt. He has a 20-pack-year smoking history and drinks one 6-pack of beer a week. His temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 129/71 mmHg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 17/min. On exam, he has conjunctival pallor. A stool sample is positive for occult blood. A colonoscopy reveals a small hemorrhagic mass at the junction of the ascending and transverse colon. Which of the following processes is likely impaired in this patient?
- A. Mismatch repair (Correct Answer)
- B. Homologous recombination
- C. Non-homologous end joining
- D. Nucleotide excision repair
- E. Base excision repair
Double-strand break repair Explanation: ***Mismatch repair***
- The patient's presentation with **colorectal cancer** at a relatively young age and a strong family history of various cancers (colorectal, endometrial) in **first-degree and second-degree relatives** suggests Lynch syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer).
- **Lynch syndrome** is caused by inherited mutations in genes responsible for **DNA mismatch repair**, leading to an accumulation of errors and increased cancer risk.
*Homologous recombination*
- This repair mechanism is crucial for fixing **double-strand DNA breaks** using a homologous DNA template, important for genetic stability and primarily associated with genes like BRCA1/2.
- While defects in homologous recombination can lead to cancer (e.g., **breast and ovarian cancers**), it is not the primary mechanism implicated in Lynch syndrome or the patient's specific presentation of colorectal and endometrial cancer families.
*Non-homologous end joining*
- This is another major pathway for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**, but it does so by directly ligating the broken ends, often with some loss of genetic information, and does not rely on a homologous template.
- Defects in non-homologous end joining are not typically linked to the specific spectrum of cancers seen in **Lynch syndrome**.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- This pathway is responsible for removing bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by **UV light (e.g., pyrimidine dimers)** or certain chemical mutagens, and its defects are associated with conditions like xeroderma pigmentosum.
- The clinical picture and family history are not characteristic of disorders related to impaired **nucleotide excision repair**.
*Base excision repair*
- This repair pathway primarily corrects small, non-bulky DNA lesions, such as **oxidized, alkylated, or deaminated bases**, that do not distort the DNA helix.
- While important for maintaining genomic integrity, defects in base excision repair are typically associated with different cancer susceptibilities and not the specific features of **Lynch syndrome**.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 8: An investigator is studying the replication of bacterial DNA with modified nucleotides. After unwinding, the double-stranded DNA forms a Y-shaped replication fork that separates into two strands. At each of these strands, daughter strands are synthesized. One strand is continuously extended from the template strands in a 5′ to 3′ direction. Which of the following is exclusively associated with the strand being synthesized away from the replication fork?
- A. Reverse transcriptase activity
- B. Repeated activity of ligase (Correct Answer)
- C. Elongation in the 3'→5' direction
- D. Synthesis of short RNA sequences
- E. 5' → 3' exonuclease activity
Double-strand break repair Explanation: ***Repeated activity of ligase***
- The lagging strand, synthesized away from the replication fork, is made in fragments (**Okazaki fragments**) due to the 5' to 3' synthesis direction of DNA polymerase.
- **DNA ligase** repeatedly joins these Okazaki fragments together, forming a continuous strand.
*Reverse transcriptase activity*
- **Reverse transcriptase** synthesizes DNA from an RNA template, which is not involved in normal bacterial DNA replication.
- This enzyme is characteristic of **retroviruses** and certain eukaryotic telomere maintenance.
*Elongation in the 3'→5' direction*
- DNA polymerases only synthesize new DNA strands in the **5' to 3' direction**.
- While reading the template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, the daughter strand is always built from 5' to 3'.
*Synthesis of short RNA sequences*
- **RNA primers** are synthesized by **primase** on both the leading and lagging strands to initiate DNA synthesis.
- This process is not exclusive to the strand synthesized away from the replication fork; the leading strand also requires an initial RNA primer.
*5' → 3' exonuclease activity*
- The **5' to 3' exonuclease activity** of DNA polymerase I in bacteria is responsible for removing RNA primers.
- This activity occurs on both the leading and lagging strands, as both require primer removal.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 9: An 84-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of lower back pain and lower extremity weakness for 3 weeks. Over the past week, he has also found it increasingly difficult to urinate. He has a history of prostate cancer, for which he underwent radical prostatectomy 8 years ago. His prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level was undetectable until a routine follow-up visit last year, when it began to increase from 0.8 ng/mL to its present value of 64.3 ng/mL (N < 4). An MRI of the spine shows infiltrative vertebral lesions with a collapse of the L5 vertebral body, resulting in cord compression at L4–L5. The patient receives one dose of intravenous dexamethasone and subsequently undergoes external beam radiation. Which of the following cellular changes is most likely to occur as a result of this treatment?
- A. Intercalation of neighbouring DNA base pairs
- B. Disruption of microtubule assembly
- C. Formation of DNA crosslinks
- D. Generation of hydroxyl radicals (Correct Answer)
- E. Formation of pyrimidine dimers
Double-strand break repair Explanation: ***Generation of hydroxyl radicals***
- **External beam radiation** primarily causes cellular damage through the **ionization of water molecules**, leading to the formation of highly reactive **hydroxyl radicals**.
- These radicals directly damage **DNA**, proteins, and cell membranes, leading to **cell death or apoptosis**, especially in rapidly dividing cells like cancer cells.
*Intercalation of neighbouring DNA base pairs*
- This mechanism is characteristic of certain **chemotherapeutic agents** (e.g., **doxorubicin**, **daunorubicin**) that insert themselves between stacked DNA base pairs.
- This process distorts the DNA helix, interfering with replication and transcription, but it is **not the primary mechanism of radiation therapy**.
*Disruption of microtubule assembly*
- **Microtubule inhibitors** (e.g., **vincristine**, **paclitaxel**) disrupt the formation or disassembly of microtubules, which are essential for cell division and intracellular transport.
- While this is a common mechanism of action for some **chemotherapeutic drugs**, it is **not how radiation therapy works**.
*Formation of DNA crosslinks*
- **Alkylating agents** (e.g., **cyclophosphamide**, **cisplatin**) form covalent bonds within or between DNA strands, creating crosslinks that prevent DNA replication and transcription.
- Though highly damaging to DNA, this is a distinct mechanism of action typically associated with **chemotherapy**, not direct radiation.
*Formation of pyrimidine dimers*
- **Ultraviolet (UV) radiation** causes the formation of **pyrimidine dimers** (e.g., thymine dimers) in DNA.
- This type of DNA damage is characteristic of UV light exposure and is **not the primary mechanism of action for external beam radiation therapy**, which uses higher-energy ionizing radiation.
Double-strand break repair US Medical PG Question 10: Replication in eukaryotic cells is a highly organized and accurate process. The process involves a number of enzymes such as primase, DNA polymerase, topoisomerase II, and DNA ligase. In which of the following directions is DNA newly synthesized?
- A. 3' --> 5'
- B. N terminus --> C terminus
- C. C terminus --> N terminus
- D. 3' --> 5' & 5' --> 3'
- E. 5' --> 3' (Correct Answer)
Double-strand break repair Explanation: ***5' --> 3'***
- DNA polymerase can only add **nucleotides** to the 3' end of a growing strand, meaning synthesis always proceeds in a **5' to 3' direction**.
- This is true for both the **leading strand** (synthesized continuously) and the **lagging strand** (synthesized discontinuously via Okazaki fragments).
*3' --> 5'*
- While the parental template strand is read in the 3' to 5' direction, the *newly synthesized* DNA strand is always built in the **opposite, antiparallel 5' to 3' direction**.
- DNA polymerase lacks the ability to add new nucleotides to the **5' phosphate group** of the growing strand.
*N terminus --> C terminus*
- This directional notation refers to the synthesis of **proteins**, where amino acids are added to the C (carboxyl) terminus of the growing polypeptide chain.
- It does not apply to the synthesis direction of **nucleic acids (DNA or RNA)**.
*C terminus --> N terminus*
- This directional notation is incorrectly applied; protein synthesis always proceeds from the **N (amino) terminus to the C (carboxyl) terminus**.
- This has no relevance to the synthesis direction of **DNA**.
*3' --> 5' & 5' --> 3'*
- Although DNA replication involves two strands, one is synthesized continuously in the **5' → 3' direction (leading strand)** and the other discontinuously, but still *each fragment* is synthesized in the **5' → 3' direction (lagging strand)**.
- No new DNA strand is synthesized in the **3' → 5' direction**.
More Double-strand break repair US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.